Metrics Ventures Report: Why Axelar Is the Most Market-Driven Multichain Protocol?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Metrics Ventures Report: Why Axelar Is the Most Market-Driven Multichain Protocol?
The full-chain赛道 will gain more growth potential and market attention as bull market trading volume increases, the number of public blockchains grows, and other conditions improve.
Authors: Charlotte, Kevin, Metrics Ventures
TL;DR:
-
Axelar sits at the intersection of two major narratives: omnichain interoperability and the Cosmos ecosystem. The omnichain sector is poised for growth as bull market trading volumes rise and the number of blockchains increases. A direct catalyst could come from token launches by LayerZero and Wormhole. Meanwhile, the Cosmos ecosystem is developing healthily, with broad-based gains across its ecosystem in late 2023 drawing renewed market attention.
-
Axelar has built deep technical advantages in the omnichain space, positioning it as a core player in this narrative. It already enables interoperability across 56 blockchains—surpassing competitors like LayerZero. Its General Message Passing (GMP) and Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) simplify multi-chain development, enabling full-chain smart contract deployment and liquidity aggregation.
-
In this cycle, cross-chain protocols capable of omnichain deployments are largely limited to externally validated bridges. Compared to peers, Axelar delivers strong performance in security, number of connected chains, and dApp integrations. Against direct rivals LayerZero and Wormhole, Axelar’s valuation remains significantly below their private round levels.
-
Axelar serves as the primary bridge between the Cosmos ecosystem and EVM chains—especially linking Osmosis to EVM networks. As a key liquidity gateway, it stands to directly benefit from the expansion of the Cosmos ecosystem.
1 Fundamental Analysis: Axelar Unlocks Greater Cross-Chain Possibilities
1.1 Axelar Cross-Chain 101
Built on the Cosmos SDK and compatible with all EVM chains, Axelar is an application-specific blockchain designed to connect all blockchains and achieve true interoperability—supporting the transfer of any information or asset. In implementation, Axelar is an externally validated cross-chain protocol: a standalone PoS public chain with its own decentralized network and validator set.
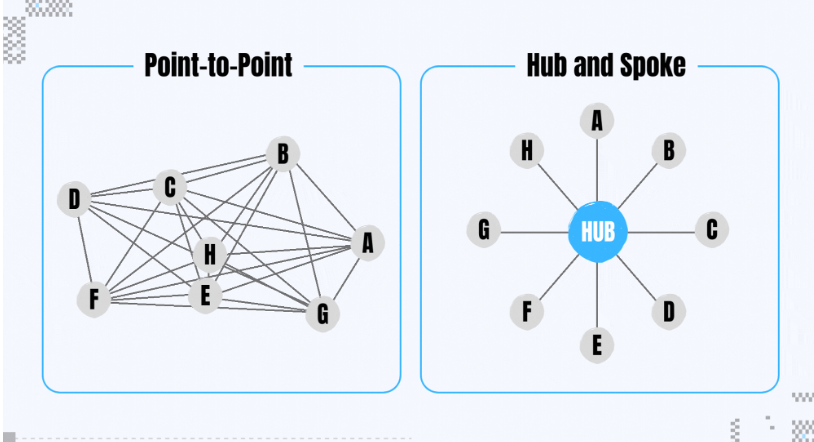
Axelar uses a hub-and-spoke topology, similar to the Hub-Zone architecture in the Cosmos ecosystem. Each blockchain connects directly to Axelar (the hub), enabling indirect connectivity rather than peer-to-peer links. This reduces connection complexity and improves scalability in terms of the number of supported chains.
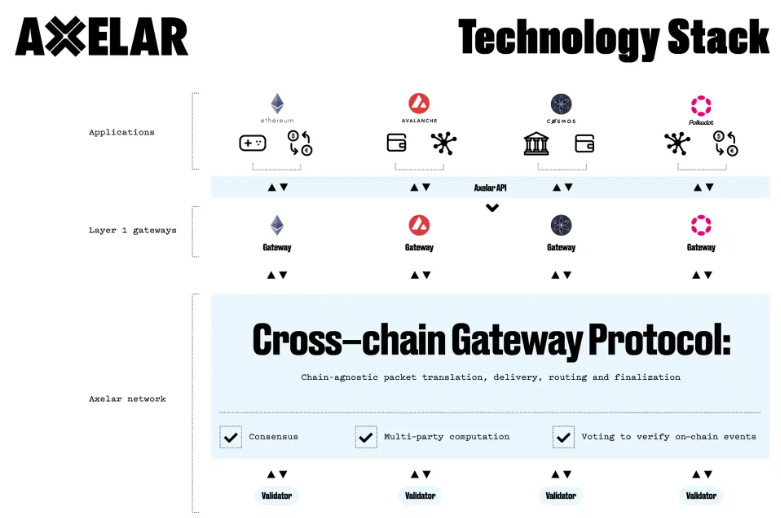
Axelar’s tech stack consists of three core components: the decentralized network, gateway smart contracts, and APIs/developer tools. The decentralized network forms the trust and transport layer, composed of a dynamic, decentralized group of validators that verify on-chain events and perform read/write operations on gateway contracts deployed across connected blockchains. Gateway smart contracts sit atop each connected chain, forming the foundational infrastructure layer together with the decentralized network. Validators monitor source chain gateways, read transactions, reach consensus on validity, and write instructions into target chain gateways to execute cross-chain transfers. APIs and developer tools form the application development layer, enabling developers to easily add universal interoperability to their apps.
