How Taiko is Pioneering the Decentralized Path for Rollups?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

How Taiko is Pioneering the Decentralized Path for Rollups?
Decentralization is the core value of blockchain, but Rollup technology, while enhancing Ethereum's scalability, sacrifices a certain degree of decentralization.
Authors: @xparadigms and @IngsParty
Translation: weizhi, BlockBeats
Decentralization is one of the core values of blockchain. However, to enhance Ethereum's scalability, Rollup solutions have sacrificed part of decentralization in their operations. Achieving full decentralization still faces challenges in sequencing and proof settlement, especially for Optimistic Rollups and zero-knowledge (zk) Rollups.
Despite these challenges, development toward decentralized Rollups is accelerating. Some Optimistic Rollups have already introduced permissionless challenge mechanisms and are testing hybrid proof systems. The Taiko project stands out due to its clear decentralization roadmap. Let’s explore why.
1. Background – Core Components: BCR and BBR
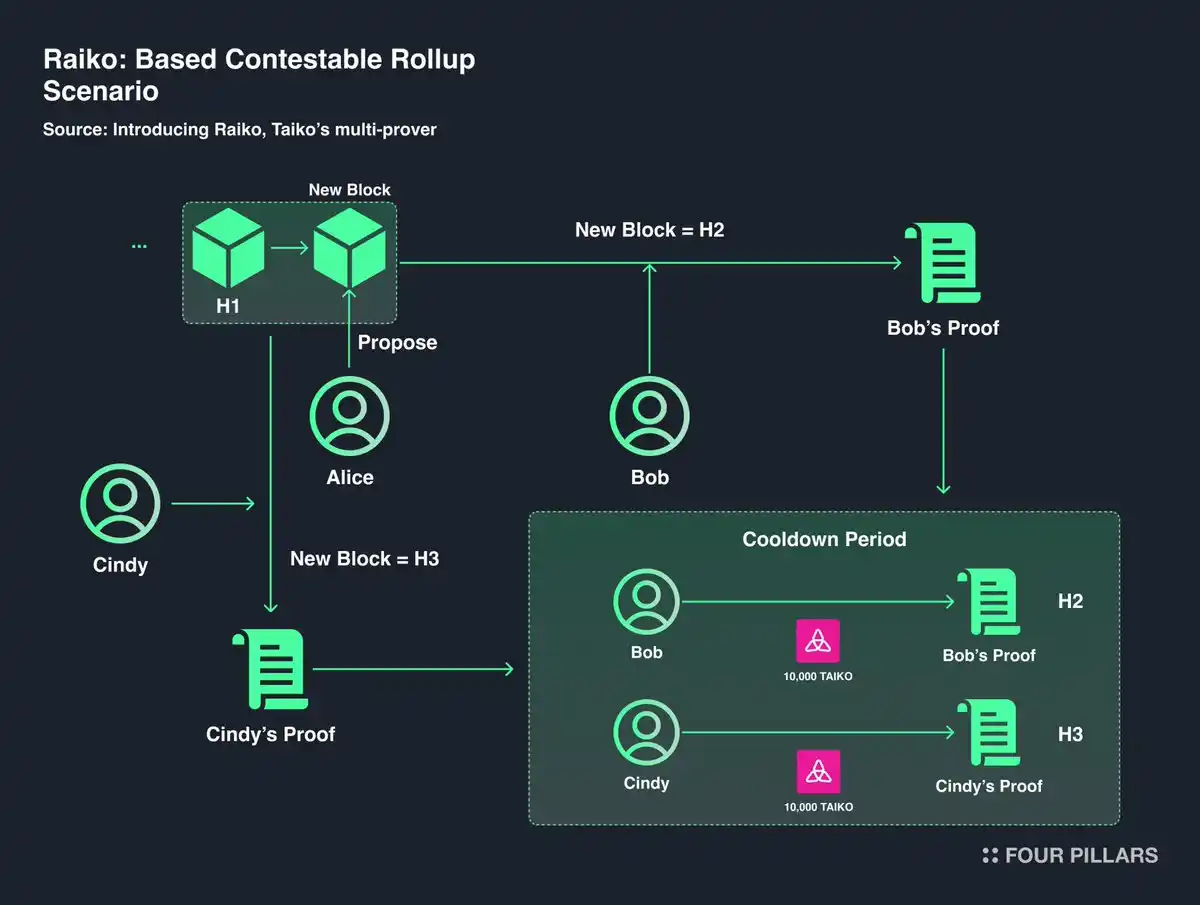
Taiko’s "path to decentralized Rollups" introduces two proof systems and frameworks: Based on Competitive Rollup (BCR) and Based on Booster Rollup (BBR).
