The Grand Odyssey of Superchains: From Cosmos IBC to Polygon 2.0
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

The Grand Odyssey of Superchains: From Cosmos IBC to Polygon 2.0
This article will focus on a detailed study of Avax Subnets, OP Stack, Arbitrum Orbit, Op BNB, ZK Stack, and Polygon 2.0 at critical stages.
Author: Hercules
Translation: Cryptobeats, Web3 Map
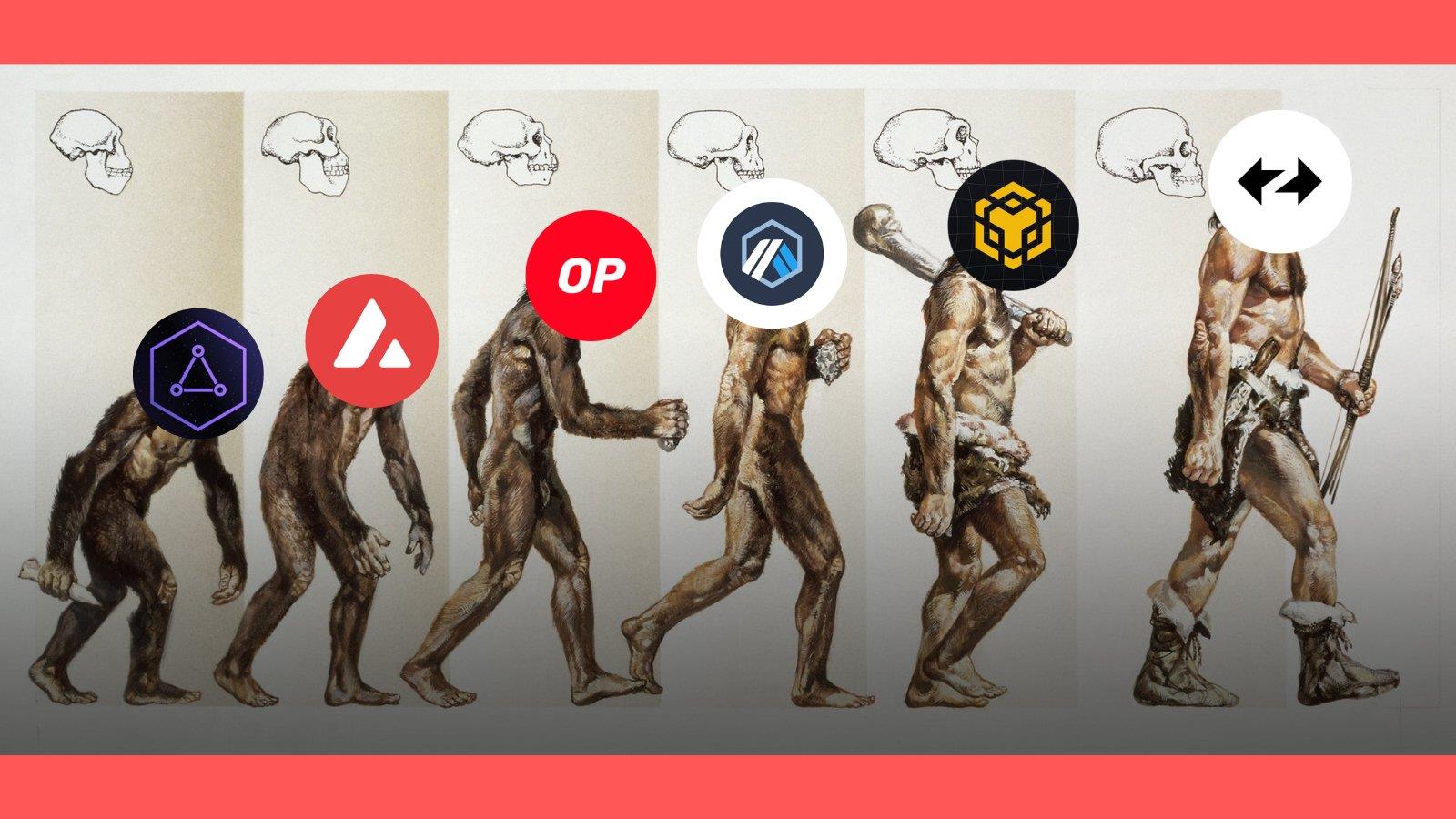
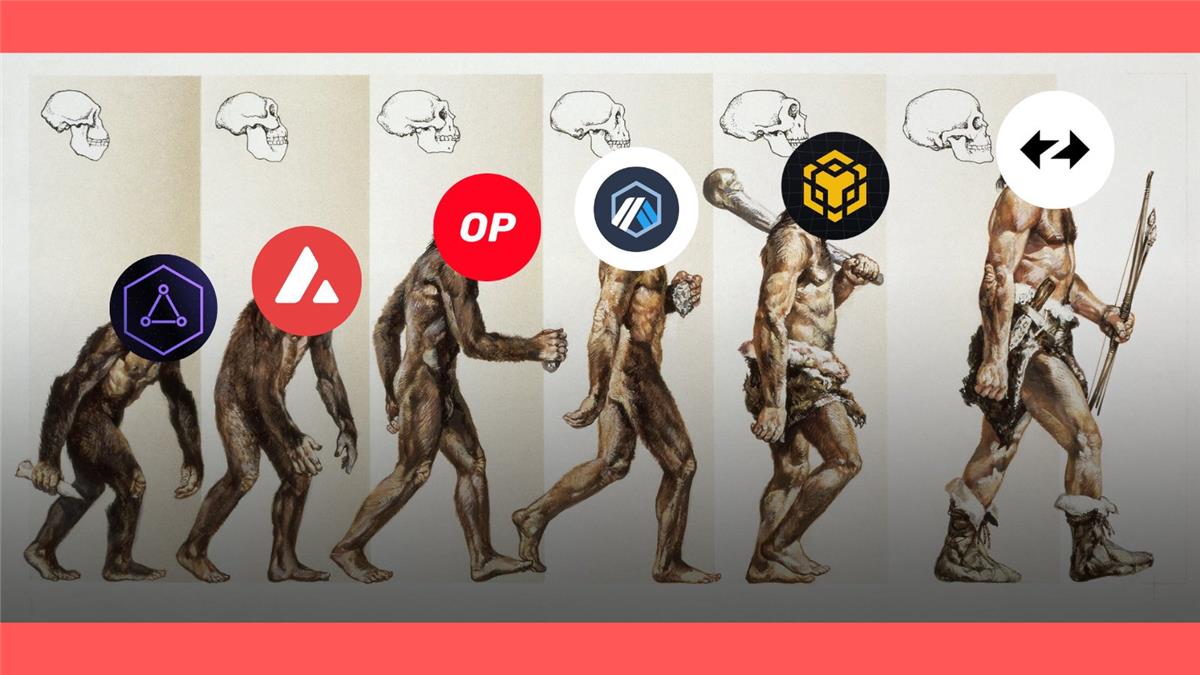
In the rapidly evolving blockchain landscape, a technology known as "Superchains" is drawing increasing attention. From the early days of Cosmos IBC to today's Polygon 2.0, each phase marks technological maturity and breakthroughs.
This article will take you on an in-depth exploration of this ongoing evolution, focusing on detailed insights into key milestones including Avax Subnets, OP Stack, Arbitrum Orbit, Op BNB, ZK