Huobi Growth Academy | Crypto Market Macro Research Report: A Critical Window for Macro Liquidity, Institutionalization, and Risk Reassessment
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Huobi Growth Academy | Crypto Market Macro Research Report: A Critical Window for Macro Liquidity, Institutionalization, and Risk Reassessment
Overall, this round of rebound has significantly improved market sentiment, reshaped key technical support levels, and released potential willingness for participation from a funding perspective, but it still remains at a stage away from a trend-driven bull market.
Executive Summary
Recently, the crypto market has experienced a significant rebound, with Bitcoin regaining key levels after breaking above $94,000. Sentiment and liquidity have seen a temporary recovery, but this rally is primarily driven by improved macro liquidity expectations, capital inflows following panic-driven sell-offs, and technical rebound dynamics—insufficient evidence to confirm a systematic bull market launch. Medium-term trends will depend on actual policy implementation, capital flows, and market structure evolution, potentially leading to further breakout highs, prolonged consolidation at elevated levels, or pullbacks under continued policy and liquidity pressures. While institutionalization enhances long-term potential, it also makes Bitcoin more sensitive to systemic risks, amplifying procyclical volatility. The altcoin market remains constrained and embedded in a high-risk structure. Amid unconfirmed trends, the market is in a "repair–test–wait" phase, requiring balanced optimism and caution. A new growth cycle is possible if trading volume and policy conditions continue improving; however, if expectations fail, the current rally may reverse. Overall, flexible participation and risk management remain core strategies for navigating uncertainty.
1. Cryptocurrency Market Macroeconomic Overview
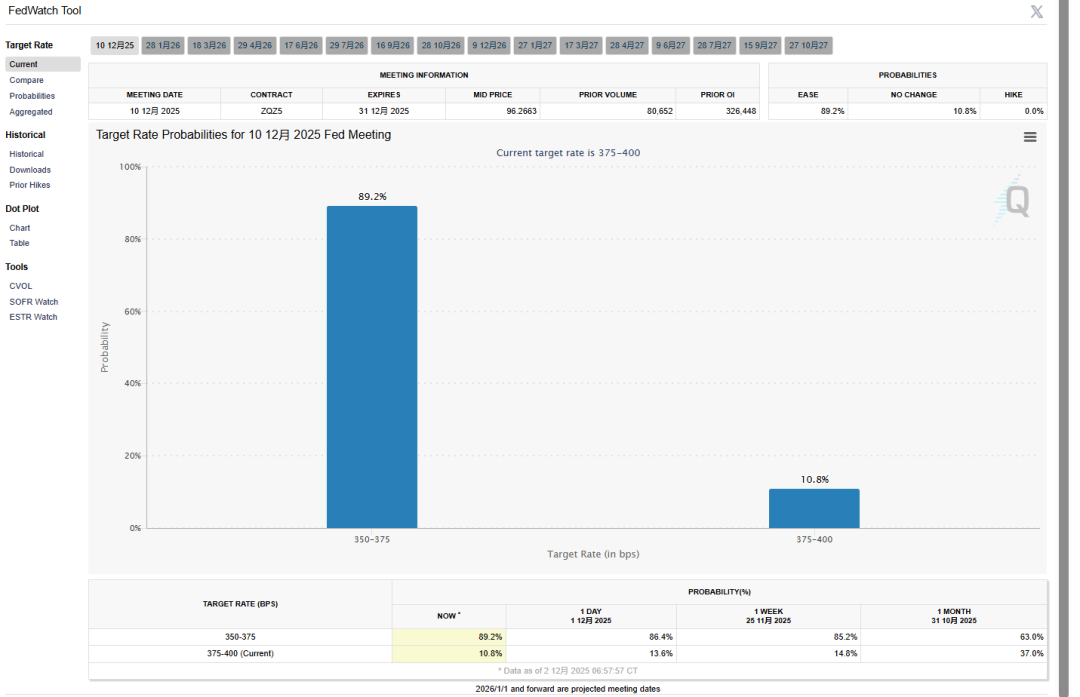
Over the past few weeks, after a sharp correction, the cryptocurrency market has seen notable recovery in both sentiment and price. As the benchmark asset, BTC once dropped to $80,000, triggering widespread panic across the market, forced liquidation of highly leveraged positions, and a rapid decline in short-term risk appetite. However, driven by shifts in macro expectations and structural market reactions, BTC has recently rebounded sharply, reclaiming the $94,000 level, with multiple institutional platforms reporting 24-hour gains of 7%–8%. This price action reflects not only a relief from prior downward pressure but also suggests the market is attempting a structural recovery from extreme pessimism. This rebound was not caused by a single factor but rather the combined effect of macro liquidity, market structure changes, technical conditions, and capital behavior. From a macro perspective, global monetary policy expectations have become a key variable influencing risk assets. Growing market anticipation of future rate-cut cycles by major central banks and expectations of marginal liquidity improvement have renewed interest in high-risk assets. With November's PPI data significantly below forecasts, inflationary pressures continue to ease, and Fed officials repeatedly emphasizing a "soft landing" as the primary goal before 2026, avoiding premature tightening. According to the latest CME FedWatch tool data, the market’s probability of a 25-basis-point rate cut at the December 10 Fed meeting has surged from 35% one week ago to 89.2%. On December 1 (U.S. time), the Federal Reserve officially announced the end of its Quantitative Tightening (QT) policy. On the same day, the crypto market saw a broad-based rally. Historical experience shows that both U.S. equities and BTC tend to perform better during periods of monetary easing or easing expectations, which aligns precisely with current market sentiment. Although macro policies have not yet definitively reversed, expectations alone are enough to drive asset prices. Moreover, amid growing pressure from high interest rates on the real economy, markets tend to front-run policy shifts, creating more room for speculation in risk assets.
