WOOFi Research Report: Analysis of Cross-Chain Decentralized Exchange and Staking Mechanism
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

WOOFi Research Report: Analysis of Cross-Chain Decentralized Exchange and Staking Mechanism
Through WOOFi mining, WOOFi offers Supercharger Earn Vaults, a single-sided yield product that does not incur impermanent loss.
Written by: ASXN
Translated by: TechFlow
WOOFi is a cross-chain decentralized exchange (DEX) that enables users to swap assets, earn yield, and stake across 10 different blockchains. The platform utilizes a novel synthetic proactive market making (sPMM) algorithm for asset pricing, drawing order book data from centralized exchanges and employing a sophisticated hedging mechanism to operate as a market maker. Compared to traditional automated market makers (AMMs), this approach delivers more accurate pricing, higher capital efficiency, minimized impermanent loss, and protection against frontrunning.
Over the past year, WOOFi has pursued an aggressive cross-chain expansion strategy, frequently becoming one of the first non-native DEXs deployed on newly launched EVM-compatible chains.
Through WOOFi Earn, the platform offers Supercharger Earn Vaults—a single-sided yield product that avoids impermanent loss. These vaults function essentially as low-leverage lending products similar to Maple Finance, generating real yield.
WOO token holders benefit from protocol fees through WOOFi staking. Users can stake WOO across multiple chains to earn these fees, with stakers consistently receiving yields around 4%, paid out in USDC.
Over the past month, WOOFi’s average daily trading volume reached $13.63 million, ranking it the 20th largest DEX by volume in the blockchain space. Additionally, the platform averaged approximately 7,000 daily active traders during this period.

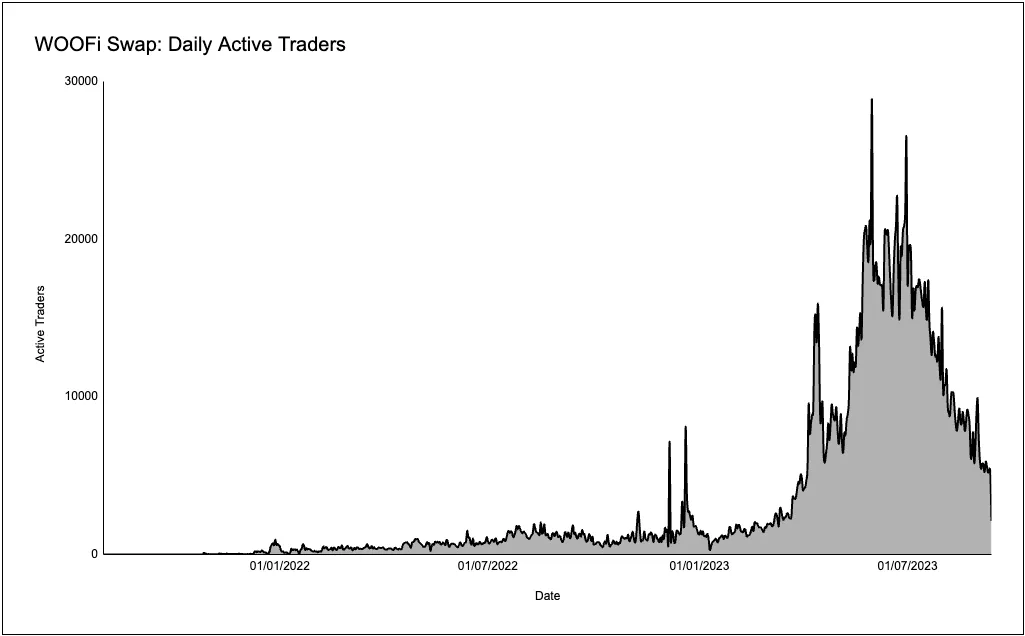
Trading Mechanism
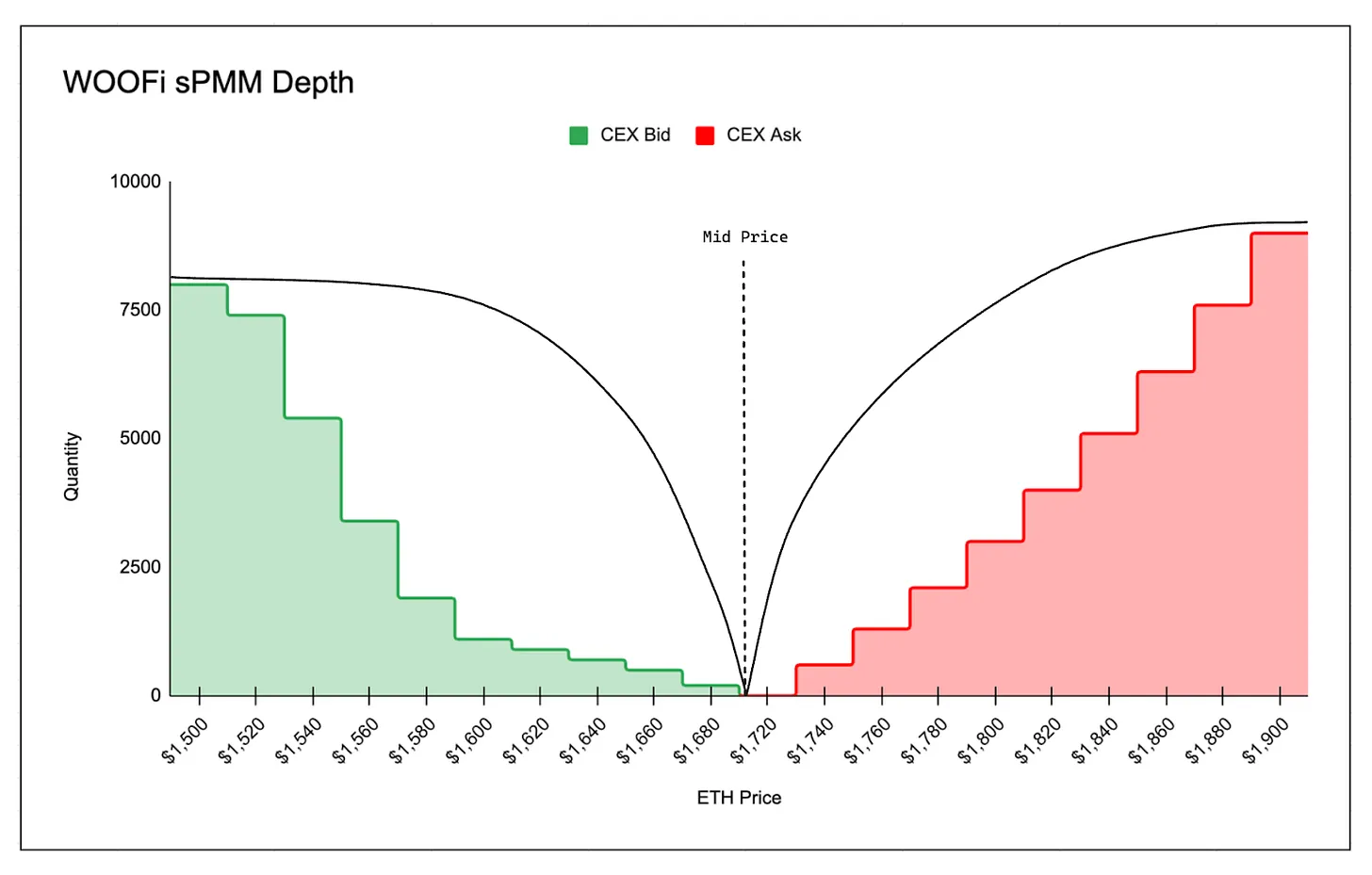
WOOFi Exchange employs the sPMM algorithm, designed to emulate centralized exchange quotes, bid-ask spreads, and market depth.
