IGO Born on ZKFair: A Revolution in Fair Launches
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

IGO Born on ZKFair: A Revolution in Fair Launches
Both inscription projects and the IGO model reflect the current cryptocurrency market's strong emphasis on innovation and fairness.
ZKF Fair Launch
In the current Ethereum ecosystem, zk-rollup technology has gained widespread industry recognition for its significant advantages in network scalability and reducing transaction costs. By bundling numerous transactions and processing them off-chain, this technology greatly enhances network throughput while lowering users' transaction fees, making blockchain applications more practical and economically viable.
Against this backdrop, ZKFair—the first EVM-compatible Layer 2 (L2) platform built on Polygon’s CDK and Celestia’s data availability layer—launched a 48-hour Fair Launch event on Christmas Eve 2023 to distribute its new token, ZKF. A total of 10 billion ZKF tokens are planned for issuance. Participants earned airdrop eligibility by conducting transfers and consuming gas on the ZKF chain. This mechanism ensured fair token distribution, as the number of tokens received was proportional to the amount of gas consumed. Additionally, 25% of the ZKF tokens will be airdropped after the event to community contributors, while the remaining 75% will be fairly distributed among participants in the Fair Launch.
Token Issuance Models
1. Traditional Token Issuance
Traditional token issuance typically refers to projects directly issuing tokens to investors through private sales, pre-mining, or public sales. This method often lacks standardized procedures and third-party involvement such as exchanges. It may include early private investment rounds and token allocations to early supporters, development teams, or advisors. Due to full control by the project team, this approach generally offers lower transparency and security.
2. ICO (Initial Coin Offering)
ICO is an early token sale model analogous to IPOs in traditional finance. In an ICO, projects sell newly created tokens to the public, primarily to raise funds for development and operations. Investors usually buy tokens expecting future price appreciation. ICOs fueled the 2017–2018 bull market but suffered reputational damage due to regulatory issues and fraudulent projects, leading to minimal usage today.
3. IEO (Initial Exchange Offering)
IEO is a token issuance method conducted through centralized cryptocurrency exchanges. The exchange performs due diligence on the project and hosts the token sale on its platform. Investors must register an account with the exchange and purchase tokens via its interface. IEOs are generally considered safer than ICOs because exchange involvement provides investors with a degree of trust and validation.
4. IDO (Initial DEX Offering)
IDO takes place on decentralized exchanges (DEXs), bypassing centralized platforms by using smart contracts to issue and sell tokens directly. Advantages include higher transparency and lower entry barriers, making it a fairer and more web3-aligned issuance method. IDOs help projects gain immediate liquidity since tokens can be traded on the DEX right after launch. However, in practice, IDOs are mostly used as supplementary mechanisms and represent a relatively small portion of total token issuance.
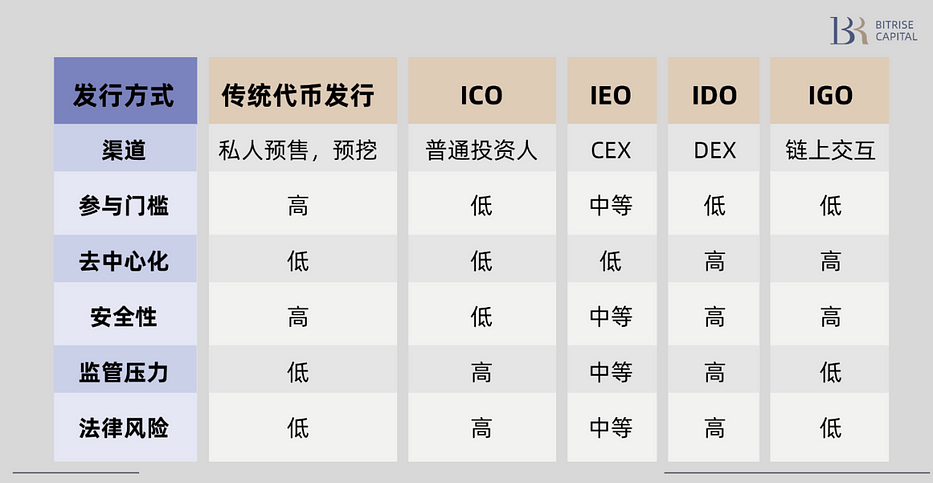
IGO (Initial Gas Offering)
