Hotcoin Research | Awakening BTCFi's "Sleeping Golden Mountain": Babylon Protocol Progress and Ecosystem Landscape Analysis
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Hotcoin Research | Awakening BTCFi's "Sleeping Golden Mountain": Babylon Protocol Progress and Ecosystem Landscape Analysis
This article will provide an in-depth analysis of Babylon's technical mechanisms and innovations, summarize its staking data and performance results, review representative projects within the Babylon ecosystem, and explore the current challenges and opportunities facing Babylon, along with outlooks for its future development.
Author: Hotcoin Research

Introduction
With the rapid development of DeFi, Bitcoin—the cornerstone of the cryptocurrency world—has become a focal point for ecosystem expansion and innovative use cases. However, due to its Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, the Bitcoin network does not natively support staking, leaving vast amounts of BTC assets in a "dormant" state within DeFi. The emergence of Babylon Protocol introduces a new model for Bitcoin staking: without altering Bitcoin’s mainnet or requiring bridges or custodianship, users can leverage their BTC to secure other blockchains and earn yield. This brings Bitcoin into the PoS economy, enabling BTC to serve dual roles—as both a store of value and an income-generating asset—and drives the rise of the BTCFi ecosystem.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of Babylon Protocol's technical mechanisms and innovations, summarizes its staking data and achievements, reviews representative projects within the Babylon ecosystem, and explores current challenges, opportunities, and future outlook.
I. Technical Innovation of the Babylon Protocol
1. Non-Custodial BTC Staking Model
Babylon enables native BTC to participate in staking while maintaining user self-custody through a clever design. Unlike traditional cross-chain bridges that lock BTC and issue wrapped tokens such as WBTC, Babylon avoids third-party custody or token bridging—all operations occur directly on the Bitcoin mainnet. Its core lies in Bitcoin script locking and signature verification: BTC holders generate special staking transactions on-chain, locking BTC in script addresses with time locks and multi-signature conditions. The PoS chains served by Babylon—including its beacon chain—can recognize these locked transactions and verify associated Bitcoin signatures, thereby recording which public key addresses have staked how much BTC. During staking, the BTC remains under the control of the user’s own Bitcoin address and can only be unlocked upon meeting predefined conditions (e.g., maturity or authorized withdrawal). This design achieves a trustless, non-custodial staking model without moving BTC off the mainnet, significantly reducing risk.
2. Overcoming Native BTC Staking Limitations
About 27% of ETH is currently staked, yet nearly 0% of BTC earns staking rewards. Babylon unlocks this untapped potential through a “time-space separation” design that allows BTC to share security across chains: BTC remains secured on the Bitcoin network, while Babylon and the PoS networks it serves reference this BTC as economic collateral. This requires no upgrade to Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities or hard fork changes—Babylon staking transactions are standard Bitcoin transactions that utilize existing scripting functionality to establish staking and withdrawal conditions.
3. Finality Providers and BTC Security Integration
Babylon makes no modifications to the Bitcoin protocol itself but instead introduces a “control plane” atop Bitcoin—its PoS beacon chain. Built using the Cosmos SDK, this chain acts as the management layer of the Babylon system, aggregating the security provided by BTC staking and offering finality services to other blockchains. When generating staking transactions, BTC holders delegate their BTC to a “Finality Provider.” These providers act as validator nodes on the Babylon chain, operated by professional entities. They cannot access users’ BTC but are authorized to represent users by applying the economic weight of their staked BTC toward voting, checkpoints, and finality proofs on PoS networks.
4. Security and Withdrawal Mechanism
BTC staked via Babylon can be withdrawn early at any time. The maximum lock-up period is approximately 64,000 Bitcoin blocks (about 15 months). To unlock early, users initiate an unstaking transaction, which must be validated and co-signed by a constraint committee via multi-sig. After approval, the BTC enters a 7-day on-chain unlocking period before being returned. Throughout this process, the committee can only approve valid withdrawals—they cannot unilaterally transfer user BTC or prevent automatic unlocking when the staking period ends. Additionally, Phase-1 BTC staking has no slashing mechanism—users do not sign messages consenting to penalty, so even if their delegated PoS validators fail, their BTC remains unaffected. This alleviates early adopters’ security concerns.