1.1 Based on Competitive Rollup (BCR) – A Robust L2 Proof System
BCR is a Rollup design incorporating a competitive mechanism. This design verifies transactions by allowing participants to challenge transaction validity when fraud is suspected. This mechanism enhances decentralization by enabling Ethereum validators to use the challenge mechanism for transaction ordering without relying on a central sequencer, thus maintaining blockchain integrity.
The BCR mechanism combines the advantages of Ethereum transaction ordering with challenge functionality, aiming to reduce transaction fees while maintaining security and decentralization. Moreover, Taiko employs multiple proof systems within BCR, including SGX, ZK, and SGX+ZK at different stages of Rollup proofs, ensuring system flexibility and more stable operations.
Despite these advantages, BCR has a potential drawback: when competition frequency is low, provers may lack activity. The prover structure requires substantial competition to generate profit, so in environments with less competition, they might prefer not to participate. To address this, Taiko implements dynamic adjustments across different Rollup proof systems to resolve the issue.
1.2 Based on Booster Rollup (BBR)
BBR aims to scale Ethereum DApps without requiring redeployment across all L2 solutions. By sharding transaction execution and storage, it reduces developers’ workload and lowers redeployment costs. This design addresses liquidity fragmentation across L2s and enhances network scalability.
In November 2023, Taiko launched Gwyneth, a booster Rollup initiative designed to enhance Ethereum’s capabilities. Gwyneth uses Ethereum L1 validators for transaction ordering and L1 builders for block construction. Its key features include synchronous composability for seamless L1 integration, scalability to meet growing demands, and pre-confirmation capability for fast transactions.
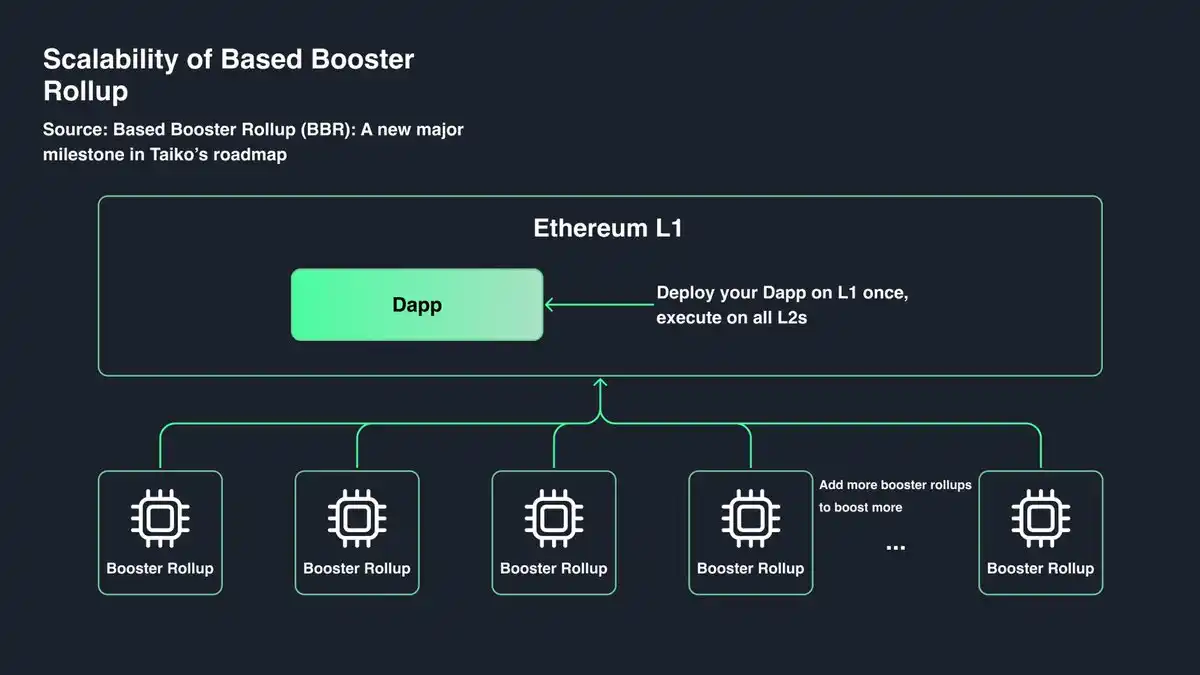
Gwyneth is “finalized” from the start, with its security guaranteed by Taiko’s multi-proof system Raiko, utilizing Trusted Execution Environments (TEE), and plans to introduce zkVM in the future. Both BCR and BBR are part of Taiko’s effort to provide efficient scaling solutions for Ethereum, ensuring high transaction throughput while maintaining security and decentralization.
