Can the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 bring the BTC ecosystem into the mainstream?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Can the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 bring the BTC ecosystem into the mainstream?
As Bitcoin Ordinals transaction volume continues to hit new highs, the BTC ecosystem is once again drawing market attention.
Abstract
As Bitcoin Ordinals transaction volume continues to reach new highs, the BTC ecosystem has once again drawn market attention. This article analyzes the impact of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 on the BTC ecosystem, reaching the following conclusions:
-
The emergence of new technologies has brought new possibilities and broader application scenarios to the Bitcoin ecosystem, while also addressing the issue of miners'单一 revenue streams;
-
Market enthusiasm for BRC-20 and Ordinals transactions has surged, pushing average fees to their highest level in nearly three years;
-
Due to the blockchain trilemma—difficulty in simultaneously achieving scalability, decentralization, and security—the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem is constrained, making the evolution of Bitcoin Layer 2 an inevitable trend;
-
Issues such as network congestion and poor scalability remain unresolved; the Bitcoin ecosystem is still in its early stages, with immense growth potential as new technological advancements emerge.
1. Curious Phenomena in the BTC Ecosystem
For a long time, development within the Bitcoin ecosystem has faced challenges, primarily due to scalability limitations. However, recent technological innovations—such as the Ordinals protocol, NFTs, and BRC-20 tokens—have thrust the Bitcoin ecosystem back into the spotlight. The recent surge in popularity of $ORDI, the first BRC-20 project launched on the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol, demonstrates significant market interest and optimism toward the BTC ecosystem. These emerging technologies and protocols have introduced new possibilities and broader use cases for Bitcoin, indicating that the industry could reach unprecedented heights.
Web3 multi-chain wallet BitKeep announced on Twitter that starting May 2023, it will fully integrate asset display features to support BRC-20 inscription tokens and NFT trading markets based on the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol. It will enable Bitcoin network transfers, storage, and trading of BTC NFTs built on the Ordinals protocol. Additionally, it will support Taproot address formats and the BRC-20 protocol.
1.1 The BTC Ecosystem
Due to the blockchain trilemma—where it's impossible to achieve scalability, decentralization, and security all at once—Bitcoin prioritizes decentralization and security over scalability. As a result, its inherent design allows only transaction records on blocks, with little room for other data storage. Since Bitcoin does not support smart contracts, issuing NFTs via contract is unfeasible. While Bitcoin is widely regarded as secure and decentralized digital gold, its potential for supporting applications remains underdeveloped.
In March this year, as Bitcoin NFT protocol Ordinals minting volumes hit record highs, the BTC ecosystem re-entered public focus. Today, the first BRC-20 token on the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol, $ORDI, is sweeping across the blockchain market. Starting in April, the meme coin craze brought BRC-20 into view, with the total market cap of BRC-20 now exceeding $120 million. BRC-20 transactions already account for over 50% of all activity on the Bitcoin blockchain.
BRC-20 has reignited excitement in the BTC network. Since March, average transaction fees have doubled, reaching their highest levels in two years. On May 7 alone, over 400,000 inscriptions were created, including nearly 323,000 text-based inscriptions. That day, Bitcoin transaction fees exceeded 403.9 BTC, with nearly 330,000 unconfirmed transactions pending on the network. Market enthusiasm for BRC-20 has driven up fees abnormally. Notably, popular current BRC-20 tokens like pepe, punk, bayc, and domo are mostly meme coins with little intrinsic value.
1.2 Significance of the Emergence of the Ordinals Protocol and BRC-20
The emergence of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 represents a new narrative for Bitcoin. Currently, Bitcoin’s primary use case is limited to BTC transfers. Without smart contract support, NFT issuance isn't possible—but the introduction of the Ordinals protocol increased the number of non-zero Bitcoin addresses to a historic high of 44 million. Effectively, the Ordinals protocol expands Bitcoin's utility from merely recording BTC creation and transfer to also tracking NFT generation and movement.