5. Multi-Chain Sharing and Scalability
Babylon’s long-term vision, to be realized in Phase-3, is “one BTC, multiple stakes.” A single user’s staked BTC could simultaneously secure multiple PoS networks (referred to by Babylon as Bitcoin Secured Networks, or BSNs). Babylon’s PoS chain will act as the central coordinator, managing how the same BTC allocates voting power across different networks, allowing BTC holders to earn rewards from multiple chains concurrently. This liquid restaking concept mirrors Ethereum’s EigenLayer, except the underlying staked asset is BTC. By introducing BTC as shared staking collateral, Babylon aims to enhance the anti-volatility resilience and overall security of the PoS ecosystem. Moreover, since Babylon does not rely on cross-chain bridges, it greatly reduces the risk of bridge hacks.
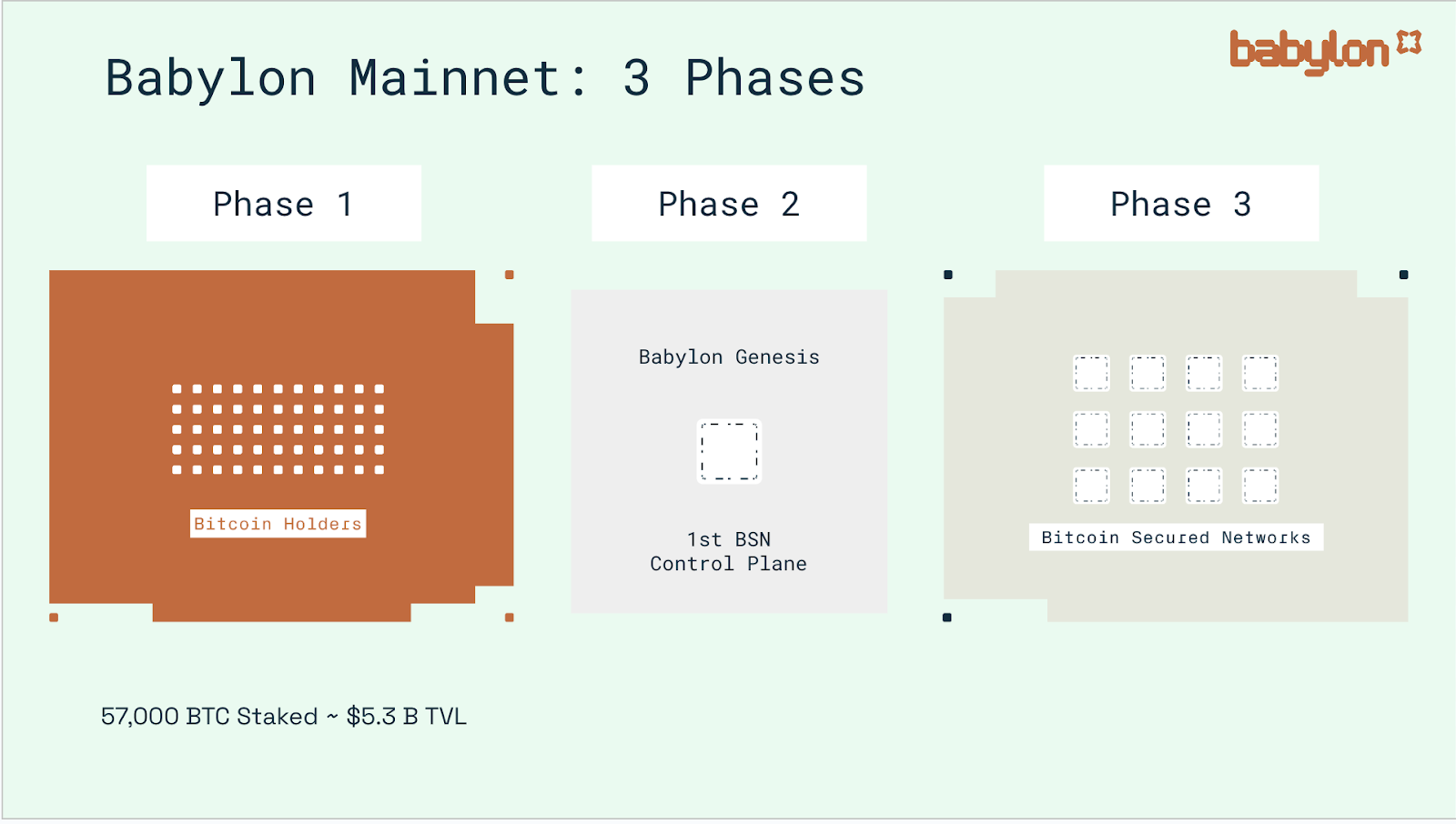
Source: https://babylon.foundation/blogs
II. Progress and Performance of Babylon BTC Staking
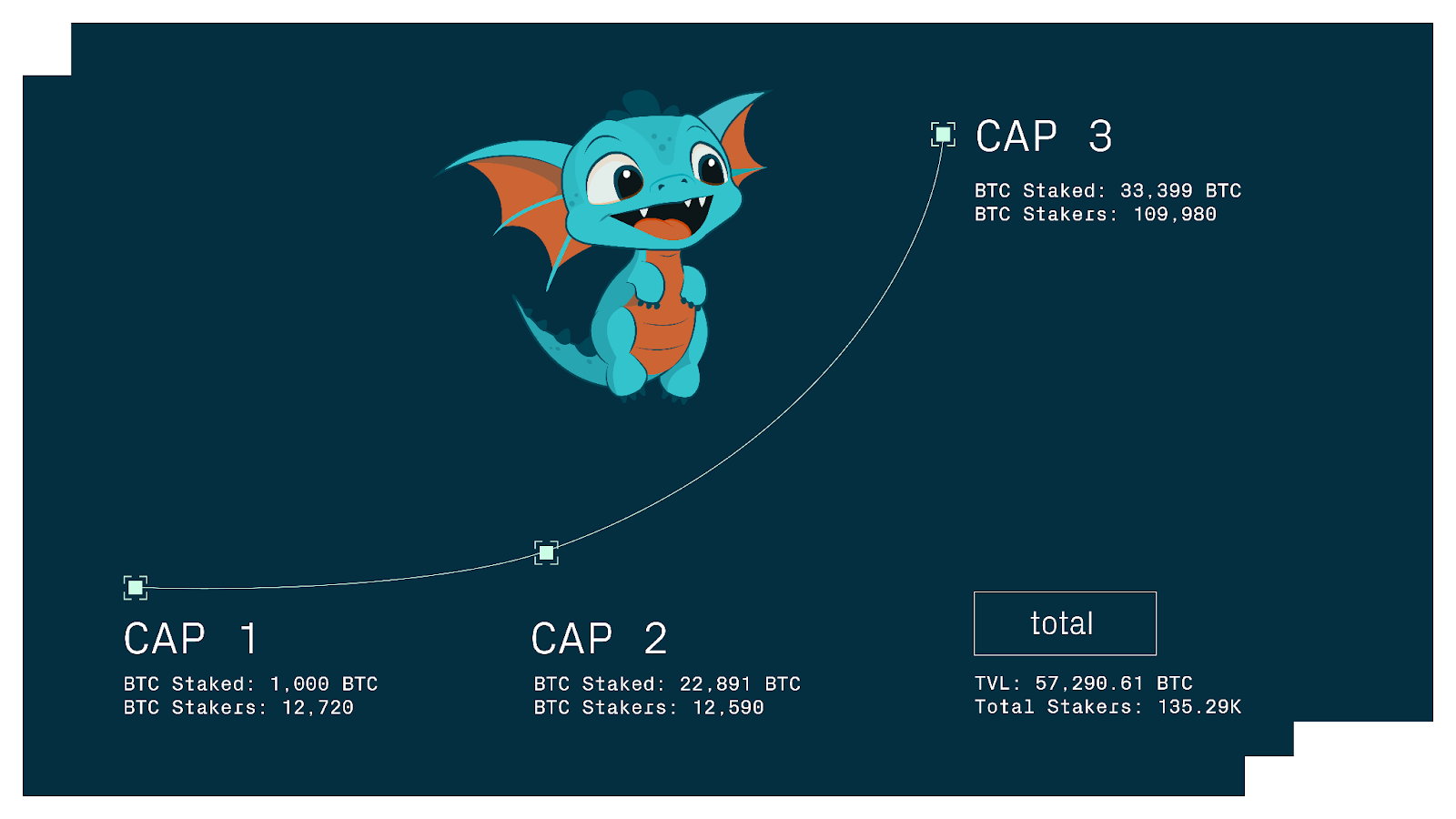
Babylon launched Phase-1 of its Bitcoin staking protocol in 2024, gradually opening staking access in stages. Officially divided into three phases (Cap-1, Cap-2, Cap-3), each stage varied in staking caps and participation rules to incrementally test and scale BTC staking volume.