Stack, and Polygon 2.0. Whether you're passionate about the latest blockchain technologies or eager to understand the field’s developmental trajectory, this piece will serve as a valuable guide. Let us soar together across the magnificent skies of superchains and uncover their boundless potential and opportunities.

Cosmos IBC
It all began with Cosmos IBC, a protocol designed to handle authentication and data transfer between two blockchains.
Although Inter Blockchain Communication (IBC) launched in April 2021, the platform gained prominence due to Terra's success.
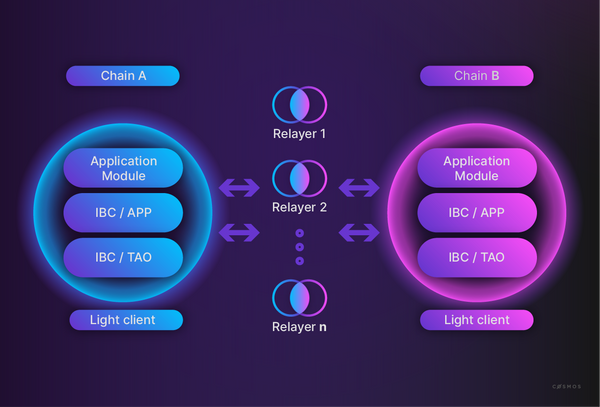
However, things didn't go as planned for Terra, a blockchain relying on Cosmos IBC—$LUNA began collapsing and UST lost its peg.
This was a black swan event in cryptocurrency history, resulting in massive losses for many investors, which in turn damaged Cosmos' brand reputation.