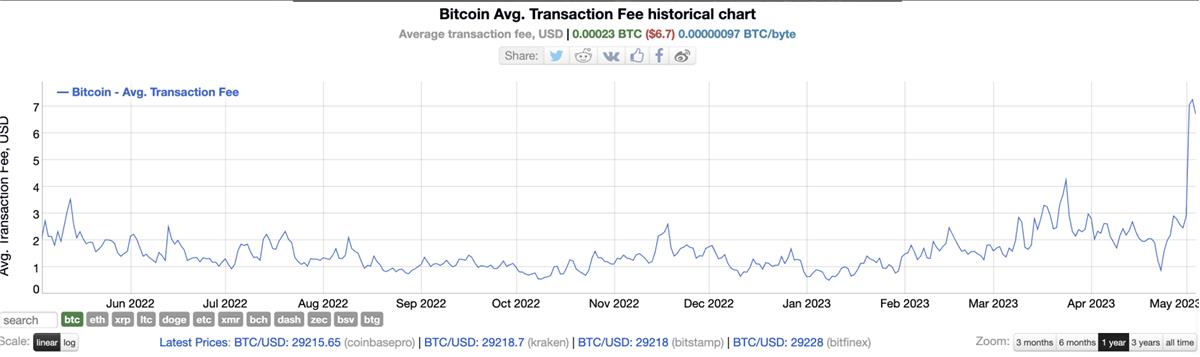
Additionally, with the upcoming Bitcoin halving, we must consider the role of miners. Bitcoin's mechanism places critical importance on miners. Next year, block rewards will drop from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. Miners currently earn income from two sources: block rewards and transaction fees. With each halving cycle, block rewards will eventually approach zero, leaving miners increasingly dependent on transaction fees. How can miner incentives be sustained? Relying solely on block rewards creates growing pressure. NFTs and tokens generate transactions—when the Bitcoin ecosystem supports them, overall transaction volume increases, boosting miner fee revenues. The rise of Ordinals and BRC-20 offers a new incentive model for miners. Recently, BRC-20-related transaction surges have increased miner fees by 484% over the past 14 days. Beyond solving miner revenue issues, these developments foster positive growth in the BTC Layer 2 ecosystem.
2. About the Ordinals Protocol
With rapid advancements in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, NFT adoption has expanded significantly. Ethereum dominates as the main NFT platform, but the emergence of the Ordinals protocol challenges that status quo. The Ordinals protocol extends Bitcoin's functionality by assigning unique serial numbers to individual satoshis (sats), enabling uniqueness. Inscriptions etch text, images, audio, and video onto sats, allowing BTC NFTs and tokens to be issued directly on the Bitcoin chain.
2.1 Technical Principles of the Ordinals Protocol
The Ordinals project consists of two components: Ordinal theory and Inscription.
Ordinals is a numbering system that assigns a unique identifier to each individual satoshi (the smallest unit of Bitcoin, where one BTC equals 100 million sats), enabling traceability and transfer. Ordinal NFTs operate using inscriptions—each satoshi receives a sequence number through the Ordinals protocol, then data such as images can be inscribed via Bitcoin transactions. Once confirmed in a block, an Ordinal NFT becomes permanently anchored on the blockchain. Originally interchangeable, sats become non-fungible once inscribed under the Ordinals system.
Bitcoin transactions consist of two parts: transaction data and witness data. Witness data originally stored digital signatures. Separating these elements helps better utilize the 1MB block size limit, improving Bitcoin network efficiency and reliability.
Inscriptions leverage the Taproot upgrade, storing data through Taproot spending scripts. SegWit relaxed signature size limits (with a 4MB cap for witness data), and Taproot further simplifies storing arbitrary data in Bitcoin transactions.
2.2 Advantages of the Ordinals Protocol
-
Higher Security:
While both Ordinals and traditional NFTs represent unique digital assets, conventional NFTs are typically built using smart contracts on various blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, or Polygon. Moreover, metadata for most ERC-721 NFTs is stored off-chain, risking permanent loss if servers fail. In contrast, Ordinals inscribe data directly onto individual sats and embed them into the Bitcoin blockchain, ensuring metadata is permanently stored on-chain.
-
Stronger Uniqueness and Traceability:
Since Ordinals are created directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, they benefit from immutability and do not rely on third-party projects. As long as the Bitcoin network exists, inscriptions remain permanently recorded and cannot be deleted or lost, offering superior uniqueness and traceability. Traditional NFTs depend on smart contracts for authenticity and are vulnerable to counterfeiting and forks.