Source: https://babylonlabs.io/blog
1. Cap-1: Initial 1,000 BTC Cap Ignites Enthusiasm
Timeline & Rules: As the starting phase of Phase-1, Cap-1 opened on August 22, 2024. For safety, Babylon set an initial cap of 1,000 BTC. Participation followed a first-come-first-served model: staking transactions were recorded chronologically on the Bitcoin blockchain until cumulative deposits reached 1,000 BTC. To encourage broad participation, each transaction was limited to between 0.005 BTC minimum and 0.05 BTC maximum. The 0.05 BTC upper limit ensured thousands of transactions would be needed to fill the cap, preventing whale dominance. Thus, Cap-1 functioned more like a community event, attracting many retail BTC holders.
Participation: Market response was overwhelming—1,000 BTC filled up in just three hours. In total, 12,720 BTC stakers participated, submitting about 20,610 staking transactions. This surge caused Bitcoin network fees to spike 120-fold: average hourly transaction fees jumped from 0.5 BTC to 60 BTC during the launch window, as users paid high miner fees to secure spots.
Ecosystem Protocol Performance: LSD protocols captured significant share in Cap-1, offering one-stop BTC staking entry with additional incentives. Solv Protocol staked 250 BTC (25% of total), leveraging its product SolvBTC.BBN to aggregate user BTC and fully reimbursing all related miner fees—a move that lowered user costs. RockX’s Bedrock contributed ~297.8 BTC (~30%), Lorenzo Protocol ~129.4 BTC (12.9%), PumpBTC ~118.4 BTC (11.8%), Persistence’s pSTAKE ~10 BTC (1%), with the remainder coming from散户via exchanges and wallets. Babylon introduced a “Babylon Points” scoring system to measure contribution. During Cap-1, 3,125 points were distributed per Bitcoin block, allocated proportionally based on active staked BTC in that block. These points, tied to public keys, may influence future reward distribution.
2. Cap-2: Capacity Expansion and Institutional Entry with Billions in TVL
Timeline & Rules: Following Cap-1’s success, Babylon launched Cap-2 on October 9, 2024. This phase adopted a different strategy: removing the total cap and limiting the staking window to only 10 Bitcoin blocks (~90 minutes), accepting all valid transactions during this interval. The per-transaction limit increased to 500 BTC, enabling institutions to stake large volumes. Block reward points also rose to 10,000 per block—over 3x Cap-1 levels. With higher rewards and looser caps, Cap-2 aimed to attract institutional players.
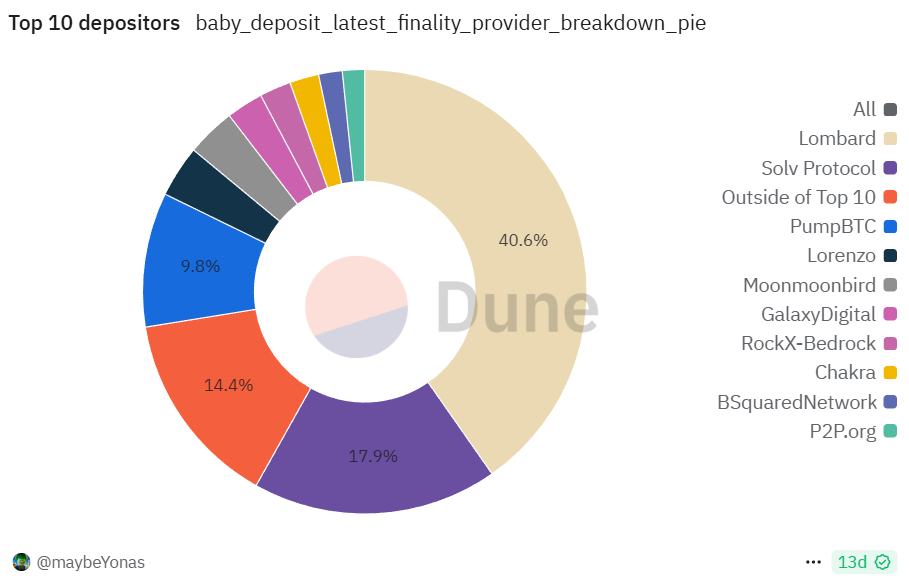
Participation: Cap-2 successfully drew major institutions and custodians. Within 10 blocks, ~22,891 BTC was staked—over 22 times Cap-1’s volume—pushing Babylon’s total staked value into the billions and establishing it as the “world’s largest BTC staking platform.” Despite the surge in BTC volume, the number of participating addresses was 12,590—similar to Cap-1—indicating dominance by large stakers. Statistics show around 1,000 addresses collectively staked over 23,000 BTC, with Lombard Finance receiving ~22,503 BTC (~98%) during the window, effectively dominating Cap-2.
