BTCFi: Building Your Mobile Bitcoin Bank – A Comprehensive Guide from Lending to Staking
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

BTCFi: Building Your Mobile Bitcoin Bank – A Comprehensive Guide from Lending to Staking
This research report provides an in-depth analysis of multiple key sectors within BTCFi.
Authored by: Freya, Knight, Ausdin, ZJUBCA;
Elaine, Youyu, Satoshi Lab
Executive Summary
As Bitcoin (BTC) solidifies its position in financial markets, BTCFi (Bitcoin Finance) is rapidly emerging as the frontier of innovation within the cryptocurrency space. BTCFi encompasses a wide range of Bitcoin-based financial services, including lending, staking, trading, and derivatives. This report provides an in-depth analysis of key sectors within BTCFi, exploring stablecoins, lending services, staking, restaking, and the convergence of centralized and decentralized finance (CeDeFi).
The report begins by outlining the market size and growth potential of BTCFi, emphasizing how institutional participation enhances market stability and maturity. It then examines the mechanisms of stablecoins—both centralized and decentralized—and their roles within the BTCFi ecosystem. In the lending sector, it analyzes how users can unlock liquidity through Bitcoin-backed loans while evaluating major platforms and products.
In staking, the report highlights pivotal projects like Babylon, which leverage Bitcoin’s security to provide staking services for other Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chains, creating yield opportunities for BTC holders. Restaking further unlocks staked asset liquidity, offering users additional revenue streams.
The report also explores the CeDeFi model, combining the security of centralized finance with the flexibility of decentralized finance to deliver seamless financial experiences.
Finally, by comparing different asset classes across dimensions such as security, yield, and ecosystem richness, the report reveals BTCFi’s unique advantages and inherent risks relative to other crypto-financial domains. As BTCFi continues to evolve, it is poised to attract more innovation and capital inflows, reinforcing Bitcoin’s leadership in the broader financial landscape.
Keywords: BTCFi, Stablecoin, Lending, Staking, Restaking, CeDeFi, Bitcoin Finance
BTCFi Landscape Overview:
• Squirrels gather acorns before hibernation and store them in hidden, secure locations; pirates bury their gold and silver treasures beneath soil known only to themselves; today, people deposit cash into fixed-term accounts—not just for less than 3% annual returns, but for peace of mind. Now imagine you hold cash and are bullish on the crypto market but want to avoid excessive risk while seeking higher ROI assets. You choose BTC, known as "digital gold." Your goal is long-term holding without unnecessary trading that could erode value due to price volatility. What's needed is a way to put your BTC to work—unlocking its liquidity and utility, much like DeFi on Ethereum. Such solutions not only help you hold your assets longer but also generate passive income, enabling secondary or even tertiary utilization of your asset’s liquidity. The variety of strategies and projects involved warrants deep exploration.
• BTCFi functions like a mobile Bitcoin bank—a suite of financial activities centered around Bitcoin, including lending, staking, trading, futures, and derivatives. According to data from CryptoCompare and CoinGecko, the BTCFi market reached approximately $10 billion in 2023. DefiLlama projects the market could grow to $1.2 trillion by 2030, encompassing both total value locked (TVL) in Bitcoin-focused DeFi ecosystems and the broader market for Bitcoin-related financial products and services. Over the past decade, BTCFi has demonstrated significant growth potential, attracting increasing institutional involvement. Firms such as Grayscale, BlackRock, and JPMorgan have begun entering the Bitcoin and BTCFi space. Institutional participation brings substantial capital inflows, improves market liquidity and stability, and enhances overall market maturity and credibility, elevating trust and recognition in BTCFi.
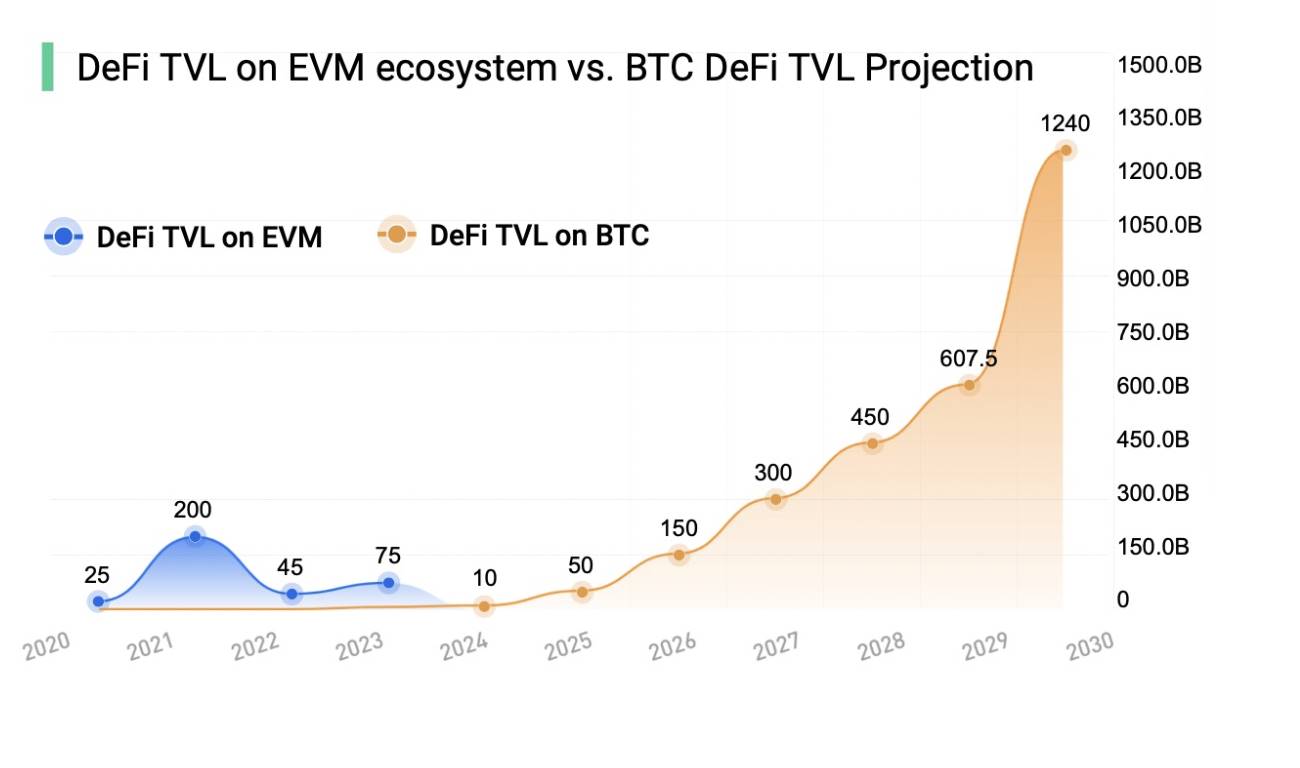
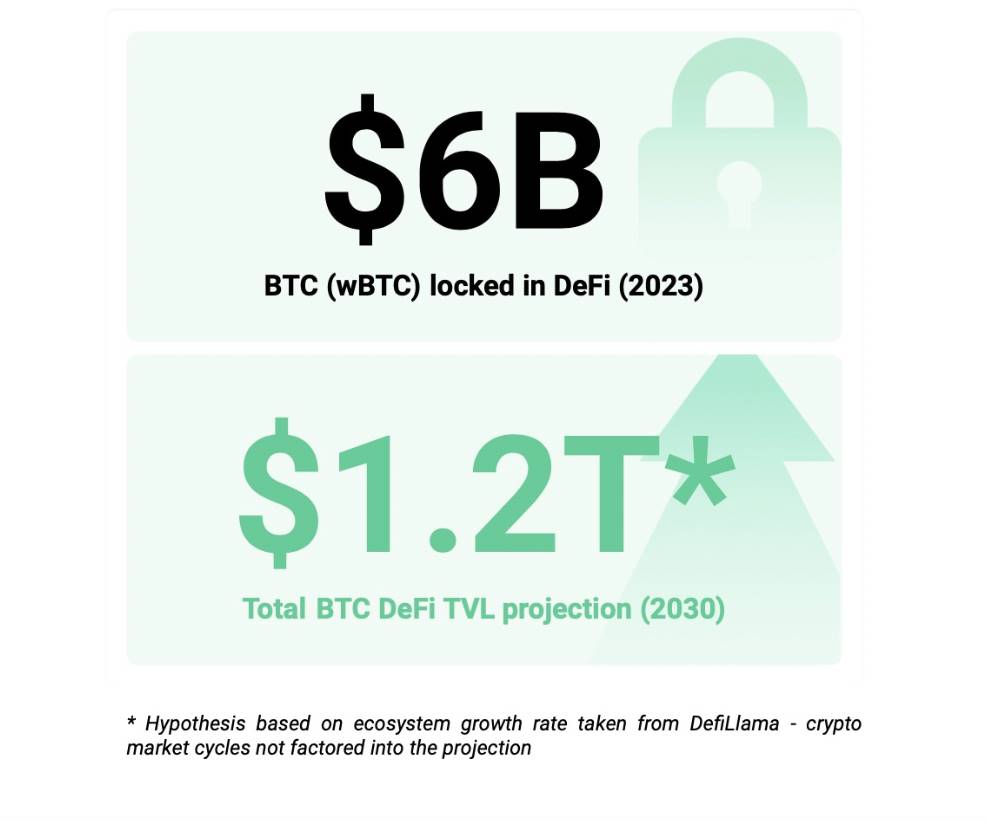
• This report will delve into several prominent areas within the current cryptocurrency financial market, including Bitcoin lending (BTC Lending), stablecoins, staking services, restaking services, and CeDeFi—the integration of centralized and decentralized finance. Through detailed analysis of these domains, we aim to understand their operational mechanisms, market developments, leading platforms and products, risk management practices, and future trends.