In contrast, most decentralized exchanges operate as Automated Market Makers (AMMs) using the constant product market maker model. These models rely on the xy = k function to calculate prices between two tokens based on their available reserve balances (x and y). This curve operates under the principle that trades should not alter the product (k) of the pair's reserve balances. According to the constant product formula, the price of token x is calculated as price_x = reserve_token_y / reserve_token_x.
On the other hand, the sPMM algorithm ingests order book data from centralized exchanges, using the mid-price (P₀)—the average of buy and sell prices—the spread (s)—the ratio of the difference between ask/bid prices and the mid-price—and slippage to determine trade execution prices.

The centralized exchanges providing order book data are selected by market makers depending on where they choose to hedge. Data is received via a custom on-chain price oracle. The oracle actively pushes price updates—meaning new prices replace old ones as prices move on centralized exchanges. When users execute swaps, they receive prices based on the latest valid parameters on-chain. On-chain data is updated at the discretion of market makers based on price deviation, typically around 0.1% (i.e., when prices move by 0.1%).
In addition to mid-price and spread data, WOOFi uses a slippage coefficient (k) to simulate the liquidity of the centralized exchange from which order book data is pulled. This ensures on-chain slippage matches that on the centralized exchange’s order book—users executing the same trade on both the centralized exchange and WOOFi will experience similar slippage.
The slippage coefficient ensures on-chain quotes remain competitive enough to attract aggregator traffic while managing risks associated with hedging on-chain volume to maintain market neutrality and profitability.
Price of Asset X:
AMM:
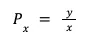
Where: y is the balance of token y in the pool, x is the balance of token x in the pool
WOOFi Swap:
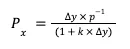
Here’s an overview of how WOOFi Swap works:
Example: A user wants to buy ETH with USDC:
-
User initiates a transaction to buy ETH with USDC.
-
The sPMM algorithm retrieves mid-price and spread data from the order books of centralized exchanges via a custom on-chain price oracle.
-
Based on the spread and liquidity, the amount of ETH the user will receive is estimated to match the centralized exchange.
-
The user receives ETH from the liquidity pool and pays USDC.
-
The sPMM pool manager hedges by taking an offsetting position to maintain market neutrality (e.g., since the market maker sold ETH and received USDC, they buy ETH or use perpetual contracts to increase their ETH exposure).
WOOFi Exchange Overview
Minimized Impermanent Loss
Liquidity providers depositing into traditional AMMs face significant impermanent loss. AMM pools rebalance through arbitrageurs buying undervalued tokens and selling overvalued ones until the AMM price aligns with broader markets. This profit comes at the expense of liquidity providers, who suffer impermanent loss and negative slippage as pool balances are reweighted.
In the sPMM model, user deposits are managed by the sPMM operator. There is no adversarial arbitrage—no arbitrageurs extracting profits from LPs. The sPMM manager hedges positions to stay market-neutral, so even if the swap pool becomes unbalanced, they cover the gap via positions on WOO X.
For example:
-
A user buys 10 ETH with 20,000 USDC on WOOFi Swap.
-
Theoretically, the pool would become unbalanced—with less ETH and more USDC.
-
The sPMM manager offsets this imbalance by purchasing 10 ETH off-chain.
MEV Protection
Since WOOFi Swap does not use an AMM pricing model—prices are not derived from underlying asset pools—it is immune to frontrunning bots. Users are protected from sandwich attacks, and liquidity providers (and users) are shielded from just-in-time (JIT) liquidity attacks.
First, here’s how sandwich attacks work, resulting in poor execution prices for users:
-
User submits a transaction to buy asset X via an AMM.
-
Frontrunning bots detect the pending transaction in the mempool and place trades before and after the user’s transaction.
-
Because asset prices in AMMs derive from the liquidity pool’s reserves, the bot can push up the price of asset X by buying it first.
-
The user ends up buying asset X at an inflated price.
-
The bot then sells asset X at the inflated price.
Just-in-time liquidity attacks are slightly more complex. In most cases, JIT liquidity actually provides better swap rates for users. Here’s how it works:
-
A user submits a large swap transaction on an AMM-based DEX, often using concentrated liquidity AMMs.
-
Frontrunning bots/searchers see this transaction in the mempool, aiming to capture trading fees from liquidity providers in the target pool.
-
Before the swap executes, the bot adds liquidity to the specific pool handling the trade, often concentrating it at the exact price point most relevant to the upcoming swap.
-
The swap executes, and the bot earns fees for providing necessary liquidity.
-
Immediately after, the bot withdraws its liquidity and collected fees.
-
The bot may hedge inventory risk on another exchange; its final profit equals the difference between LP fees earned, hedging costs, and liquidity add/remove gas fees.
-
This usually results in better swap prices for users due to deeper effective liquidity. However, passive LPs lose out because JIT liquidity dilutes their fee share without adequate compensation for the added risk.
-
Recent findings show that when combined with sandwich attacks, JIT liquidity can actually lead to worse execution prices for swappers.
Cross-Chain
Over the past year, WOOFi has aggressively expanded across chains, frequently being among the first non-native DEXs on newly launched EVM-compatible chains like Linea and Base. This is driven by their cross-chain swaps. Using LayerZero’s cross-chain messaging protocol and Stargate’s liquidity, WOOFi enables cross-chain transactions via single-signature transactions.
However, it’s worth noting that WOOFi Swap relies on Stargate for token bridging, which tends to be more expensive than other bridge solutions. To address this, WOOFi has announced future support for LayerZero’s OFT (Omnichain Fungible Token) standard and Chainlink’s CCTP.
Limited Listing Availability
WOOFi cannot support swaps for many tokens because its sPMM model depends on centralized exchanges for pricing. New listings require viable hedging mechanisms, so the platform prioritizes tokens with strong centralized exchange liquidity—especially those with deep perpetual markets. So far, WOOFi natively supports only 11 trading pairs: USDC, USDT, WOO, ETH, BTC, ARB, AVAX, BNB, MATIC, FTM, and OP.
