LayerZero: Cross-chain interoperability is the new paradigm of connectivity
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

LayerZero: Cross-chain interoperability is the new paradigm of connectivity
Only by enabling interoperability between various blockchains can data and assets achieve full circulation, and solving omnichain interoperability makes the emergence of super applications more likely.

Interoperability has long been an unsolved but critical need
In blockchain, if we consider each blockchain as an independent ledger, the lack of connectivity between these ledgers means that data and user assets on different chains remain relatively isolated. Each individual blockchain functions like a standalone island, with very poor interoperability—this severely limits the potential of blockchain technology.
Only by enabling interoperability across blockchains can we achieve comprehensive circulation of data and assets. Solving omnichain interoperability is key to unlocking the emergence of true super applications.
Omnichain interoperability is the new paradigm for connectivity
In the early days before cross-chain protocols existed, users had to rely on centralized exchanges to transfer assets—completing asset conversion on the exchange and then withdrawing to the target chain. This process involved complex operations, high transaction fees, low efficiency, and only enabled asset transfers—not message passing across chains.
Currently, there are two main types of blockchain interoperability solutions that support both asset and message transfers:
1. Trusted Relayers: This approach sends transactions from the source chain, which are verified and reach consensus via a relay chain before being delivered to the target chain;
2. Light Node Model: This method involves deploying lightweight nodes of each chain on the other chain, synchronizing full block headers bidirectionally to verify transactions on the opposite chain.
The first model lacks decentralization, often results in closed ecosystems rather than open ones, and carries single-point-of-failure risks. The second model incurs high costs—for example, running a light node on Ethereum requires significant daily expenses per connected chain.
To address current limitations in blockchain interoperability, LayerZero proposes a novel solution:
Ultra-Light Node (ULN) Model: This approach deploys an Endpoint on each chain, which runs an Ultra-Light Node (ULN). It uses an Oracle to stream only required block headers containing cross-chain information (rather than all headers sequentially, reducing cost), while a Relayer transmits Proof data. These two components cross-validate each other to ensure message integrity.
The ULN model makes native cross-chain transactions possible.
How LayerZero Achieves Omnichain Interoperability
LayerZero is an omnichain interoperability protocol. It introduces a completely new ultra-light node architecture, providing a secure and reliable infrastructure for various cross-chain applications.
LayerZero operates like an ultra-light node across all chains. It relies on Oracles and Relayers to transmit messages between LayerZero Endpoints on different chains. The Oracle delivers block headers (containing transaction details and message m), while the Relayer delivers transaction proofs (Proof data); mutual verification ensures security.
The diagram below illustrates how a User Application (UA) on Chain A sends a message to a User Application on Chain B via LayerZero:
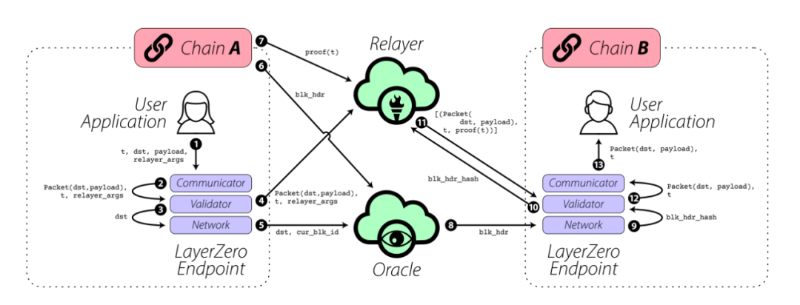
LayerZero consists of three core components: Endpoint, Oracle, and Relayer. Specifically:
1. Endpoint: Directly interacts with users or applications, represented on the user side as a User Application. An Endpoint can be understood as a set of smart contracts deployed on each chain. Each Endpoint contains three modules—Communicator, Validator, and Network;
2. Oracle: More accurately an external component—a third-party oracle service independent of the LayerZero protocol. Currently, LayerZero uses Chainlink. The Oracle's role is to send block header information to the target chain, which is then combined with Proof data from the Relayer to verify transaction validity;
3. Relayer: Responsible for fetching and transmitting Proof data for specific transactions. Currently provided by LayerZero itself, this role could eventually be taken over by application-specific parties. The Relayer earns most of the cross-chain transaction fees.
Advantages of Omnichain Interoperability Based on LayerZero
Omnichain interoperability offers distinct advantages over traditional cross-chain protocols. Beyond delivering both security and low cost through its innovative design, building on LayerZero brings numerous benefits to application-layer protocols.
Application-layer protocols can focus more on their core business development. Applications built on LayerZero are less dependent on the future prospects of underlying blockchains and can instead concentrate on growing their own projects. As more omnichain applications emerge, it may even shift the long-standing industry dynamic of “fat protocols, thin applications,” empowering more startups to build user-attracting application-layer products.