Secondly, from the perspective of market structure and funding flows, this rebound exhibits classic characteristics of “panic clearance + institutional accumulation.” During the prior downturn, exchange data showed large-scale forced liquidations among highly leveraged longs and some shorts, releasing concentrated liquidity. Historically, such phases often involve exaggerated directional moves and extreme sentiment, followed by countercyclical shifts in capital flows. Some long-term capital began positioning after the steep sell-off, forming support at lower levels. Additionally, when short positions become highly concentrated, rebounds can trigger “short squeezes,” further accelerating price increases and reinforcing a typical pattern of “structural short squeeze + capital reversal.” Technical analysis also supports the rebound narrative. BTC repeatedly tested and held support around $86,000–$88,000, indicating this zone has become a temporary bottom and area of dense position concentration. The rapid short-term rebound is also linked to prior oversold conditions. When technical support coincides with capital inflows, momentum typically improves and trading behavior shifts. Recent market movements show rising volume alongside price breakouts above key levels, suggesting active buying rather than mere short-covering. However, since overall market volume still lacks clear signs confirming a sustained trend, this rebound remains within an observation window, and whether higher structures can form requires further validation.
Beyond BTC’s recovery, the market is closely watching whether the rebound will drive联动 and rotation into ETH and the broader altcoin market. The Fusaka upgrade activated on December 4 marks another major milestone for Ethereum post-merge. Its core PeerDAS technology increases Blob capacity from 9 to 15, enabling Layer 2 transaction fees to drop another 30%-50% from current levels, while also granting regular accounts social recovery and batch operation capabilities—the first mainstream implementation of “Account Abstraction (AA).” This upgrade not only optimizes data availability management but crucially paves the way for Verkle Trees-based stateless clients, reducing node sync time from weeks to hours. Historically, each crypto market rebound follows a capital migration pattern: from core assets → secondary assets → high-risk assets. The stabilization and rebound of the ETH/BTC exchange ratio suggest capital may begin rotating from Bitcoin into altcoins. However, such rotation depends on several conditions: first, risk appetite must improve sustainably, not just temporarily; second, sufficient market liquidity must exist beyond short-term trading activity; third, core assets must exhibit stable trends rather than high volatility without direction. Currently, BTC’s rebound has helped repair market sentiment and prompted some capital to shift attention toward ETH and select large-cap altcoins. ETH rose in tandem during this rebound and reclaimed key support zones, positively impacting overall market confidence.
Notably, institutionalization is reshaping market structure. Over the past year, institutional investors have increasingly treated BTC as a distinct asset class rather than pure speculation in their allocation strategies. This leads capital to favor assets with clear attributes and stable value propositions over high-risk tokens. As a result, even during market recoveries, altcoins may significantly underperform BTC or ETH. Meanwhile, changes in stablecoin supply, derivatives liquidity distribution, and exchange funding rates serve as key indicators for tracking capital flows—yet these metrics currently do not clearly signal the start of a strong new cycle. On the risk side, significant uncertainties continue to influence market direction. First, the global interest rate cycle has not definitively reversed—should monetary policy expectations falter, risk assets could face renewed pressure. Second, technically driven rallies lacking volume support are prone to “fragile rallies” and may quickly reverse upon macro news shocks. Furthermore, the altcoin market still harbors systemic risks, especially vulnerable to amplified volatility when risk appetite and capital absorption are weak. More importantly, over the past year, the crypto market has undergone a rapid phase of “valuation recovery + new highs.” In this context, investors are particularly sensitive to new risk-return ratios, making it difficult for the market to form a consensus trend.