Nevertheless, Cosmos has since recovered, and here are some notable projects building on Cosmos:
-
@berachain,
-
@SeiNetwork,
-
@dYdX,
-
@noble_xyz
-
@CelestiaOrg
Avax Subnets
In April 2022, Avalanche launched its subnets—subsets or partitions within the broader Avalanche network.
A subnet consists of a group of nodes called validators, which work together to achieve consensus on transactions within a chain or across interconnected chains.
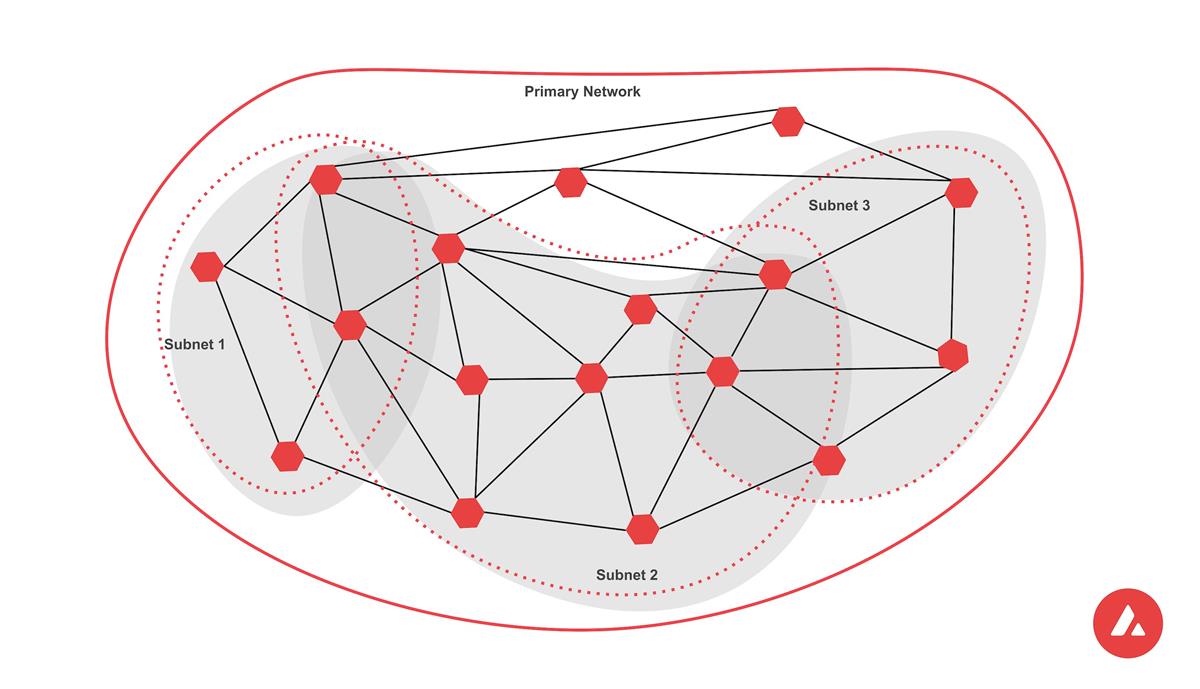
You can think of a subnet as a network within the larger Avalanche ecosystem.
It has its own set of validators and its own rules and parameters for achieving consensus.
Subnets provide Avalanche with enhanced scalability and flexibility.
OP Stack
OP Stack refers to the suite of software components supporting the Optimism ecosystem, including OP Mainnet and OP Superchain.
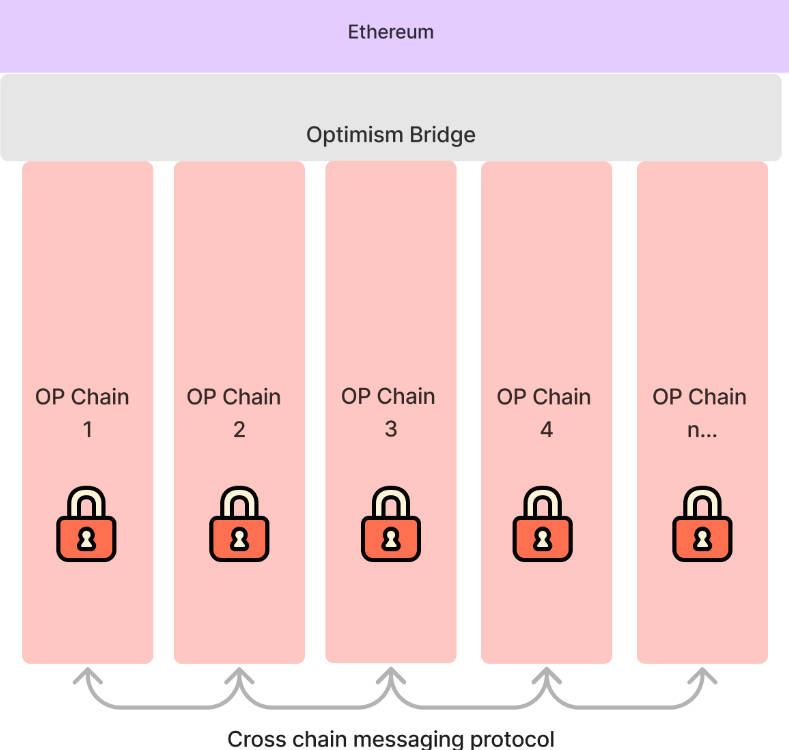
The goal of OP Stack is to support the creation of new Layer 2 blockchains that can interoperate within the ecosystem.