Unfortunately, despite the advantages of the sPMM model—such as reduced impermanent loss and resistance to frontrunning—one major drawback is the inability to quickly list new tokens due to stringent liquidity requirements, particularly for perps.
Additionally, listing availability is limited because adding more assets increases systemic risk—if one asset drops to zero, it affects all others. This is due to WOOFi’s single-pool design. WOOFi is exploring separate pools for long-tail assets to expand listings. WOOFi has already integrated 1inch to mitigate limited listing issues: assets unavailable on WOOFi are routed through 1inch.
For example, if a user trades asset A (unavailable on WOOFi):
-
User swaps asset A on Ethereum for ARB on Arbitrum.
-
1inch executes the swap from asset A to USDC.
-
WOOFi executes the cross-chain swap from USDC to ARB.
Capital Efficiency
Traditional AMMs require substantial liquidity and are relatively capital inefficient because most trades occur within narrow price ranges. WOOFi achieves comparable pricing with less total value locked (TVL) by leveraging order book data and professional market makers instead of underutilized "lazy liquidity."
WOOFi Earn
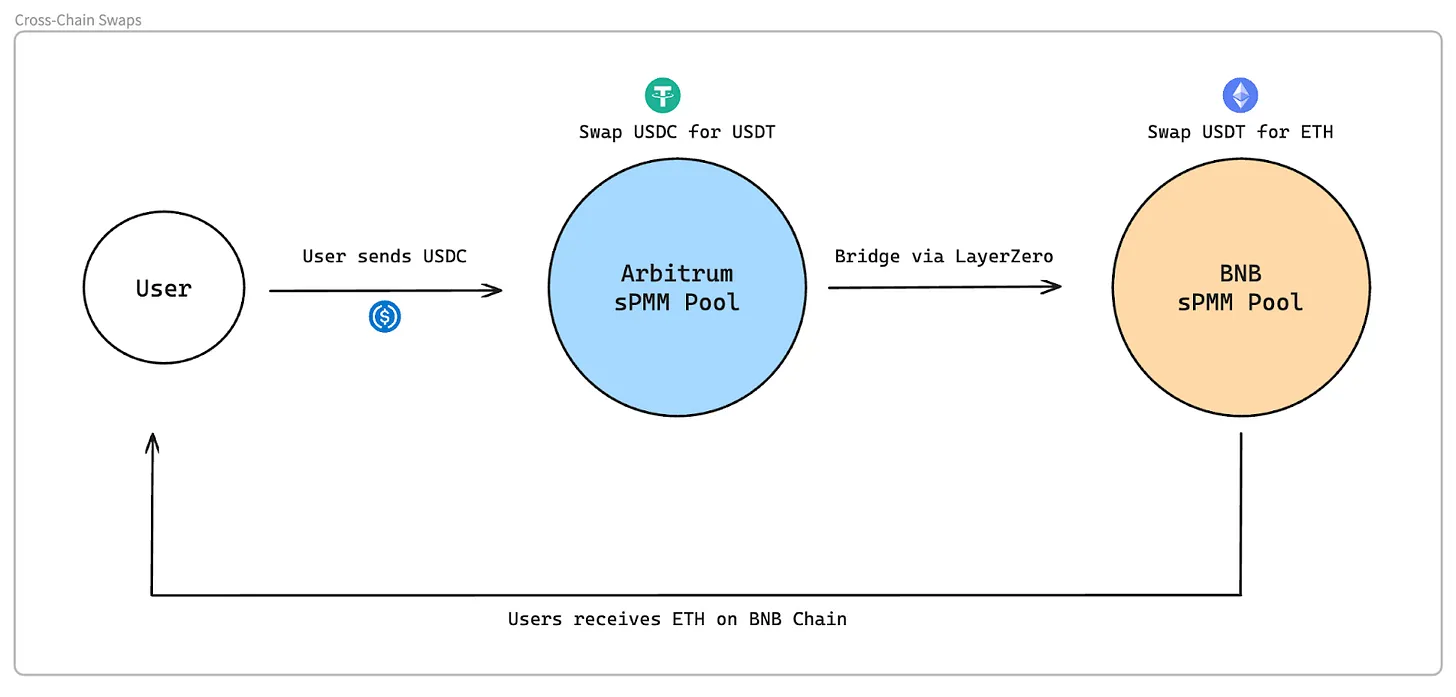
WOOFi offers Supercharger Earn Vaults through its WOOFi Earn interface—a single-sided yield product with no impermanent loss. Supercharger Earn Vaults allow users to lend tokens to the sPMM pool manager at a fixed interest rate by depositing assets into an insurance vault. Notably, the sPMM pool manager does not provide collateral for these loans. Essentially, WOOFi has built an uncollateralized lending and asset-backed securities product akin to Maple Finance.
The sPMM pool manager borrows from depositors and allocates funds into the liquidity pool. Users interact solely with the liquidity pool, where settlements occur.
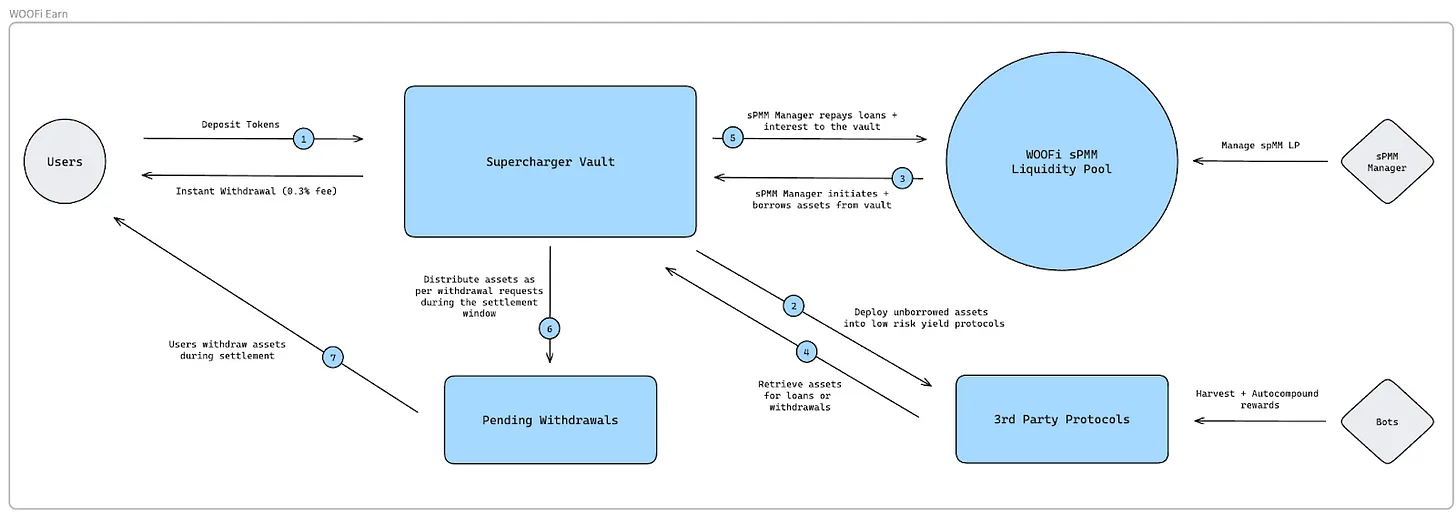
Lending rates are estimated based on overcollateralized borrowing rates for non-stablecoin assets and adjusted using a leverage multiplier derived from lending platforms.
