Huobi Growth Academy | In-Depth Research Report on Stock Futures: The Next Trillion-Dollar Battlefield for On-Chain Derivatives
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Huobi Growth Academy | In-Depth Research Report on Stock Futures: The Next Trillion-Dollar Battlefield for On-Chain Derivatives
Perpetual stock contracts are at a critical breakthrough stage—from zero to one.
Executive Summary
Stock perpetual contracts—a groundbreaking product bridging traditional financial markets and crypto derivatives ecosystems—are rapidly reshaping on-chain trading landscapes. This report delves into the product’s fundamental nature, growth logic, technical architecture, and market ecosystem, while systematically analyzing its regulatory challenges and future outlook. Our findings reveal that stock perpetuals are far more than a conceptual novelty: they represent a structural opportunity built upon the global equity market’s $160+ trillion market capitalization and the mature trading paradigm of perpetual contracts. Today, leading Perp DEXs—including Hyperliquid, Aster, and Lighter—have already established comprehensive stock perpetual product suites, achieving clear leadership in trading depth, user experience, and asset coverage. Yet regulatory uncertainty remains the sector’s greatest constraint; the path to compliance will directly determine its long-term scalability. Looking ahead, stock perpetuals are poised to drive the on-chain derivatives market’s evolution from crypto-native assets toward “full-asset perpetualization,” emerging as a potential next trillion-dollar growth frontier.
I. Product Essence: Structural Integration of Traditional Assets and On-Chain Derivatives
A stock perpetual contract is an on-chain synthetic derivative whose value tracks the price movements of traditional equities. Users deposit stablecoin margin to gain long or short exposure to U.S. equities such as Apple, Tesla, and NVIDIA—without physically owning shares or receiving dividends, voting rights, or other shareholder privileges. This design elegantly merges the foundational asset base of traditional financial markets with the battle-tested perpetual contract mechanism of crypto markets, creating a novel financial instrument that preserves equity price risk characteristics while delivering on-chain trading flexibility.
Product positioning demands a clear distinction between stock perpetuals and tokenized stocks (RWA Stock Tokens). Tokenized stocks typically involve custodians holding the underlying equities and issuing on-chain tokens representing genuine equity ownership; their legal status and regulatory framework closely mirror those of traditional securities. Stock perpetuals, by contrast, entail no equity relationship whatsoever: they rely solely on oracles to track stock prices and build a purely price-risk trading market on-chain via funding rates, margin requirements, and liquidation mechanisms. This fundamental divergence places them in entirely separate categories—tokenized stocks constitute asset-onboarding and custody solutions, whereas stock perpetuals represent risk-trading innovations in derivatives.
The rise of stock perpetuals is no accident but the result of multiple converging forces. On the demand side, global users harbor long-suppressed appetite for U.S. equity trading—traditional brokerages impose cumbersome account-opening procedures, restrict cross-border fund flows, and enforce fixed trading hours, all of which starkly contrast with crypto users’ expectations of “24/7 trading, stablecoin settlement, and flexible high leverage.” Stock perpetuals offer an alternative pathway to participate directly in U.S. equity price movements—bypassing traditional financial infrastructure altogether. On the supply side, since 2025, maturing oracle technology, widespread adoption of high-performance blockchain infrastructure, and intensifying competition among Perp DEXs have collectively laid the technical foundation and market impetus for product rollout. Crucially, stock perpetuals sit precisely at the intersection of two dominant narratives—“RWA (Real World Assets)” and “on-chain derivatives”—combining the massive capital base of traditional assets with the high-growth potential of crypto derivatives, naturally drawing intense market attention.