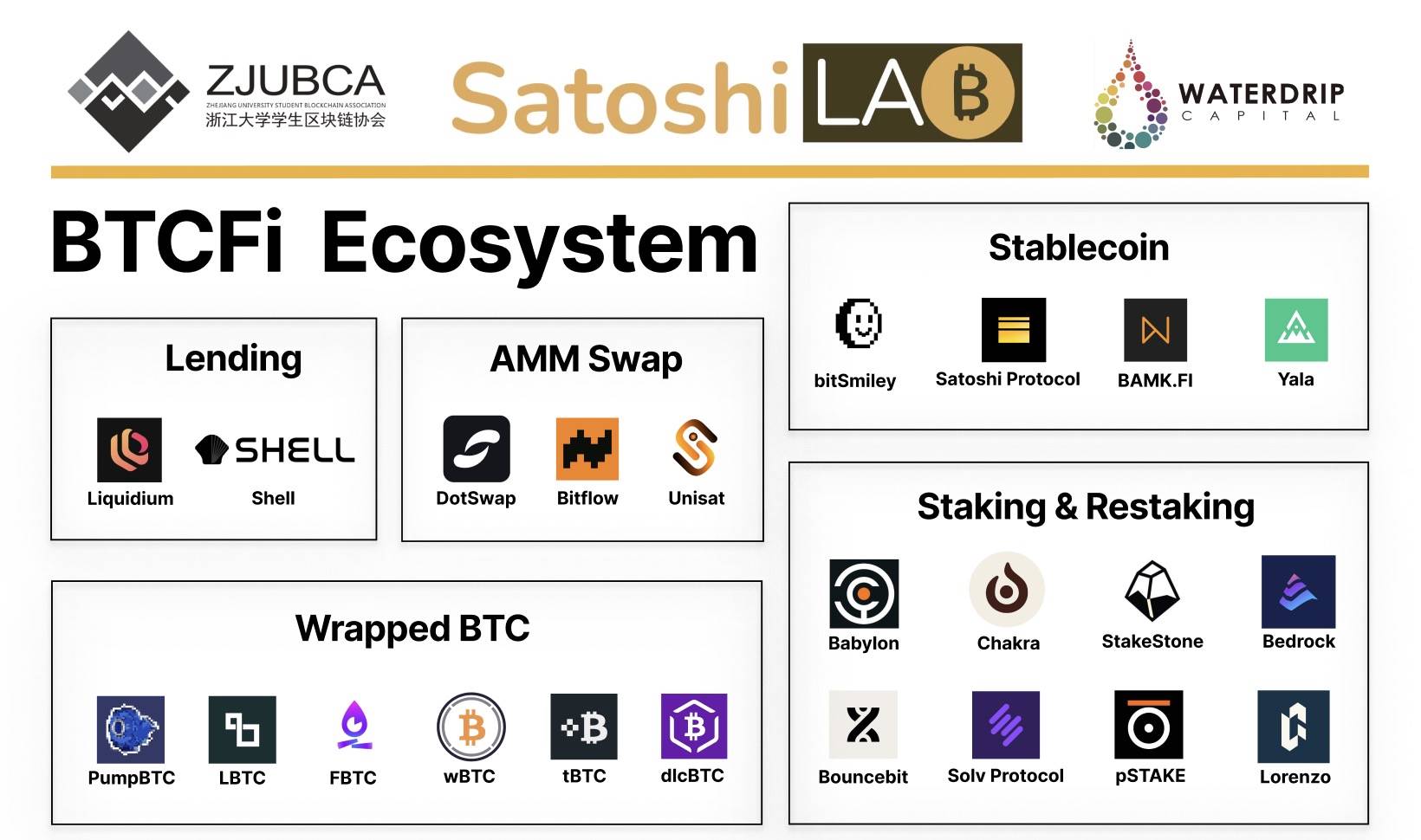
Part Two: BTCFi Sector Breakdown
1. Stablecoin Sector
Introduction
• A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to fiat currencies or other tangible assets to minimize price volatility. Stablecoins achieve price stability either through reserve-backed issuance or algorithmic supply adjustments. They are widely used in transactions, payments, and cross-border transfers, allowing users to benefit from blockchain technology while avoiding the extreme volatility associated with traditional cryptocurrencies.
• In economics, there exists an “impossible trinity”: a sovereign nation cannot simultaneously maintain a fixed exchange rate, free capital flow, and independent monetary policy. Similarly, in the context of crypto stablecoins, another impossible trinity arises—price stability, decentralization, and capital efficiency cannot all be achieved at once.
• Stablecoins can be categorized intuitively by degree of centralization and collateral type. Among mainstream stablecoins, those classified by centralization include centralized stablecoins (e.g., USDT, USDC, FDUSD) and decentralized stablecoins (e.g., DAI, FRAX, USDe). By collateral type, they fall into three categories: fiat/physical asset-backed, crypto-collateralized, and under-collateralized.
• According to DefiLlama data as of July 14, the total market cap of stablecoins stands at $162.372 billion. In terms of market share, USDT and USDC dominate, with USDT leading significantly by capturing 69.23% of the entire stablecoin market cap. DAI, USDe, and FDUSD follow, ranking third to fifth. All other stablecoins currently account for less than 0.5% of total market cap.
• Centralized stablecoins are generally backed by fiat or physical assets—essentially representing real-world assets (RWA)—such as USDT and USDC, which are pegged 1:1 to the U.S. dollar, or PAXG and XAUT, which track gold prices. Decentralized stablecoins, on the other hand, are typically backed by crypto assets or operate without full collateral (or are under-collateralized). DAI and USDe are examples of crypto-collateralized stablecoins, further divisible into fully or over-collateralized models. Under-collateralized or non-collateralized stablecoins are commonly referred to as algorithmic stablecoins, exemplified by FRAX and the former UST. Compared to centralized stablecoins, decentralized versions have lower market caps, more complex designs, yet have produced several standout projects. Within the BTC ecosystem, notable stablecoin initiatives are decentralized, so we focus below on their mechanisms.
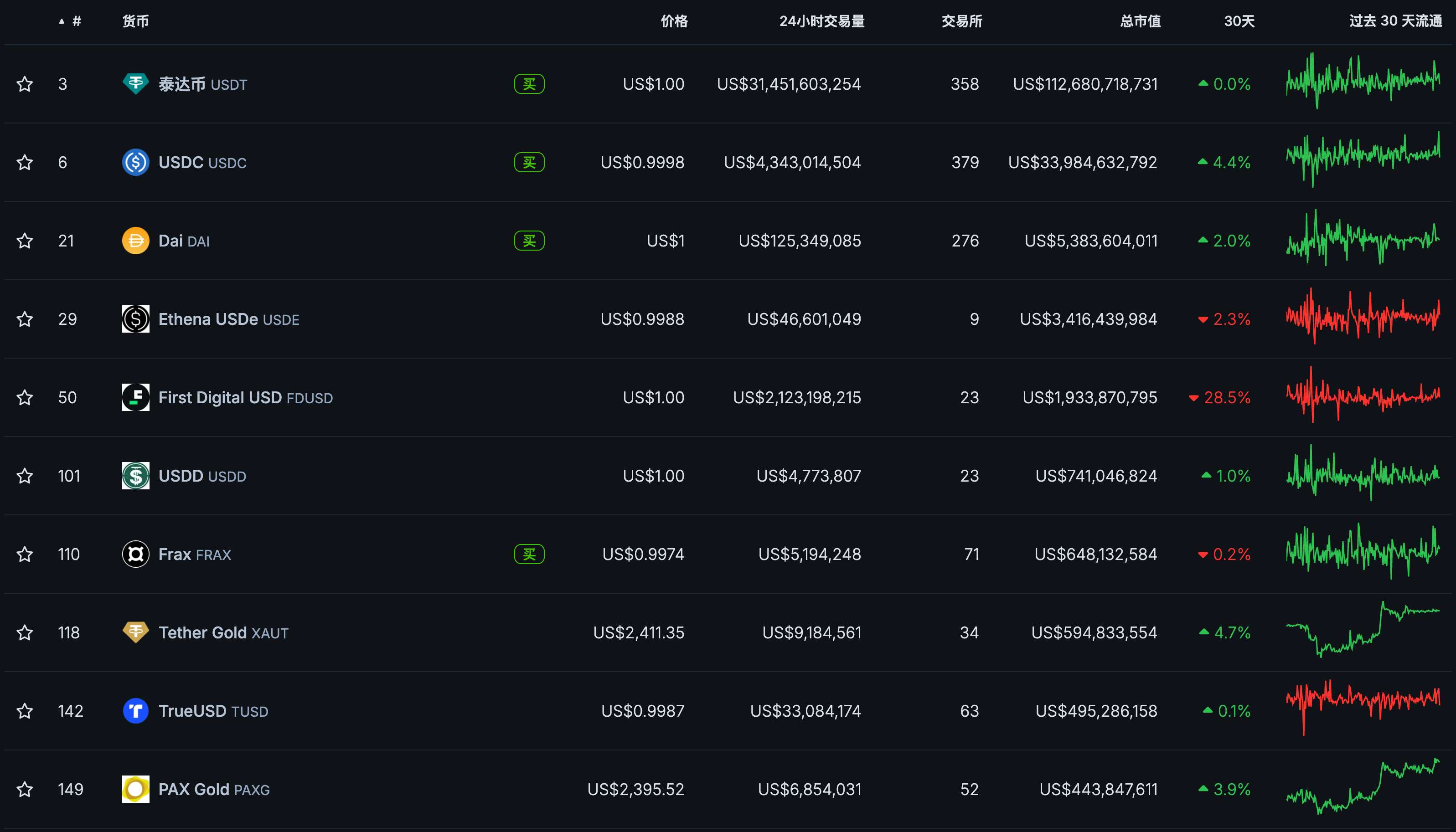
Top 10 stablecoins by market cap on July 14, 2024. Source: Coingecko
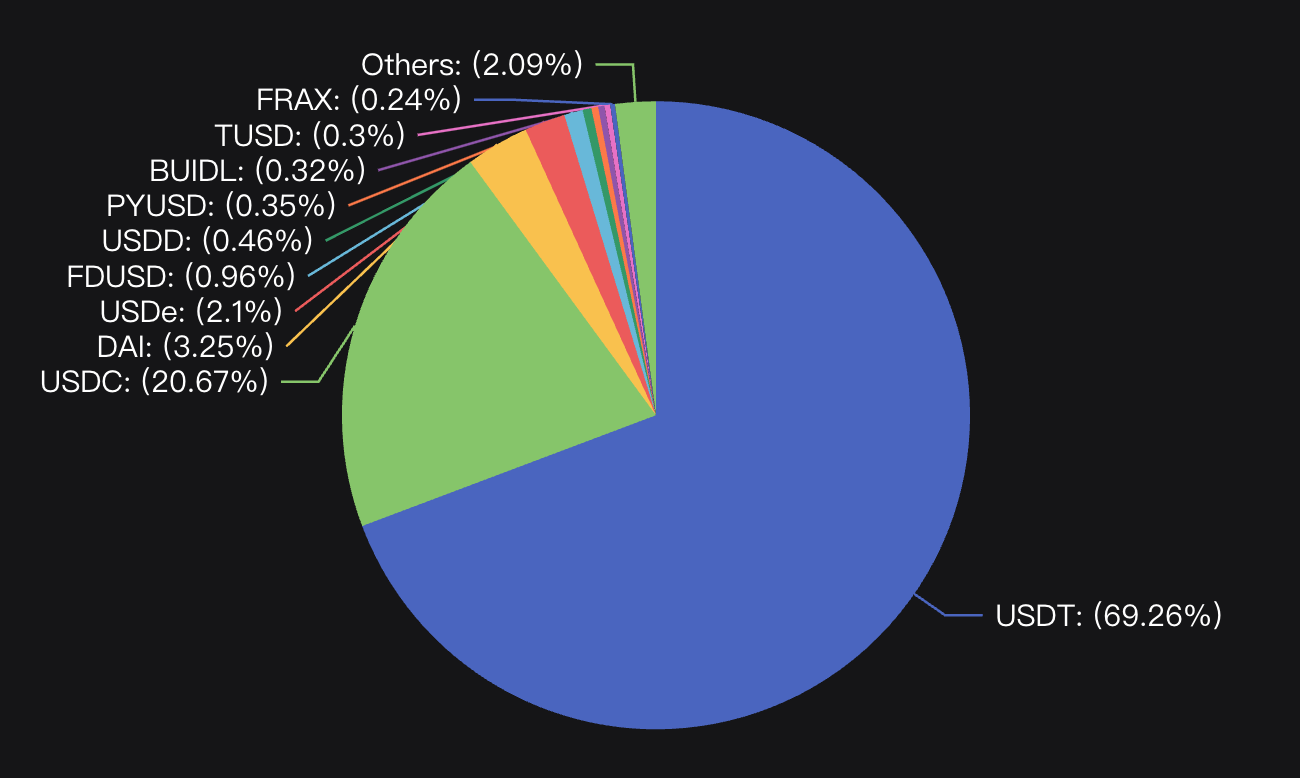
Market share distribution of top 10 stablecoins on July 14, 2024. Source: DefiLlama
Decentralized Stablecoin Mechanisms
• Below we introduce two primary mechanisms: CDP (over-collateralization), represented by DAI, and contract hedging (full collateralization), exemplified by Ethena. Algorithmic stablecoin mechanisms exist as well but won't be covered in detail here.
• CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) refers to a mechanism in decentralized finance where users lock up crypto assets to mint stablecoins. First pioneered by MakerDAO, this model has since been adopted across various DeFi and NFTFi projects.
○ DAI is a decentralized, over-collateralized stablecoin created by MakerDAO, designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the U.S. dollar. Its operation relies on smart contracts and a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) to ensure stability. Core components include over-collateralization, Collateralized Debt Positions (CDPs), liquidation mechanisms, and the role of the governance token MKR.
○ CDP is a key mechanism in the MakerDAO system for managing the process of generating DAI. In MakerDAO, CDPs are now called Vaults, though their core functionality remains unchanged. The detailed operation of CDP/Vault works as follows:
i. Generating DAI: Users deposit crypto assets (e.g., ETH) into a MakerDAO smart contract, creating a new CDP/Vault, and subsequently mint DAI based on the deposited collateral. The generated DAI represents borrowed debt, with the collateral serving as security.
ii. Over-Collateralization: To prevent liquidation, users must maintain a collateral ratio above the system’s minimum threshold (e.g., 150%). This means borrowing 100 DAI requires locking at least $150 worth of collateral.
iii. Repayment / Liquidation: Users must repay the borrowed DAI plus a stability fee (denominated in MKR) to reclaim their collateral. If the required collateral ratio is not maintained, the collateral will be liquidated.
• Delta measures the percentage change in a derivative’s price relative to changes in the underlying asset price. For example, if an option has a delta of 0.5, a $1 increase in the underlying asset price leads to a $0.5 rise in the option price. A delta-neutral position is an investment strategy that offsets price movement risks by holding a combination of the underlying asset and derivatives, aiming to make the portfolio’s overall delta zero—thus maintaining value despite fluctuations in the underlying asset. An example would be holding spot ETH while shorting an equivalent amount of ETH perpetual futures.
Ethena tokenizes delta-neutral arbitrage trades involving ETH by issuing USDe, a stablecoin whose value reflects delta-neutral positions. Therefore, USDe generates returns from two sources:
○ Staking rewards
○ Basis spread and funding rate differentials
○ Ethena achieves full collateralization and additional yield through hedging.
Project One: Bitsmiley Protocol
Overview
• The first native stablecoin project in the BTC ecosystem.
• On December 14, 2023, OKX Ventures announced a strategic investment in bitSmiley, a stablecoin protocol on the BTC network that allows users to over-collateralize native BTC to mint the stablecoin bitUSD. Additionally, bitSmiley includes lending and derivatives protocols, aiming to build a new financial ecosystem for Bitcoin. Previously, bitSmiley was selected as a top project in the BTC Hackathon hosted jointly by ABCDE and OKX Ventures in November 2023.
• On January 28, 2024, it announced completion of its first token financing round led by OKX Ventures and ABCDE, with participation from CMS Holdings, Satoshi Lab, Foresight Ventures, LK Venture, Silvermine Capital, and individuals from Delphi Digital and Particle Network. On February 2, Hong Kong-listed company Bluehole Interactive’s subsidiary LK Venture announced via X that it had participated in bitSmiley’s seed round through its Bitcoin ecosystem investment fund, BTC NEXT. On March 4, KuCoin Ventures tweeted about its strategic investment in the Bitcoin DeFi project bitSmiley.
Mechanics
• bitSmiley is a native Bitcoin stablecoin project built on the Fintegra framework. It consists of the over-collateralized decentralized stablecoin bitUSD and a native trustless lending protocol (bitLending). bitUSD is based on bitRC-20, a modified version of BRC-20 that maintains compatibility with BRC-20 standards while adding Mint and Burn operations to support stablecoin creation and redemption.
• In January, bitSmiley launched bitRC-20, a new DeFi inscription protocol. Its first asset, OG PASS NFT (also known as bitDisc), comes in Gold and Black card tiers. Gold cards were distributed to Bitcoin OGs and industry leaders, with fewer than 40 holders. Starting February 4, Black cards became available to the public via whitelist and public mintage events in BRC-20 format, temporarily causing network congestion. The team later offered compensation for failed inscriptions.
• $bitUSD Operational Mechanism
The $bitUSD mechanism mirrors that of $DAI: users over-collateralize, then the bitSmileyDAO on Layer 2 receives oracle data, validates consensus, and sends a mint request for bitRC-20 tokens back to the BTC mainnet.
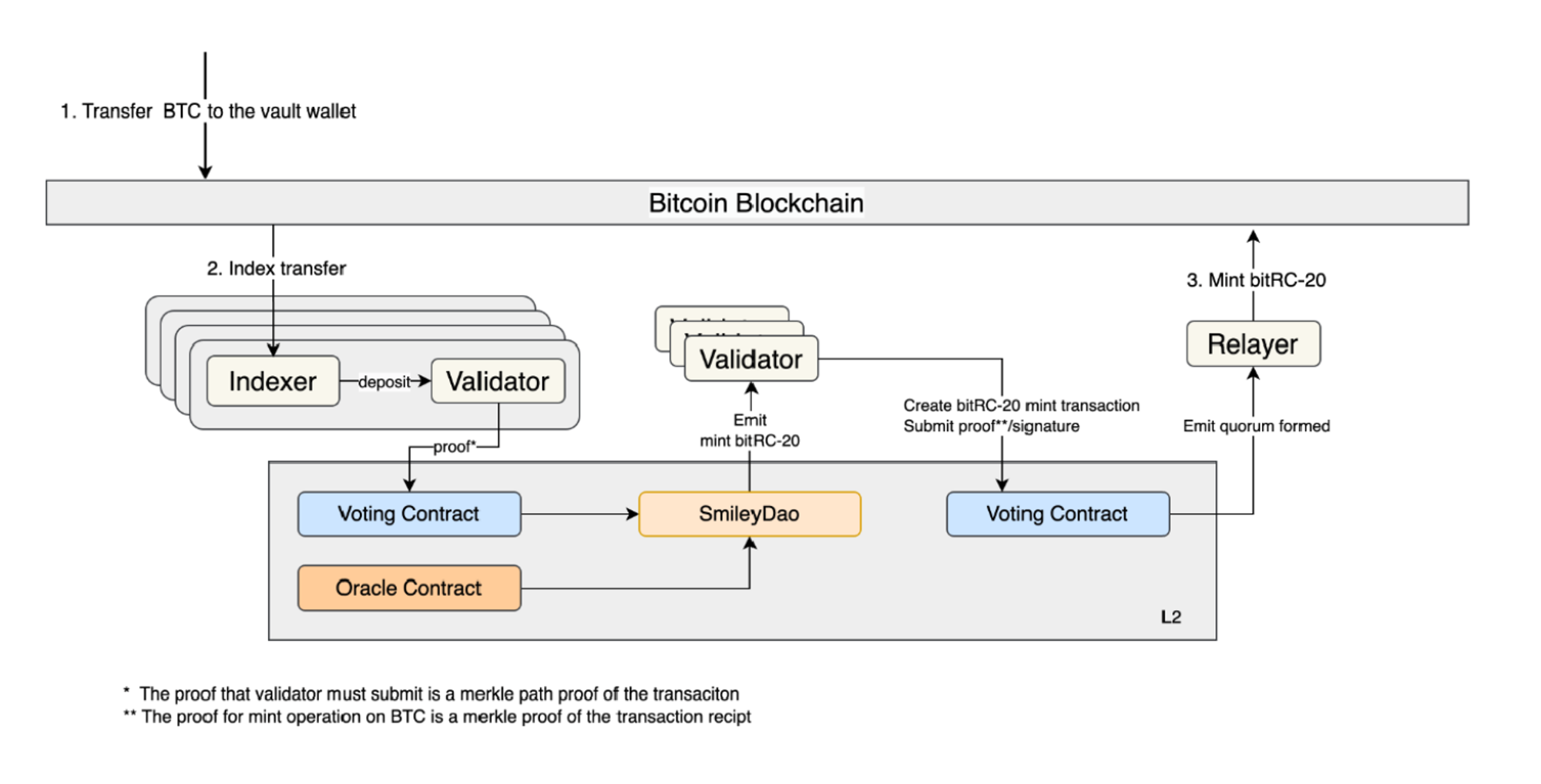
Source: https://github.com/bitSmiley-protocol/whitepaper/blob/main/BitSmiley_White_Paper.pdf
• The logic for liquidation and redemption is similar to MakerDAO, using Dutch auctions for liquidations.