For cross-chain protocols, security is paramount. Axelar ensures system security through three mechanisms:
First, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus secured by $AXL tokens. This is the mechanism by which external validators reach agreement on cross-chain transactions. Essentially, Axelar’s security depends on the security of its PoS-based blockchain. It relies on a dynamic, permissionless validator set, offering higher security than bridges relying on PoA or multisig setups.
Second, Quadratic Voting, which enhances decentralization within the consensus mechanism. Under quadratic voting, voting cost = votes². This mitigates oligopolistic control and prevents large token holders from censoring transactions. Axelar implemented quadratic voting in August 2022 during its Maeve upgrade for validating and processing cross-chain messages.
Third, additional security measures beyond consensus, including rate limiting and regular key rotation. Axelar gateways include rate limits to cap the volume of assets transferred within a given time window. Validators are encouraged to rotate keys every two months to defend against persistent attackers. Additionally, all Axelar network code and contracts are 100% open-source, and a bug bounty program incentivizes vulnerability reporting.
1.2 General Message Passing (GMP)
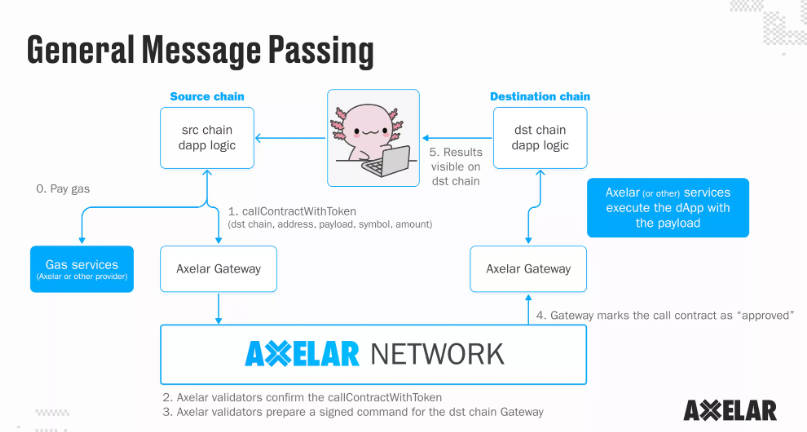
General Message Passing goes beyond simple asset bridging, enabling developers to build native cross-chain applications with chain abstraction—allowing cross-chain function calls and state synchronization. Here’s how GMP works:
A user initiates a call on the source chain. The call enters the Axelar gateway contract and is relayed to Axelar’s decentralized network. Validators confirm the call, deduct fees, and prepare to trigger a transaction on the target chain. Once approved, the call proceeds via the target chain’s gateway and is executed. This gateway-to-gateway process takes approximately 120 seconds and is secured by Axelar’s PoS mechanism.
1.3 Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM)
Building on GMP, Axelar is evolving into a foundational cross-chain protocol for Dapp development. To enhance customization and streamline multi-chain development, Axelar developed the AVM. Supported by CosmWasm, it transforms interoperability into a programmable layer, allowing developers to write smart contracts on Axelar that abstract away cross-chain complexities and improve user experience. Currently, AVM supports three main functions:
- Interchain Amplifier: Allows developers to establish permissionless connections to the Axelar network. By paying the setup cost once, they gain access to all chains in the Axelar ecosystem—“amplifying” their reach. Permissionless connectivity accelerates ecosystem expansion.
- Interchain Maestro: Enables developers to deploy a contract once and run it across multiple chains, eliminating repetitive deployment and reducing time and costs associated with scaling or cloning contracts.
- Interchain Token Service: A component of Interchain Maestro, launched on testnet in July 2023. It allows one-click issuance of cross-chain tokens, reducing redundant deployment efforts. These tokens are interoperable, solving fragmented liquidity across chains. This enhances DeFi liquidity, simplifies cross-chain yield farming and staking, enables cross-chain collateralization, and supports chain-agnostic wallets. Sushi was among the first to adopt this service.
1.4 Tokenomics: New Proposal Will Effectively Reduce Inflation
The $AXL token serves three main purposes:
- Rewards: Token holders can stake AXL or delegate to validator pools to earn rewards. Validators generate blocks and validate messages by staking AXL, earning commissions in return.
- Fees: Used to pay for cross-chain transaction costs on the Axelar network.
- Governance: Enables token holders to vote on proposals such as parameter changes or protocol upgrades.