Ecosystem Growth & Partnerships: Cap-2 marked the formal entry of institutions and custodians into Babylon. Top-tier compliant custodians Anchorage Digital and Hex Trust announced support for client participation, simplifying yield generation for large holders. On the exchange front, Binance enabled one-click staking via its Web3 Wallet and launched promotional campaigns; OKX Earn partnered with Solv and others to offer Babylon staking. While Lombard led, Solv remained active, and platforms like Bedrock, Lorenzo, and PumpBTC ran pre-staking campaigns to gather user funds ahead of Cap-2.
3. Cap-3: Open Window and Incentive Surge
Timeline & Rules: The final Phase-1 stage, Cap-3, began December 10, 2024, at 11:00 UTC and lasted until December 17—covering roughly 1,000 Bitcoin blocks (~one week). Cap-3 removed quantity limits entirely and used a time-based window to accept all staking transactions. The per-transaction limit increased further to 5,000 BTC (from 500 BTC in Cap-2), with a minimum still at 0.005 BTC. To boost short-term participation, Babylon introduced tiered point rewards: 100,000 points per block for the first 300 blocks, then 21,000 points per block for the remaining 700. The initial rate was about 10x higher than Cap-2.
Participation: With relaxed rules and generous rewards, Cap-3 attracted a broader base. Over seven days, 109,980 addresses participated, staking 33,399 BTC—the highest per-phase total yet. Participant count surged far beyond previous phases combined, showing widespread adoption among small and mid-sized BTC holders. Cap-3 demonstrated growing awareness of turning “idle” BTC into productive assets. Without hard caps and with a longer duration, Bitcoin fees did not spike again, allowing smooth transaction processing.
Ecosystem Synergy & Campaigns: Multiple partners launched joint incentive programs during Cap-3. Corn Network, as a BSN candidate, offered extra “Kernels” points to BTC stakers. Babylon hosted community events like the “BTC Staking Marathon” with wallets and node providers, awarding badges and raffle entries to users who staked continuously or above certain thresholds. These efforts amplified social media visibility and boosted Babylon’s profile. Overall, Phase-1 successfully onboarded 57,290.61 BTC (~0.27% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply) from 135,290 addresses. Babylon called Phase-1 a “supply-side launch”—with massive BTC now “in reserve,” Phase-2 will shift focus to demand: launching Babylon’s own PoS chain and connecting more BSNs so this BTC can begin securing networks and generating real yields.
III. Babylon Ecosystem Landscape
During its rapid growth, Babylon has built a multi-layered partner network spanning infrastructure, protocol collaborations, wallet, and exchange support. This robust ecosystem fuels Babylon’s momentum and creates strong synergies.

1. LST Protocols
Liquid Staking Token (LST) protocols address post-staking liquidity issues by issuing tradable tokens representing staked BTC. Currently, 12 major LST protocols use Babylon as their underlying staking channel, including Lombard, Bedrock, PumpBTC, Lorenzo, Solv, pSTAKE, Chakra, and emerging projects like Allo and Stakestone. Babylon provides them with security and yield sources, while they drive user traffic and increase staking stickiness. For example, users staking via LSD protocols can earn dual rewards: Babylon Points plus proprietary tokens or points from the protocol. Furthermore, LSTs like LBTC and uniBTC can be used in lending, liquidity provision, and other DeFi applications, enhancing BTC capital efficiency.
2. Bitcoin Secured Networks (BSN)
BSNs refer to blockchain networks integrating Babylon’s BTC staking security. So far, 25 projects/networks have announced plans to join as BSN candidates once Babylon Phase-2 launches. Notable examples include:
-
BOB (Build on Bitcoin): A hybrid Layer2 combining Bitcoin and Ethereum features to create a Bitcoin-native DeFi platform. BOB integrates with Babylon to gain Bitcoin-level finality security, boosting trust and credibility. It brands itself as a “Bitcoin-secured hybrid chain” and plans to use Babylon for bridging BTC, ETH, and other cross-chain assets.
-
Corn: An innovative network deployed on Arbitrum, becoming the world’s first BSN by stacking dual security layers from both Bitcoin and Ethereum on an Ethereum L2. To incentivize BTC stakers, Corn launched its “Kernels” points program, distributing Corn ecosystem points based on users’ staked BTC amounts over time.
