DeFi New Paradigm: Can NESTFi with Infinite Liquidity Break Through in the Derivatives Market?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

DeFi New Paradigm: Can NESTFi with Infinite Liquidity Break Through in the Derivatives Market?
As long as Nest has sufficient liquidity, replicating traditional financial markets becomes extremely simple, and its capabilities will be immensely powerful.

Author: michaeljin.eth, R3PO
NestFi Project Background:
In early 2022, the NEST team began exploring decentralized derivatives protocols and launched a new project called FORT based on the NEST oracle—a decentralized derivatives trading platform built on an infinite liquidity model (OMM), offering products such as perpetual futures and options.
Following the Terra collapse in March and deteriorating macroeconomic conditions, NESTDAO proposed merging NEST and FORT. At the protocol level, the codebases of both projects were integrated and restructured. Operationally, the NEST team consolidated resources from both projects, merging their Twitter and Telegram communities into a single community.
Theoretically, while Bitcoin established a new paradigm for monetary networks and Ethereum created a new paradigm for asset networks, the NEST team believes that the infinite liquidity model pioneered by NEST represents a fundamentally new trading network paradigm—the most significant paradigm shift since Ethereum. In its updated whitepaper, NEST defines itself as blockchain infrastructure providing all developers and users with access to financial assets of any risk-return structure.
Progress in 2023: "Martingale Network"
NEST is about to launch the "Martingale Network," a next-generation infrastructure paradigm succeeding Ethereum. NEST will act as the sole seller via smart contracts in on-chain financial transactions, fulfilling buyer demand while aggregating and hedging transferred risks. Risks that cannot be hedged are shared among all traders—fundamentally solving the problem of insufficient liquidity in risk-hedging assets.
NEST has defined a new trading paradigm derived from a stochastic process concept: martingale trading is a transaction model based on a stochastic process known as a martingale. A martingale is a random process satisfying Xt = E(Xt+s | Ft), where Xt denotes the random value at time t, and s represents the time difference between cash inflows and outflows. Martingale trading occurs under this information flow, considered capable of producing fair outcomes. In this model, traders pay Xt at time t and receive Xt+s at time t+s.

The decentralized martingale trading network based on digital currencies uses NEST tokens (developed on ERC20) as underlying assets traded on-chain. All traders transact directly with an infinitely supplied seller (ILM – Infinite Liquidity Maker), which is the NEST contract itself. Purchased digital assets are burned upon entering the contract, while settlement assets are instantly minted through the contract. R3PO believes that NESTFi, the perpetual futures trading platform built on the martingale network, could become the representative of a new generation of trading network paradigms powered by NEST.
According to DefiLlama statistics, NESTFi currently ranks 6th among decentralized derivatives platforms, behind only Gains Network and ApolloX. (Source: Oracle)
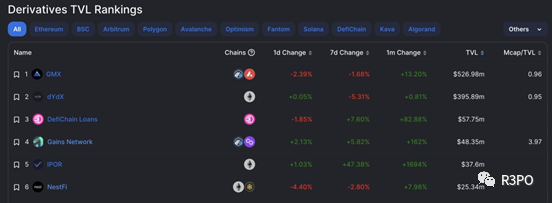
Can NESTFi Solve Pain Points in the DeFi Industry?
(https://nestfi.org/)
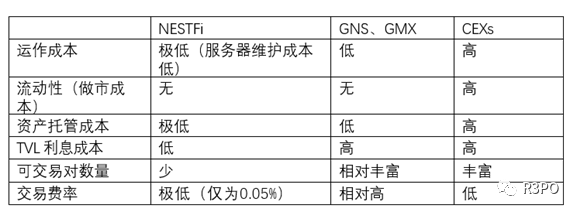
1. Liquidity is the most critical challenge for on-chain applications. To address liquidity issues, previous DeFi solutions have experimented with traditional order books and AMM models, but these are not ideal and fail to integrate all financial services within a single protocol sharing unified liquidity—leading to resource waste and low efficiency.
2. Inadequate risk-matching mechanisms: Whether using AMMs or liquidity pools, current approaches solve liquidity at the expense of seller flexibility—requiring sellers to lock in trading strategies and bear market volatility. When prices favor sellers, buyers may exit; when arbitrage opportunities arise, buyers flood in. Throughout this process, sellers have no agency, relying solely on mining incentives or statistical fee/interest equilibrium over large numbers.
3. Low capital efficiency: While LP designs temporarily alleviate on-chain liquidity shortages, long-term problems persist: massive capital lockup leads to resource waste—huge TVL supports minimal trading volume, much of it driven purely by liquidity mining rewards. Moreover, core variables like price and interest rates depend on pool size, making them vulnerable to arbitrage and limiting trade/lending activity when pools are small. Different products cannot share TVL, so所谓的 composability remains superficial rather than enabling true liquidity sharing.