In sum, the current crypto market is at a critical juncture of structural repair and trend assessment. BTC’s rebound reflects a transition from panic to recovery, but does not yet prove a full bull cycle recovery. If prices break through key resistance with accompanying volume, the market could enter a new trending phase and reshape longer-term price ranges; otherwise, if momentum fades or macro pressures return, prices may retest lower support zones. The performance of ETH and the altcoin market heavily depends on BTC’s stability and continuity of capital flows—not independent drivers. In the coming period, the market will continue to revolve around structural adjustments, shifts in macro expectations, and fluctuations in risk appetite, with trend direction only becoming clearer after key level breaks and capital confirmation.
2. Structural Opportunities and Risk Analysis in Macroeconomics
When assessing whether the current rebound in crypto assets is sustainable, relying solely on price action, technical signals, or short-term sentiment recovery is insufficient to build a long-term thesis. The market’s future trajectory depends more profoundly on institutional environments, capital structures, macro policy directions, and the evolution of capital cycles—factors that may simultaneously create structural opportunities and harbor latent risks. In recent years, as the crypto market becomes increasingly intertwined with traditional financial markets, its price behavior is ever more influenced by macro liquidity and policy expectations. This means Bitcoin’s valuation logic is no longer an isolated “crypto-native” framework, but gradually tied to interest rate cycles, inflation trends, asset allocation preferences, and even institutional risk budgets.
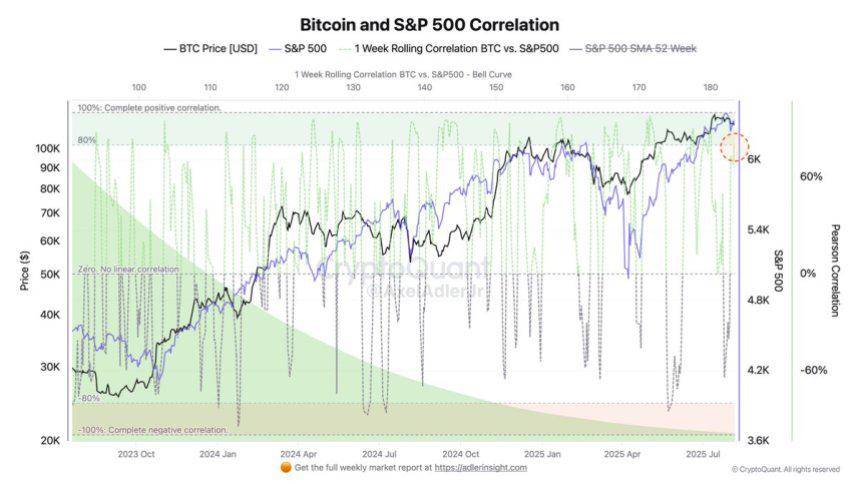
Recent research shows increasing correlation between Bitcoin and traditional financial market indices—a trend indicating crypto assets are transitioning from “fringe speculative assets” to “mainstream financial assets,” with institutional adoption playing a pivotal role. When Bitcoin correlates highly with the S&P 500 or Nasdaq, it signals a shift in how the market prices its risk: no longer decoupled from macro cycles, but integrated into the basket of risk assets. This change reduces Bitcoin’s diversification benefits as an “alternative asset,” yet enhances its appeal as a “configurable asset.” Especially as institutional investors, ETFs, pension funds, or large asset managers enter, the capital pool for crypto assets may structurally expand, reducing reliance on retail-driven sentiment swings. Behind this shift in capital structure—ETF inflows, improved custody infrastructure, compliance frameworks, and reporting systems—could redefine valuation bands and risk premium structures. This implies not only broader funding sources for crypto assets but also a potential convergence of volatility and risk-return profiles toward those of traditional assets. Particularly amid improving macro liquidity and stronger rate-cut expectations, institutions may begin including crypto as part of strategic “risk exposure” allocations, rather than treating them merely as short-term trades. If this mechanism takes hold, market rallies could be built on deeper capital foundations, beyond exchange rollovers and retail FOMO. Such a development would have profound implications for future cycles. However, institutionalization and financial integration do not eliminate market risk—they may instead introduce new structural vulnerabilities. If Bitcoin behaves more like a high-beta asset, then during liquidity tightening or declining risk appetite, the crypto market becomes more susceptible to systemic macro shocks. In traditional finance, such assets typically underperform during downturns, and if crypto moves in sync, risk exposure expands rather than contracts. This “institutionalization-induced procyclicality” is a critical issue for future market dynamics.