-
High Tradability:
Sats follow the same data format as Bitcoin and are traded on the Bitcoin blockchain, providing high liquidity. Combined with relatively low transaction costs, this may drive higher trading volumes. Traditional NFTs are usually traded on online marketplaces like OpenSea, SuperRare, Rarible, and Nifty Gateway, which provide platforms for users to showcase, buy, and sell NFTs, requiring secure platforms and anti-fraud measures during transactions.
3. About BRC-20 Tokens
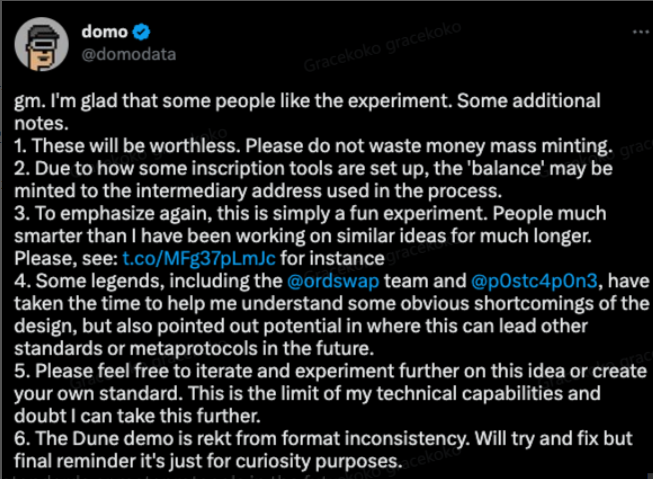
Inspired by Ordinals, developers explored whether similar logic could apply to fungible tokens. In March, @domodata conducted an experiment, launching BRC-20 tokens using the Ordinals protocol. This proved that tokens on Bitcoin could function similarly to ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum.
3.1 What Is BRC-20?
The creator of BRC-20 publicly stated the standard was "worthless" and urged users not to waste money mass-producing what he called a "fun experiment":
Unlike traditional token standards managed by smart contracts on EVM-compatible chains, BRC-20 tokens are essentially script files stored on the Bitcoin network. This means they act as metadata attached to Bitcoin transactions, enabling the creation of fungible tokens on Bitcoin via the Ordinals protocol. Although linked to Bitcoin, BRC-20 tokens are distinct from BTC itself.
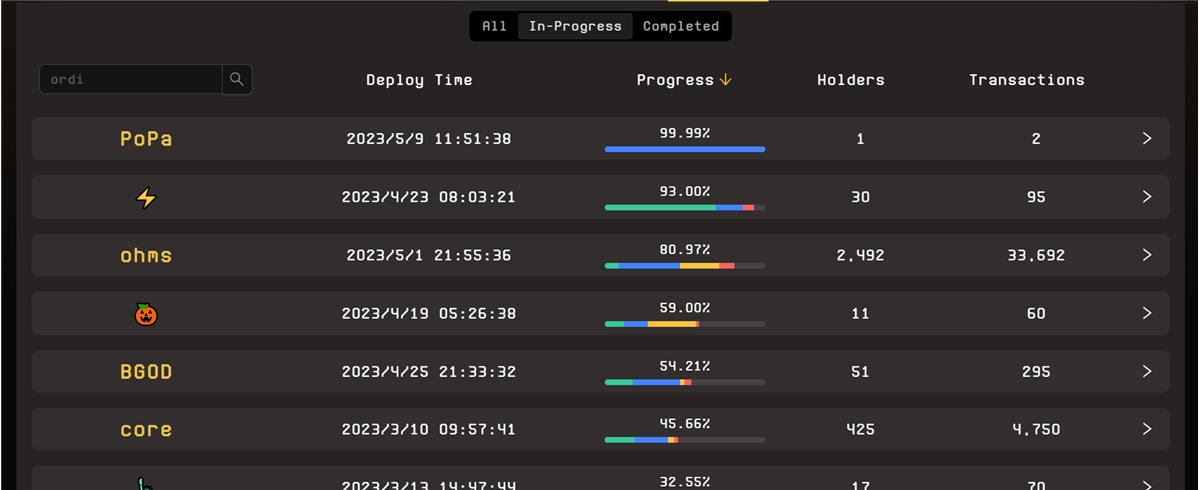