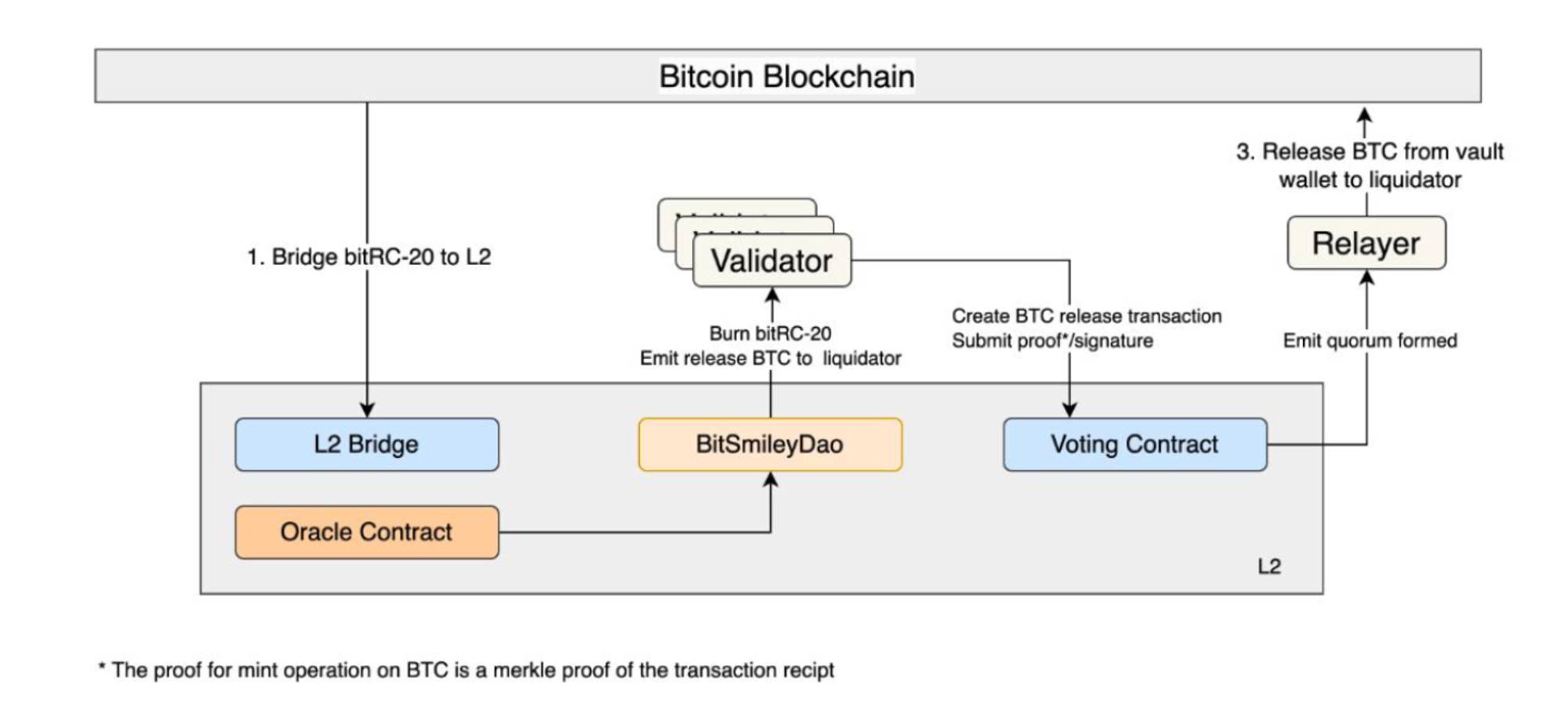
Source: https://github.com/bitSmiley-protocol/whitepaper/blob/main/BitSmiley_White_Paper.pdf
Project Progress & Participation Opportunities
• bitSmiley launched its Alphanet on BitLayer on May 1, 2024, with a maximum loan-to-value ratio (LTV) of 50%. This conservative LTV helps prevent user liquidations. As adoption of bitUSD increases, the team plans to gradually raise the LTV.
• Starting May 15, 2024, bitSmiley and the Merlin community launched an exclusive liquidity incentive grant to boost bitUSD liquidity. Details are as follows:
○ bitSmiley will distribute up to 3,150,000 $BIT tokens as rewards to Merlin community members. Rewards will unlock based on user behavior. Program duration: May 15 – August 15, 2024.
○ Reward methods: Users earn incentives by reaching bitUSD minting targets or providing liquidity to the bitUSD pool on bitCow. Liquidity rewards are distributed proportionally based on bitPoints earned by users on the Merlin chain—the more points, the greater the token incentives.
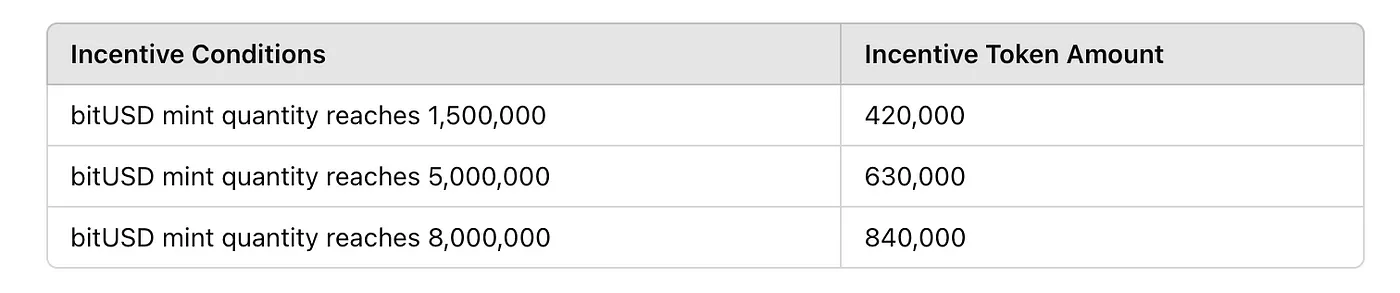
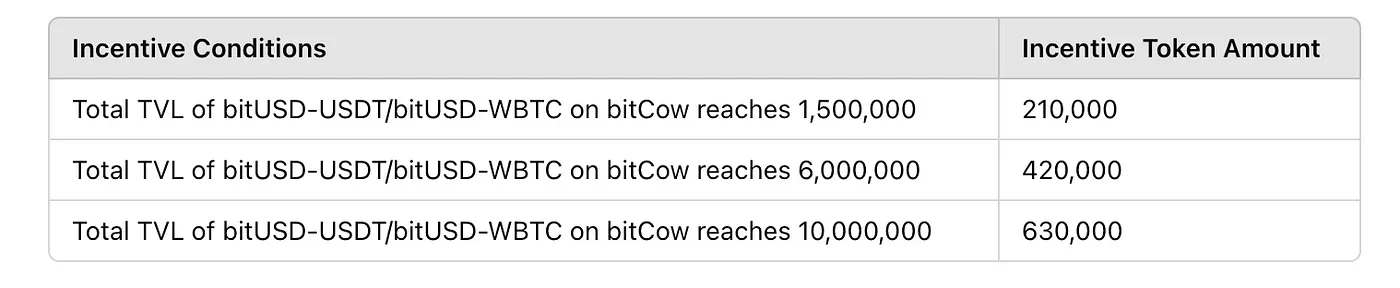
Source: https://medium.com/@bitsmiley/exclusive-liquidity-incentive-grant-details-bitsmiley-x-bitcow-alpha-net-on-merlin-chain-3f88c4ddb32d
Project Two: Bamk.fi (NUSD)
Overview
• Bamk.fi is the issuer of NUSD (Nakamoto Dollar), a synthetic dollar on Bitcoin L1. NUSD circulates on BRC-20-5-byte and Runes protocols (currently equivalent).
Mechanics
• The project has two phases. In Phase 1, NUSD is backed 1:1 by USDe, and NUSD holders accumulate BAMK tokens each block—the earlier one holds NUSD, the more BAMK they receive. In Phase 2, NUSD will be fully backed by delta-neutral Bitcoin positions, earning native yields ("Bitcoin bonds"), and enable BTC-based minting and redemption. Currently, however, the official minting method involves 1:1 USDT minting.
• The project token BAMK is issued as a Rune with code BAMK•OF•NAKAMOTO•DOLLAR, inscribed on April 21, 2024, with a max supply of 21,000,000,000 (21 billion). 6.25% of the supply was allocated as rewards to all NUSD holders. Simply holding NUSD in a wallet starts accumulating BAMK. Between blocks 844,492 and 886,454—totaling 41,972 blocks—31,250 BAMK will be distributed per block, proportionally allocated based on each user’s NUSD balance divided by the total NUSD TVL at that block height.
Project Three: Yala Labs
Overview
• Yala leverages its proprietary modular infrastructure to enable its stablecoin $YU to move freely and securely across ecosystems, unlocking BTC liquidity and injecting significant capital vitality into the broader crypto ecosystem.
• Core products include:
○ Over-collateralized stablecoin $YU: Generated by over-collateralizing Bitcoin, the infrastructure is natively compatible with Bitcoin protocols and can be deployed securely across EVM and other ecosystems.
○ Metamint: A core component of $YU that enables users to easily mint $YU using native Bitcoin across various ecosystems, thereby injecting Bitcoin liquidity into these networks.
○ Insurance derivatives: Offering comprehensive insurance solutions within DeFi ecosystems, creating arbitrage opportunities for users.
Mechanics
• To simplify $YU usage across ecosystems, Yala introduced the Metamint solution. Whether using native Bitcoin or wrapped BTC on EVM as collateral, users can easily mint $YU on any target chain. To lower barriers, users don’t need to manually wrap Bitcoin—they simply deposit BTC, and the system automatically generates the required wrapped BTC in the background to mint $YU on the target chain.
• This seamless asset conversion enables users to participate in DeFi protocols across ecosystems—including cross-chain yield farming, staking, and other DeFi activities—opening new avenues for returns. This multi-chain approach significantly enhances users’ earning potential. Unlike traditional stablecoin companies that centralize profits, Yala redistributes system-generated fees to core $YU holders, ensuring users directly benefit from ecosystem growth.
• Features and Advantages
○ Uses Bitcoin as primary collateral, benefiting from Bitcoin network security and resilience.
○ Users can engage in diverse DeFi activities via $YU to earn yield.
○ Yala follows a user-centric decentralized governance model, returning revenue to core users.
Project Progress & Participation Opportunities:
Through partnerships with leading projects, Yala offers users multiple yield opportunities without compromising security. For instance, through collaboration with Babylon, Yala users can over-collateralize BTC to mint $YU, then further stake their collateral on Babylon, achieving multi-layered yield generation. Since Babylon’s staking protocol requires no third-party custody, this integration enhances yield while guaranteeing absolute asset security.