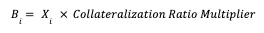
Where: B_i is the lending rate on platform i, X_i is the overcollateralized borrowing rate for non-stablecoins on platform i, and the leverage multiplier comes from the lending platform.
The final lending rate B is calculated using data from multiple lending platforms and applying an exponential moving average to the individual B_i rates.
For example, suppose the ETH lending rate considers only three platforms: Aave, Compound, and Radiant:
Aave: Lending Rate: 3%, Collateral Ratio: 105%
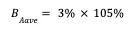
Compound: Lending Rate: 3.2%, Collateral Ratio: 102%

Radiant: Lending Rate: 2.8%, Collateral Ratio: 110%
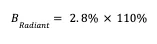
Then the final ETH lending rate is:
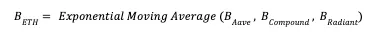
The sPMM pool manager can borrow up to 90% of the vault’s assets. The vault operates on a 7-day cycle, with a 24-hour settlement window at the end where the manager must settle with users. Users can withdraw deposits freely during this 24-hour window. Alternatively, users can withdraw immediately with a 0.3% fee.
Through Supercharger Earn Vaults, users lending assets to sPMM managers earn lending fees but assume counterparty risk. Additionally, Supercharger Earn Vaults minimize impermanent loss.
WOOFi Staking Mechanism
WOOFi Staking 1.0
The WOOFi protocol introduced utility for the WOO token through a real-yield staking mechanism, offering WOO stakers a consistent ~4% APY paid in USDC. Initially, WOOFi launched WOO staking in December 2021 using unique per-chain staking contracts, allocating 80% of each chain’s swap fees to WOO stakers on that chain. WOO stakers had a 7-day redemption period or could redeem instantly with a 5% fee. In this version, users could stake on Polygon, Arbitrum, BNB Chain, and Avalanche.

