BTC Ecosystem Race in the Second Half: Who Is the Optimal Solution for Value承载?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

BTC Ecosystem Race in the Second Half: Who Is the Optimal Solution for Value承载?
The real prosperity of the BTC ecosystem has yet to come.
Author: Evan Lu, Waterdrip Capital
Since the Ordinals protocol sparked widespread attention in 2023, igniting a wave of construction across the BTC ecosystem, the BTC ecosystem has traversed in just one and a half years an evolutionary path that ETH took many years to complete. By the end of Q1 this year, BTC's 1.0 cycle has gradually come to a close. BTC’s price has broken past its traditional summer slump, continuously surpassing $110,000 and then $120,000 per coin, reaching a new all-time high (ATH). However, market performance of tokens related to the BTC ecosystem on exchanges has been underwhelming. Yet, for any technology—from conception to development, deployment, and broad adoption—just one year is clearly insufficient, let alone implementing new technologies on BTC, the largest value storage network.
Observing the various technical paths within the BTC ecosystem reveals we are still in a developmental phase. The true prosperity of the BTC ecosystem has not yet arrived. Therefore, the debate over BTC L2 roadmaps has only just begun.
BTC Ecosystem 1.0 and 2.0
Given BTC is widely recognized as "digital gold," why push forward with developing the BTC ecosystem? This is because BTC's scripting language is extremely minimal, combined with PoW consensus, ensuring exceptionally high security and decentralization—but at the cost of limiting Bitcoin’s scalability and programmability. As the foundational anchor asset of the entire crypto industry, a vast amount of value within BTC remains untapped. Imagine if just 10% of BTC (approximately 2.1 million coins) were used in DeFi—at $100,000 per coin, this would unlock up to $210 billion in liquidity!
In terms of ecosystem composition, the BTC ecosystem can be divided into infrastructure layers (L2) and upper-layer financial protocols (BTCFi). This article will focus primarily on interpreting and comparing BTC infrastructure technical paths.
The defining feature of the BTC ecosystem’s 1.0 era was “TVL first”—transferring BTC to L2 networks via asset bridges or custodial solutions first, then deploying DeFi protocols on L2 to activate BTC liquidity. This mirrors early ETH sidechain strategies, exemplified by Polygon, and is familiar and accessible to users from the ETH ecosystem—the logic being essentially EVM-based L2s, only built atop the BTC network. This approach allows rapid accumulation of capital and user base, but comes with a critical flaw: BTC asset security cannot be guaranteed.
The 2.0 era of the BTC ecosystem returns to fundamental technological innovation: breakthroughs in security, efficiency, and native compatibility. From the mainnet launch of the Lightning Network to active progress in ZK Rollup, RGB, and BitVM, more projects are exploring how native on-chain assets can achieve safer, more efficient, and more natively integrated yield generation and transfer on L2. For developers, this means greater potential for innovation; for VCs, it marks a pivotal shift from “valuation-driven” to “product-market fit (PMF)-driven” growth in the BTC ecosystem.
