Derivatives protocol focusing on cross-chain staking
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Derivatives protocol focusing on cross-chain staking
This article will guide readers through staking-focused derivative projects and explore how they are shaping the vision of a staking economy in a multi-chain future.
Author: Kyle Liu, Investment Manager at Bing Ventures
With the successful Ethereum Merge, Ethereum has officially transitioned from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). In PoS networks, staking remains a central topic. Users can earn staking rewards by locking tokens to secure the network, but these staked assets become illiquid during the lock-up period. Staking derivatives solve this issue by unlocking liquidity from staked assets, thereby improving capital efficiency. This article explores staking-focused derivative projects and their vision for building a staking economy in a multi-chain future.
The Foundation of Cross-Chain Liquidity
Cross-chain liquidity is a major focus in today’s crypto market, involving conflicts between DeFi yields and staking rewards under PoS consensus, cross-chain transaction costs, and the balance between security and liquidity in PoS systems. To address these issues, staking derivatives have emerged as a key innovation.
Staking derivatives essentially issue tradable tokens representing staked native assets. Holders of these derivative tokens receive ongoing staking rewards. After the staking period ends, these tokens can be redeemed 1:1 for the original native tokens. This design resolves the conflict between DeFi and staking yields by transforming staked assets into liquid instruments that users can trade or deploy in DeFi protocols—enabling both yield generation and liquidity.
Moreover, staking derivatives help reduce cross-chain transaction costs. Traditional cross-chain transfers involve high fees and long confirmation times, degrading user experience. By converting staked tokens into unified cross-chain derivative assets, users can seamlessly trade across blockchains without paying heavy bridging fees or enduring delays.
Additionally, staking derivatives reconcile the tension between network security and token liquidity under PoS. While locking up tokens enhances network security, it reduces liquidity and limits usability. Derivatives allow users to stake tokens for yield while maintaining the ability to use equivalent liquid tokens in DeFi, achieving an optimal balance between security and liquidity.
Value Capture of Derivatives
When discussing staking derivatives, we believe this sector will become essential infrastructure, capturing value from both base-layer blockchains and higher-level applications. As PoS networks mature, the value of staking protocols continues to grow. Lido on Ethereum 2.0 exemplifies this success—following the Merge, Lido's market valuation reached new highs.
For users, staking derivatives unlock novel DeFi strategies. One example is arbitrage opportunities: if derivative tokens trade at a discount, long-term holders can profit by purchasing them and later redeeming at par value. This creates a low-risk, high-reward arbitrage window. Users who understand derivative mechanics can thus generate superior returns within the ecosystem.
From a broader DeFi ecosystem perspective, staking derivatives enhance yield competitiveness. If Layer 1 ecosystems adopt staking derivatives broadly, the combined yield from base staking rewards and DeFi activities could surpass standalone DeFi returns—even without project subsidies. For instance, top Ethereum DeFi projects currently offer stable long-term yields above 5%—considered strong performance. However, combining 5% DeFi yield with 15% staking yield results in a compelling 20% annualized return, attracting more users into the ecosystem. Key players in cross-chain staking include:
-
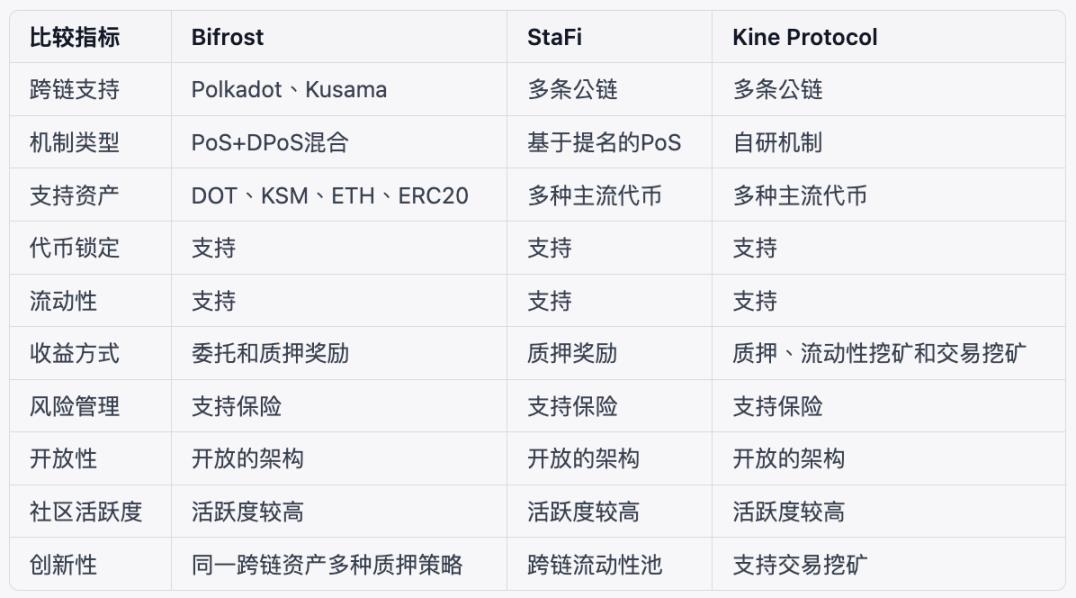
Bifrost is a Web3 infrastructure providing cross-chain liquidity for staking. Leveraging the Cross-Chain Messaging Protocol (XCMP), Bifrost offers decentralized, cross-chain Liquid Staking services across multiple chains. Its mission is to aggregate over 80% of PoS chain staking liquidity through cross-chain derivatives, delivering standardized, interoperable interest-bearing tokens for Polkadot relay chains, parachains, and heterogeneous chains connected via Polkadot bridges. By lowering staking barriers, increasing multi-chain staking ratios, and enhancing application yields, Bifrost aims to build a self-reinforcing StakeFi ecosystem empowering users, chains, and dApps alike.