Yala’s roadmap focuses on building a robust liquidity layer connecting Bitcoin to top-tier Layer 1 and Layer 2 ecosystems. To ensure security and optimal user experience, Yala will launch its mainnet and testnet in phases:
• Testnet V0: Launch of $YU stablecoin, Pro mode, oracle and oracle;
• Testnet V1: Lightweight $YU stablecoin with meta-yield;
• V1 Release: Insurance module and security upgrades.
• V2 Launch: Governance framework activation.
With the testnet launch approaching, Yala has secured backing from top-tier funds. Specific institutions and valuation details will be announced in upcoming funding news.
Project Four: Satoshi Protocol
Overview
• The first CDP-based stablecoin protocol in the BTC ecosystem, built on the BEVM ecosystem.
• On March 26, 2024, Satoshi Protocol announced completion of its seed round led by Web3Port Foundation and Waterdrip Capital, with participation from BEVM Foundation, Cogitent Venture, and Statoshi Lab. On July 9, 2024, it announced a $2 million funding round.
Mechanics
• Designed to release liquidity for Bitcoin holders at low interest rates, Satoshi Protocol is a multi-chain protocol with its stablecoin SAT featuring highly compatible multi-token standards. The protocol currently issues two tokens: SAT, a USD-pegged stablecoin, and OSHI, a utility token rewarding ecosystem participants. Users can deposit BTC and BTC-based yield-bearing assets (LSTs) at a minimum collateral ratio of 110% to mint $SAT, then use it in trading, liquidity pools, and lending to earn yield.
• When opening a position, users must maintain at least 110% collateralization to avoid liquidation. For example, borrowing 100 SAT requires locking BTC worth more than 110 SAT. If BTC price drops and collateral value falls below 110%, the protocol triggers liquidation.
• The Stability Pool is a core mechanism in Satoshi Protocol, designed to absorb defaulted debt by providing liquidity. When an under-collateralized position (below 110%) is liquidated, the protocol uses SAT to repay the debt and acquires the seized BTC collateral. Stability Pool participants can purchase this BTC at a discount, while the protocol uses the collected SAT to settle debts.
Project Progress & Participation Opportunities
• Recent announcements indicate Satoshi Protocol is developing a Rune-based stablecoin on the Bitcoin mainnet. Additionally, through collaborations with projects like Omni Network, it aims to bridge Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems to realize its vision of an “omnichain stablecoin.”
• Currently running an $OSHI airdrop points campaign, users can earn points via four actions: voting in the BVB program, depositing collateral to borrow $SAT, providing liquidity, and referrals. $OSHI will be distributed based on accumulated points.
Project Five: BTU
Overview
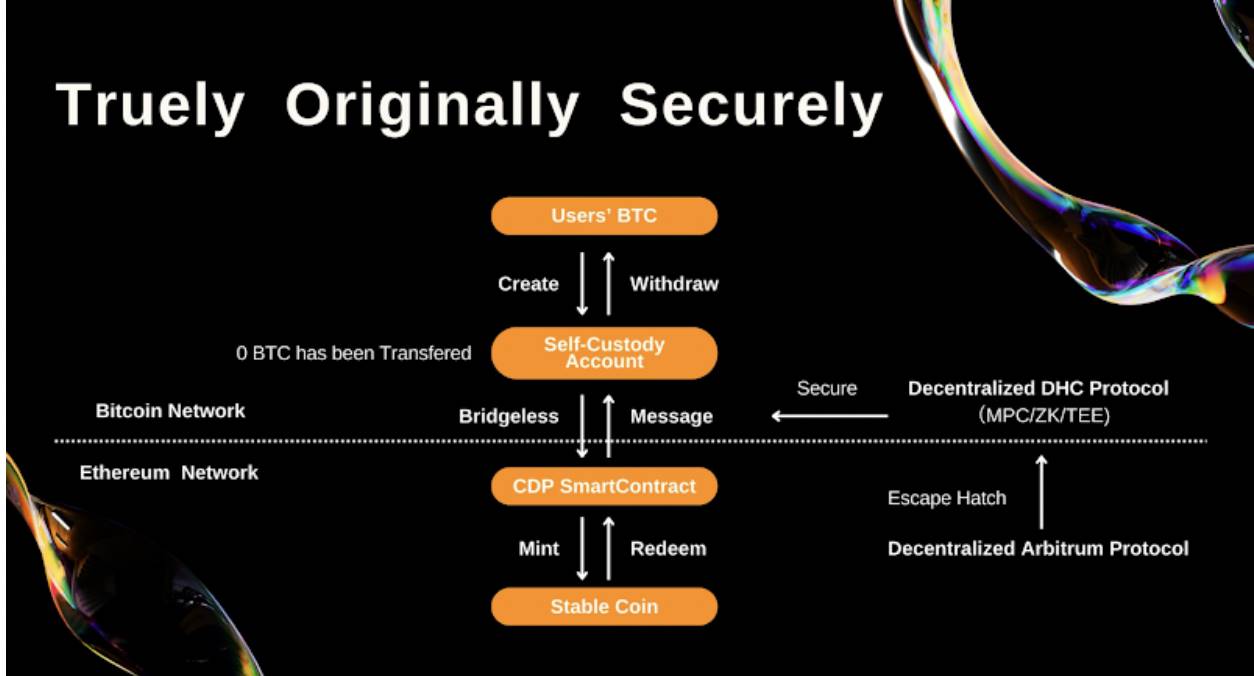
• BTU is the first decentralized stablecoin project in the Bitcoin ecosystem, utilizing a Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) model that allows users to issue stablecoins backed by BTC assets. BTU addresses the liquidity constraints Bitcoin holders face in existing decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems through seamless, trustless design, offering a safer, non-custodial stablecoin solution.
Mechanics
1. Bitcoin-Backed Stablecoin: BTU is a fully Bitcoin-collateralized decentralized stablecoin. Users lock BTC within the BTU protocol to directly mint stablecoins, without transferring assets off-chain or relinquishing control over their BTC. This design ensures decentralization and avoids risks associated with centralized exchanges or custodians.
2. No Cross-Chain Bridge Required: Unlike bridge-dependent solutions, BTU operates entirely within the Bitcoin network. Users do not need to transfer BTC across chains, eliminating third-party risks during cross-chain transfers and enhancing asset security and control.
3. Non-Transactional Asset Proof: BTU introduces a mechanism to prove BTC holdings without requiring transactions. Users can verify ownership without moving their Bitcoin, providing added flexibility and enabling DeFi participation while retaining full control over BTC assets.
4. Decentralized CDP Model: BTU employs a decentralized CDP model, giving users full autonomy over when to issue or redeem BTU stablecoins. The protocol ensures BTC can only be used with user consent, maintaining high levels of decentralization and control.
5. Enhanced Liquidity and Leverage: BTU is the first protocol to map BTC and enhance its liquidity and leverage directly on the Bitcoin network. This mechanism allows BTC holders to bring their assets into DeFi ecosystems safely, gaining greater flexibility and investment opportunities without sacrificing decentralization.
• By unlocking Bitcoin’s liquidity, BTU provides BTC holders with a trustless, decentralized way to participate in DeFi. Traditionally, Bitcoin holders struggle to access DeFi and on-chain financial activities without relying on centralized exchanges or custodians. BTU opens new opportunities, enabling safe stablecoin issuance, increased liquidity, and retained control over BTC.
• This innovative decentralized stablecoin solution not only expands financial options for BTC holders but also unlocks new growth potential for the DeFi ecosystem. By facilitating the release of Bitcoin liquidity, BTU could catalyze a new generation of DeFi applications and protocols, broadening the user base and use cases of the DeFi market.
• BTU’s infrastructure prioritizes decentralization and security. By operating entirely within the Bitcoin network, BTU eliminates the need for cross-chain bridges or third-party custodians, significantly reducing exposure to centralized risks. Its decentralized model ensures seamless integration with the existing Bitcoin ecosystem without introducing additional technical or security vulnerabilities.
Project Progress & Participation Opportunities
• The project has received investment support from Waterdrip Capital, Founder Fund, and Radiance Ventures.
2. Lending Sector
Introduction
• Bitcoin lending (BTC Lending) is a financial service where users borrow against Bitcoin or lend Bitcoin to earn interest. Borrowers deposit Bitcoin into a lending platform, which issues loans based on the BTC’s value. Borrowers pay interest, and lenders earn yield. This model provides liquidity for Bitcoin holders and creates new income channels for investors.
• BTC lending resembles traditional mortgage loans. If a borrower defaults, the platform can auction the pledged Bitcoin to recover the loan. BTC lending platforms typically implement the following risk management measures:
1. Managing collateral ratios and loan-to-value (LTV): Platforms set an LTV limit. For example, if Bitcoin is worth $10,000, the maximum loan might be $5,000 (LTV of 50%), providing a buffer against price volatility.
2. Margin calls and collateral top-ups: When Bitcoin price drops, borrowers may be required to add more collateral to reduce LTV. Failure to do so may trigger forced liquidation.
3. Forced liquidation mechanism: If borrowers fail to meet margin requirements, the platform sells part or all of the collateralized Bitcoin to repay the loan.
4. Risk management and insurance: Some platforms establish insurance funds or partner with insurers for additional protection.
• From 2013–2017, Bitcoin gained acceptance as a new asset class, and early lending platforms like Bitbond and BTCJam emerged, primarily operating via peer-to-peer (P2P) models. From 2018–2019, rapid growth in the crypto market brought new platforms like BlockFi, Celsius Network, and Nexo, while the rise of DeFi concepts fueled decentralized lending platforms.
• Since 2020, global financial turmoil caused by the pandemic increased attention on cryptocurrencies as safe-haven assets, driving strong demand for BTC lending and rapid expansion of lending volumes. Platforms continuously innovate, launching new products such as flash loans, liquidity mining, and crypto-reward credit cards, attracting more users.
• The BTC Lending sector has become a vital part of the crypto market, supporting major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Products include secured loans, deposit accounts, and unsecured loans. Platforms profit from interest spreads and fees. Popular platforms include Aave, offering flash loans and liquidity mining rewards; MakerDAO, offering the DAI Savings Rate (DSR); and Yala, providing DeFi yield through stablecoins. Below, we explore leading products in the BTC Lending space.
Project One: Liquidium
Overview
• Liquidium is a P2P lending protocol running on Bitcoin, enabling users to lend and borrow native Bitcoin using native Ordinals and Runes assets as collateral.