In the first version of the staking mechanism, the WOO protocol used 80% of WOOFi-generated swap fees to buy back WOO tokens and distribute them to stakers. This was highly successful, with over 100 million tokens staked across multiple chains, and stakers collectively earning 4.6 million WOO tokens.
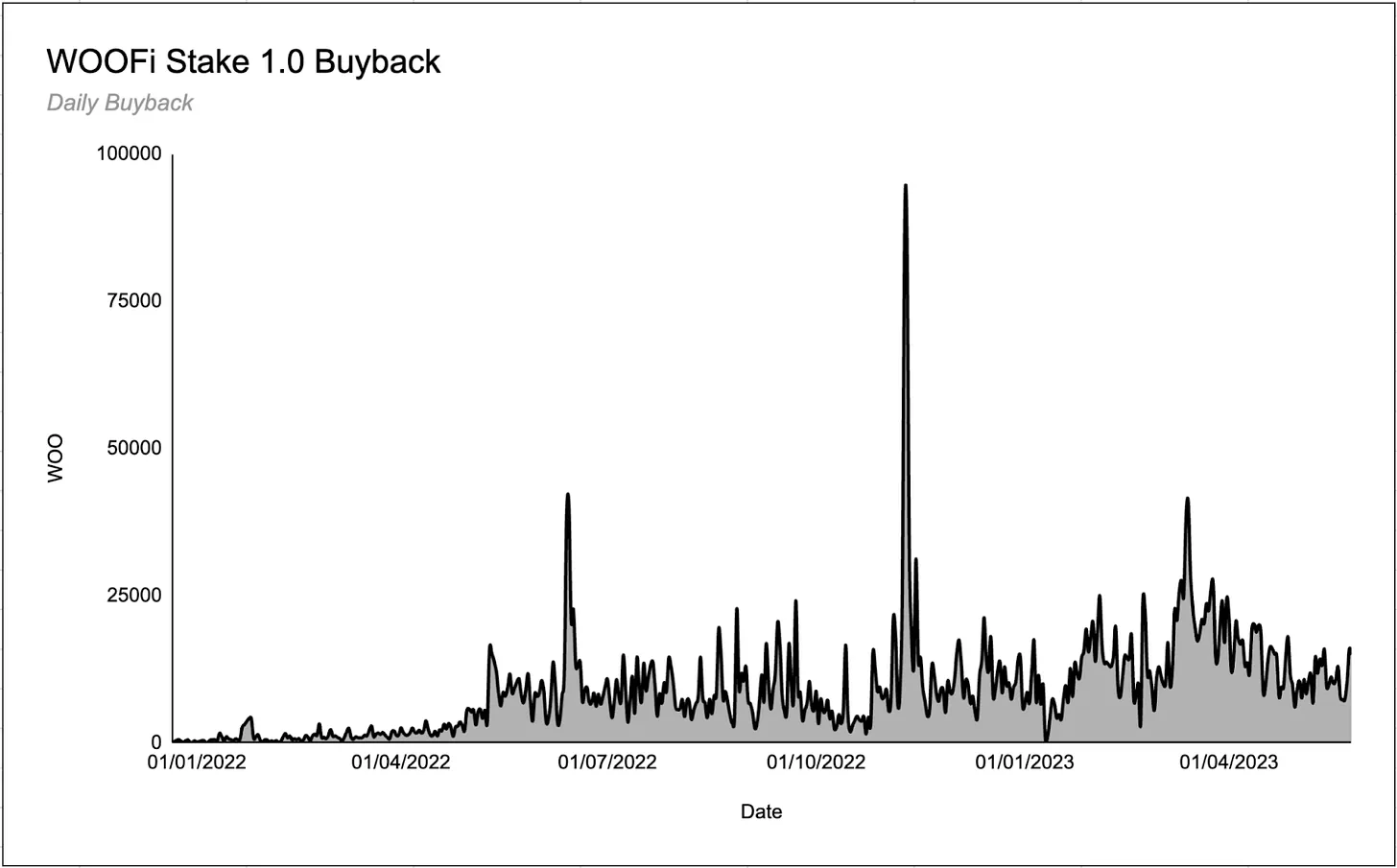
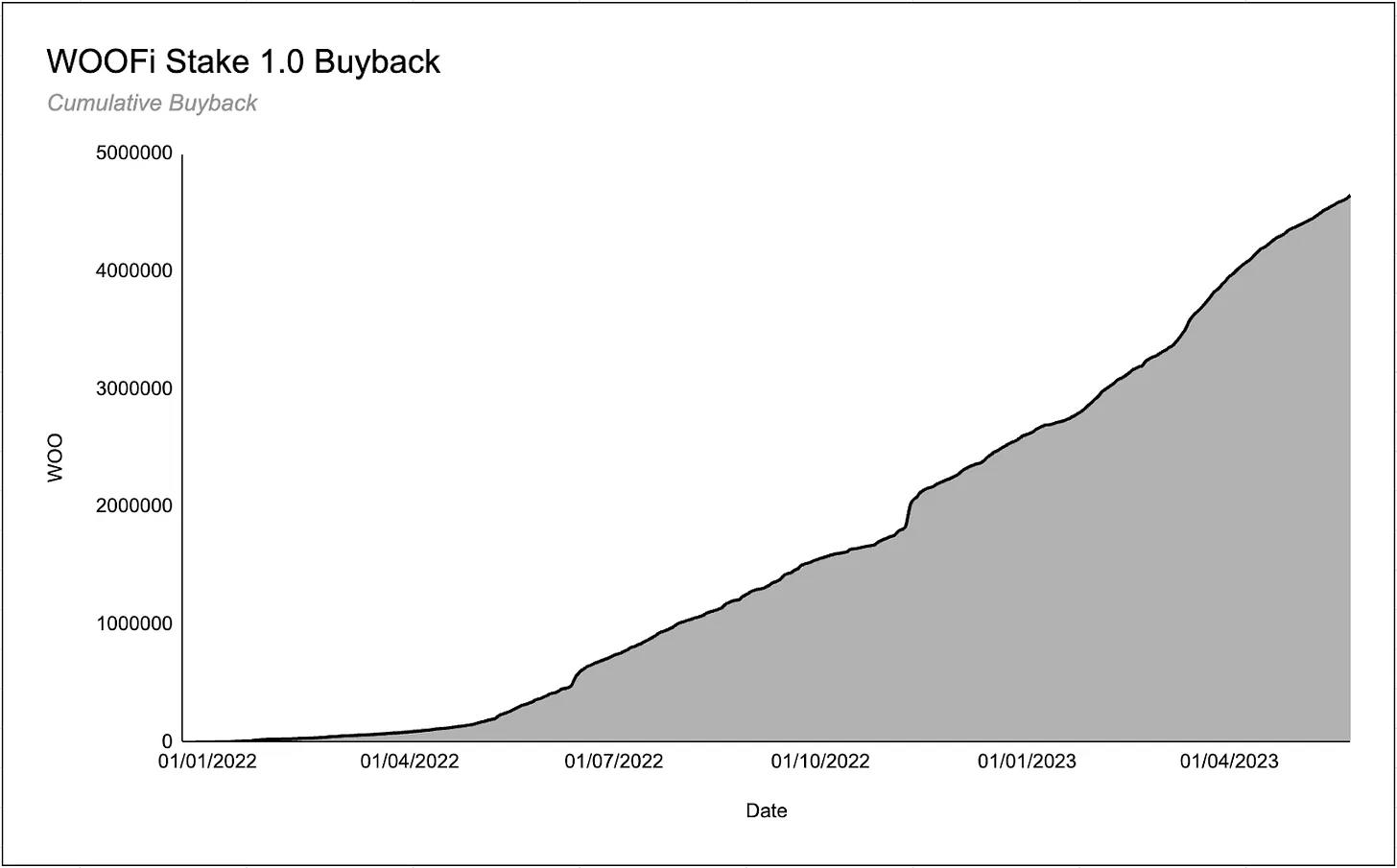
However, WOOFi’s deployment across multiple chains, each with its own staking contract, led to variations in staking APRs across chains. This meant users staking WOO on chains with high swap volume relative to staked WOO amounts earned higher APRs. This design was suboptimal, leading to the creation of WOOFi Staking 2.0.
WOOFi Staking 2.0
After addressing some drawbacks of WOOFi Staking 1.0, WOOFi launched WOOFi Staking 2.0, or cross-chain staking. By integrating with LayerZero’s cross-chain messaging protocol, WOOFi now allows users to stake WOO across multiple supported chains and earn identical rewards regardless of where WOO is staked. Swap fees collected on each chain are denominated in that chain’s quote currency (USDC everywhere except BSC, which uses USDT) and distributed as USDC rather than previously minted WOO tokens.
A new opt-in “Auto-Compound” feature was added to the staking interface. Users must claim their USDC rewards, convert them to WOO, and re-stake them. This is the source of WOO buybacks in Staking 2.0, which have already repurchased over 1 million WOO since launch.
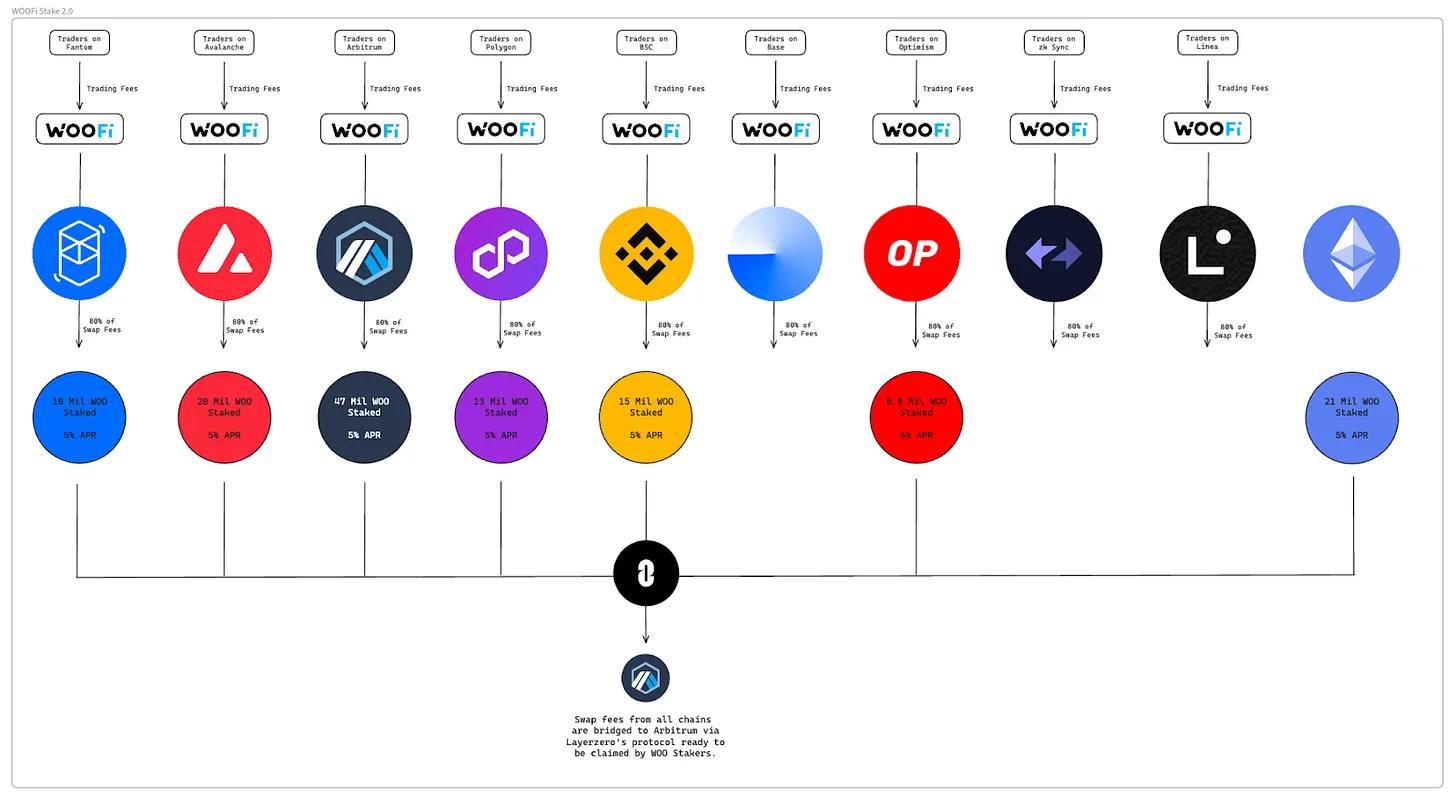
Cross-Chain Mechanism:
-
Users can stake WOO on these chains: Polygon, Arbitrum, BSC, Avalanche, Optimism, and Ethereum.