OP Stack provides a shared, high-quality, fully open-source system for creating new Layer 2 blockchains.
By coordinating shared standards and avoiding duplicated efforts in isolated silos, the Optimism Collective aims to streamline the process of developing new L2 chains.
Arbitrum Orbit
On March 16, 2023, the Arbitrum Foundation announced the launch of Arbitrum Orbit, a permissionless solution enabling any developer to build Layer 3 blockchains using Arbitrum technology.

Arbitrum Orbit is a platform allowing developers to create their own dedicated chains connected to Arbitrum’s Layer-2 (L2) chains—Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, or Arbitrum Goerli.
A key advantage of dedicated AppChains built with Arbitrum Orbit is that developers gain flexibility to customize various aspects of their chains.
Customization options include privacy settings, permissions, fee tokens, governance mechanisms, and more.
opBNB
opBNB is a high-performance Layer 2 solution operating within the BNB ecosystem and built using the OP Stack.
By leveraging the OP Stack, opBNB maintains stable and affordable gas fees.
opBNB achieves significant performance improvements through enhanced caching efficiency.
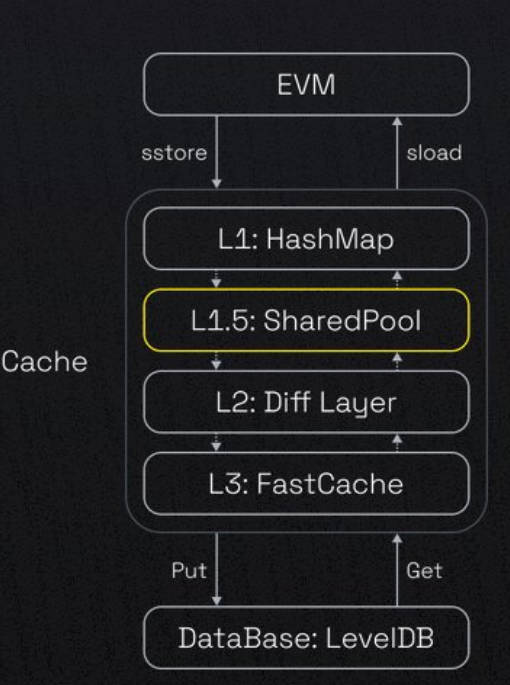
It aims to address scalability challenges faced by blockchain networks, particularly in terms of transaction throughput and cost.
With a block size of 100M, opBNB enables a significantly higher number of transactions to be processed per block.
ZK Stack
The primary purpose of ZK Stack is to enable the creation of customized Zero-Knowledge (ZK)-driven Layer-2 (L2) and Layer-3 (L3) solutions, known as Hyperchains.
It is based on code from the previous zkSync Era implementation.
ZK Stack is a modular and open-source framework developed in response to the challenges outlined in the ZK Credo.Reference link
Polygon 2.0
On June 20, Polygon Labs’ engineering team introduced a proposal to upgrade Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to a zkEVM validium.
zkEVM validium is a novel concept combining elements of zero-knowledge proofs and EVM-compatible environments.

Validium describes a blockchain scaling solution that combines aspects of Rollups and Sidechains.
It aims to deliver higher throughput and lower costs than the main chain while still benefiting from its security and decentralization.
Polygon 2.0 is a ZK-powered Layer 2 blockchain network unified by a new cross-chain coordination protocol.
The vision centers on every Polygon chain being a ZK L2.
The goal is to enhance user security while maintaining existing functionality and low fees.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News