Despite this, builders like Unisat are enthusiastically embracing BRC-20. Some centralized exchanges, such as Bitget, are taking responsibility for deeper research around the standard. With the explosion of BRC-20, new tokens like $ORDI, $MEME, and $PEPE have emerged rapidly. According to UniSat data, over 2,280 tokens have been successfully deployed, with more than 13,960 additional BRC-20 tokens currently being minted.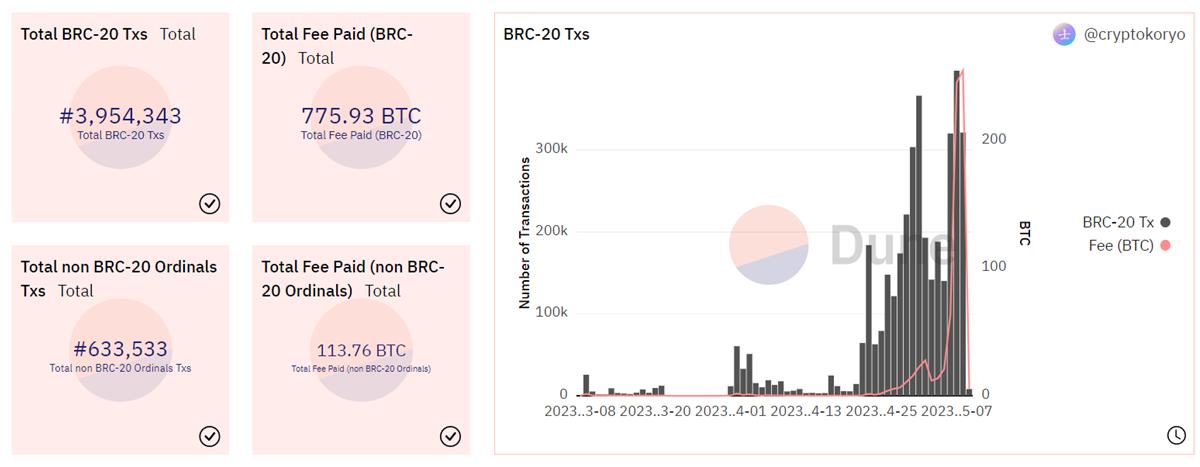
BRC-20 transaction volumes are rising rapidly, especially as $ORDI’s price surge energized the entire BRC-20 market. To date, BRC-20 has seen nearly 3.96 million transactions, with total fees surpassing 775 BTC.
3.2 Differences and Advantages Between BRC-20 and ERC-20
As mentioned earlier, BRC-20 follows a similar issuance model to ERC-20. While BRC-20 has gained popularity recently, it still has a long way to go compared to the vast number of ERC-20 tokens circulating on Ethereum.
Both BRC-20 and ERC-20 are token standards, but differ in implementation. BRC-20 leverages ordinal numbering and inscription technology, benefiting from Bitcoin’s security and stability. However, lacking smart contract functionality and flexibility, BRC-20’s application scope is narrower. In contrast, ERC-20 relies on smart contracts, offering richer features and greater flexibility.
Security is another key advantage of BRC-20 tokens, as they are built on the highly secure Bitcoin network. Bitcoin’s robust security has consistently thwarted hacking attempts, ensuring BRC-20 tokens remain safe and tamper-proof.
Being natively built on Bitcoin, BRC-20 tokens seamlessly integrate into the Bitcoin ecosystem. Developers can leverage Bitcoin’s relatively low entry barrier to build innovative applications, potentially accelerating BRC-20 adoption.