-
WOOFi collects 80% of swap fees from WOOFi deployments on each chain.
-
Every Thursday, these swap fees are bridged via LayerZero to Arbitrum and then distributed to WOO stakers over the next 7 days.
-
Rewards are calculated based on the user’s total staked WOO balance (and multiplier points) across all chains.
Multiplier Points
In Staking 1.0, WOO stakers had a 7-day redemption period or could redeem instantly with a 5% fee. WOOFi Staking 2.0 removes these redemption restrictions and instead uses a GMX-like Multiplier Point (MP) system to incentivize long-term WOO staking. This MP system rewards long-term stakers without increasing inflation.
The multiplier system works as follows:
-
Users stake their WOO tokens on any supported chain.
-
All WOO stakers earn MP at a base annual rate of 50% (e.g., if you stake 1,000 WOO for a year, you accumulate 500 MP).
-
These MPs can also be staked, and each MP has the same yield potential as one staked WOO token (one staked MP earns the same USDC yield as one staked WOO token).
-
If a user redeems part of their WOO tokens, an equivalent number of MPs are burned, meaning they lose that MP’s earning potential. For example, if a user stakes 1,000 WOO and 1,000 MP, they earn USDC yield equivalent to 2,000 staked WOO. If they then redeem 100 WOO (10% of total staked WOO), 10% of their MPs (100 MPs) are permanently destroyed.
Challenges (MP APR Boost)
As mentioned, the base MP APR is 50%. However, by completing “challenges” or WOOFi protocol-specific tasks, users can boost their MP earning rate up to a maximum of 109.85% APR.
There are three ways to boost MP yield: WOOFi swap volume, Supercharger Vault deposits, and using the Auto-Compound feature. To complete these challenges, WOO stakers must hold at least 1,800 WOO, and there is a tiered system based on the amount of WOO staked. If a user completes all challenges corresponding to their staking tier, they receive a 1.3x MP yield boost in each of the three categories. To earn these boosted MP rewards, their MPs must be staked.
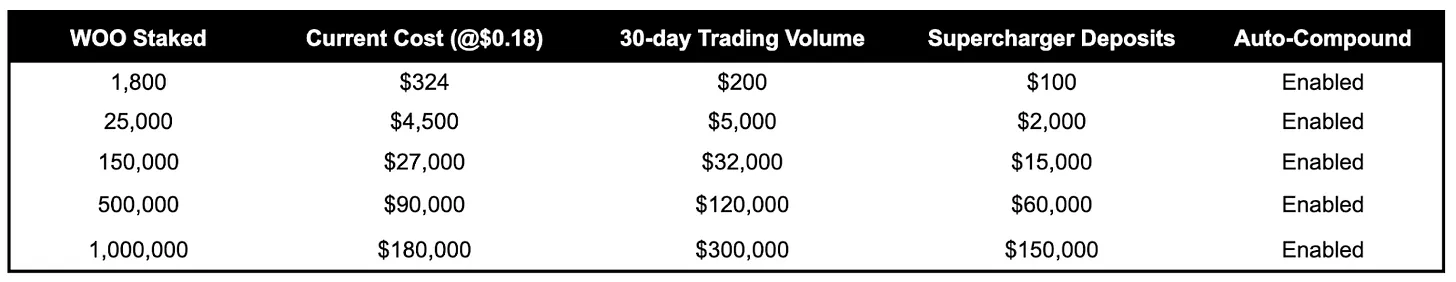
Example: A user staking 2,000 WOO falls into the lowest effective tier. To get a 1.3x MP yield boost from trading volume, the user must accumulate at least $200 in trading volume (including cross-chain swaps) over a 30-day observation period. Similarly, they must deposit at least $100 into the Supercharger Vault for 30 days. To get the final 1.3x boost, the WOO staker must enable the Auto-Compound feature.
WOOFi NFT Yield Enhancement
In the future, WOOFi will introduce new ways to boost staking rewards via NFTs. Two planned NFT types will enhance WOO staking yields:
-
Consumable NFTs — These NFTs are earned through tasks or challenges and can be staked for temporary yield boosts. The boost magnitude depends on the rarity of the acquired NFT.
-
Avatar NFTs — These NFTs will offer permanent staking yield boosts.