The ZKFair Fair Launch represents a revolution in token distribution. Its format does not fit into any previous model. Participants earn token airdrops based on the proportion of gas they burn through on-chain transfer activities, while the project team uses the collected gas fees as revenue from the token issuance. This is innovative both in airdrop rules and fundraising structure. After internal discussion, Bitrise Capital proposes naming this new form of token issuance IGO (Initial Gas Offering). The key characteristics of IGO can be summarized as follows:

1. Issuance Criteria
ZKFair’s Fair Launch demonstrates fairness in its token issuance mechanism. Crucially, there are no restrictions on participant identity: whether large institutions or individual retail users, anyone who performed eligible actions on the ZKFair chain during the event automatically qualified for the ZKF airdrop. Moreover, there was no whitelist or pre-sale phase, ensuring equal participation opportunities. Out of the total 10 billion tokens, 2.5 billion were allocated to community contributors, while the remaining 7.5 billion were fairly distributed via airdrop to all participants. The event was divided into four phases, each lasting 12 hours. A total gas cap of 3 million USDC was set, with 1.875 billion ZKF tokens (valued at 750,000 USDC) allocated per phase. If gas consumption exceeded 750,000 USDC in a phase, the airdrop allocation was prorated based on each user’s share of total gas spent. Excess gas payments would be refunded proportionally after the event.
For example, if 1 million USDC worth of gas was consumed in Phase 1, a user who spent 10,000 USDC would receive approximately 18.75 million ZKF tokens and a refund of 2,500 USDC. This mechanism ensures that regular participants aren’t priced out by large capital players. By refunding excess gas fees proportionally, it also eliminates wasteful gas burning common in prior airdrop events. This thoughtful design reflects deep consideration for fair distribution and demonstrates ZKFair’s commitment to equity in practice.
2. Nature of Issuance
Under the Initial Gas Offering (IGO) framework, participants’ roles and motivations differ significantly from traditional token issuance models. This new mechanism is not based on direct financial investment but on active participation and contribution to the ecosystem. Participants earn airdrop eligibility through interactions and transactions on the ZKFair chain—including using dApps and spending gas. This form of engagement resembles consumer behavior: users actively participate by utilizing services and applications within the ecosystem and are rewarded with token airdrops as an additional incentive.
This model can be compared to traditional promotional campaigns. For instance, during a mall anniversary sale, customers who spend a certain amount receive free gifts. Here, the mall (i.e., the ZKFair ecosystem) offers various goods and services, and the gifts are analogous to the token airdrops users receive for engaging with the ecosystem. This approach not only encourages deeper user involvement but may also reduce legal risks associated with traditional token sales, as it emphasizes participation and consumption rather than direct financial investment.
Moreover, the design of the IGO model reflects the blockchain and crypto space’s growing emphasis on user engagement, highlighting the importance of building a more inclusive and dynamic ecosystem. It incentivizes users to experience and support blockchain projects through real application usage, thereby promoting technological adoption and innovation. In the long term, the IGO model can help projects build broader user bases and foster a more active and healthy blockchain ecosystem.