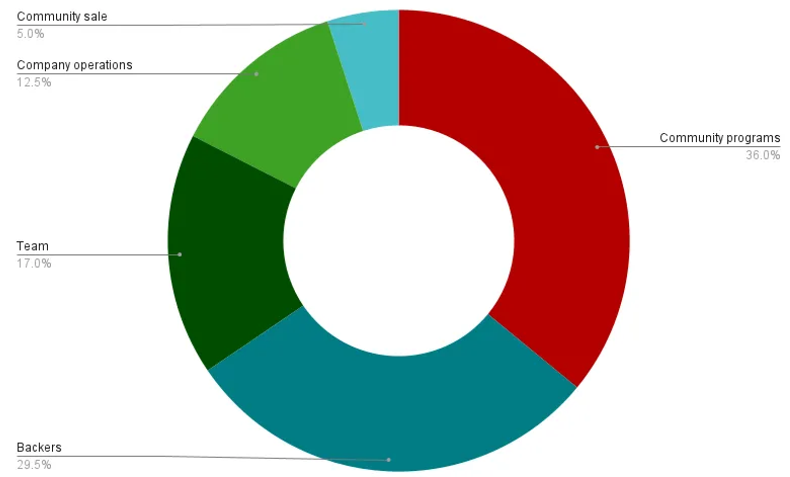
$AXL was launched in September 2022 with an initial supply of 1 billion and no maximum cap. The token distribution and unlock schedule are shown below. Current circulating supply is 535,564,229, total supply is 1,128,220,669 (per Coingecko), staked amount is 761 million (per Axelarscan), and inflation rate is 6.1%.
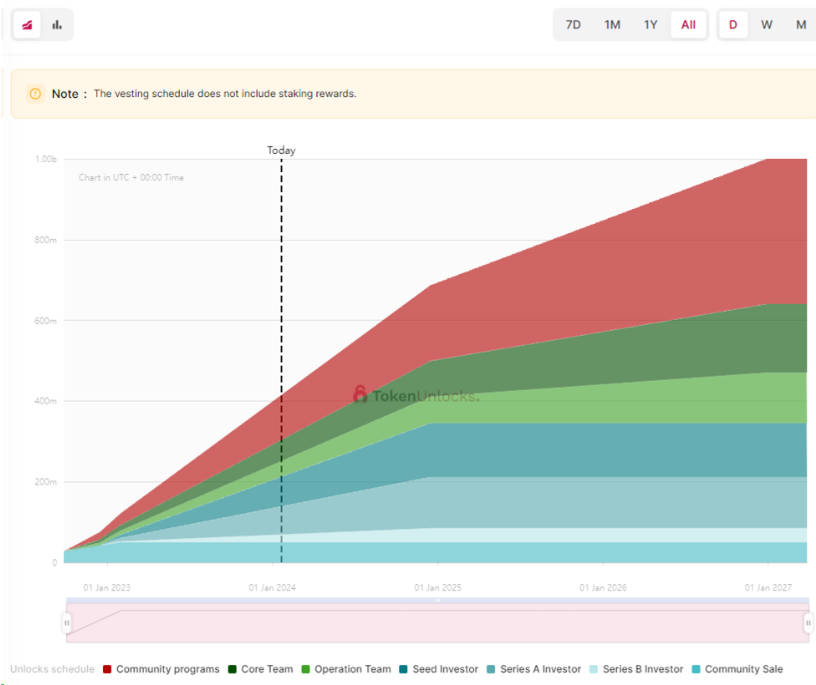
In December 2023, the community passed a proposal to reduce AXL’s inflation rate. Inflation is composed of three parts: Tendermint (TM) consensus, MSigs inflation, and external chain inflation. The first two constitute base inflation. External chain inflation rewards nodes for verifying non-Cosmos chains: 1% per chain in Year 0–1, 0.75% in Year 1–2, and 0.5% in Year 2–3.
The proposal reduces inflation through two main methods: lowering external chain inflation and introducing gas burning.
Previously, external chain inflation was 0.75%, leading to a total inflation rate of 11.5% (1% base + 0.75% × 14). The proposal reduces external chain inflation to 0.3%, bringing total inflation down to 5.2%. With five new EVM chains expected, inflation would rise slightly to 6.7%. This lowers overall inflation while increasing Axelar’s capacity to support more external chains.
Second, the gas burning mechanism: users pay gas for cross-chain transactions, which was previously redistributed to stakers. The proposal instead burns this gas, permanently removing it from circulation.
1.5 Recent Project Developments: High-Quality Ecosystem Expansion
Since mid-2023, Axelar has partnered with multiple blue-chip projects, rapidly increasing its market share in the interoperability space:
- June 16: Uniswap Foundation released a cross-chain bridge evaluation report, approving Axelar for specific use cases within the Uniswap protocol. Uniswap noted: “Axelar is the only decentralized cross-chain platform with 75 nodes, robust security practices, and a general message passing mechanism enabling one-click interaction with any contract function on any chain.”
- June 23: Axelar became the official cross-chain bridge for Filecoin, bringing liquidity to DEXs and AMMs on FVM. Axelar-wrapped assets will become the standard cross-chain assets in the Filecoin ecosystem.
- July 11: Microsoft and Axelar announced a partnership. Axelar offers cross-chain services to Microsoft customers via Azure Marketplace.
- September 12: Squid enabled direct token swaps between Ethereum, various EVM-compatible chains, and the Cosmos ecosystem, supporting 14 EVM chains and 48 Cosmos chains.
- September 14: Lido selected Axelar and Neutron to launch wstETH on Cosmos. Neutron and Axelar provide liquidity.
- November 13: Ondo Finance partnered with Axelar to launch the Ondo Bridge. Any chain integrated with Axelar can now issue USDY.
- November 15: JPMorgan, Apollo, and Axelar formed a collaboration.
- November 21: Frax passed a proposal to use Axelar for expanding to new chains.
- December 14: Announcement of Vertex integration, making Vertex another flagship DEX—after dYdX, Uniswap, and PancakeSwap—to adopt Axelar.