Enables shared global state across chains (Omnichain State Sharing). Traditional multi-chain applications operate in isolation. For example, if Uniswap were deployed on three separate chains using conventional bridging methods, a bridge would need to be built between every pair of chains—requiring three bridges, three separate codebases, three distinct interfaces, and three different security models. Deployment across more chains exponentially increases engineering complexity. With LayerZero, however, only one unified interface and codebase is needed for all cross-chain interactions.
Enables unified liquidity bridging. Conventional bridge protocols suffer from poor capital efficiency. Taking the same Uniswap example: under standard approaches requiring three bridges, each bridge needs a liquidity pool on both the source and destination chains—resulting in six pools total, each needing liquidity seeding, leading to extremely low capital efficiency. With LayerZero, only one bridge is needed, with just one pool per chain. This allows deeper liquidity pools and significantly higher capital efficiency with the same amount of funds.
LayerZero’s omnichain interoperability enables many previously difficult-to-implement use cases, such as:
-
Omnichain bridges;
-
Cross-chain trading;
-
Omnichain yield aggregators;
-
Cross-chain lending;
-
Omnichain tokens / Omnichain NFTs;
-
Omnichain NFT bridges;
-
……
In summary, LayerZero has achieved a game-changing breakthrough in solving the blockchain silo problem through its omnichain vision.
Current State of LayerZero’s Ecosystem
Although LayerZero has been around for less than two years and has only been live on mainnet for three to four months, it already boasts impressive performance.
In terms of platform metrics, it reached $4.4 billion in TVL within just two weeks of mainnet launch, along with billions of dollars in trading volume.
Regarding ecosystem growth, over 700 smart contracts were deployed during the testnet phase. By August, this number had grown to over 4,300 contracts, with more than 600 being highly active.
In blockchain coverage, LayerZero is a clear leader and pioneer in the omnichain space. Initially supporting only seven EVM-compatible chains (including both Layer1 and Layer2), it is now expanding to non-EVM blockchains such as Solana, Aptos, and SUI, aiming to cover most major Layer1 and Layer2 networks in the industry.
Beyond its strong internal metrics, LayerZero’s ecosystem projects are also thriving. Notable examples include:
1. Omnichain Bridge: Stargate
Stargate is an omnichain bridge built on LayerZero, focusing on cross-chain transfers of USDC, USDT, and ETH, offering unified liquidity and fast finality.
It launched with $4 billion in TVL and currently maintains $590 million in TVL. Backed by top-tier investors including FTX, a16z, Sequoia, Binance, and Coinbase, it was valued at $1 billion during its IEO on FTX. Stargate serves as a flagship demonstration project developed by the LayerZero founding team.
2. Cross-Chain DEX: Hashflow
Hashflow is a bridgeless cross-chain trading service built on LayerZero. To date, it has processed over $9 billion in total trading volume, with $23.6 million traded in the last 24 hours and 1,335 daily active users. Hashflow recently announced a Series A round, raising $25 million at a $400 million valuation.
Its standout feature is the Request-for-Quote (RFQ) model, which helps professional market makers better manage liquidity pools, while also providing MEV protection.
3. Omnichain NFT: Gh0stlyGh0sts
Launched on April 4, Gh0stlyGh0sts was the first omnichain NFT collection built on LayerZero. Its free mint and omnichain features quickly captured widespread market attention.
Gh0stlyGh0sts can be minted and transferred on any of seven supported chains. The original chain (mint chain) and current chain influence the NFT’s background and border colors respectively, making it easy to identify its history. However, some controversy exists—the claim that any NFT can be minted on any chain is technically inaccurate; instead, pre-allocated subsets of the NFTs are distributed across chains, rather than allowing any instance to be freely minted anywhere. This design choice by the Gh0stlyGh0sts team might stem from unresolved challenges related to global finality and consistency across chains. Nonetheless, this represents a genuine implementation of omnichain NFTs using the LayerZero protocol.
Following Gh0stlyGh0sts’ success, other projects such as Holograph, Tiny Donos, and Yakuza Pandas have also launched Omnichain NFTs on LayerZero.
Future Outlook for LayerZero and Omnichain
Finally, here are perspectives from Wang Xi, Partner at Bixin Ventures, and Zi, Partner at NGC Ventures, on the future of LayerZero and the omnichain vision:
“LayerZero will become the industry standard for omnichain interoperability—essentially defining what omnichain means. As a foundational infrastructure layer, it will play a pivotal role in advancing the entire web3 ecosystem. Like pioneering companies such as Tesla or DJI, LayerZero is a company that has defined an entirely new sub-industry and major technological frontier.”
— Wang Xi, Partner at Bixin Ventures
“While there are already many cross-chain bridges and applications, the user experience remains fragmented. LayerZero’s true goal with omnichain is to make cross-chain interaction invisible to users, enabling seamless interaction with all assets without awareness of underlying chains.”
— Zi, NGC Ventures
“LayerZero has defined a new standard for omnichain connectivity. It is poised to become a strongly networked omnichain infrastructure with long-term value in the blockchain industry—perfectly aligned with our long-term investment philosophy.”
— Alva Xu, Managing Partner at IOBC Capital
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