• On December 11, 2023, Liquidium raised $1.25 million in a Pre-Seed round, with investments from Bitcoin Frontier Fund, Side Door Ventures, Actai Ventures, Sora Ventures, Spicy Capital, and UTXO Management.
• On July 18, 2024, it completed a $2.75 million seed round led by Wise 3 Ventures, with participation from Portal Ventures, Asymmetric Capital, AGE Fund, and Newman Capital.
Mechanics
• The platform enables Bitcoin lending securely and non-custodially using Partially Signed Bitcoin Transactions (PSBT) and Discreet Log Contracts (DLC) on Bitcoin L1. Currently supports lending of Ordinals and Runes assets (BRC-20 testing underway).
• Tokenomics: Rune-formatted LIQUIDIUM•TOKEN launched on July 22, 2024, with a total supply of 100M. Genesis airdrop completed. As of September 3, LIQUIDIUM•TOKEN traded at ~$0.168, with a market cap of $2M.
• According to Geniidata, as of September 3, the protocol’s total transaction volume reached approximately 2,400 BTC, mostly Ordinals with a small portion in Runes. Transaction volume peaked in April–May, averaging 15–20 BTC daily in Ordinal transactions. Following the Rune launch, DAU and volume saw a new peak before declining. By August and September, daily volume dropped to 5–10 BTC.
Project Two: Shell Finance
Overview
• A stablecoin protocol on BTC L1 that accepts BTC, Ordinals NFTs, Runes, BRC-20, and ARC-20 assets as collateral to mint $bitUSD.
Mechanics
• Similar to Liquidium, Shell Finance uses PSBT and DLC technologies to enable native BTC lending. PSBT allows secure, collaborative transaction signing, while DLC enables conditional, trustless contract execution based on verified external data.
• Unlike Liquidium’s P2P model, Shell Finance adopts a peer-to-pool (P2Pool) approach to maximize capital utilization.
• Testnet has not yet launched.
3. Staking Sector
Introduction
• Staking is commonly recognized for its secure and steady yield characteristics. When users “stake” tokens, they typically gain access rights, privileges, or reward tokens over time, while being able to withdraw their tokens at any time. Staking occurs at the network level and is primarily used to secure the network. Ethereum’s proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism is the most prominent example, with over 565,000 validators each holding the standard 32 ETH—worth over $32 billion today. Staked assets are often linked to DeFi liquidity, yield rewards, and governance rights. Locking tokens into a blockchain network or protocol generates returns, with those tokens powering critical user services.
• Today, staking introduces the concept of shared security, adding a new dimension to the modular blockchain narrative—leveraging the potential of “digital gold and silver.” Narratively, this unlocks trillions in market cap liquidity and serves as a cornerstone for future scalability. Recent massive funding rounds—$70 million for Bitcoin staking protocol Babylon and $100 million for Ethereum restaking protocol EigenLayer—demonstrate strong VC confidence in this sector.
• Currently, this sector splits into two camps: 1. Layer 1s with sufficient security acting as functional layers for rollups; 2. Building new blockchains that match or exceed the security of Bitcoin/Ethereum with better performance. For example, Celestia aims to quickly create a secure, decentralized, high-performance data availability (DA) layer through pure DA architecture and low gas costs. However, this approach faces challenges in achieving full decentralization and lacks legitimacy. In contrast, newer projects like Babylon and EigenLayer offer a more neutral path—preserving legitimacy and security while expanding application value for native assets by leveraging PoS to create shared security services using Bitcoin or Ethereum’s asset value.
Project One: Babylon
Overview
• Babylon is a Layer 1 blockchain founded by Professor David Tse of Stanford University. Its mission is to bring Bitcoin’s unparalleled security to all PoS blockchains without additional energy costs. The team comprises Stanford researchers, experienced developers, and seasoned business advisors.
• Babylon is a Bitcoin staking protocol whose core component is a Cosmos IBC-compatible PoS public chain. It enables users to lock Bitcoin on the Bitcoin mainnet to provide security for other PoS consumer chains, while earning staking rewards on Babylon or the PoS chains. Babylon allows Bitcoin to leverage its unique security and decentralization to economically secure other PoS chains, enabling faster project launches.

Source: https://www.rootdata.com/zh/Projects/detail/Babylon?k=MjgwNQ%3D%3D
• The Babylon team consists of 32 technical staff and advisors, with strong technical expertise. Advisors include Sunny Aggarwal, co-founder of Osmosis Lab, and Sreeram Kannan, founder of Eigenlayer, serving as strategic advisor. As of June 1, 2024, Babylon has disclosed multiple funding rounds totaling over $96.8 million. The table below shows Babylon’s relatively high fundraising amount compared to other Bitcoin Layer 2 projects, supported by numerous institutions.
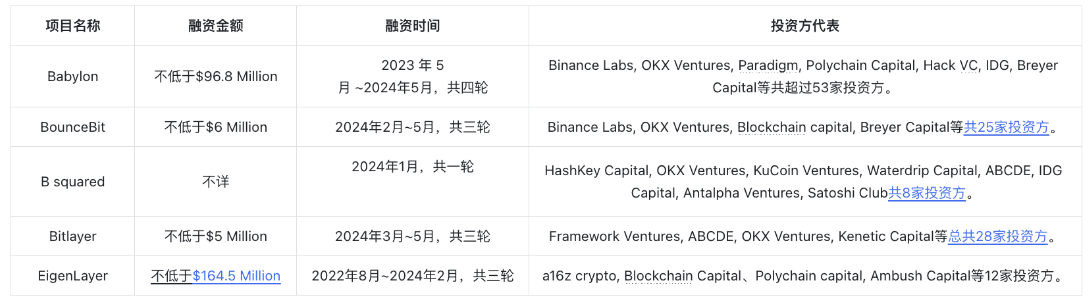
Mechanics
• Babylon’s operational model aligns with Ethereum’s restaking protocol EigenLayer. “Bitcoin + Babylon” parallels “Ethereum + EigenLayer.” However, since Bitcoin lacks smart contract support, Babylon must first solve the fundamental challenge of making non-stakable Bitcoin stakable—before advancing to restaking.
• Babylon uses UTXOs to implement staking contracts, termed Remote Staking. BTC security is remotely relayed via an intermediary layer to PoS chains. The implementation cleverly combines existing opcodes in four steps:
a. Locking Funds
Users send funds to a multisig-controlled address. Using OP_CTV (OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY), which allows predefined transaction templates ensuring execution only under specific conditions, the contract specifies that funds can only be spent when certain conditions are met. Once locked, a new UTXO is created, indicating the funds are staked.
b. Condition Verification
OP_CSV (OP_CHECKSEQUENCEVERIFY) enables time-locking based on transaction sequence numbers, preventing funds from being withdrawn within a specified period. Combined with OP_CTV, this enables staking, unstaking (allowing UTXO spending after the staking period), and slashing (forcing UTXO to a locked, unspendable state—akin to a black hole address—if the staker acts maliciously).
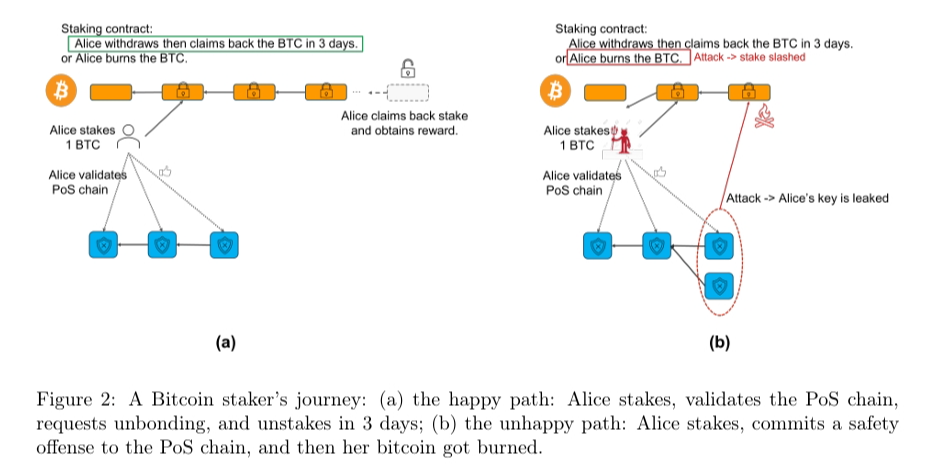
Source: https://docs.babylonchain.io/assets/files/btc_staking_litepaper-32bfea0c243773f0bfac63e148387aef.pdf
c. State Updates
Each staking or unstaking action involves creating and spending UTXOs. New transaction outputs generate new UTXOs, while old ones are marked as spent. Every transaction and fund movement is accurately recorded on-chain, ensuring transparency and security.
d. Reward Distribution
Rewards are calculated based on staked amount and duration, then distributed via new UTXOs. These rewards can be unlocked and spent once script-defined conditions are met.
• Babylon’s overall architecture consists of three layers: Bitcoin (as timestamp server), Babylon (a Cosmos Zone acting as intermediary), and PoS demand layer. Babylon refers to the latter two as Control Plane (Babylon itself) and Data Plane (various PoS consumer chains).
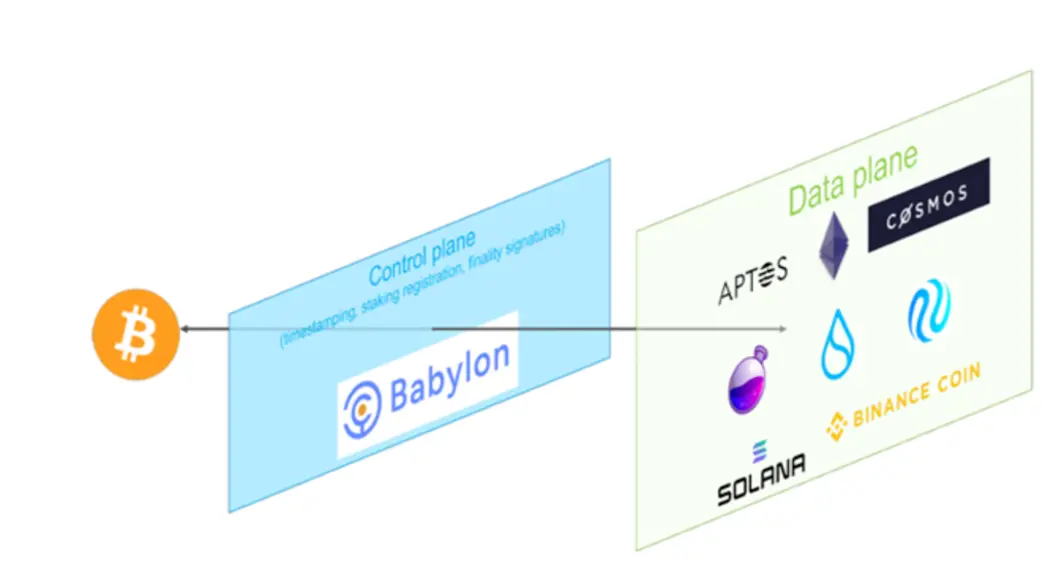
• Validators on each PoS chain download Babylon blocks and check whether PoS checkpoints appear in Bitcoin-verified Babylon blocks. This allows PoS chains to detect discrepancies—for example, if a Babylon validator creates an unavailable block verified by Bitcoin and falsely claims inclusion of PoS checkpoints.