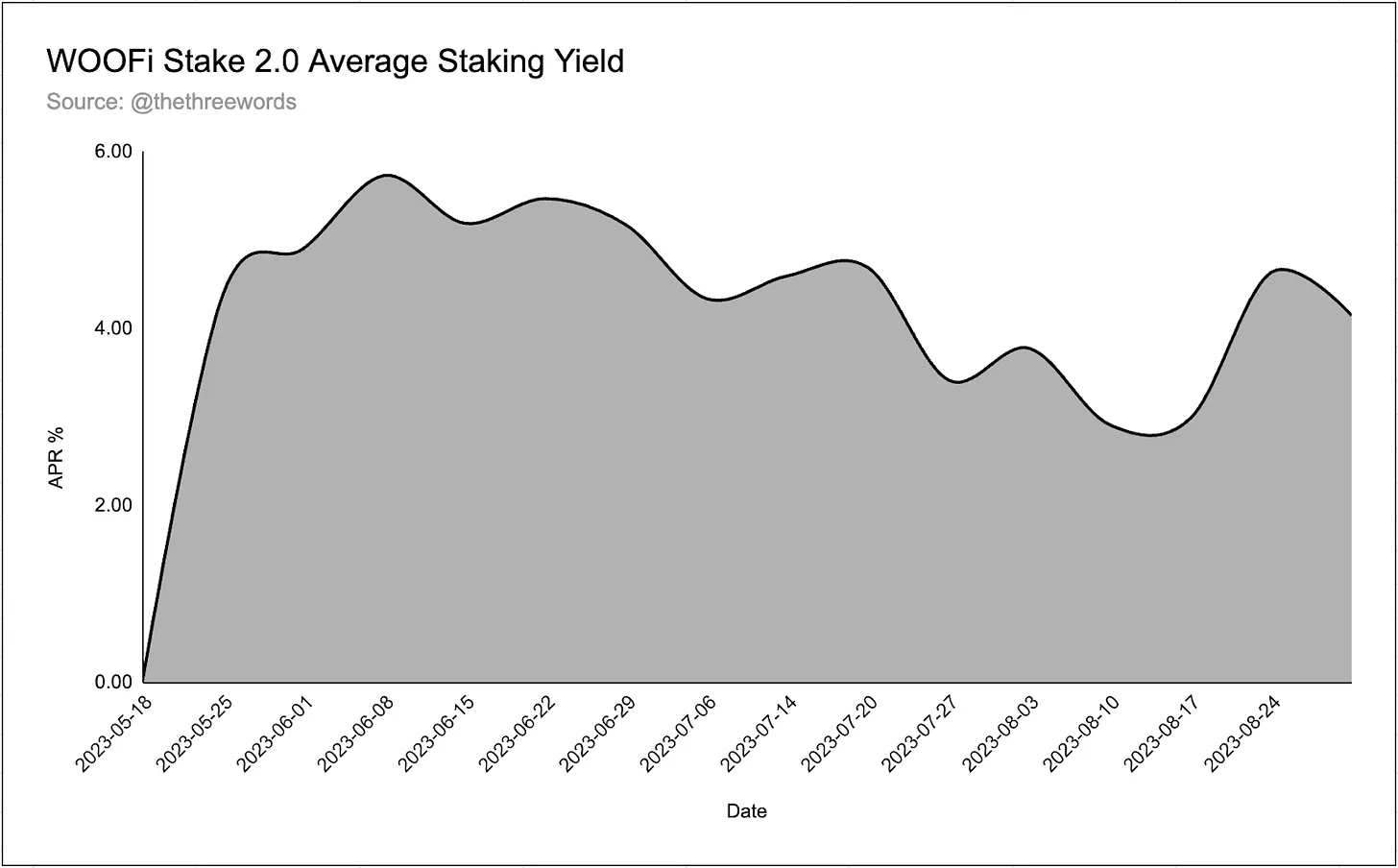
WOOFi Staking 2.0 Metrics
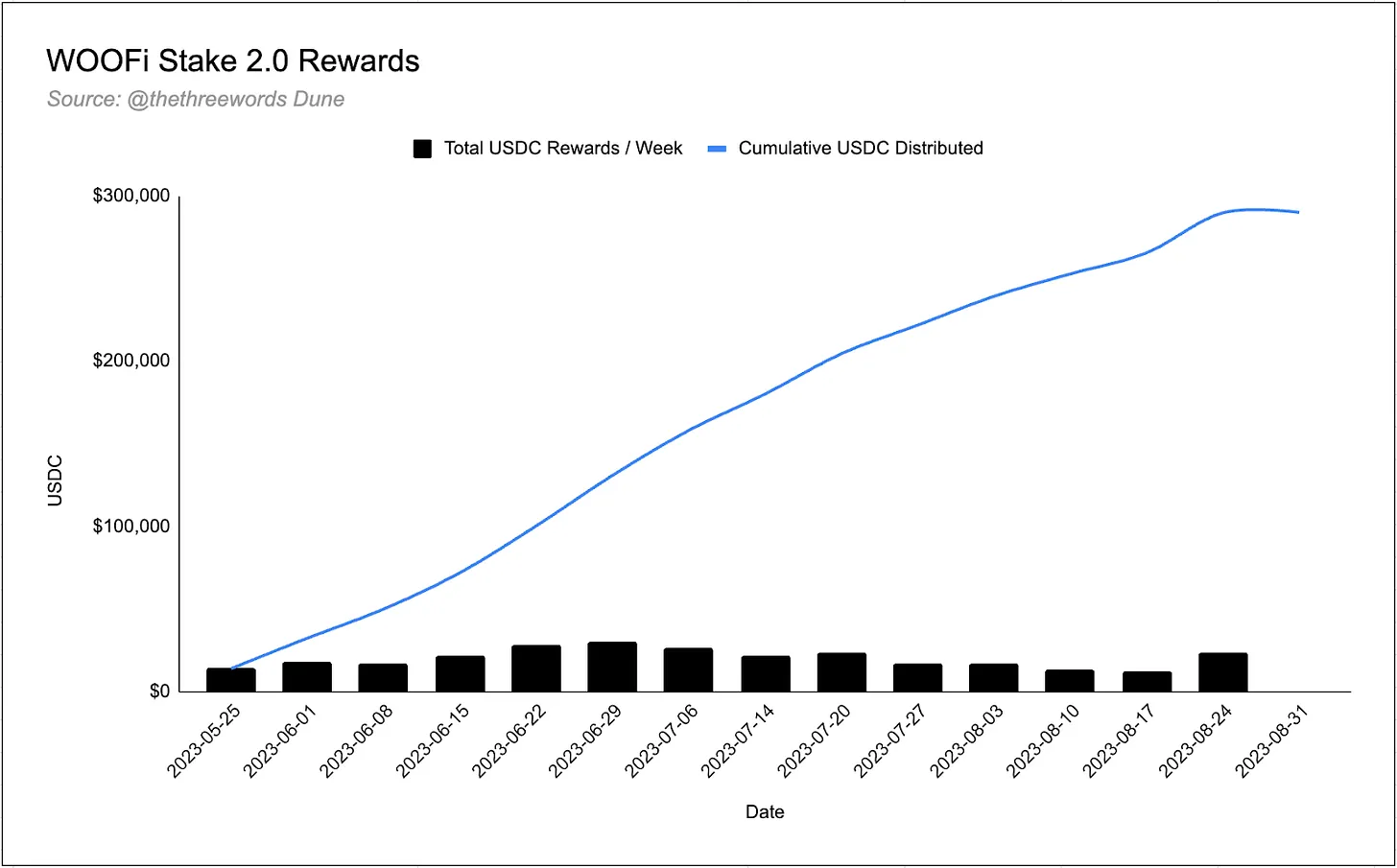
Since migrating from WOOFi Staking 1.0, a total of 132 million WOO have been staked on WOOFi. These WOO tokens have earned over $300,000 in USDC rewards since May 18, averaging a 4.15% APY.