1.6 Summary: Axelar Holds Leading Technical Advantages in Omnichain
“Interoperability is the future.” Axelar has accumulated significant technical expertise in the omnichain space and is positioned as a core project in this narrative. Omnichain encompasses two dimensions: achieving interoperability with as many blockchains as possible—including both EVM and non-EVM chains—and going beyond asset transfers to enable arbitrary message and data transmission. Anchored in the Cosmos liquidity hub, Axelar already supports interoperability across 56 chains—outpacing competitors like LayerZero. Moreover, Axelar supports arbitrary message passing, and the AVM further enhances this functionality, simplifying multi-chain development and enabling full-chain contract deployment and liquidity integration. Combined product delivery and ecosystem growth demonstrate Axelar’s deep technical foundation and solid fundamentals.
2 Competitive Landscape Analysis: Why Is Axelar the Most Market-Aligned Cross-Chain Protocol?
2.1 Sector Analysis: What Kind of Cross-Chain Protocol Do We Need?
Before analyzing Axelar’s competitors, it’s important to review the broader cross-chain landscape: Why is the cross-chain sector still growing? What kind of cross-chain protocol do we need? And what types exist today?
Why is the cross-chain protocol sector still promising?
First, rising demand for blockchain scalability and customization has led to more public chains being developed. Many Dapps, including dYdX, are migrating toward appchains. Growth in modular blockchains, general-purpose rollups, and appchains is rapidly increasing the number and diversity of blockchains. Interoperability is crucial in this multi-chain era, making cross-chain protocols essential foundational infrastructure.
Second, according to L2beat, the TVL of the cross-chain bridge sector is $6.7 billion—down nearly 90% from its peak of $56 billion. However, the next bull market will increase on-chain interactions and cross-chain demand. More blockchains mean greater reliance on cross-chain technology. With new architectures and innovations emerging, the sector still has massive growth potential.
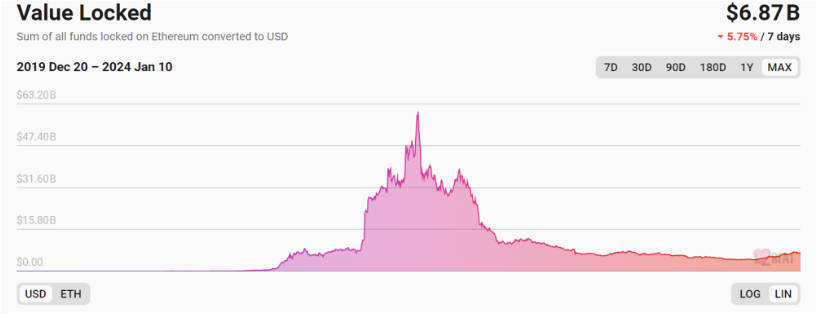
Third, despite its importance, cross-chain development has been underwhelming. Cross-chain bridges remain among the most frequently attacked and compromised components, raising serious security concerns. Additionally, most existing protocols focus on asset bridging, while solutions enabling seamless cross-chain application development are still in early stages. Given how critical this infrastructure is, there remains substantial room for technical advancement.
What kind of cross-chain protocol do we need?
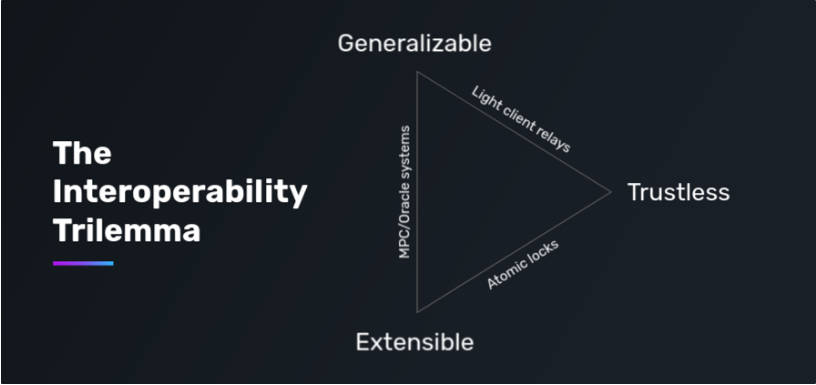
As defined by Connext founder Arjun Bhuptani, cross-chain interoperability faces an impossibility trilemma: Trustlessness (security), Generalizability (functionality), and Extensibility (scalability). These represent the market’s core demands.
Security means adding no additional trust assumptions beyond the underlying chains—achieving equivalent security. Security remains the top concern. The most recent major attack occurred on January 1, when Orbit Chain was hacked for $81.5 million.
Generalizability refers to supporting arbitrary message passing between different blockchains. The current market is dominated by asset bridges focused on transferring or swapping assets—but this is insufficient. Liquidity (capital, users, traffic) remains fragmented across chains, and users still face complex processes when moving between chains. Therefore, protocols are now exploring arbitrary message passing to enable cross-chain contract calls, liquidity aggregation, and native cross-chain applications.
Extensibility means easily adapting to more blockchains, especially heterogeneous ones, with minimal development time and cost. Connecting more chains brings broader user bases, capital, and traffic.