• Hence, slashing rules apply: if validators fail to withdraw stakes upon detecting an attack, validators producing conflicting PoS blocks with double signatures can be slashed. Malicious PoS validators might fork the PoS chain when assigning Bitcoin timestamps to canonical PoS blocks. Later PoS clients would see the canonical chain switch from top to bottom. Though a successful security breach, this results in slashing the malicious validator’s stake due to conflicting double-signed blocks, provided they haven’t yet withdrawn.
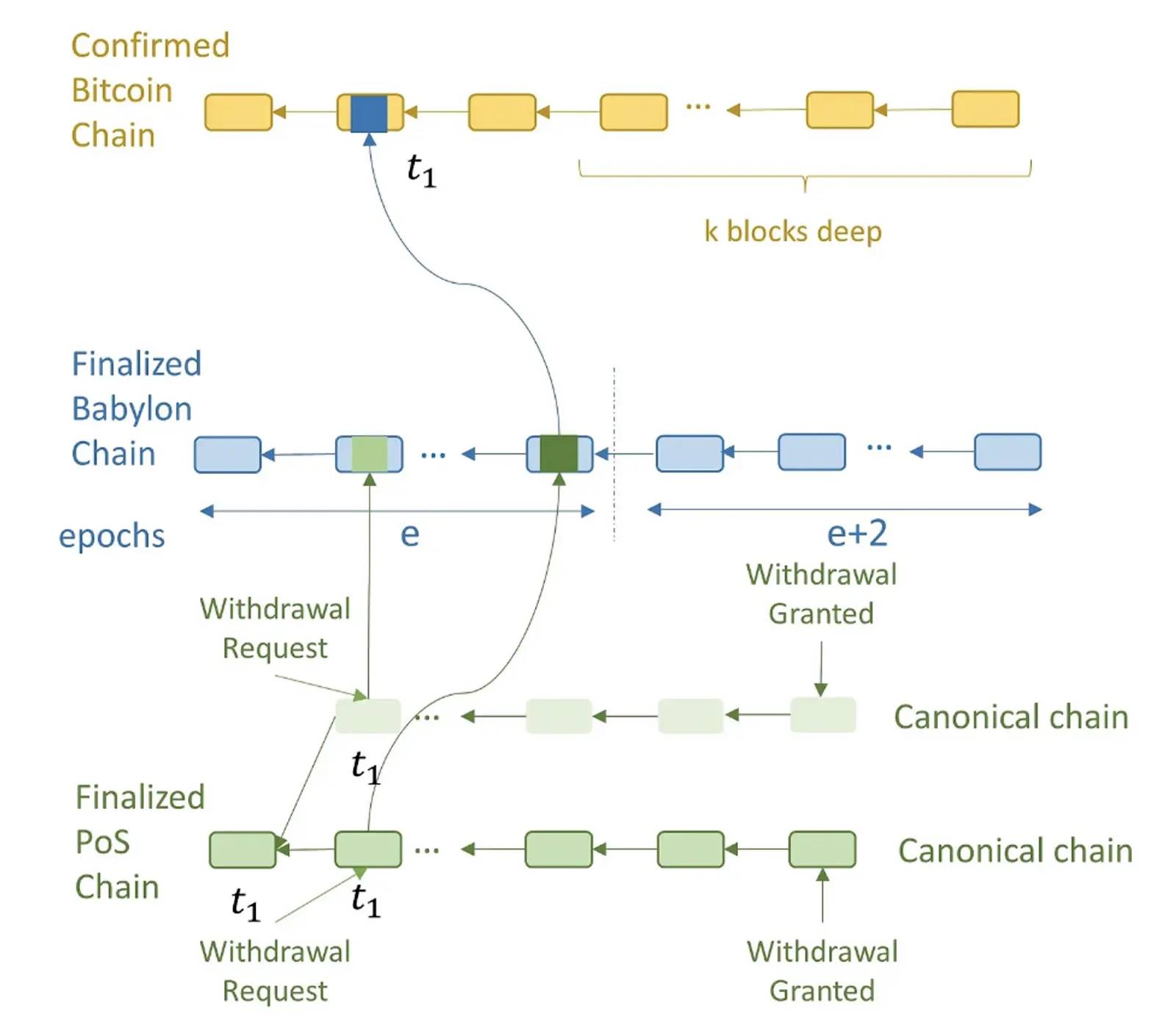
Source: https://docs.babylonchain.io/assets/files/btc_staking_litepaper-32bfea0c243773f0bfac63e148387aef.pdf
Project Progress & Participation Opportunities
• In February 2023, Babylon launched its BTC timestamping testnet. In July, it achieved BTC staking PoC and plans to launch BTC staking testnet in Q4.
• In Q2 2024, Babylon will launch its mainnet. In Q3–Q4 2024, it will roll out Data Availability. Currently on testnet 4, users participating in testing receive project points as incentives, which can be exchanged for governance token airdrops upon mainnet launch.
• Mainnet launch is imminent. On August 1, 2024, Babylon began pre-staking collaborations with popular restaking projects including Chakra, Bedrock, Solv Protocol, and Pstake. Users can already participate in Babylon pre-staking via these platforms and claim shares—an ideal entry point. After mainnet launch, users staking on-chain will earn governance tokens and receive annualized yield from the staking network at any time.
4. Restaking Sector
Introduction
• Building on staking, Ethereum first introduced the concept of restaking. Restaking involves using liquid staking tokens (LSTs) as collateral to stake on other networks or blockchains, earning additional yield while contributing to the security and decentralization of new networks. Through restaking, investors earn dual returns—from the original network and the restaking network. While restaking offers higher yields, it also carries risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and validator misconduct.
• Beyond accepting native assets, restaking networks also accept other assets like LSD tokens and LP tokens, enhancing network security. While generating real revenue for protocols and users, restaking unlocks infinite liquidity sources for the DeFi market. Revenue for restaking and standard networks comes from security leasing, validator and dApp fees, and protocol-layer charges. Participants receive a share of network revenue and may also earn inflationary rewards in native tokens.
• Many BTC holders stake their BTC in projects like Babylon and Bedrock, earning attractive annual yields and governance tokens—with early adopters receiving particularly strong returns. However, their BTC loses other utility once staked. How can new liquidity be unlocked to enhance BTC’s value? Since direct BTC liquidity expansion is limited, the focus shifts to LSDs—unlocking liquidity from staking-derived assets. Users enthusiastically embrace this: restaking staking receipts unlocks fivefold returns—annual yield from staking, governance tokens from staking, annual yield from restaking, and governance tokens from restaking.
Project One: Chakra
Overview
• Chakra is an innovative modular settlement infrastructure leveraging zero-knowledge proofs to ensure trustless security and efficiency. By consolidating fragmented Bitcoin liquidity, Chakra delivers a safer, smoother settlement experience. Users can one-click stake Bitcoin and leverage Chakra’s advanced settlement network to access enhanced liquidity yield opportunities across Babylon’s LST/LRT ecosystem.
• Backed by Starknet ecosystem, Chakra announced in March 2024 securing early investments from StarkWare, CoinSummer, and several whale investors and miners.

Mechanics
• Chakra provides a highly modular Bitcoin settlement network, enabling free movement of BTC derivative assets across major public chains and injecting liquidity into DeFi protocols—addressing Bitcoin’s liquidity and interoperability challenges in today’s blockchain ecosystem. Chakra also helps Layer 2s, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and DeFi protocols bypass the complexity of building their own Bitcoin settlement infrastructure, avoiding resource waste and security risks from redundant development.
• Leveraging finality provided by the Babylon network, Chakra enhances economic security and prevents settlement errors due to consensus attacks. Chakra delivers efficient zero-knowledge proof aggregation for Layer 2 state and liquidity settlement, enabling frictionless cross-chain circulation of Bitcoin assets. The team’s Parallel VM, designed with multithreading optimization, achieves over 5,000 TPS on 4 threads and up to 100,000 TPS in high-end 64-thread environments.
Progress
• Chakra launched its Devnet in May, incentivizing developers to build the app ecosystem and forming deep ties with multiple Starknet local communities. Supported by Starknet, it will host developer education programs and Devnet incentives. In June, during a joint testnet event with Babylon, Chakra became Babylon’s top Finality Provider network-wide, contributing 41% of Babylon’s total stakers.
• From August 1 to 7, 2024, Chakra partnered with Binance Web3 Wallet on a Babylon pre-staking campaign, offering participants dual rewards: potential Babylon yields and ChakraPrana tokens, with future eligibility for additional ecosystem token rewards. The campaign concluded with 48,767 users participating in staking.