Overall, NESTFi’s martingale network differs significantly from other decentralized perpetual contracts and centralized exchanges in the following ways:
1. Infinite supply: As long as users hold NEST tokens, they never need worry about illiquidity. Any transaction based on the martingale information flow can be fulfilled—the supply is not constrained by counterparty availability.
2. Easy copy trading: The copy trading feature on NEST’s decentralized exchange offers advantages even over centralized exchanges—users can click a follow-trade link to open positions almost instantly.
3. No LP costs, shared risk: All NEST holders collectively bear the risks and gains associated with fluctuations in NEST supply. Traders interact directly with the protocol—an embodiment of blockchain and distributed network principles. In traditional markets, risk management relies heavily on market makers who hedge and pass risk to the broader market, incurring high hedging costs.
NEST Oracle
The NESTFi perpetual contract exchange relies on price feeds from the NEST Oracle. Given an off-chain price stream, the NEST Oracle Price Model addresses how to design a decentralized game-theoretic mechanism whose equilibrium produces a price feed closely tracking the external reference price. This is achieved through modules including quotation mining, dual-option verification, validation cycles, price chains, and β coefficients. The price series provided by NEST does not alter the underlying asset's price distribution but approximates a discrete sampling model determined by the structure of decentralized gameplay. Quotation accuracy and frequency depend on arbitrage market depth and the NEST token price. Overall, NEST delivers an effective decentralized oracle preserving essential price characteristics.
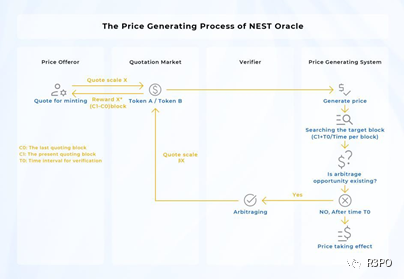
The NEST Oracle is a fully open博弈 network, theoretically capable of delivering any price information stream. However, for network security reasons, price streams used in martingale functions will likely remain limited to a few highly efficient decentralized assets such as BTC/ETH.
Future Development Directions
1. Expand U-based trading functionality: When NEST liquidity grows sufficiently, introducing a NEST/USD oracle would allow trading pairs to shift from X NEST tokens to X USD worth of NEST, meeting demands for building hedging positions denominated in fiat equivalents.
2. Explore multi-pair possibilities: Beyond NEST as the native unit of the martingale network, we could introduce synthetic assets like PUSD, PETH, PBTC—pegged representations of USD, ETH, BTC—as alternative units of exchange, greatly expanding the network’s utility.
3. Extend applications beyond DEX perpetuals: Foundational games relying on randomness—such as lotteries, item crafting, gambling games—can directly utilize NEST’s martingale functions that resolve deterministic mathematical relationships, probabilistic logic, and stochastic processes. In other words, NEST can serve as a direct counterparty, pricing assets in NEST and creating new use cases and consumption pathways for the token.
Conclusion
NESTFi introduces a completely new paradigm: viewing financial products as programmable basic discount functions, where cost equals the fee to invoke such functions—similar to EVM, except the economic relationships in this discount computer are endogenous. This new paradigm can encompass nearly all financial products (services), allowing instant purchase and infinite-liquidity settlement without market makers, collateral, margin calls, or settlement concerns. As long as NEST liquidity is sufficient, replicating traditional financial markets becomes remarkably simple—and immensely powerful. Furthermore, by resolving complex issuance and settlement challenges, traditional derivatives exchanges can focus purely on secondary markets, dramatically reducing operational costs.
Risk Warnings:
1. Martingale trading is essentially a novel trading paradigm that may not yet be widely adopted or proven effective. Therefore, further research and evaluation are required regarding its specific mechanics and real-world applicability.
2. From a user perspective, NESTFi does not offer competitive advantages in terms of maximum leverage, supported currencies, number of tradable pairs, or trading fees. Although it eliminates LP costs, this also means it cannot incentivize users to stake assets, potentially limiting NEST adoption.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