Comprehensive Comparison of BTC L2 Technical Paths
Based on existing tech stacks, several distinct technical paths can be identified. However, deep exploration into each path and its representative projects reveals overlaps—different paths may adopt similar solutions, and subsets often exist between different technologies and stacks.
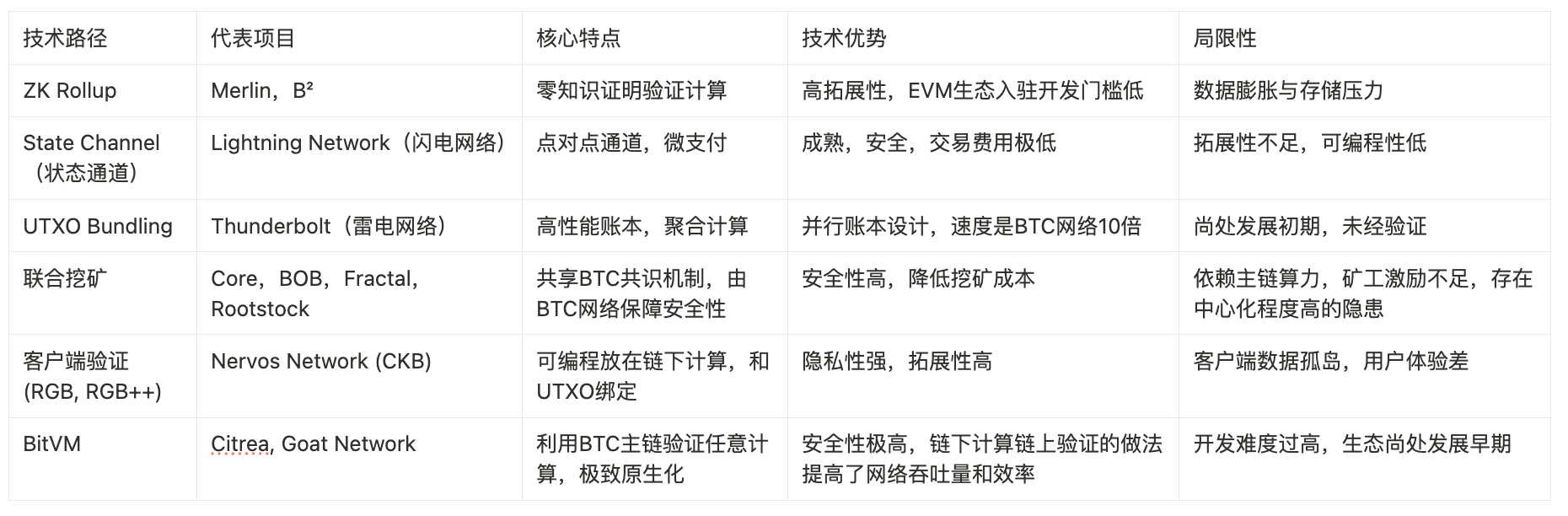
Comparison of different BTC L2 technical paths, data source: https://worried-eagle-e5b.notion.site/BTC-21b34b2a8d7a80cb83c1d0021e3a5696
According to six well-known technical paths, this table visualizes and compares TVL data and adopted technical solutions across 15 BTC L2s:
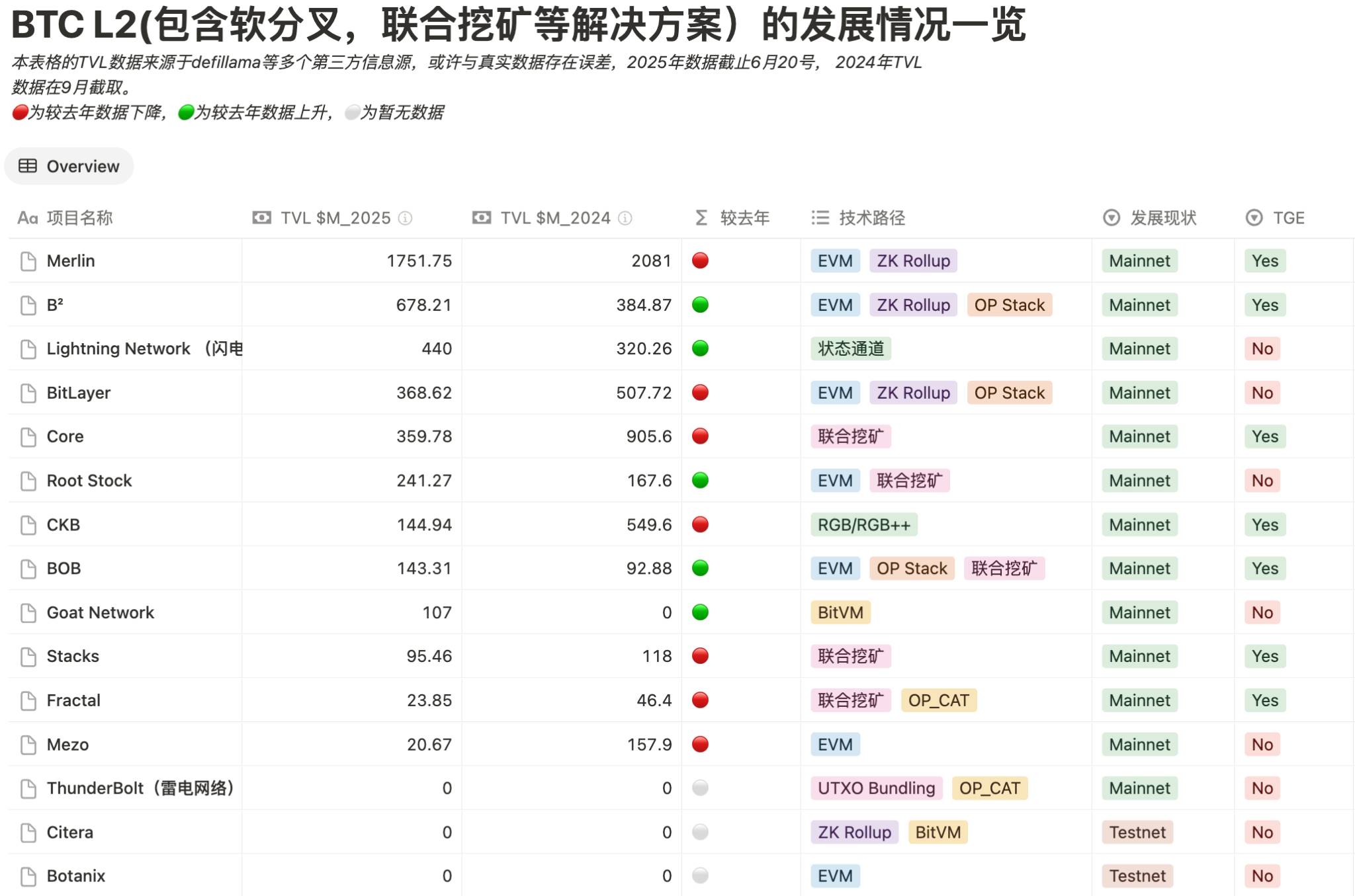
Overview of BTC L2 development status, data source: https://worried-eagle-e5b.notion.site/BTC-21b34b2a8d7a80cb83c1d0021e3a5696
It can be seen that most L2s have experienced significant declines in TVL due to market conditions. Additionally, although Lightning Network’s TVL increased compared to last year, measured in BTC quantity, its locked value has actually declined this year.
Overview of Different BTC L2 Technical Paths
1. The Most Orthodox BTC L2 Solution: Lightning Network
One of the earliest L2s on BTC. Its basic mechanism involves users creating a 2-of-2 multi-sig address on-chain to establish a bidirectional payment channel, secured by Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLC), ensuring both parties can safely settle the latest state on-chain after multiple off-chain interactions. Only the opening and closing transactions are recorded on-chain, while numerous intermediate transactions occur off-chain, greatly saving block space and improving efficiency.
However, early versions of the Lightning Network supported only BTC as a payment currency, severely limiting real-world applications. To address this, Lightning Labs introduced the Taproot Assets protocol (TA Protocol), enabling issuance of native assets on the BTC network while maintaining seamless compatibility with the Lightning Network. Based on BTC’s UTXO model and the 2021 Taproot upgrade, TA records asset states using sparse Merkle trees (MS-SMT), writing only root hashes of transaction data on-chain to keep Bitcoin’s main chain clean. TA assets can also be embedded within Lightning Network channels for fast transfers, realizing the vision of circulating stablecoins on the Bitcoin network.
Beyond stablecoins, RWA assets and project tokens can now be issued on BTC. With the introduction of TA, a multi-asset trading network on BTC is beginning to take shape.
Development Progress
As of June 2025, the Lightning Network has been live for 10 years, operating stably with over 16,000 nodes and 41,000 active channels. Last year, when BTC surpassed $100,000 per coin, total locked capacity exceeded 5,000 BTC. It currently holds around 4,000 BTC.
