Fed's $400 Billion Liquidity Signal: Bitcoin Awaits Breakout
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Fed's $400 Billion Liquidity Signal: Bitcoin Awaits Breakout
As the Federal Reserve's policy increasingly impacts the cryptocurrency market, Bitcoin investors are preparing for potential liquidity changes.
Author: Oluwapelumi Adejumo
Translation: Saoirse, Foresight News
Bitcoin's price movement is fluctuating alongside the Federal Reserve's final policy decision of the year, appearing nearly flat on the surface, yet the underlying market structure tells a very different story.
Beneath the seemingly stable price range lies a period of concentrated pressure: on-chain data shows investors are losing close to $500 million per day, leverage in the futures market has dropped sharply, and nearly 6.5 million bitcoins are currently in an unrealized loss position.
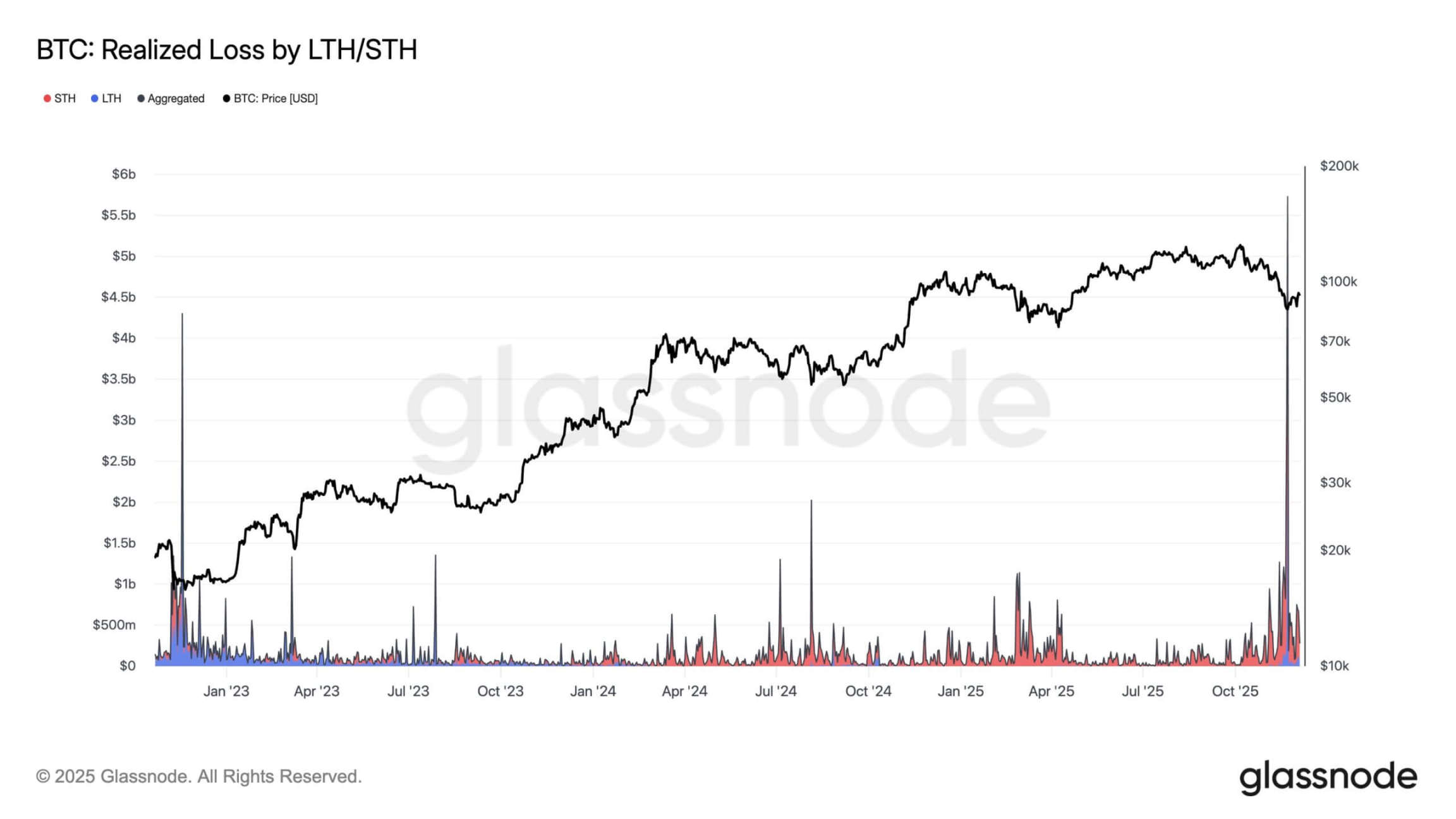
Bitcoin realized loss levels, Source: Glassnode
This situation resembles the late stages of previous market contractions rather than a healthy consolidation phase.