As cross-chain protocols evolve, expectations have shifted—from multi-chain (Multi-Chain) to cross-chain (Cross-Chain), then to omnichain (Omnichain), interchain operations (Interchain), chain abstraction (Chain Abstraction), or chain-agnostic (Chain-Agnostic).
Specifically, Multi-Chain means deploying a Dapp across multiple blockchains, resulting in fragmented instances across ecosystems. Users rely on asset bridges for interaction—characteristic of the asset bridging era. Cross-Chain refers to any process enabling communication and transactions between chains. Unified applications consist of multiple smart contracts across chains, executing coordinated tasks without requiring duplicate deployments. Such cross-chain Dapps depend on general message passing. Omnichain further expands breadth and depth, enabling interoperability across diverse heterogeneous chains. Interchain operations, chain abstraction, and chain-agnosticism aim to hide cross-chain details (gas, native assets, etc.) from users, optimizing UX. Cross-chain protocols will be central to achieving chain abstraction.
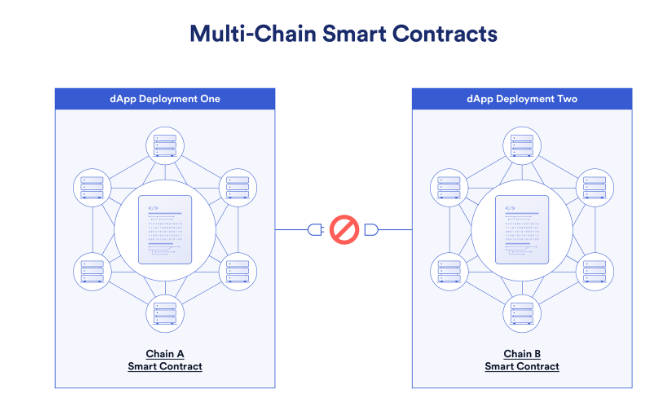
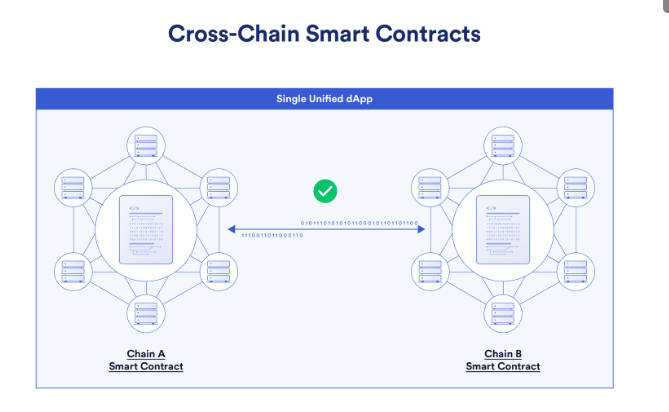
(Source: Chainlink)
Thus, the market seeks secure cross-chain protocols capable of enabling cross-chain deployment and chain abstraction, maximizing both depth and breadth of connectivity.
What types of cross-chain protocols exist today?
While the ideal is clear, reality is more constrained. Cross-chain technology remains early-stage, and current solutions cannot overcome the impossibility trilemma—they must sacrifice some attributes to achieve balance. What types exist today? Which come closest to market needs?
By trust layer, existing protocols fall into three categories: native validation, external validation, and local validation. Native validation involves deploying light clients of the source chain on the target chain to verify messages. Relayers only transmit block headers—not involved in validation. This approach offers the highest security with no added trust assumptions but is costly and technically challenging to implement, limiting extensibility.
External validation introduces a group of external validators (“watchers”) who verify cross-chain messages via internal consensus. These can take various forms: MPC networks, PoS/PoA networks, TEE networks, or multisig groups. External validation offers high extensibility and supports arbitrary message passing but faces criticism over security.
Local validation requires counterparties to directly verify transactions—exemplified by hash time-locked atomic swaps—but only works for asset transfers.
Additionally, new approaches are emerging—most notably ZK Bridges, which apply zero-knowledge proofs to scale light client verification. Proofs are generated off-chain and submitted on-chain, reducing validation costs. However, this technology is still in R&D, with long development cycles and high complexity. It also struggles with differing consensus and signature schemes, limiting scalability.
In summary, while light-client-based bridges offer superior security, they’re currently chain-specific. Thus, external validation remains the dominant model in this cycle. In this cycle, cross-chain protocols capable of omnichain deployment are essentially limited to externally validated bridges. The more decentralized the validator network and the stronger the consensus security, the better they meet market expectations.
2.2 Comparative Analysis: Axelar Is the Best-Matched Cross-Chain Solution
Based on the above analysis, externally validated protocols supporting general message passing are the main players this cycle—and Axelar’s direct competitors. Key examples include Wormhole, LayerZero, Chainlink CCIP, and Celer. After comparison, we believe Axelar is the strongest overall solution in security, general message passing, and ecosystem growth.