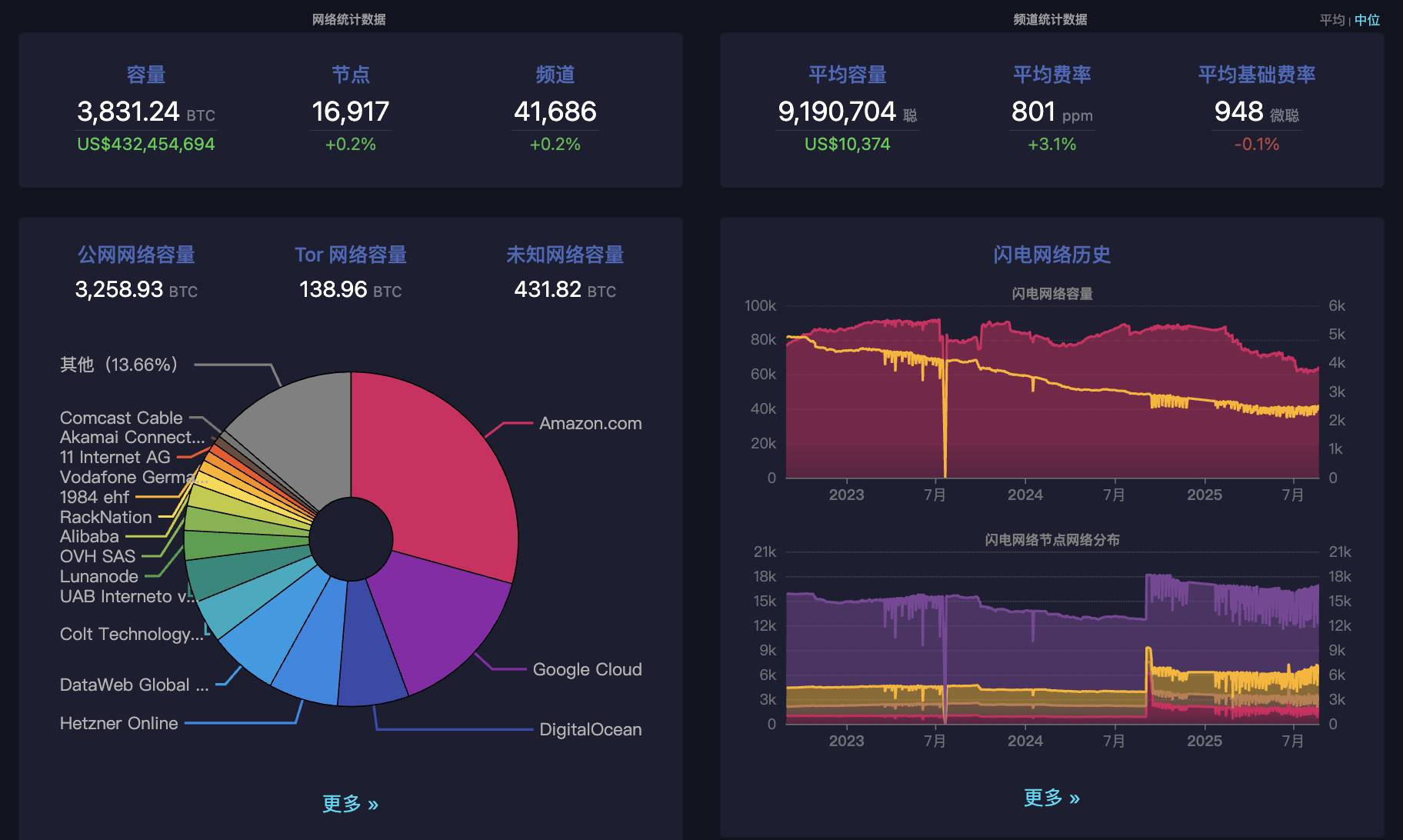
Lightning Network key metrics, data source: https://mempool.space/zh/lightning
In Q1 this year, Tether, issuer of USDT, announced plans to issue USDT via the TA protocol into the Lightning Network ecosystem—a clear endorsement of Lightning by Tether.
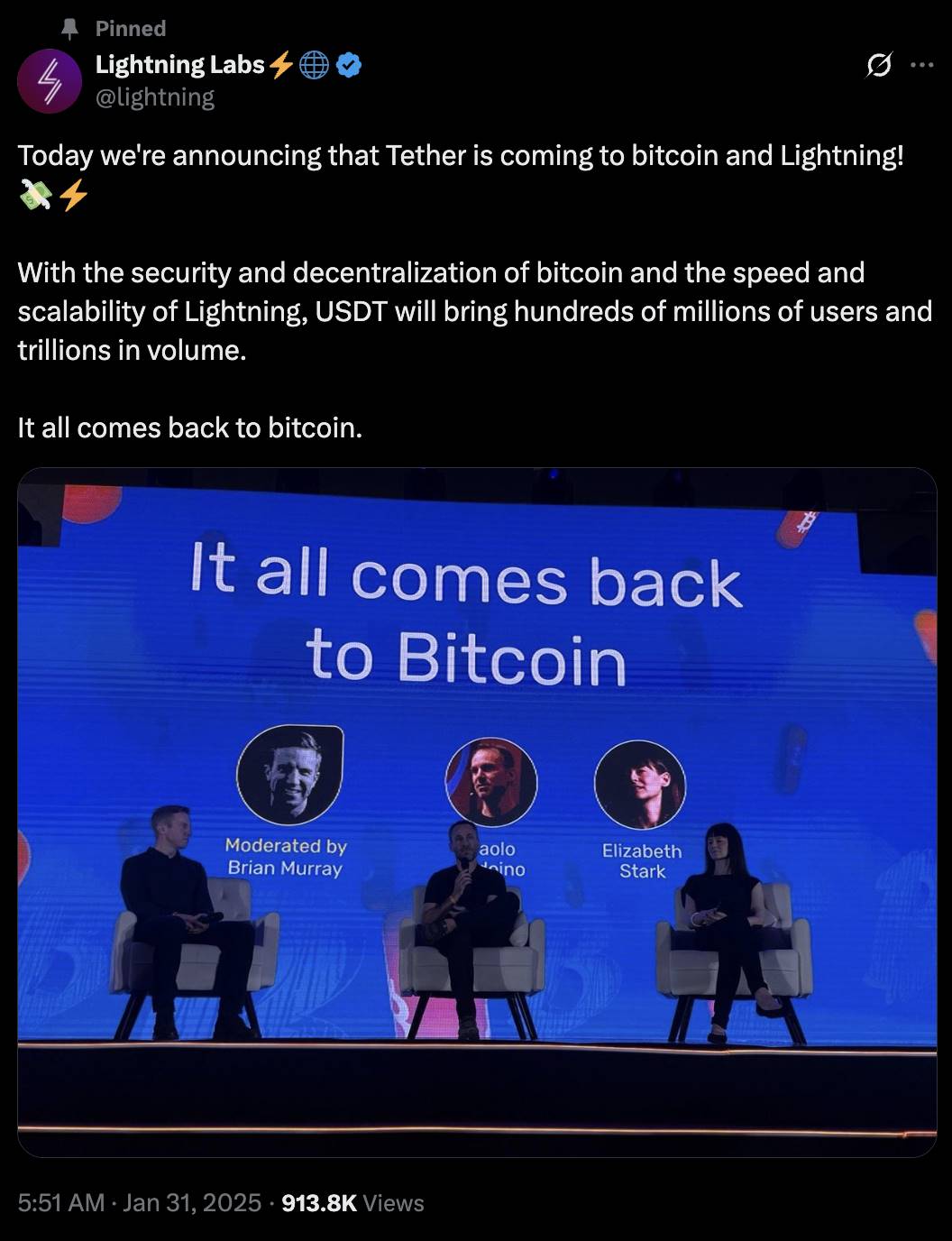
Lightning Lab (parent company of Lightning Network) announces Tether integration, data source: https://x.com/lightning/status/1885083485678805424
Ecosystems based on the Lightning Network are also emerging. For example, financial infrastructure protocol Lnfi aims to become the go-to platform for BTC and Taproot assets, covering full-cycle services including asset issuance, fundraising, yield, and trading. Core products include LN Exchange, achieving daily trading volumes of $30 million, and LN Node, offering over 5% trustless BTC yields. Recently, Lnfi partnered with Tether and Lightning Labs for an X Space discussion on opportunities and challenges of issuing stablecoins on Lightning.

X Space of USDT ON LIGHTNING, data source: https://x.com/i/spaces/1vOxwXmjVbRKB
Additionally, “AI Agent + micropayments” is leveraging BTC’s security to build a new payment system. AIsa is a prime example, utilizing Lightning’s millisecond-level responsiveness and BTC’s robust security to solve massive microtransaction challenges unfeasible in traditional systems. It provides AI service providers and enterprises with real-time, efficient, low-cost payment capabilities. AIsa supports automatic micropayments as low as $0.0001 per API call, real-time DePIN node settlements, and intelligent cross-chain path optimization—all nearly autonomous.
Limits and Challenges
Despite maturity in recent years, Lightning’s scalability remains constrained by network effects and channel routing design, limiting overall capacity. While TA fills the asset layer gap, requiring users to run their own nodes for security raises entry barriers. Product completeness still needs improvement.
Solutions like BitTap offer self-custody wallets for TA users. Focused on decentralization and usability in the Lightning and TA ecosystems, BitTap has launched a decentralized browser plugin wallet and is preparing a stablecoin payment app, enabling stablecoin payments and transfers across Lightning and TA layers, along with secure, free cross-layer bridging.