II. Core Mechanisms: The Triple Challenge of Pricing, Liquidation, and Leverage
The stable operation of stock perpetuals depends on a finely tuned set of underlying mechanisms spanning price discovery, synthetic asset construction, risk control, and leverage management. Among these, the pricing source (i.e., the oracle) serves as the system’s bedrock. Because on-chain protocols cannot directly access real-time Nasdaq or NYSE feeds, decentralized oracles must reliably transmit traditional-market price data onto blockchains. Current mainstream solutions include Pyth Network, Switchboard, Chainlink, and some protocols’ proprietary oracle systems. Pyth sources first-hand quotes directly from market makers and exchanges, emphasizing high-frequency updates and anti-manipulation resilience; Switchboard offers highly customizable price-source aggregation, enabling protocols to dynamically adjust update strategies across timeframes; Chainlink leverages a decentralized node network to deliver robust, continuous, and verifiable price feeds. A select few top-tier protocols—such as Hyperliquid—deploy proprietary oracles, aggregating multi-source market data, constructing internal indices, and performing off-chain risk validation to achieve greater pricing autonomy.
The oracle’s core challenge extends well beyond mere data transmission. U.S. equity markets feature unique structural traits—including non-24/7 trading hours, pre-market and after-hours volatility, and trading halts—which require intelligent handling of market-state transitions. Leading solutions incorporate market open/close flags, TWAP smoothing algorithms, and outlier filtering to ensure on-chain prices remain anchored to reality during U.S. market closures and mitigate manipulation risks arising from low liquidity. For instance, after U.S. markets close, oracles may automatically switch to lower-frequency updates or generate internal reference prices based on the last valid price plus on-chain supply/demand signals—preserving trading continuity while containing tail risks.
In synthetic asset construction, stock perpetuals do not mint tokens representing actual equity ownership. Instead, smart contracts create virtual positions that move in tandem with underlying stock prices. Users post stablecoins like USDC as margin to open long or short positions; profits and losses are determined exclusively by contract price and settlement rules. Protocols use funding rate mechanisms to balance long/short positions: when one side becomes excessively dominant, funding rates incentivize users to open counter-directional positions, maintaining overall systemic risk neutrality. Compared to crypto perpetuals, stock perpetual funding rates must also factor in U.S. equity-specific overnight financing costs and real-world trading rhythms—exhibiting more complex cyclical behavior.
Liquidation mechanisms form the core of stock perpetual risk-control frameworks, confronting the dual challenge of two asynchronous markets: U.S. equities trade only during specific hours, while crypto markets operate 24/7. When U.S. markets are closed but crypto markets experience sharp volatility, users’ collateral values can erode rapidly—triggering liquidation risks for stock perpetual positions. To address this, leading protocols deploy cross-asset risk engines and dynamic parameter adjustment. During U.S. market closures, systems automatically raise maintenance margin ratios, lower maximum leverage caps, and tighten liquidation thresholds to hedge against gap-risk stemming from information discontinuity. Once U.S. markets reopen, risk parameters gradually revert to normal. This design preserves on-chain trading continuity while mitigating systemic cross-market mismatch risks through adaptive risk controls.
Leverage design further highlights the distinction between traditional assets and crypto products. While crypto perpetual platforms sometimes offer >100x leverage, stock perpetuals generally cap leverage between 5x and 25x. This reflects multiple considerations: First, stock prices respond to fundamentals—earnings reports, macro events, industry policies—producing volatility patterns distinct from crypto assets. Second, U.S. equities feature gap openings and after-hours trading, making high leverage prone to cascading liquidations. Third, regulators maintain a consistently cautious stance toward equity-linked derivatives; conservative leverage helps reduce compliance exposure. Even if a platform’s interface displays “up to 20x leverage,” actual usable leverage is often dynamically adjusted based on market conditions, underlying liquidity, and user position concentration—creating a “flexible on the surface, strict at the core” risk-control architecture.
III. Market Landscape: Differentiated Competition and Ecosystem Evolution Among Perp DEXs
The current stock perpetual market features a competitive landscape dominated by leading Perp DEXs—including Hyperliquid, Aster, Lighter, and ApeX—each demonstrating clear differentiation in technical architecture, product design, and liquidity strategy.