2. Key Perspectives
2.1 "Are We Considering Decentralization in Rollups?"
FourPillars researcher Heechang believes that currently, most Rollups remain centralized. Decentralized sequencing and proof systems are still under development. Two prominent proof systems—Optimistic Rollups and Zero-Knowledge Rollups—are moving toward decentralization.
Optimistic Proof Systems: These systems have implemented forced L1 transactions and are exploring shared sequencing and permissionless challengers. Arbitrum and Optimism allow permissionless challenges, although recently Optimism suspended this mechanism due to suspected vulnerabilities.
Zero-Knowledge Proof Systems: Most zk-Rollups do not allow forced transactions on L1. While zk-proofs offer secure state transition guarantees, operations remain centralized, and technical challenges persist.
Although not yet fully decentralized, Rollup frameworks such as OP-Stack, ZK-Stack, Polygon zkEVM, and Arbitrum Orbit have been adopted by hundreds of L2 projects. This trend continues, with Rollup framework teams actively working toward decentralization. However, not all projects have clear roadmaps addressing decentralization challenges.
In this regard, Taiko excels. From its inception, it has had a clear roadmap aiming to become an L2 and decentralized Rollup framework. It possesses a well-defined path forward and operational tokenomics capable of providing sustainable utility for its L2 token—a feature lacking in most other projects.
As other projects also improve their codebases and infrastructure, whether Taiko can successfully realize its vision at the right market timing remains to be seen. As one of the teams closely collaborating with the Ethereum Foundation, Taiko’s progress in decentralization deserves particular attention.
2.2 "It’s Time to Consider Rollup Decentralization"
FourPillars researcher IngeunKim believes major Rollup projects are now striving for decentralization. Yet, none have made significant progress toward full decentralization. The main reason is that today’s mainstream Rollups initially prioritized performance and functionality over decentralization during their design phase. Now they find it extremely difficult to integrate decentralization into their established architectures. This is understandable, as in early stages, Rollups needed to deliver high-performance results while meeting Ethereum’s scalability demands.
However, the concept of Rollup decentralization is becoming increasingly important. It mirrors the natural transition from the performance-driven Web2 era to the decentralized Web3 era. Fortunately, many Rollup projects have laid foundational groundwork paving the way for future decentralization. In this context, Taiko’s efforts in decentralized Rollups deserve close attention. Particularly, its Based on Competitive Rollup (BCR) mechanism includes fundamental elements for achieving full decentralization—open participation, fair rewards, and penalties.
Certainly, many areas still require improvement, and the path to full decentralization is fraught with challenges. Nevertheless, Taiko’s efforts are considered highly significant and could positively impact the entire Ethereum L2 ecosystem. Their progress is absolutely worth watching.
3. Additional Perspectives
3.1 "The Choice Is Not Just Technical—It’s About Decentralization"
Taiko member Junger notes that as Rollups gain popularity, fragmentation and isolation have become critical issues. There’s a trade-off between choosing Rollup-based versus shared sequencer architectures. Shared sequencers offer faster finality and cross-chain composability but introduce new trust assumptions and potential points of failure. Rollup-based designs leverage Ethereum’s infrastructure, offering liquidity and L1 composability, but face challenges related to block time and revenue.
Future improvements may include pre-confirmations and faster L1 block times to enhance user experience while staying aligned with Ethereum. The goal is to build a scalable and truly Ethereum-aligned decentralized ecosystem.
Junger emphasizes that choosing whether to develop on a Rollup-based architecture is not merely a technical decision—it reflects the direction of a decentralized Rollup “framework.”
3.2 "The Endgame Is Rollup-Based"
Ethereum Foundation researcher Justin Drake has been actively involved in discussions about Ethereum scaling solutions, particularly focusing on Rollup-based approaches and the Taiko project. Drake emphasizes the importance of decentralized sequencing, which mitigates monopolistic control and censorship risks in transaction ordering. He believes integrating technologies like zero-knowledge proofs and shared sequencers can enhance the functionality and security of Rollup-based systems.
Justin Drake sees Taiko as an important step toward a decentralized and scalable Ethereum ecosystem, highlighting its mainnet’s permissionless sequencing and proving system as a standout feature. He also stated, “The endgame will be Rollup-based.”
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News