2. Native Ledger Scaling: Bitcoin Thunderbolt
Last month, Bitcoin Thunderbolt officially launched its mainnet—and was featured in an official press release by HSBC. This marks the first time a traditional financial institution has positively acknowledged blockchain infrastructure represented by BTC.
Technically, Thunderbolt is not a conventional BTC L2, but a soft-fork-compatible native ledger scaling solution built on the BTC mainnet. Its core technology extends BTC’s OP_CAT opcode and combines it with UTXO Bundling to enable high-performance contract execution.
Differences from and similarities with Lightning Network:
Unlike Lightning, which requires open, interactive payment channels, Thunderbolt adopts a non-interactive asynchronous design, allowing users to transfer UTXO ownership off-chain without direct trust or continuous connection. The key lies in introducing a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) Committee managing Schnorr signatures to delegate asset ownership off-chain, with final confirmation on-chain. Under the 3f+1 model, this tolerates up to f malicious nodes, ensuring safety and consistency even in asynchronous networks.
Additionally, UTXO Bundling enables Thunderbolt to aggregate multiple UTXOs, achieving transaction speeds and efficiency over 10x that of the BTC network. In asset protocols, Thunderbolt proposes Goldinal, a unified Layer-1 asset standard for BTC, combined with its BitMM (Bitcoin Message Market) system to implement native on-chain AMM functionality on BTC.
Architecturally, Thunderbolt uses verifiable and adjustable signature components to create recursive off-chain UTXO transfer structures, running through native Bitcoin Core logic. This acceleration from the main chain architecture preserves BTC’s security and censorship resistance while supporting transfers of native BTC assets like BRC-20 and Runes.
Development Progress
Thunderbolt is driven by veteran miners, HSBC, BTC core developers, and contributors from the Nubit community—one of the few protocols in the current BTC stack with formal academic backing.
Currently, Thunderbolt is accessible only to users with a Boosting Code, distributed in limited quantities by core contributors like Nubit, accompanied by rare native BTC airdrops.