-
B² Network: A modular Bitcoin Layer2 project embedding Babylon’s BTC staking into its Hub consensus. Leveraging Bitcoin data availability sampling (DAS) and ZKRollup technology, B² aims to build a “BTC-secured execution layer.” Babylon staking provides economic backing for B² Rollup validation, while B² supports DeFi operations with BTC-staking derivatives on its rollup.
Through its BSN initiative, Babylon extends its reach across diverse blockchain sectors—including Layer1s, Layer2 rollups, oracle networks, and data availability layers—making “BTC-as-a-Service” a reality. Babylon contributes its pool of nearly 60,000 BTC in “security capacity” to various networks, while those networks bring in more apps and transactions, increasing activity and value capture on Bitcoin. This positive feedback loop holds immense potential and positions Babylon uniquely in the cross-chain landscape.
3. Wallet and Exchange Support
To lower participation barriers, Babylon actively collaborates with leading crypto wallets and exchanges. Binance developed a native BTC staking interface within its Web3 Wallet and launched a “Stake BTC to Earn Points” campaign in its Earn section, enabling users unfamiliar with self-custody to easily participate. OKX similarly integrated Babylon via OKX Earn and co-marketed with partners like Solv and PumpBTC. Additionally, 12 Web3 wallets announced support for Babylon Phase-1, including multi-chain and Bitcoin-native wallets. Decentralized wallets like ZenGo and Blocto published staking guides; native Bitcoin wallet Xverse joined discussions within the Ordinals community about connecting to Babylon. Endorsements from wallets and exchanges enhance user trust in Babylon, acting as a form of institutional validation.
4. Infrastructure and Service Providers
In the Babylon ecosystem, node operators and custodians play vital roles. Professional validators such as Blockdaemon, InfStones, stakefish, and Figment have joined Babylon’s Finality Provider network, offering staking-as-a-service. Custodians like Cobo and Coincover collaborate with LSD protocols (e.g., PumpBTC) to execute staking transactions on behalf of users while ensuring BTC private key security. Compliant giant Anchorage Digital offers U.S. institutions a direct Babylon staking channel, enabling “institutional-grade one-click staking”; Asian custodian Hex Trust is also involved. These infrastructure partners make it possible for large capital to securely enter Babylon and contribute to a more decentralized and reliable network.
Through this multi-faceted expansion, Babylon has cultivated a thriving ecosystem where mutual reinforcement occurs—growing staking volume attracts more partners, and partner growth further boosts staking scale.
IV. Spotlight on Key Projects in the Babylon Ecosystem
The Babylon ecosystem has already seen the emergence of several protocols and applications centered around BTC staking. Each occupies a unique niche, collectively enriching the Bitcoin DeFi landscape.
Source: https://dune.com/pyor_xyz/babylon-chain
1. Lombard Finance (LBTC)
Lombard is a Babylon-native protocol focused on liquid BTC staking, aiming to connect BTC stakers with demand from PoS chains and DeFi protocols. Users deposit BTC into Lombard, which proxies the staking on Babylon to earn yield. Simultaneously, users mint LBTC tokens 1:1 on Ethereum. LBTC is an ERC-20 token issued by Lombard, representing the principal of staked BTC. Holders accumulate Babylon Points and can deploy LBTC in DeFi to unlock liquidity. Lombard runs Lux and Luminary reward programs, granting early participants governance/reward tokens (Lux), which are not yet publicly released and may govern the protocol post-mainnet launch.
2. Bedrock (uniBTC)
Bedrock is a multi-asset liquid staking protocol incubated by veteran node provider RockX, supporting staking for ETH, BTC, IoTeX, and more. In May 2024, Bedrock raised funding from OKX Ventures and others, focusing on institutional-grade liquid staking. Its BTC staking token is named uniBTC. A key feature is WBTC support: users can stake WBTC directly on Ethereum, and Bedrock uses partner custodians to stake equivalent real BTC on the Bitcoin mainnet via Babylon. This allows WBTC holders to participate in Babylon staking without interacting with Bitcoin’s chain. Bedrock offers two modes: “proxy staking,” where WBTC stays on Ethereum while Bedrock handles BTC staking in the backend; and “one-click swap,” where Bedrock converts WBTC to BTC and stakes it. Rewards are distributed as uniBTC, Bedrock’s Ethereum-issued BTC staking receipt, usable in DeFi. Bedrock also supports BTCB on BSC and FBTC on Filecoin, extending Babylon-powered staking to BTC derivatives across chains.