-
StaFi provides a cross-chain staking solution featuring innovations such as Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS), token locking, and liquidity enhancement. NPoS, derived from DPoS, improves fairness and security by mitigating centralization tendencies. Through StaFi’s token-locking mechanism, users earn staking rewards while receiving rTokens—fungible, tradeable representations of their staked assets. These rTokens enable continuous use in DeFi, enhancing capital efficiency. StaFi supports major public chains and DeFi ecosystems, offering secure, reliable yield solutions with improved liquidity and flexibility through multi-chain integration and asset tokenization.
-
Kine Protocol is a cross-chain derivatives trading platform designed to deliver efficient, low-cost decentralized trading. It supports staking, minting, burning, reward distribution, and liquidity mining, along with cross-chain functionality across multiple blockchains. Key features include Kine Oracle for fast, reliable price feeds and support for derivative products like lending, synthetic assets, and options across arbitrary assets. Kine employs an AMM + Limit Order hybrid trading model, giving traders greater flexibility. The protocol also offers multiple incentive mechanisms—including LP rewards, liquidity mining, and KineDAO rewards—to attract users and deepen liquidity.
The Future of Cross-Chain Staking
From composability and interoperability perspectives, many mainstream blockchains still have significant room for growth in DeFi. Compared to Ethereum, these chains often feature more diverse architectural designs, enabling greater flexibility in cross-chain asset usage. As staking derivatives gain adoption, DeFi activity on these chains will intensify, with projects enhancing competitiveness through increased liquidity and participant engagement—requiring even more liquidity to sustain growth.
Furthermore, in centralized finance (CeFi), product offerings are highly diverse due to universally accepted value standards. Once technical limitations in multi-chain environments are resolved, value consensus across blockchains will increasingly align with decentralization principles. Under this paradigm, how cross-chain assets are used and applied will no longer be dictated solely by project teams or chain developers. Instead, users will enjoy greater freedom, stronger operational control, and enhanced sovereignty when interacting with smart contracts and consensus mechanisms.
Therefore, the future of cross-chain staking is clear: it will enable a truly user- and community-driven, multi-chain “Web3” reality. This future will empower users with greater autonomy and expanded capabilities, further fueling DeFi ecosystem development and contributing significantly to its prosperity. In this landscape, staking derivatives will serve as indispensable middleware, capturing value from both base layers and upper-layer applications, while continuously improving user yields to drive broader participation.
Conclusion
Cross-chain staking derivatives represent a novel PoS network solution aimed at boosting capital efficiency and liquidity while expanding DeFi opportunities for users. However, this innovative tool carries potential risks that require proactive mitigation—from strengthening market liquidity and security measures to ensuring algorithmic fairness and optimizing user experience.
Insufficient market liquidity may lead to high volatility and elevated trading costs. Projects can counter this by enhancing marketing efforts, attracting more users and capital, and building stronger brand reputation. Additionally, robust security practices—such as multi-signature wallets, cold-hot wallet separation, and regular audits—are essential to protect user funds.
Unfair algorithms and poor product design may also harm user engagement and loyalty. Therefore, projects should implement equitable algorithmic frameworks and streamline operations to ensure fast execution, low fees, and intuitive interfaces. As DeFi and PoS blockchains continue evolving, cross-chain staking derivatives are poised for wider adoption. Built on solid security and superior user experience, these solutions could become widely used passive income tools within the DeFi ecosystem.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News