Hyperliquid leverages its high-performance proprietary chain and HIP-3 third-party build framework to rapidly enter the stock perpetual space via projects like Trade.xyz. Its core strengths lie in deep order books and institutional-grade liquidity—e.g., XYZ100 (a Nasdaq-100 index synthetic contract) achieves daily volumes approaching $300 million, while commodities like SILVER and GOLD sustain open interest in the tens of millions of dollars. Hyperliquid employs a multi-source median pricing mechanism, synthesizing external oracle prices, internal EMA-smoothed values, and order-book market prices to generate robust mark prices for liquidations and margin calculations. This “professional-grade matching + synthetic pricing” dual-channel design strikes an effective balance between high-frequency trading performance and risk control.
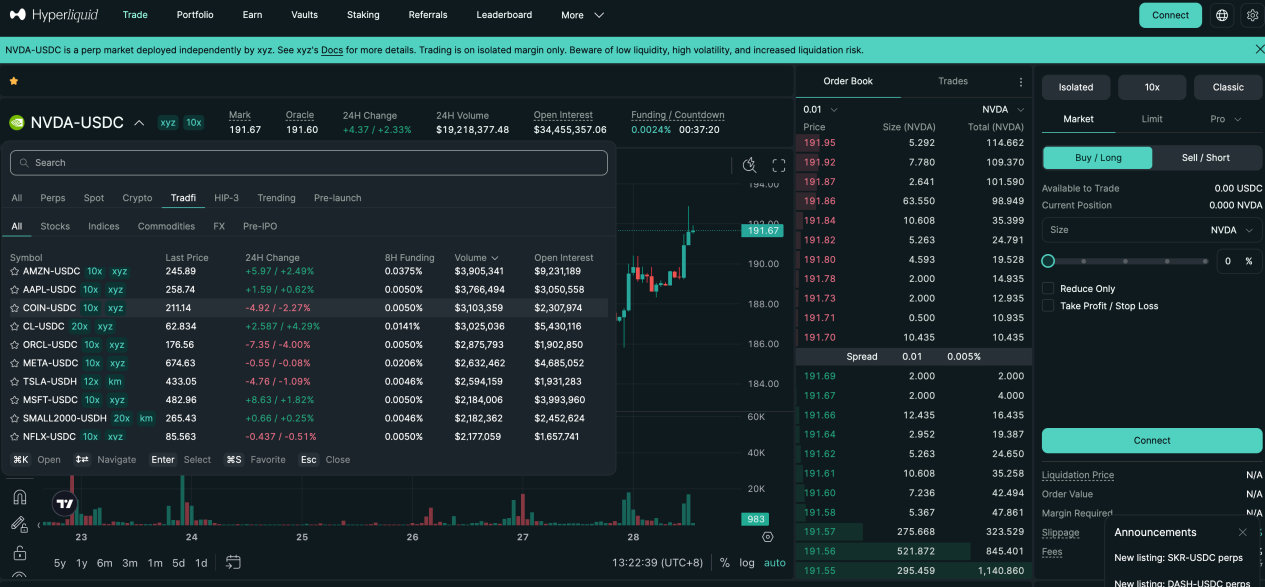
Aster innovatively launched a dual-mode architecture—Simple and Pro—catering to users with differing risk profiles. Simple mode uses an AMM pool mechanism, enabling one-click opening/closing of positions with zero slippage—ideal for high-frequency, small-size, short-term trading—with stock perpetual leverage capped at 25x. Pro mode operates on-chain order books, supporting advanced order types like limit orders and hidden orders, delivering deeper liquidity and finer-grained strategy execution—with stock perpetual leverage capped at 10x. Data shows NVDA and other tech-stock contracts on Pro mode sustain daily volumes in the millions of dollars, with steadily growing open interest—indicating sustained participation by professional traders. Through this “traffic gateway + deep market” two-tier design, Aster effectively segments its user base and expands its ecosystem.
Lighter centers its value proposition on a zk-rollup provable matching system: every trade and liquidation is verifiable on-chain via zero-knowledge proofs, emphasizing transparency and fairness. Its stock perpetuals currently support 10 U.S. equities, with uniform 10x leverage—reflecting a relatively conservative risk-control orientation. Liquidity exhibits pronounced concentration: COIN (Coinbase) routinely exceeds $10 million in daily volume, while NVDA—though mid-tier in volume—shows higher open interest, suggesting anchoring by medium-to-long-term strategic capital. Lighter cleverly balances UX: front-end interactions are ultra-simple, enabling rapid onboarding for newcomers; the underlying infrastructure remains a professional order book, meeting institutional execution needs.