3. PumpBTC (pumpBTC)
PumpBTC, launched in 2024, is a Bitcoin restaking protocol with the slogan “maximizing returns for BTC holders,” built around its pumpBTC token. It adopts a cross-chain aggregation model: users stake WBTC, BTCB, FBTC, or other BTC-backed assets to receive 1:1 pegged pumpBTC tokens. Then, through third-party custodians (e.g., Cobo, Coincover), PumpBTC delegates equivalent real BTC to Babylon on the mainnet. Yield generated by Babylon is converted back into pumpBTC, making it a yield-accumulating LST. PumpBTC also features a points reward and team referral system: staking any amount of pumpBTC earns pump points, redeemable for PUMP token airdrops.
4. Lorenzo Protocol (stBTC)
Lorenzo is a yield-generating financial layer built on Babylon, creating enhanced earning opportunities through innovative principal-yield separation. Backed by Binance Labs in October 2022, Lorenzo uses a dual-token model: when users stake BTC or BTCB, they receive stBTC (Stake BTC) as a principal-representing token and YAT (Yield Accumulation Token) that accumulates yield over time. Babylon’s staking points and future earnings are reflected in YAT, while stBTC maintains a 1:1 peg with staked BTC. This separation enables flexible strategies—users can trade YAT to lock in future yield or lend out stBTC for liquidity. Lorenzo operates via a staking agent model, with official agents currently managing all staking: they proxy user BTC to Babylon, monitor on-chain proofs, and mint corresponding stBTC and YAT.
5. Solv Protocol (SolvBTC.BBN)
Solv is a well-known decentralized financial asset issuance and management protocol. In July 2024, Solv partnered with Babylon to launch solvBTC.BBN, enabling BTC holders on Ethereum, BSC, Arbitrum, and other networks to join Babylon staking and earn points. Users lock BTC (or BTC equivalents on various chains) on Solv, which ensures these BTC are staked via custodians (e.g., Binance’s Ceffu). Users then receive SolvBTC.BBN tokens for use within Solv’s ecosystem. Solv plans to expand SolvBTC into a multi-chain BTC reserve, linking to more PoS staking scenarios beyond Babylon alone.
6. Chakra (Prana)
Chakra is a Bitcoin restaking protocol combining zero-knowledge proofs and modular architecture, aiming to build a BTC settlement network for institutions. Funded in April 2024 by StarkWare (a leading Ethereum ZK team), ABCDE Capital, and others, Chakra launched a BTC pre-staking pool allowing users to deposit BTC before Babylon’s mainnet launch. These BTC are held in a multi-sig vault jointly managed by Chakra and custodians (e.g., Cobo). Once Babylon opens staking, Chakra will stake these BTC on users’ behalf. Participants earn Prana tokens (currently in points form) and are expected to share in Babylon staking yields. Chakra emphasizes ZK proofs for transparent, privacy-preserving staking processes. It also pursues modular blockchain design, planning a standalone Chakra settlement network secured by Babylon’s consensus, with Chakra handling transaction execution.
V. Challenges and Future Outlook for Babylon
Despite Babylon’s remarkable achievements in 2024, long-term success hinges on overcoming several challenges. At the same time, market dynamics and technological trends present valuable opportunities. This section analyzes Babylon’s core challenges and future prospects.
1. Core Challenges
-
Technical Complexity and Security: Babylon combines advanced technologies—Bitcoin scripting, Cosmos chains, cross-chain verification—with extremely high security demands. Bitcoin’s constraints (1MB blocks, limited script programmability) require highly optimized staking transactions to avoid network congestion or backlash from parts of the Bitcoin community. Babylon must continuously prove it doesn’t harm the mainnet and ideally demonstrates benefits such as increased miner fees or improved UTXO utilization. Moreover, the security of the Babylon chain itself is critical: as the finality hub, any attack or malicious behavior on the Babylon chain could compromise all connected BSNs.
-
Economic Model and Sustainable Incentives: During Phase-1, users earned only Points—not tangible rewards. While acceptable short-term, lack of real yield may erode engagement over time. Babylon must deliver a clear economic model in Phase-2 and beyond. Will Babylon issue a native token and airdrop it to Points holders? Can stakers earn native rewards from PoS chains (e.g., BSN tokens or Babylon block rewards)? Without sustained incentives, large BTC holders may hesitate to commit long-term. Additionally, when enabling one BTC to stake across multiple chains, designing fair reward and risk allocation becomes complex.