By mid-June, Thunderbolt’s mainnet had nearly 50,000 users and close to 4 million total transactions:
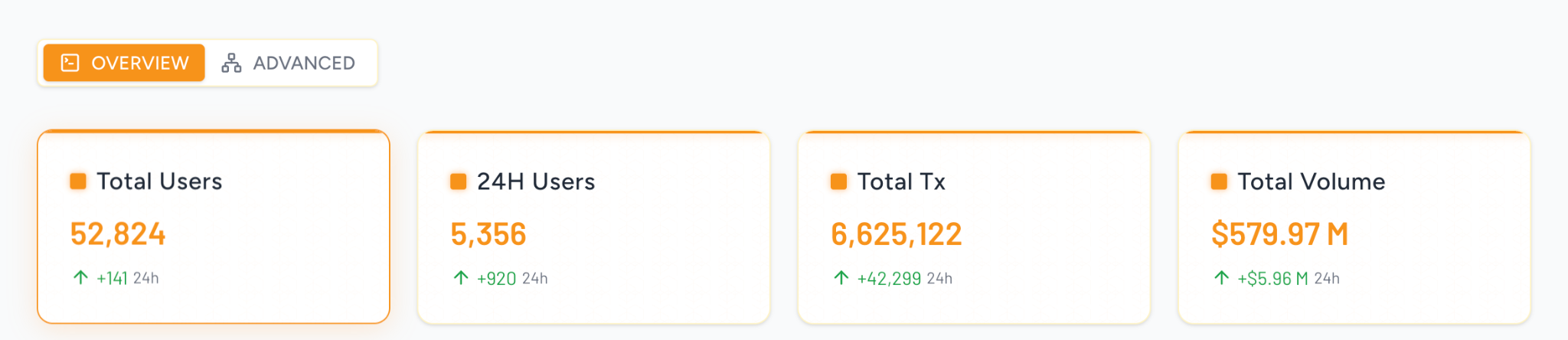
Thunderbolt on-chain data overview, data source: https://data.thunderbolt.lt/?new
Limits and Challenges
Thunderbolt’s tech stack reveals another possible path for BTC L2. However, as the mainnet is still not fully public, its product-market fit (PMF) remains unproven. Moreover, while the BFT committee model offers better security than traditional bridging, whether it gains broad acceptance from Bitcoin’s highly decentralized community remains uncertain.
3. Merged Mining
Merged Mining allows miners to mine multiple blockchains simultaneously without additional computational resources. Stacks and Fractal are two representative projects using merged mining, but differ in consensus and block validation mechanisms. Stacks employs a unique “Proof of Transfer” (PoX) consensus, where Stacks miners bid for block creation rights by sending BTC on the BTC mainnet. Successful bidders gain block packaging rights and mining rewards.
Bitflow is a DEX built on the Stacks mainnet, supporting trading of BTC, Stacks tokens, and various native BTC assets such as BRC-20 and Runes. In December 2024, Bitflow launched the first Bitcoin Rune automated market maker (AMM) on Stacks—the first Rune AMM on any BTC L2.
Core improves upon merged mining with its Satoshi Plus consensus, combining Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). BTC miners delegate their hash power to validators on the Core chain, leveraging BTC’s powerful mining infrastructure to secure Core. This delegated hash power constitutes DPoW, executed by BTC miners and pools. Meanwhile, CORE token holders can stake or delegate tokens to validators, participating in network security and governance—this forms DPoS. This hybrid model integrates BTC miners into Turing-complete smart contract security, unlocking utility beyond simple BTC ledger maintenance, and providing them with supplemental income via CORE tokens.
Fractal takes a different scaling approach, using a recursive expansion structure to create multiple independent scaling layers on the BTC mainnet, forming a tree-like architecture to improve transaction throughput and speed. While retaining PoW, Fractal introduces “Cadence Mining,” a hybrid mining mechanism: for every three blocks produced, two are mined permissionlessly, and one uses BTC merged mining.
Fractal Bitcoin re-enables the OP_CAT opcode—an instruction present in early BTC versions but long disabled. OP_CAT concatenates two strings into one. Theoretically, a script using OP_CAT could expand 1 byte into over 1 TB of data. Without strict limits, this infinite expansion could be exploited for DoS attacks, crashing nodes or congesting the network. Hence, OP_CAT was disabled early on. Now, Fractal’s “sanitized” version of OP_CAT offers developers greater script flexibility, showing promise for on-chain large integer computation and smart contracts. Despite technical improvements, OP_CAT’s revival may still pose security risks in extreme scenarios.
Current Status:
Fractal Bitcoin has achieved initial scale, with a market cap of approximately $20.12 million, daily trading volume reaching 1.43M FB, and over 1.76 million active addresses. Its merged mining hashrate stands at 648.13 EH/s, with mining difficulty at 0.01t—still in early stages.
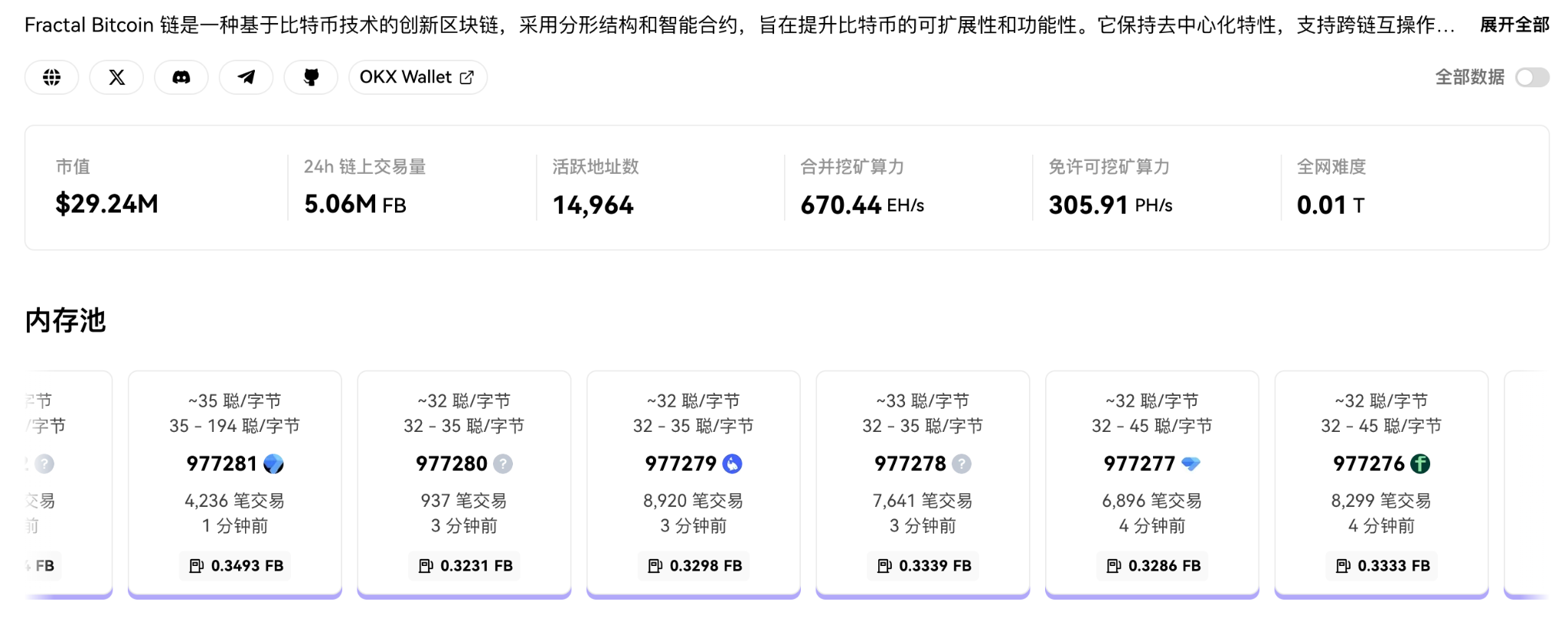
Fractal on-chain data overview, data source: https://www.oklink.com/fractal-bitcoin
4. RGB & RGB++
In the early hours of August 7, 2025, the long-anticipated BTC scaling solution RGB protocol finally launched on the BTC mainnet after two years of anticipation.