Project Two: Bedrock
Overview
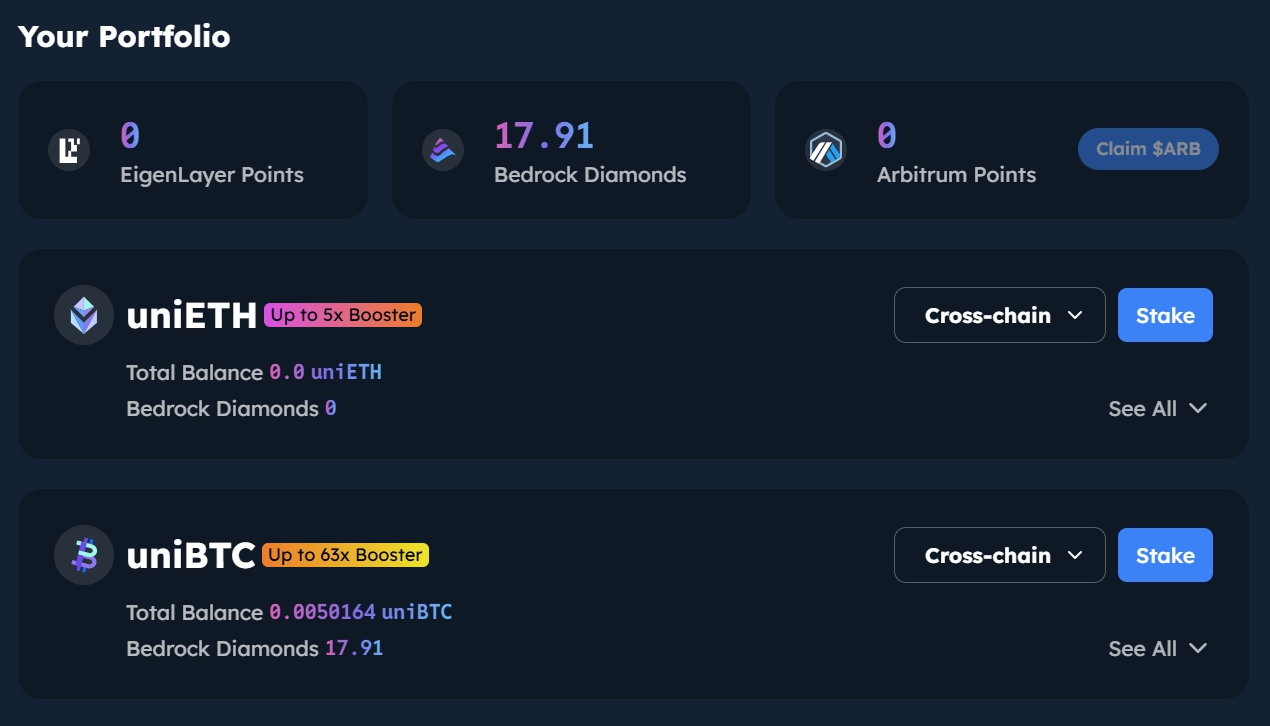
• Bedrock is a multi-asset liquidity restaking protocol supported by a non-custodial solution co-designed with RockX. Bedrock leverages a universal standard to unlock liquidity and maximize value for PoS tokens (e.g., ETH, IOTX) and existing liquid staking tokens (uniETH, uniIOTX).
• Bedrock delivers institutional-grade services, surpassing $200 million in total staked value by May 2, 2024, and built the first liquid staked Bitcoin (uniBTC) on Babylon.
Total Value Locked (TVL):
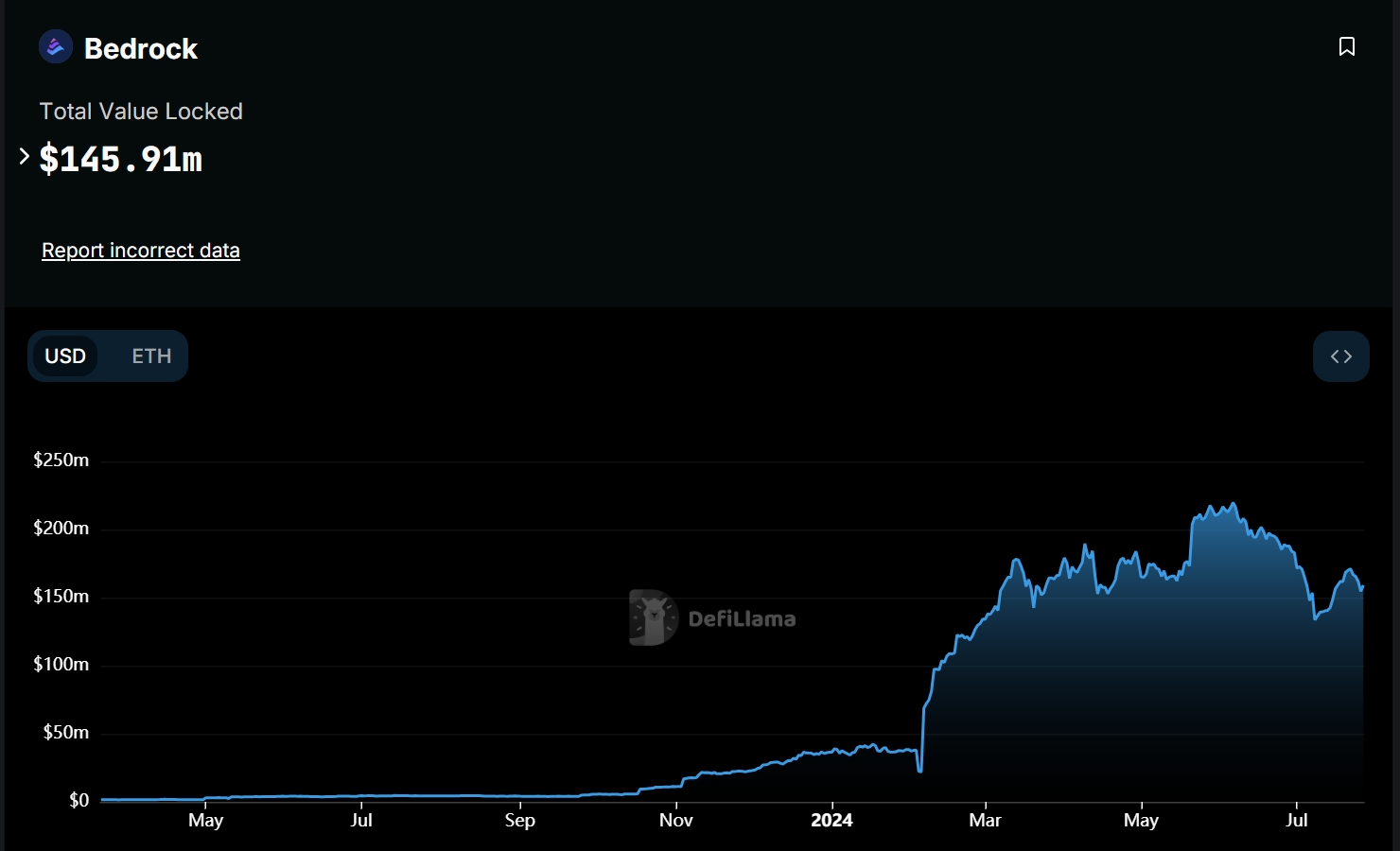
Source: https://defillama.com/protocol/bedrock#information
• TVL briefly exceeded $200 million and shows signs of rebounding. The project has also formed deep collaborations with ecosystem partners like Pendle, Karak, Celer, and zkLink, underscoring its influence in the DeFi space.

Source: https://www.rootdata.com/zh/Projects/detail/Bedrock?k=MTI1OTM%3D
• Bedrock has attracted investments from renowned institutions including OKX Ventures, Waterdrip Capital, and Amber Group. On May 2, 2024, OKX Ventures announced its lead investment in Bedrock. Dora Yue, founder of OKX Ventures, stated: “With DeFi booming and on-chain staking exceeding $93.4 billion—48% from liquidity restaking—we aim to accelerate restaking solutions. We hope to provide diversified, secure asset management options for the community. We look forward to the gradual maturation and systematization of DeFi use cases, promoting sustainable growth in the Web3 industry.”
Mechanics
• Uses uniBTC, powered by Babylon, for restaking. Users can stake wBTC on Babylon via ETH chain, receiving a 1:1 receipt—uniBTC—which can always be redeemed for wBTC. Babylon provides core technological support. Users staking wBTC and holding uniBTC earn points from both Bedrock and Babylon. By partnering with Babylon, Bedrock offers liquid staking services to support Babylon’s PoS chains. Minting uniBTC ensures stability and security for Babylon’s PoS chains while expanding Bedrock’s product suite to BTC chains.

Source: https://www.bedrock.technology/
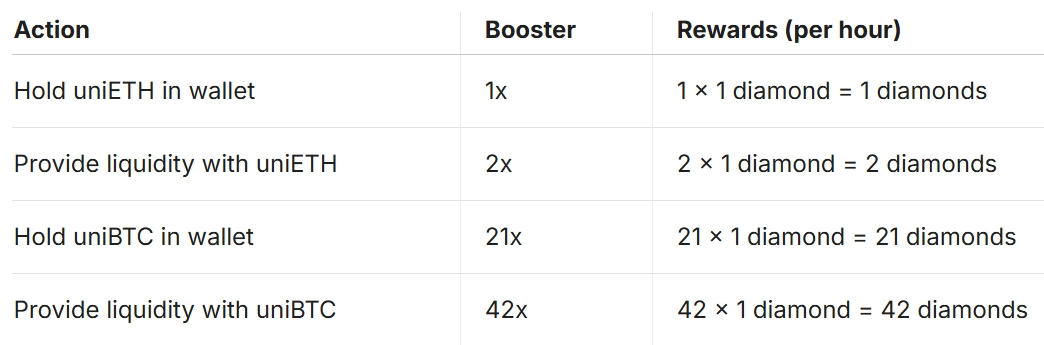
• From August 1 to 7, 2024, Bedrock partnered with Binance on a staking campaign. Starting August 1, users holding uniBTC in their wallets earn 21x Bedrock Diamond rewards per hour per token, with Binance Web3 Wallet users receiving an additional 3x bonus.
Source: https://docs.bedrock.technology/bedrock-lrt/bedrock-diamonds
5. Decentralized Custody
• Recently, BitGO, the entity behind wBTC, announced plans to relinquish control of wBTC, sparking market discussions about wBTC’s security.
wBTC
• wBTC was the earliest and most widely adopted form of wrapped Bitcoin, bridging Bitcoin assets to the Ethereum ecosystem and unlocking Bitcoin’s liquidity for Ethereum-based DeFi. However, this ERC-20 form of wrapped Bitcoin suffers from centralized management, raising concerns about asset security and transparency. MakerDAO voted to halt new borrowing against wBTC and destroyed over $30 million worth of wBTC within a week. Interest has grown in competing products like tBTC and Coinbase’s new cbBTC.
tBTC
• When bridging BTC to ETH, consider minting tBTC. Convert wBTC to tBTC and either redeem back to native BTC or continue using tBTC as DeFi collateral. tBTC enjoys strong DeFi adoption, especially on Curve Finance. Besides active trading in stable and volatile pools, tBTC can also be used to mint crvUSD stablecoin.
fBTC
• fBTC is a new omnichain synthetic asset, pegged 1:1 to BTC, enabling cross-chain BTC circulation (Omnichain). Initially launching on ETH, Mantle, and BNB Chain, it will expand to more networks, allowing fBTC to generate yield in DeFi scenarios.
• Key advantages of fBTC:
1. fBTC will use MPC (multi-party computation) custodians.
2. f
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