2.2.1 The Most Important Factor: Security
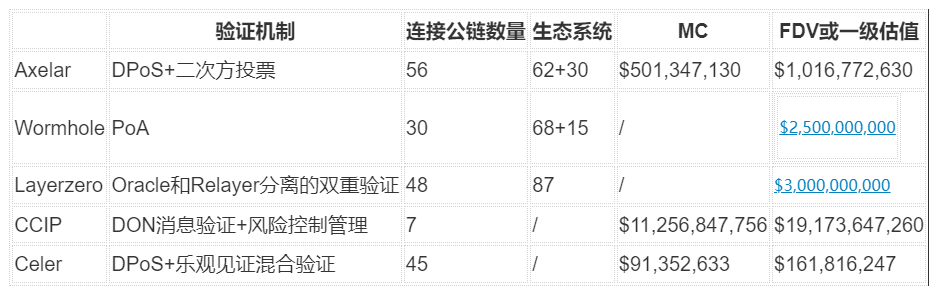
A cross-chain protocol’s security primarily depends on its trust layer’s consensus mechanism—how messages are verified. Among these projects, Axelar uses DPoS, Wormhole uses PoA, LayerZero uses a dual Oracle-Relayer model, CCIP uses its own oracle network, and Celer uses a combination of DPoS and optimistic validation.
Wormhole:
PoA-based bridges have suffered major hacks: Multichain lost over $265 million in July 2023 and has since lost competitiveness. Wormhole itself was hacked in February 2022 for ~$226 million. PoA relies on a small group of trusted entities to validate messages. With few validators, no staking, and weak economic incentives, many nodes are controlled by highly aligned or even single entities, leading to low attack costs and poor security.
LayerZero:
LayerZero V1 uses a dual-verification model with three components: Oracle, Relayer, and Endpoint. The Relayer transmits messages and proofs, the Oracle fetches and sends block headers based on the message block. The target chain’s Endpoint verifies the message using the block header. The core design separates Oracle and Relayer to prevent collusion. However, LayerZero allows projects to run their own Oracle and Relayer, reintroducing trust in those parties—leading to ongoing security criticisms.
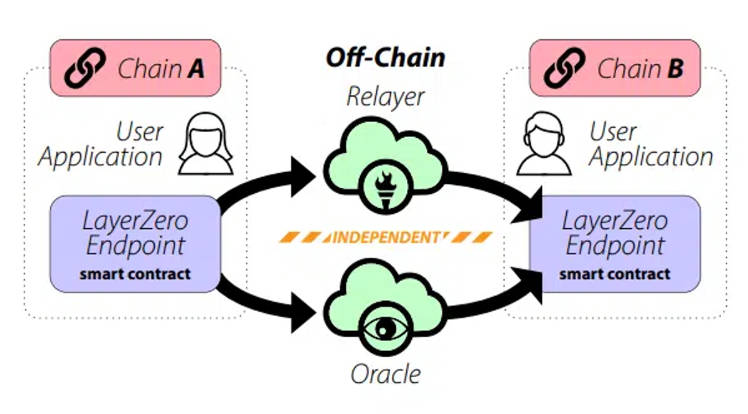
Recently, LayerZero released its V2 whitepaper. Message validation is now handled by a Decentralized Verification Network (DVN), while Executor relays validated messages and triggers transactions. Validation uses an X-of-Y-of-N scheme (e.g., 1-of-3-of-5): select 5 DVNs, require 1 mandatory, and any 2 others to validate. Current DVN operators include major players like Blockdaemon, Google Cloud, Animoca, Gitcoin, Nethermind, P2P, and Polyhedra. However, trust in these entities is still required—especially when DVN count is low—introducing more trust assumptions than PoS. Notably, LayerZero includes Axelar and CCIP as DVN adapters, indirectly validating Axelar’s security.
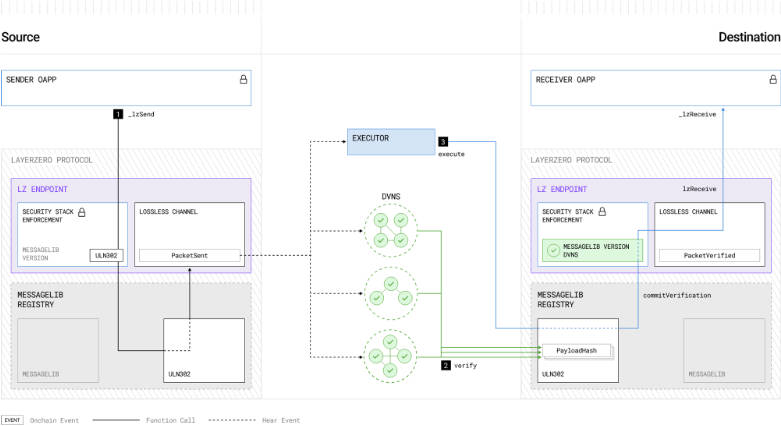
Chainlink CCIP:
CCIP uses Chainlink DONs to monitor and sign message transfers, with Relayers delivering them to target chains. It also includes a separate risk management system—a second validation layer. Risk Management Nodes monitor Merkle roots submitted on each target chain and independently reconstruct Merkle trees from source chain messages. If discrepancies are found, nodes can vote to halt CCIP. Security primarily rests on DONs, which have secured tens of billions in assets and facilitated trillions in transaction value—making them trustworthy. However, CCIP’s development has been slow: announced in 2021, it only entered mainnet early access in mid-2023.