Notably, stock perpetual traffic acquisition is expanding beyond standalone websites into diverse ecosystem touchpoints. Based.one aggregates Hyperliquid’s contract engine to deliver a more consumer-friendly trading interface; Base.app embeds Lighter as a native trading module, allowing users to open positions without leaving their wallets; super-apps like UXUY further streamline workflows, packaging stock perpetuals into near-Web2 user experiences. This division of labor—“underlying protocol + application-layer gateways”—is lowering entry barriers and propelling stock perpetuals from niche professional tools toward mass-market trading products.
IV. Regulatory Challenges: Striking Balance Between Innovation and Compliance
The most significant uncertainty facing stock perpetuals stems from regulation. Though no jurisdiction has yet enacted dedicated legislation targeting this product class, regulators are already closely monitoring its potential risks. The central question concerns legal classification: Do stock perpetuals constitute unregistered securities derivatives?
In regulatory practice, the U.S. SEC consistently applies a “substance-over-form” principle to derivatives tied to securities prices. If a product’s economic substance closely mirrors regulated securities—even if technologically packaged differently—it likely falls under securities law jurisdiction. Similarly, Europe’s ESMA has repeatedly emphasized within the MiCA framework that on-chain derivatives pegged to traditional financial assets remain subject to existing financial regulations. This implies that despite stock perpetuals’ lack of actual equity custody, their tight linkage to U.S. equity prices could classify them as securities derivatives or CFDs (Contracts for Difference), thereby triggering licensing, disclosure, investor protection, and other compliance obligations.
Current regulatory focus remains largely on direct-asset mapping products like tokenized stocks. For “synthetic risk exposures” such as stock perpetuals, regulators are still in observation mode. Potential future regulatory pathways may include: strengthening compliance responsibilities for front-end operators (e.g., trading interface providers, liquidity facilitators); mandating public transparency of price indices and oracle data sources; restricting high leverage and enforcing KYC and geo-based access controls; or explicitly placing such products under existing derivatives regulatory frameworks.
For protocols, strategies to mitigate compliance risk include: clearly distinguishing “price tracking” from “equity tokenization,” emphasizing the product’s synthetic and hedging nature; adopting multi-source decentralized oracles to avoid manipulation suspicion; setting reasonable leverage caps and risk parameters to discourage excessive speculation; and fully disclosing product risks and legal disclaimers in user agreements. Long-term compliant development may require exploring paths such as partnerships with licensed institutions, serving restricted jurisdictions, or launching innovation pilots within regulatory sandboxes.
Beyond regulatory risk, stock perpetuals face a range of market and technical risks. Oracle failures or malicious manipulation could trigger erroneous liquidations; cross-market volatility mismatches could amplify tail risks; insufficient liquidity could cause extreme slippage and difficulty exiting positions; and smart-contract vulnerabilities could be exploited, resulting in fund losses. These risks necessitate multi-layered risk-control systems—including multi-oracle redundancy and anomaly detection, dynamic margin adjustments, insurance fund buffers, smart-contract security audits, and bug-bounty programs.
V. Future Outlook: From Niche Innovation to Mainstream Financial Infrastructure
In terms of market scale, the potential for stock perpetuals is immense. Global listed-company market capitalization now approaches $160 trillion, over half of which resides outside the U.S.—forming an ~$80 trillion asset pool. Even a tiny fraction of this capital entering perpetual formats would easily yield multi-hundred-billion-dollar absolute volumes. Drawing parallels to crypto markets—where perpetual trading volume already exceeds spot volume by over threefold—stock perpetuals stand to replicate this derivatives-driven expansion within traditional assets.