3. Outlook for the Crypto Macro Market
Following several weeks of strong rebound, the crypto market has entered a strategically uncertain observation window. Bitcoin has regained the $90,000 level and briefly tested higher, shifting market sentiment from extreme pessimism to cautious optimism. Yet, whether the rebound can persist, whether a trend can form, and whether there is sustainable upward momentum remain contingent on capital structure, macro variables, policy developments, and participant behavior. Based on current conditions, historical patterns, and market structure, multiple evolutionary paths could unfold over the next three to six months—each dependent on specific triggers and feedback mechanisms.
One possible path is a continuation and acceleration of the current rebound, pushing prices toward the $95,000–$100,000 range. This scenario typically emerges when market sentiment steadily improves, volume rises, both institutional and retail capital flow in, and directional consensus forms. Should macro liquidity improve, monetary policy turn dovish, risk appetite rise, and Bitcoin break through key resistance, a secondary acceleration phase could materialize. In this case, price gains would stem not just from technical momentum but also from capital inflows and structural valuation recovery. Another possibility is BTC oscillating within a $92,000–$95,000 range without sustained upside. This usually occurs when confidence recovers but capital inflows remain unstable, macro policy expectations are ambiguous, and bulls fail to overcome key resistance. Under such conditions, price movements are driven by short-term trading, and market participants exhibit hesitation and博弈 behavior. If funding fails to strengthen consistently—with institutions观望, retail cautious, and derivative markets showing neutral or low leverage—price action is more likely to consolidate within a range than break out into a trend. A third path involves another market pullback, retesting support or entering deeper corrections, possibly targeting the $85,000–$88,000 range. This outcome could be triggered by macro risks, policy shifts, or reversed expectations—such as resurgent inflation raising rate expectations, hawkish central bank rhetoric, geopolitical tensions boosting safe-haven demand, tightening liquidity, increased regulatory scrutiny, or outflows from ETFs and other institutional channels—all of which could reshape risk appetite.
For altcoins or high-risk asset categories, while the rebound may offer short-term opportunities, their risk profile remains substantially higher than Bitcoin and Ethereum. Due to fragile valuations, limited liquidity, high speculation, and narrative-driven pricing, altcoins typically suffer larger drawdowns and slower recoveries during structural market corrections. Therefore, only investors with high risk tolerance, deep project understanding, and robust short-term trading strategies should consider participation. Ordinary investors should remain cautious during phases of unclear trends.
Overall, while the recent crypto rebound shows strength, the trend is not yet confirmed. Whether prices break resistance, consolidate, or retreat will depend on upcoming macro data, policy signals, institutional capital flows, and market participant responses over the next few weeks. Rebound phases often breed optimism and high-return expectations, yet the market remains exposed to liquidity risks, regulatory uncertainty, and structural fragility—any surprise event could alter the trend. Until a trend is confirmed, optimism must be tempered with caution, and market participation should prioritize flexibility and risk management over premature assumptions of a new cycle.
4. Conclusion
In summary, this rebound has significantly improved market sentiment, reshaped key technical supports, and signaled potential capital engagement—but it remains a transitional step away from a confirmed bullish trend. The market is currently in a “repair–test–wait” phase. Whether upward momentum evolves into a structural breakout hinges on macro policy directions, sustained capital inflows, and how market participants reprice risk in the coming weeks. For investors with sufficient risk tolerance, phased positioning and flexible allocation may offer strategic value at this stage—but only under strict position sizing and risk controls. From a long-term view, if capital inflows accelerate, macro conditions gradually improve, and Bitcoin breaks through key resistance, a new phase of structural upside becomes feasible. Otherwise, the market may face further consolidation or pullbacks. Prudent participation and rational judgment will remain the primary methodology for navigating uncertainty.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News