However, such structural adjustments beneath a calm surface are not uncommon for Bitcoin, but the timing of this adjustment is noteworthy.
The internal market "capitulation selling" coincides precisely with an external turning point in U.S. monetary policy. The Fed has concluded the most aggressive balance sheet reduction campaign in over a decade, and markets expect its December meeting to outline a clearer framework for a "shift toward reserve rebuilding."
In this context, on-chain market stress and an unresolved liquidity shift together form the backdrop for this week’s macro events.
Liquidity Shift
According to the Financial Times, quantitative tightening (QT) officially ended on December 1, during which the Federal Reserve reduced its balance sheet by approximately $2.4 trillion.
This move brought bank reserve levels down to a historically tight range associated with funding stress, while the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) repeatedly tested the upper bound of the policy rate range.
These changes indicate that the market system is no longer awash with liquidity but is gradually entering a phase where "reserve scarcity raises concerns."
Against this backdrop, the most critical signal from the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is not the widely anticipated 25-basis-point rate cut, but rather the direction of its balance sheet strategy.
Markets anticipate that the Fed will clarify through explicit statements or policy implementation documents its transition plan toward "Reserve Management Purchases (RMP)."
According to analysis by investment research firm Evercore ISI, the program could start as early as January 2026, purchasing approximately $35 billion in short-term Treasury bills monthly—funds from maturing mortgage-backed securities would be reinvested into short-term assets.
The details of this mechanism are crucial: although the Fed is unlikely to label RMP as "stimulus," continuous reinvestment into short-term Treasuries would steadily rebuild bank reserves and shorten the maturity profile of the System Open Market Account (SOMA).
This operation would gradually increase reserve levels, ultimately leading to an annualized balance sheet expansion exceeding $400 billion.
This shift would mark the first sustained expansionary policy signal from the Fed since the start of QT. Historically, Bitcoin has shown far greater sensitivity to such liquidity cycles than to changes in policy interest rates.
Meanwhile, broader monetary aggregate data suggests the liquidity cycle may already be turning.
Notably, M2 money supply has reached a record high of $22.3 trillion, surpassing its early 2022 peak after a prolonged contraction.
(Note: M2 is one of the core indicators of money supply, falling under the category of "broad money," encompassing a wider scope than base money (M0) or narrow money (M1), providing a more comprehensive reflection of overall societal liquidity conditions.)
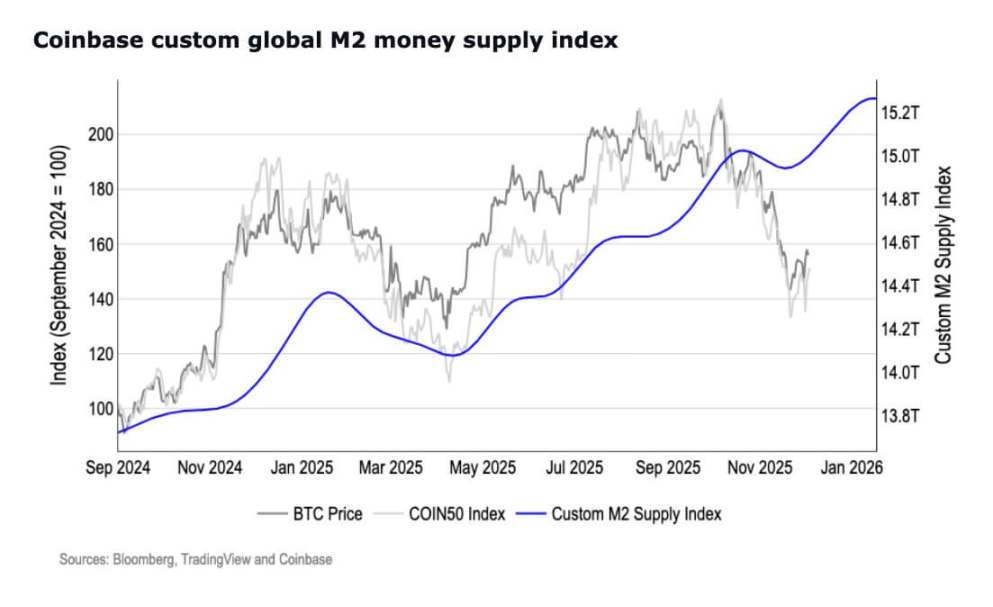
U.S. M2 Money Supply, Source: Coinbase
Therefore, if the Fed confirms the launch of "reserve rebuilding," Bitcoin's sensitivity to balance sheet dynamics could rebound rapidly.