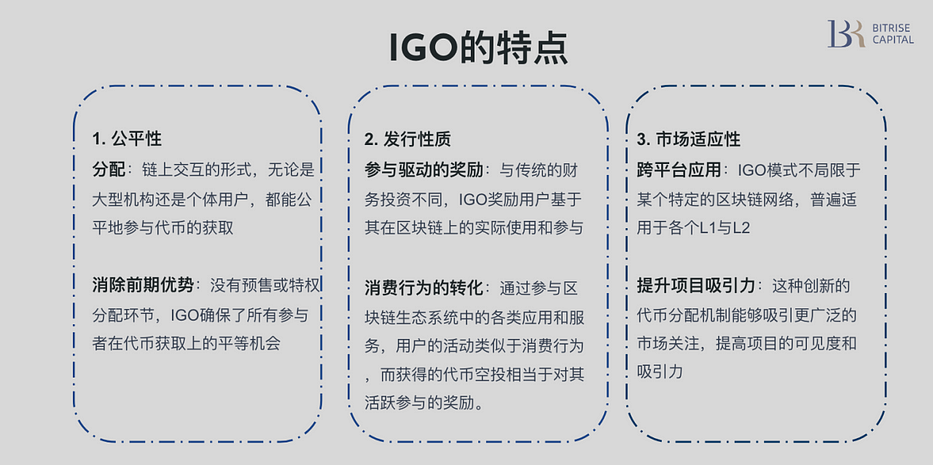
Market Prospects of IGO
During the current bull market, inscription projects have played a pivotal role in kickstarting momentum. Their success lies not only in effectively solving asset issuance within the Bitcoin ecosystem but also in adopting the "fair mint" principle as a core narrative. This principle centers on creating a fair and open market environment driven by broad retail participation, ensuring everyone has a chance to join. The openness and inclusivity of this market environment are key reasons why inscription projects have received strong market recognition.
Building on this foundation, the emergence of the IGO (Initial Gas Offering) model represents a successful adaptation of the core values of inscription projects. IGO emphasizes openness in the early stages of a project, allowing broader participation from ordinary investors. This increases the project's appeal and visibility, meets fundraising needs, and delivers tangible rewards to active users. With its flexibility and wide applicability, IGO can be adopted across various Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) blockchain networks.
Both inscription projects and the IGO model reflect the current crypto market’s high regard for innovation and fairness. They offer new opportunities for participants and promote the healthy development of the broader blockchain ecosystem. As these models evolve and expand, they are poised to make a lasting impact in the crypto space, stimulating market vitality and driving greater attention and activity across public blockchains. Just as inscription projects brought transformative breakthroughs to the BTC ecosystem, the IGO model holds the potential to spark a wave of new innovations and increased dynamism in the cryptocurrency field.

Industry Feedback
iZUMI Jimmy:
"ZKFair is the first Ethereum Layer-2 modular blockchain to launch fairly using the IGO model. iZUMi values not only the team’s strong technical expertise built over time but, more importantly, their respect for the community, user-friendly low valuation, and transparent, fair, and innovative token distribution model. As a multi-chain protocol and one of ZKFair’s earliest ecosystem supporters, iZUMi hopes more public chain partners can learn from ZKFair’s success. In 2023, iZUMi also launched the iZUMi Layer2 Fund to provide ample on-chain liquidity for partner chains from Day 1."
Bitrise Capital Kevin:
"ZKFair is a highly successful and widely watched recent project. I believe its case is textbook-worthy. I see it as an innovation and have attempted to define this new token issuance method as IGO. From this project, we see that web3 innovation can emerge organically from the community’s grassroots level. It reminds me of the concept of 'self-finance.' In ZKFair’s case, we observe not just a business model breakthrough but also a deliberate move toward de-financialization. The IGO model presents a new way to launch projects while downplaying financial attributes. It’s like going to a supermarket: you consume and receive basic services, and then the store gives you bonus points. For a project’s cold start, this attracts users while solving early funding challenges. Of course, ZKFair’s economic model still has room for improvement, but I’m very optimistic about the team’s ability to self-iterate, especially their capacity to quickly adapt when facing challenges and respond to market changes."
Lumoz Alvaro:
"Lumoz is committed to developing and promoting advanced blockchain applications. Our partnered project, ZKFair, is a Layer-2 solution based on zk-Rollup technology. By integrating Polygon’s Chain Development Kit (CDK) and Celestia’s Data Availability (DA) layer, it aims to enhance transaction processing efficiency while maintaining full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). ZKFair uses USDC as the fee payment token to reduce network congestion and improve transaction speed. Furthermore, ZKFair’s architecture supports a decentralized prover network, reflecting our commitment to network autonomy and sustainable development. This decentralized structure aims to boost network participation and enable more transparent and equitable operations through community governance.
The launch of Fair-L2 LaunchBase marks a solid step forward for Lumoz in supporting emerging ZK-L2 projects. This platform aims to provide critical technical support for future projects to ensure smooth deployment. Our collaboration with Polygon also leverages the advantages of zk-Rollups to enhance transaction efficiency and network security."
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News