Originating from a technical framework proposed by the LP/BNP Association, RGB is an off-chain asset issuance and smart contract protocol based on BTC’s UTXO model. A key technical highlight of RGB is that data it runs is compressed and encapsulated within each BTC UTXO. Through “Single-use Seals” and “Client-side Validation,” it enables private asset state changes and verification. Each asset state is tied to a specific BTC UTXO; when that UTXO is spent, the asset state updates. This design keeps asset ownership and state changes off-chain, enhancing privacy. RGB is compatible with the Lightning Network and capable of building DeFi logic.
RGB v0.12 launch, data source: https://x.com/lnp_bp/status/1943318227854950809
Bitlight Labs: First wallet supporting RGB assets, official member of RGB Association
Bitlight Labs leads native BTC Fi by developing native smart contract infrastructure for BTC and the Lightning Network. Not only is it a board member of INP/BP, the standards body for RGB, but also a core contributor to RGB protocol development—making it an indispensable part of the RGB ecosystem.
Its product, Bitlight Wallet, is designed specifically for the Lightning Network and RGB protocol. Recently, alongside the official launch of the RGB mainnet, it conducted the first minting event for the “RGB” asset token on the RGB mainnet.
BitMask Wallet:
BitMask is the first wallet supporting NFT assets on the RGB protocol. The team behind BitMask is also one of the earliest major security contributors to RGB, prioritizing privacy and user control over assets. Recently, BitMask has been advancing full interoperability between RGB and RGB++, and is actively preparing for its mainnet launch to truly combine privacy, programmability, and usability on the BTC network.
From RGB to RGB++:
Nervos (CKB) is a popular project implementing BTC L2 using RGB logic, and has proposed the concept of RGB++. RGB++ introduces “isomorphic binding,” mapping BTC’s UTXOs to Cells on Nervos CKB, leveraging CKB’s Turing-complete smart contracts and on-chain validation to enhance asset state management efficiency and security. In RGB++, asset state changes are recorded not only on BTC but also verified via corresponding transactions on CKB, enabling collaborative on-chain and off-chain validation.
Although RGB++ achieves BTC-CKB asset mapping, cross-chain interactions based on RGB characteristics remain suboptimal for certain transactions and carry potential security risks.
5. Following ETH L2 Approach: ZK-Rollup
The core of Rollup is bundling numerous off-chain transactions, generating cryptographic proofs (Proofs), and submitting them to the main chain for verification using ZK technology.
One of the Hottest BTC L2s
Merlin follows this approach as a BTC L2 network and is also EVM-compatible. Merlin uses a Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallet solution co-managed by Cobo (a Hong Kong-based crypto custodian) for user assets. In terms of verification, Merlin employs ZK-Rollup technology, compressing large volumes of transaction data before submitting it to the BTC mainnet, ensuring data integrity and security.
Since mainnet launch, Merlin has become one of the most watched Layer 2 projects in the BTC ecosystem. Reports indicate its Total Value Locked (TVL) reached $3.5 billion within 30 days of launch, attracting over 200 projects to deploy and operate on its platform. Merlin Chain supports multiple native BTC Layer-1 assets such as BRC-20 and BRC-420, and expands its ecosystem breadth through Ethereum compatibility.
Enhancing BTC Bridge Security
B² differs from traditional monolithic Rollups by adopting a “Layer 1.5 architecture”: the Rollup layer handles transaction execution and state updates, while a separate Data Availability (DA) layer stores raw transaction data. After off-chain labeling and processing, this data is periodically submitted to the Bitcoin mainnet to confirm finality.
B² Network’s DA layer—B² Hub—is a Layer 1.5 component. It slices batched data using Reed-Solomon + KZG encoding, then aggregates zero-knowledge proofs from Layer 2 into Taproot commitments submitted to the Bitcoin mainnet, inheriting Bitcoin’s finality and immutability.
B² Network uses decentralized blob storage and light node sampling: any validator can randomly sample a small fraction of shards to probabilistically verify data completeness, drastically reducing synchronization and validation costs.
In consensus, B² Hub only submits short commitments and validity proofs; the main chain avoids heavy data loads, while Rollup batch publishers are responsible for availability—forming a modular architecture of “outsourced validity + guaranteed availability.” By decoupling DA and execution layers, B² Rollup enables parallel scaling and sharded updates, with security anchored to Bitcoin, balancing high throughput, low cost, and L1-grade security.
This design offers two benefits: modular architecture allows infinite horizontal scaling without modifying or upgrading the BTC network; additionally, via B² Hub, proof aggregation and state transition proofs can be stored and submitted to Bitcoin, integrating Bitcoin’s security.