-
Competition and Alternatives: Though Babylon currently dominates BTC staking with few direct rivals, alternative solutions may emerge. For instance, Stacks and Drivechain advocates might propose different models for BTC-layer yield generation. Ethereum’s EigenLayer could extend to support WBTC staking, diverting BTCFi demand. CeFi institutions also offer BTC lending products with yield. If simpler “passive BTC yield” options arise, Babylon risks user attrition.
-
User Education and Experience: Bitcoin users are traditionally accustomed to “HODLing,” so shifting mindsets toward active staking requires education and seamless UX. Although Babylon partners with many wallets, staking still involves complexities like UTXO selection and fee setting, which deter average users. For small holders, high Bitcoin on-chain fees remain a barrier. Improving UX—through intuitive interfaces, clearer yield projections, and lower entry thresholds—is essential.
2. Development Outlook
-
Babylon Chain Launch: The centerpiece of Phase-2 is the launch of Babylon’s independent Proof-of-Stake blockchain—Babylon Genesis. According to official plans, Babylon Chain will be the first blockchain secured economically by locked BTC. It will also be the inaugural Bitcoin Secured Network (BSN), built on the Cosmos SDK. The launch means the nearly 57,000 BTC staked in Phase-1 finally find utility. Babylon Chain will serve as the backbone of the entire ecosystem: consolidating BTC staking security, delivering finality services to connected chains, and managing relationships and reward distribution between stakers and Finality Providers.
-
Babylon Token Launch and Utility: Babylon is expected to launch a native token for governance and gas payments, likely distributed via airdrops to Phase-1 Points holders, BSN partners, and contributors. If issued, the token will empower holders to vote on protocol upgrades and parameter adjustments and may capture value—for example, through service fees charged to BSNs, redistributed to token stakers. As an independent network, Babylon will need a gas fee mechanism. Since BTC cannot be used directly as gas, Babylon may adopt its own token or stablecoins for payment. The chain’s economic model will clarify incentives among stakers, validators (Finality Providers), and BSN users.
-
Multi-Chain Staking and Full Interoperability: After stabilizing the Babylon Chain, the next goal is enabling one BTC to stake across multiple chains. Users could allocate portions of their staked BTC to several BSNs simultaneously, with weights or shares assigned per network. For example, a user locking 1 BTC could choose up to N BSNs, each receiving a percentage of voting power. That single BTC would then count toward staking on each chain, earning respective rewards. This shared staking model transforms BTC into a universal “staking credential,” allowing PoS chains to tap into its security value via Babylon.
Conclusion
Babylon Protocol has successfully solved the longstanding challenge of enabling native Bitcoin staking through groundbreaking mechanisms, opening a new paradigm for BTC to secure PoS chains. Babylon tackles the fundamental question of how 21 million BTC can integrate into the broader blockchain economy. As HashKey Research noted, Babylon ushers in a new era of capital efficiency for Bitcoin. If its vision is fully realized, Bitcoin will evolve beyond “digital gold” to become “digital energy”—continuously powering security across blockchains while generating yield in return. This virtuous cycle will reinforce Bitcoin’s central role in the crypto world, establishing BTCFi as a major force in the DeFi landscape.
In 2025, we may witness a paradigm shift—from static BTC holding to dynamic staking—and see a wave of new BTC-based protocols flourish on the Babylon chain. Just as the Babylon team envisions a “BTC Renaissance,” a prosperous era for Bitcoin DeFi is on the horizon.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, the core investment research hub of the Hotcoin ecosystem, is dedicated to providing professional, in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto investors. We have built a “trinity” service framework combining trend analysis, value discovery, and real-time tracking. Through deep dives into industry trends, multidimensional project evaluations, and round-the-clock market monitoring—complemented by our weekly *Top Coin Selection* strategy livestreams and daily *Blockchain Headlines* briefings—we deliver precise market interpretations and actionable strategies for investors at all levels. Leveraging cutting-edge data analytics models and an extensive industry network, we consistently empower novice investors to build knowledge frameworks and help institutional clients capture alpha, jointly seizing value growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and investing inherently carries risk. We strongly advise investors to fully understand these risks and operate within a strict risk management framework to ensure capital safety.
Website: https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
Mail: labs@hotcoin.com
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