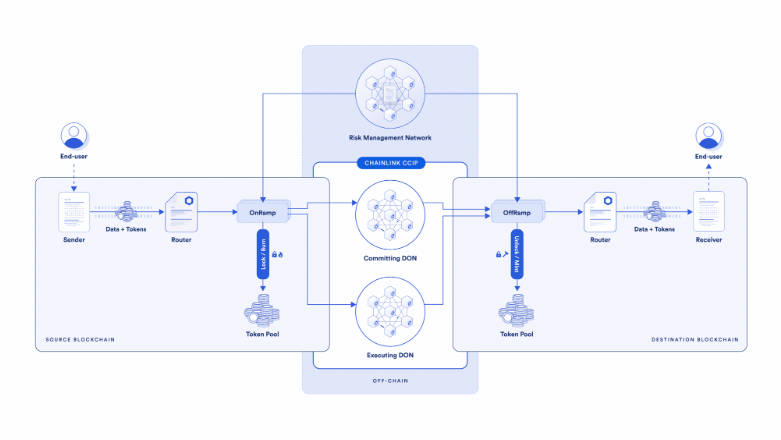
Celer IM:
Celer IM uses the State Guardian Network (SGN)—a Cosmos SDK-based PoS chain where $CELR stakers become validators—to monitor, route, and validate transactions. It also offers an optimistic validation model: messages are submitted on-chain and enter a “quarantine zone.” After a challenge period, they are finalized. During quarantine, Dapps can run App Guardian services to verify authenticity.
However, Celer currently has only 22 validators—including IOSG, Hashkey, Binance, Ankr, InfStones—raising concerns about centralization. Uniswap’s bridge evaluation highlighted risks from single entities operating multiple validators. Conditions for becoming a validator are unclear from public docs. Optimistic validation relies on Dapps running their own guardians, depending on their maintenance and trustworthiness—so trust assumptions aren’t reduced to 1/N.
**In conclusion, Axelar stands out in security among current solutions.** Its security was recognized by Uniswap in June, which praised its “robust cryptoeconomic mechanisms ensuring protocol security.”
From a mechanism design perspective, Axelar’s reliance on a dynamic, decentralized, permissionless PoS network represents the lowest-trust solution.
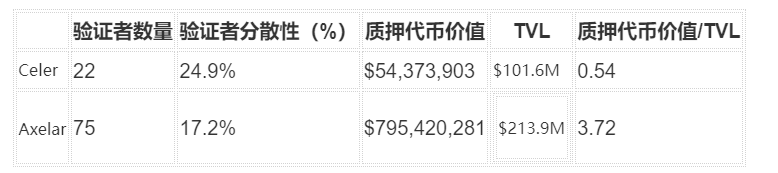
From a data standpoint, we can compare Axelar with Celer, another PoS-based protocol. Two key metrics: (1) validator-related; (2) locked token value.
(1) Validator-related: Axelar has 75 validators—over three times Celer’s 22. Validator decentralization is measured by the cumulative voting power of the top 10%. Lower values indicate better distribution. Axelar’s validators are more evenly distributed, reducing centralization risks.
(2) Locked token value: Axelar’s staked value is $795.4 million—about 15 times Celer’s. The ratio of staked value to TVL is 3.72 for Axelar—healthy—while Celer’s is below 1, meaning security collateral is less than protected assets, increasing attack risk.
2.2.2 Scalability and Ecosystem Growth
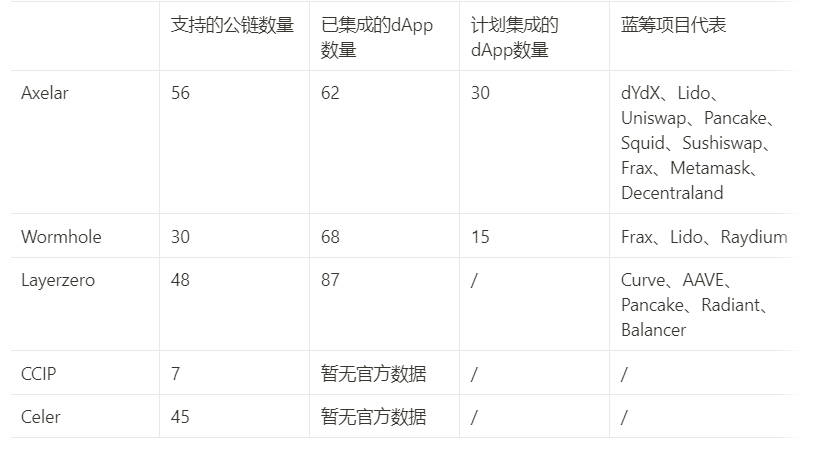
First, for Dapps, connecting to a protocol with more supported chains means access to richer capital, users, and markets. Axelar currently supports the most chains and is integrating Solana, Ripple, Sui, and others. It has also developed auto-L2 integration. Its hub-and-spoke architecture scales better than point-to-point models. LayerZero, Celer, and Wormhole have relatively high scalability, while CCIP is early-stage, supporting only a few Ethereum ecosystem chains.
Second, in terms of dApp integrations, Axelar’s ecosystem is expanding rapidly, leading in capturing interoperability market share. Nearly 100 dApps are integrating Axelar—more blue-chips than any other bridge—and it has partnered with enterprises like Microsoft and JPMorgan. Its integrations span diverse sectors, with standout performance in cross-chain DEXs: dYdX, Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and Vertex all use Axelar. Axelar already holds over 50% market share in cross-chain DEX volume.