However, final confirmation of L2 transactions requires confirmation and aggregation by B² Hub first, followed by on-chain confirmation on BTC—operating in optimistic mode with passive BTC confirmation. Furthermore, aggregating zero-knowledge proofs into Taproot commitments for optimistic validation on BTC remains in POC stage and hasn’t been fully implemented.
Project Progress: From Technical Implementation to User Ecosystem
To date, BSquare’s TVL has surpassed $600 million, with peak daily on-chain transaction volume reaching $900 million and 500,000 active platform users. Its ecosystem spans over 100 DApps across DeFi, lending, and AI Agent applications.
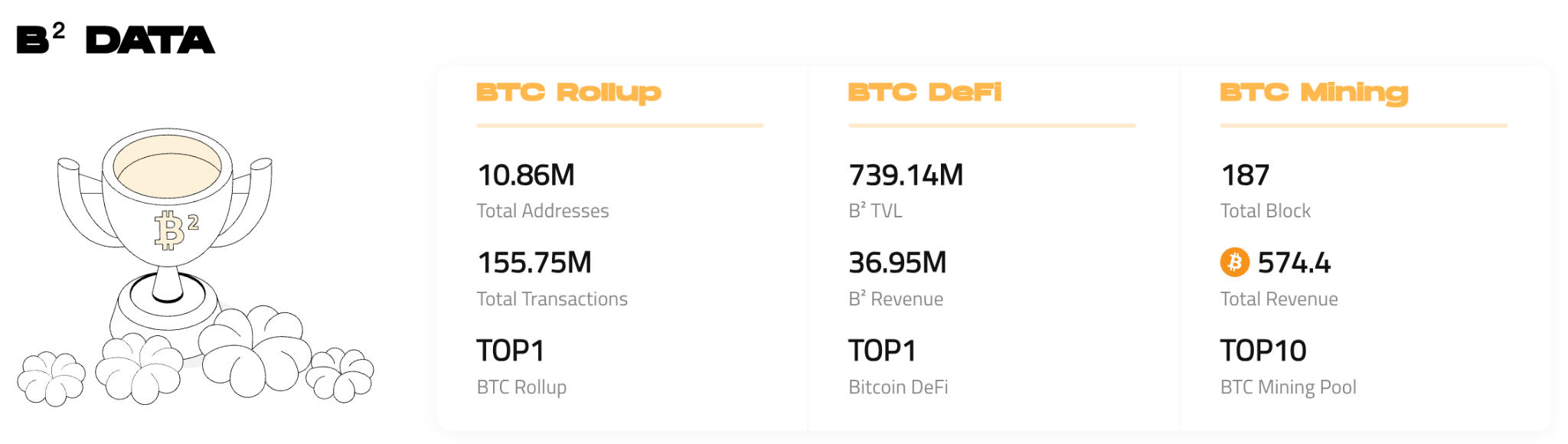
BSquare on-chain data overview, data source: https://www.bsquared.network/
Meanwhile, BSquare launched the first BTC yield-generating mining pool, “Mining Square”—a “Yu’ebao” for miners, providing a BTC-native yield solution. The pool already controls 1% of total network hash power and ranks among the top 10 in mining pool rankings.
6. Can BTC Script Simulate a Turing Machine? Decoding BitVM
BitVM is a scaling protocol built on the BTC mainnet, aiming to support arbitrary verifiable computations in a general-purpose virtual machine environment without changing consensus. It draws inspiration from optimistic rollups: most computation occurs off-chain, with only dispute resolution involving “fraud proofs” submitted on-chain for verification. Similar to Arbitrum on Ethereum, BitVM uses off-chain computation and on-chain verification, but uniquely leverages Bitcoin Script to construct “logic gate circuits” simulating a Turing-complete VM (akin to Emperor Qin’s human-computer in *The Three-Body Problem*).
BitVM does not directly run EVM or WASM on-chain. Instead, it translates high-level VM operations into combinations of basic logic gates (AND, OR, NOT, etc.) in Bitcoin Script, building a massive “fraud verification circuit.” All transaction data and computation happen off-chain, with data and steps (via Merkle Proofs, etc.) submitted on-chain only during disputes.
BitVM2 optimizes the original BitVM, introducing more modular computation structures and circuit compression, along with interactive fraud proofs, timelock scripts, and multisig to enhance practicality and security. BitVM2 focuses on minimizing on-chain data submission and explores future activation of opcodes like OP_CAT to improve circuit efficiency.
Current Status
BitVM is gradually moving from theory to practice. Citrea is a representative project, executing large volumes of transactions off-chain and submitting results and proofs via BitVM to BTC for validation—achieving efficient scaling and security for BTC L2. Citrea is the first solution enabling general-purpose L2 settlement on BTC, with all proofs natively verified within BTC blocks. Currently, Citrea’s mainnet is not yet live, still in testnet phase.
Goat Network explores possibilities of BitVM2. Its whitepaper demonstrates a fraud proof mechanism based on circuit logic and Merkle trees. Goat emphasizes expanding BTC computation into a Turing-complete state machine, attempting to build a new BTC L2 framework allowing native smart contract execution and asset interaction on the Bitcoin main chain. Goat’s implementation includes integration of a data availability layer (DA) and circuit compression optimizations, advancing BitVM from experimental to deployable.
As of June this year, Goat Network’s TVL has exceeded $100 million.