Macro Trap
The core rationale behind this policy shift stems from changes in employment data.
Over the past seven months, nonfarm payroll growth declined in five; meanwhile, job openings, hiring rates, and voluntary quit rates have all slowed, shifting the labor market narrative from "resilient" to "vulnerable and pressured."
As these indicators cool, the theoretical framework of a "soft landing" becomes increasingly difficult to sustain, narrowing the Fed's policy options.
While inflation has eased, it remains above target; at the same time, the cost of "maintaining restrictive policy for longer" continues to rise.
The key risk is that labor market weakness may deepen before inflation fully returns to target. Therefore, the information conveyed at this week's Fed press conference may carry more weight than the rate decision itself.
Markets will closely watch how Chair Powell balances two objectives—supporting labor market stability while maintaining credibility on the inflation path. His comments on "reserve adequacy," "balance sheet strategy," and the "timing of RMP initiation" will shape market expectations for 2026.
For Bitcoin, this means price action won't be a simple binary outcome of "up or down," but will depend on the specific direction of policy signals.
If Powell acknowledges labor market weakness and clearly outlines a reserve rebuilding plan, markets may view the current range-bound price as disconnected from policy direction—if Bitcoin breaks above the $92,000–$93,500 range, it would signal traders positioning for liquidity expansion.
Conversely, if Powell emphasizes caution or delays clarifying RMP details, Bitcoin could remain within a lower consolidation range of $75,000–$82,000—a zone encompassing ETF holding bottoms, corporate inventory reserve thresholds, and historical structural demand areas.
Will Bitcoin Experience Capitulation Selling?
Meanwhile, Bitcoin's internal market dynamics further support the view that the asset is undergoing a reset beneath the surface.
Short-term holders continue to sell tokens during market weakness; as mining costs approach $74,000, mining economics have deteriorated significantly.
At the same time, Bitcoin mining difficulty recorded its largest single drop since July 2025, indicating marginal miners are cutting capacity or shutting down operations entirely.
Yet, these stress signals coexist with early signs of supply tightening.
BRN Research told CryptoSlate that large wallets collectively accumulated around 45,000 bitcoins over the past week; exchange bitcoin balances continue to decline; and stablecoin inflows suggest capital stands ready to re-enter should market conditions improve.
Additionally, Bitwise’s supply metrics show that despite retail sentiment being in "extreme fear," various wallet types continue to accumulate Bitcoin. Tokens are moving from high-liquidity platforms to long-term custody accounts, further reducing the proportion of supply available to absorb selling pressure.
This pattern of "forced selling, miner stress, and selective accumulation" is typically a foundational condition for forming long-term market bottoms.
Bitwise added:
"Bitcoin capital inflows continue to contract, with the 30-day real market value growth rate dropping to just 0.75% per month. This indicates that profit-taking and stop-loss selling are roughly balanced, with losses only slightly outweighing gains. This rough equilibrium suggests the market has entered a 'calm period,' with neither bulls nor bears holding clear dominance."
Technical Assessment
From a market structure perspective, Bitcoin remains confined within two key ranges.
A sustained breakout above $93,500 would place the asset in a region where momentum models become easier to trigger, with subsequent targets at $100,000, $103,100 (the short-term holder cost basis), and the long-term moving average.
Conversely, if the market fails to break resistance amid cautious Fed signals, it may fall back into the $75,000–$82,000 range—a zone that has repeatedly served as a "reservoir" for structural demand.
BRN Research notes that cross-asset performance also confirms this sensitivity: ahead of the Fed meeting, gold and Bitcoin exhibited divergent trends, reflecting "liquidity-driven asset rotation" rather than volatility driven purely by risk sentiment.
Therefore, if Powell's remarks reinforce expectations that "reserve rebuilding is the next phase of policy," capital may quickly shift toward assets that respond positively to liquidity expansion.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News