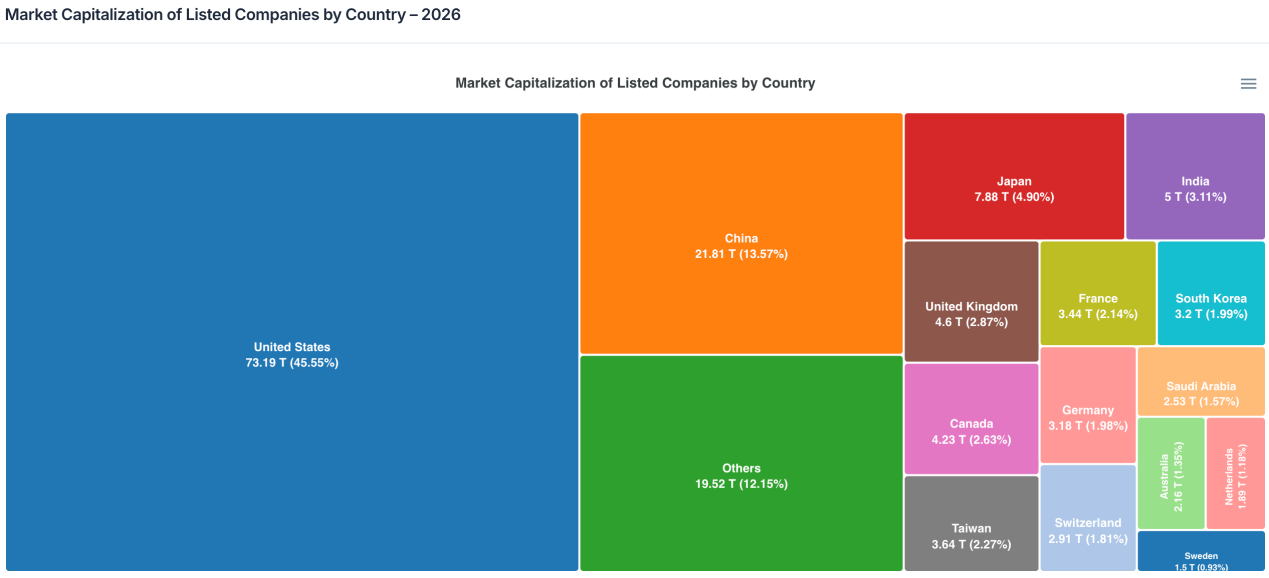
In product evolution, stock perpetuals may merely mark the starting point of a broader “full-asset perpetualization” wave. As pricing mechanisms, liquidation systems, and liquidity infrastructure mature, commodities (gold, oil), equity indices (S&P, Nasdaq), foreign exchange (EUR, JPY), and even macroeconomic assets like interest rates could all be incorporated into perpetual frameworks. Perp DEXs will gradually evolve from crypto-native trading venues into multi-asset-class derivatives markets—serving as critical interfaces connecting traditional finance and on-chain ecosystems.
Regulatory environments will progressively shift from ambiguity toward clarity. Over the next 2–3 years, major jurisdictions are expected to issue classification guidelines and regulatory frameworks specifically for on-chain derivatives, thereby clarifying the compliance boundaries for stock perpetuals. This may cause short-term friction but will ultimately foster industry consolidation and standardized development. Platforms that proactively build compliance capabilities, establish robust risk-management systems, and maintain open dialogue with regulators will gain competitive advantage under new rules.
In summary, stock perpetuals are at a pivotal breakthrough stage—from zero to one. They represent both a natural growth narrative for Perp DEXs seeking new frontiers and a live testbed for integrating traditional assets with crypto finance. Although significant technical hurdles and regulatory uncertainties remain, the enormous underlying market demand and asset scale ensure this is a sector impossible to ignore. In the future, stock perpetuals may not only become a pillar category in on-chain derivatives markets but also fundamentally reshape how global retail investors access U.S. equities—and indeed global assets—enabling truly borderless, 24/7, democratized financial markets. In this journey, protocols best able to balance innovation, risk management, and regulatory compliance will most likely emerge as builders of the next-generation financial infrastructure.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News