2.2.3 Summary: Axelar Is the Most Comprehensive and Mature Cross-Chain Solution
In summary, Axelar is currently the best solution meeting market demands for security, scalability, and general message passing. Wormhole and LayerZero are gaining attention due to anticipated token airdrops. Axelar’s fundamentals match theirs, yet its FDV is less than half their private valuations—indicating it is undervalued in the cross-chain space.
3 Axelar: A Key Gateway to the Cosmos Ecosystem
Another compelling reason to watch Axelar is its role in the Cosmos ecosystem narrative. We consider two questions: Why is the Cosmos ecosystem worth watching? And if investing in Cosmos, why is Axelar a must-have exposure?
First, why is the Cosmos ecosystem worth attention?
First, the appchain narrative is a key theme this cycle. Cosmos was built around this idea—each chain purpose-built for hosting applications, seamlessly connected via shared communication standards.
Of course, Cosmos faces competition from Ethereum’s rollup ecosystem, but its technical standards offer unique advantages:
-
Cosmos allows developers to build more sovereign Layer 1s with greater autonomy in tokenomics and technology—rather than relying on Ethereum as an L2/L3.
-
Cosmos achieves interoperability via IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication), enabling seamless asset and data transfer between chains—an advantage unmatched by other ecosystems.
Moreover, dYdX’s migration from Ethereum to build an appchain on Cosmos brought significant visibility to Cosmos’ appchain narrative. Technologically and in market perception, Cosmos will hold a strong position in this trend.
Second, recent upgrades in Cosmos are fostering healthier ecosystem growth. Two key developments: First, Replication Security launched March 15, 2023, allowing Cosmos chains to adopt Cosmos Hub’s validator set for security—boosting ATOM utility and lowering appchain development barriers. Second, Noble’s partnership with Circle brings native USDC to Cosmos. After UST’s collapse, Cosmos lacked native stablecoins, relying on bridged versions that introduced systemic risk.
Finally, the Cosmos ecosystem is thriving. It’s growing rapidly, with several projects seeing massive gains in 2023—Celestia, Injective, Osmosis, Kujira, Neutron. Broad-based appreciation has rekindled market interest, and sentiment toward Cosmos is generally positive.
Second, why is Axelar a top pick for Cosmos exposure?
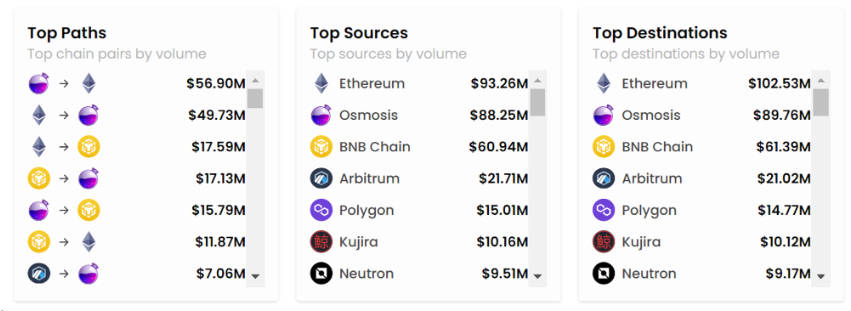
Axelar is the primary bridge between the Cosmos ecosystem and EVM chains—especially connecting Osmosis to EVM networks. In the past 30 days, cross-chain volume between Osmosis and Ethereum via Axelar totaled $106.63 million. Axelar is Osmosis’ main path to EVM chains. As more applications build on Cosmos, demand for cross-ecosystem connectivity will grow. Axelar is the most critical conduit between Cosmos and other ecosystems, directly capturing value from Cosmos’ expansion.
4 Conclusion: Strong Fundamentals, Right Timing
In conclusion, we believe Axelar is a compelling investment opportunity at this stage, for two main reasons: solid fundamentals and favorable timing.
First, from a fundamental perspective, Axelar has clear technical advantages in the omnichain space, with deep expertise evident in the number of connected chains, message/data transmission capabilities, and full-chain application development. It is currently the most market-aligned cross-chain protocol, delivering strong performance in both security and scalability as a general message passing solution.
In security, Axelar uses a dynamic, permissionless validator set with quadratic voting, backed by sufficient validator count, token lock-up value, and decentralization—making it one of the most secure externally validated protocols.
In scalability, Axelar supports the most connected chains and serves as the primary link between Cosmos and EVM chains. Its hub-and-spoke architecture reduces integration costs, and AVM lowers the barrier for developers to build on Axelar. Recent partnerships with blue-chip projects and enterprises validate its ecosystem momentum and growth potential.
Second, from a timing perspective, Axelar operates within two high-potential narratives—omnichain and Cosmos—that are expected to grow significantly in market attention and value.
Axelar benefits from both the omnichain and Cosmos ecosystem narratives. The omnichain sector will expand as bull market volumes rise and more blockchains emerge. A direct catalyst may come from token launches by LayerZero and Wormhole, potentially sparking a market-wide surge in interest. LayerZero has confirmed plans to distribute tokens in the first half of 2024.
As a direct competitor, Axelar’s FDV is significantly below their private valuations and could undergo meaningful revaluation following these events. Meanwhile, the Cosmos ecosystem is growing healthily, with late-2023 gains drawing market attention. As the primary liquidity gateway between Cosmos and EVM chains, Axelar is poised to directly benefit from Cosmos’ growth.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