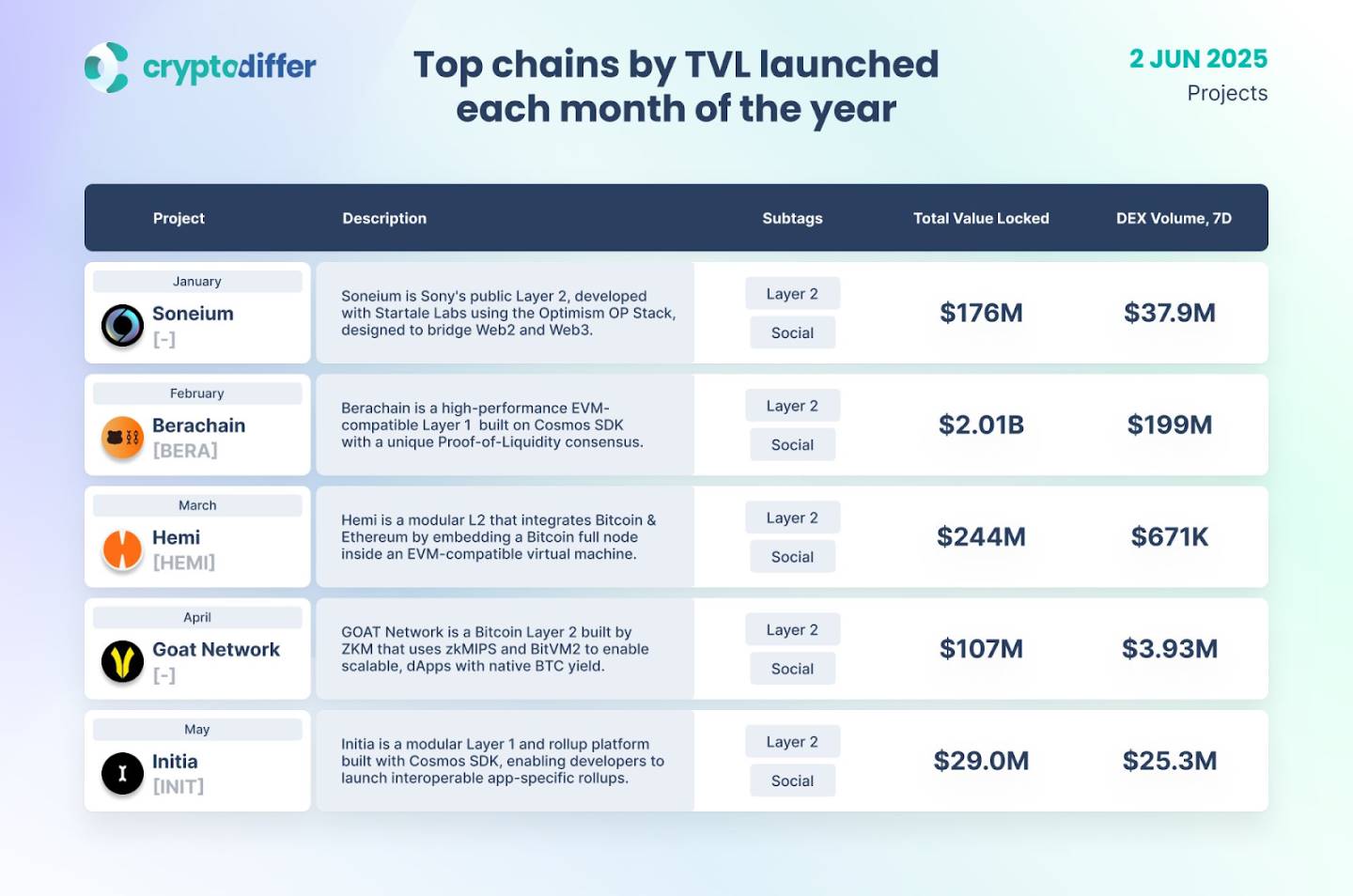
Top chains by TVL launched each month, CryptoDiffier; data source: https://x.com/GOATRollup/status/1929596963286114614
Despite clear advantages—extreme native compatibility, Turing-complete computation without altering BTC consensus, high security and decentralization—BitVM’s disadvantages stem from its complexity. Simulating EVM or WASM using logic gates built from BTC Script creates an astronomically complex and massive structure, resulting in extremely high development difficulty and enormous circuit construction workload. Moreover, it currently lacks a mature developer ecosystem and standardized tools.
7. Multiple Paths Forward—Value Carrier Battle Remains Unresolved
Different BTC L2 solutions emphasize distinct technical approaches. For instance, the Lightning Network focuses on payment efficiency, having developed a mature node network over years, ideal for micropayments and off-chain settlements. RGB and RGB++ prioritize asset security, using client-side validation to protect asset states. ZK-Rollup paths, leveraging mature EVM frameworks and modular security verification, currently offer strong composability and cross-chain scalability, adapting faster to use cases like DeFi and AI Agents. BitVM pushes further toward ultimate native compatibility, enabling smart contract capabilities on-chain without changing BTC consensus—still early but representing an extreme attempt at BTC’s computational limits.
While no clear winner has emerged, truly sustainable long-term solutions must meet three criteria: native BTC compatibility, verifiable security, and strong support for upper-layer applications. Moreover, convergence among tech stacks is increasingly evident—examples include Lightning Network integrating stablecoins, and explorations combining ZK Rollup with RGB.
Looking ahead, BTC L2 will likely evolve into a multipolar competitive landscape, with different solutions serving distinct core scenarios—payment, contracts, assets, storage, AI—collaborating to sustain the long-term prosperity of the BTC ecosystem. This race is far from over; the ultimate winner will be determined by asset accumulation and developer ecosystem strength. As BTC—the world’s strongest consensus asset—sees its boundaries expand through dollar-pegged stablecoins and modular L2 innovations, it will undergo a dual upgrade in “payment sovereignty + contract extensibility.”
Recently, with the passage of the U.S. GENIUS stablecoin bill, global stablecoin regulation is becoming clearer and more comprehensive. “Payment stablecoins” are now legally integrated into the dollar system, paving the way for USDT, USDC, and other emerging stablecoins to accelerate adoption in on-chain payment scenarios. As Tether’s CEO noted, emerging markets are the primary battleground for stablecoin adoption, with 60% of USDT growth coming from real-world payment demand outside the crypto space.
The GENIUS Act provides a clear legal pathway for stablecoin usage on-chain, opening compliant channels for BTC L2 to carry dollar-denominated assets. USDT, the first stablecoin born on the BTC network, is now leading the return to the BTC ecosystem—not just a technical homecoming, but a recognition of BTC’s strategic value as a settlement layer. It is foreseeable that building stablecoin payment systems on BTC L2 will represent the most native, secure, and Bitcoin-aligned path. Leveraging BTC L2’s composability and asset protocol capabilities, the BTC network could fulfill real-world payment and settlement demands, achieving a symbiotic ecosystem of stablecoin circulation and value anchoring.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News