Although users can stake on seven different chains, staking is concentrated on Arbitrum (36.8%), Avalanche (24.5%), and Ethereum (16.3%).


WOOFi Pro
In addition to its standard sPMM implementation on EVM chains, WOOFi is experimenting with a centralized limit order book (CLOB) model. Built on Orderly Network’s “plug-and-play CLOB” exchange protocol, WOOFi Pro outsources the risk engine, matching engine, and asset custody.
WOOFi Pro targets professional traders, enabling advanced order types, a sophisticated trading interface, and self-custody of assets.
WOOFi Pro’s initial deployment was on Near. Trading volumes on these spot and perpetual markets were minimal, with total daily volume in the low six figures, possibly due to Near’s overall low activity.
The team has since shifted focus toward becoming cross-chain, supporting cross-chain deposits from Arbitrum, Optimism, BSC, Ethereum, Base, Linea, and Polygon. Additionally, WOOFi Pro trading fees will be shared with WOOFi stakers after mainnet launch (expected in Q4 2023).
Competitive Landscape
Currently, cross-chain swaps remain relatively underdeveloped, with only a few protocols besides WOOFi Exchange—including Hashflow and SushiXSwap—implementing such solutions.
SushiSwap
SushiXSwap is Sushi’s cross-chain AMM built using LayerZero’s Stargate. Sushiswap originally launched on Ethereum in 2020 as a fork of Uniswap.
SushiXSwap is currently integrated with Optimism, Arbitrum, BSC, Avalanche, and Polygon. Future plans include aggregating more bridges, focusing on building SushiXSwap in a modular and composable manner. SushiXSwap leverages Sushi’s liquidity on each chain for cross-chain swaps.
Hashflow
Hashflow is a decentralized exchange similar to WOOFi Exchange, offering non-AMM cross-chain swaps. Unlike AMMs, Hashflow uses a Request-for-Quote (RFQ) model powered by professional market makers.
An off-chain RFQ engine receives quotes from market makers who manage on-chain liquidity pools. The RFQ model handles settlement and asset swaps on-chain, while market makers price assets off-chain.
Comparison
Sushi uses the AMM model, which applies the xy = k function to determine prices between two tokens based on their respective reserve balances (x and y).
In contrast, WOOFi’s sPMM algorithm and Hashflow use order book data from centralized exchanges to set trade prices. Since both Hashflow and WOOFi do not rely on AMM pricing models, they are resistant to manipulation by frontrunning bots, protecting users from sandwich attacks and shielding liquidity providers and users from JIT liquidity attacks.
Moreover, traditional AMMs are known to pose risks to liquidity providers. Those supplying liquidity to these AMMs often suffer significant impermanent loss.
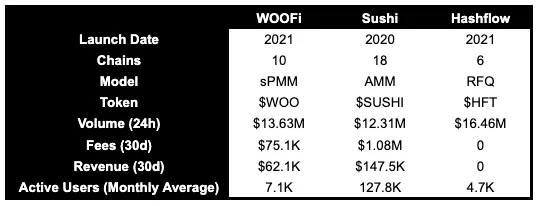
As of September 2023, Sushi spans the most chains with 18, followed by WOOFi on 10 chains, and Hashflow on 6. In terms of 24-hour trading volume, Hashflow leads at ~$16.46 million, followed by WOOFi at $13.63 million, and Sushi at $12.31 million.
However, in terms of fees earned over the past 30 days, Sushi dominates with $10.8 million, while WOOFi generated only $751,000 and Hashflow earned no fees. In revenue, Sushi again leads with $14.75 million, followed by WOOFi at $6.21 million. Examining monthly active users, Sushi holds a significant advantage with 1.278 million users, far exceeding WOOFi’s 71,000 and Hashflow’s 47,000.
Notably, despite having only a fraction of Sushi’s user base, WOOFi’s daily trading volume exceeds Sushi’s. Additionally, WOOFi has a relatively higher revenue-to-fees ratio compared to Sushi, indicating more efficient revenue capture.
History and Partnerships
Overview
WOO Trade and the WOO ecosystem were founded in 2019 by Kronos Research. Kronos actively engages in various trading strategies, including market making, arbitrage, commodity trading advisory services, and high-frequency trading. Having achieved daily trading volumes of $5–10 billion at the time, they gained recognition in the digital asset market.
Initially, the WOO token was named KRON, later renamed to WOO in December 2019. Throughout late 2019 and early 2020, WOO continued product development, successfully launching WOO Trade 2.0. Their success attracted attention from top capital allocators in the space, culminating in a successful $10 million seed round on September 28, 2020, backed by Dragonfly Capital, Distributed Global, QCP Capital’s venture arm, Hashkey, and 3AC.
Throughout 2020, the platform continued setting new volume records while attracting institutional traders and forming strategic partnerships with major players in the industry. On October 29, 2020, the WOO token began trading on Gate.io, followed by listing on Huobi the next day. However, the WOOFi Exchange did not officially launch until 2021, well after the Woo team had proven themselves in the centralized exchange space.
WOOFi Development Roadmap
-
October 27, 2021: Woo Network announced the alpha testnet launch of WOOFi Swap 1.0 on BSC, marking Woo’s official entry into on-chain liquidity and DeFi participation.
-
November 2021: Woo completed its Series A funding, raising over $30 million from Binance Labs.
-
December 15, 2021: The first version of WOOFi staking launched on BSC, allowing users to stake WOO.
-
February 9, 2022: Woo launched WOOFi Earn.
-
March 2, 2022: WOOFi Exchange launched on Avalanche.
-
March 9, 2022: Woo announced a series of WOOFi developments: completion of Verilog audit, integration with Yield Yak aggregator, and simultaneous launch on DeBank.
-
April 14, 2022: WOOFi Exchange launched on Fantom.
-
March 19, 2022: Woo launched WOOFi Broker.
-
July 16, 2022: Woo announced cross-chain swaps between Avalanche, Fantom, and BSC. Two weeks later, Polygon was added.
-
July 20, 2022: Polygon Adventurer NFT launched, showcasing WOOFi’s cross-chain NFT infrastructure capabilities.
-
November 9, 2022: WOOFi Exchange launched on Arbitrum.
-
December 12, 2022: WOOFi Exchange launched on Optimism.
-
January 10, 2023: Woo Network released a revised tokenomics model, including burning 24% of the total supply.
-
February 3, 2023: WOO Ventures airdropped venture tokens to WOO X and WOOFi Exchange stakers.
-
March 9, 2023: WO
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News