3.3 Overview of Popular BRC-20 Tokens
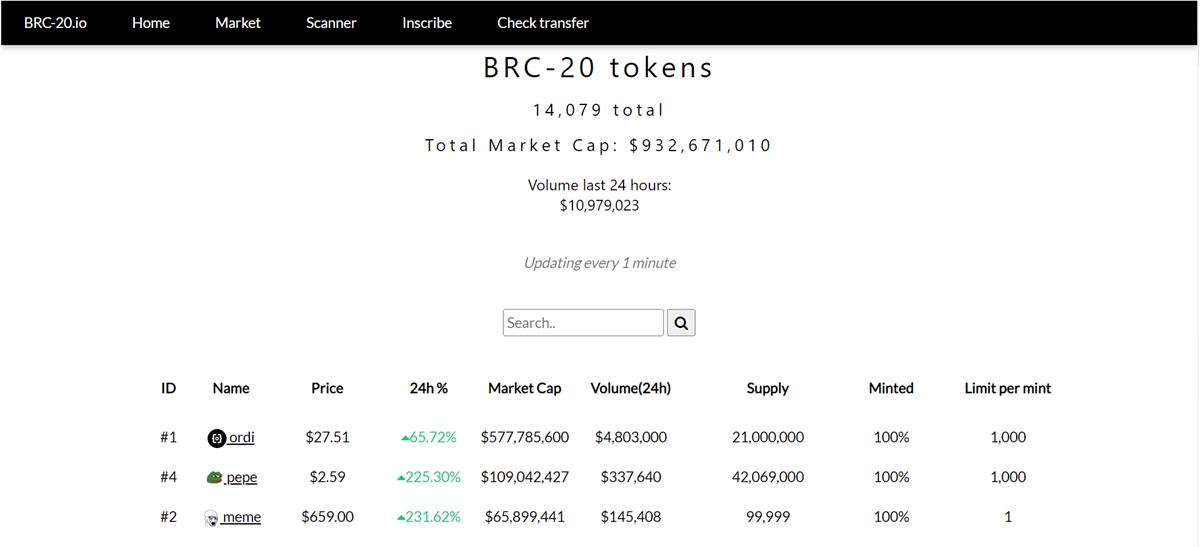
At the time of writing, the total market cap of BRC-20 stands at $932,671,010, with 24-hour trading volume at $10,979,023.
-
$ORDI — the first BRC-20 token deployed, now fully minted, rose from $0.01 (1,000 $ORDI = $10) to $27.51, a 2,700x increase, with market capitalization exceeding $600 million.
-
Nals — derived from a meme (Ordi + Nals = Ordinals), launched on March 10 and fully minted by May 1, with a total supply of 21 million. Current price: $0.57, holder count: 1,933, transaction count: 44,466.
-
Meme — currently priced at $91, total supply: 99,999;
-
PEPE — a meme coin, currently priced at $8.32, total supply: 42.096 million.
It is reported that BitKeep wallet will soon support the Ordinals and BRC-20 protocols, offering asset display, transfers, and trading services for BRC-20 tokens. Users can conveniently manage BTC Taproot addresses, BRC-20 tokens, and BTC NFTs via mobile or browser extension wallets, lowering the barrier to participation in the Bitcoin Web3 ecosystem.
4. The BTC Ecosystem
In the current market environment, Ordinals and BRC-20 have opened new narratives and doors for the Bitcoin ecosystem. With increasing NFT minting on the Bitcoin mainnet and BRC-20 token growth, demand for Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions is rising. The BTC ecosystem remains in its infancy, with few projects and vast room for expansion.
4.1 BTC Layer 2 Projects
-
Stacks
Stacks is a public blockchain project whose v2.0 enables independent scaling separate from the Bitcoin network, while final settlement occurs on Bitcoin.
The Stacks ecosystem is relatively mature. Its most notable project is Secrets, aiming to offer a decentralized NFT marketplace where users can create, display, trade, and purchase NFTs. Other projects include Stacks DEX (a decentralized exchange), SmartWeave (a smart contract protocol), Boomboxes (a music app), and btc.us (a domain service offering .btc suffixes).
-
Lightning Network
The best-known Bitcoin Layer 2 solution is the Lightning Network, designed to solve Bitcoin’s slow transaction speeds and high fees. Using multi-signature and atomic swap technologies, it establishes off-chain payment channels, enabling fast, low-cost transactions. The core idea is moving transactions off the main Bitcoin chain to a second layer, reducing congestion and improving efficiency and security. It also allows direct peer-to-peer channels—similar to private messaging—eliminating intermediaries and lowering costs.
-
RSK
RSK, launched in January 2018 by Rootstock Labs, is a Bitcoin sidechain known as a “smart contract platform extending Bitcoin’s protocol.” By adding smart contract capabilities atop Bitcoin, RSK inherits Bitcoin’s security and reliability while enabling broader dApp usage. RSK also offers very low fees and extremely fast transactions, making it ideal for micropayments.
-
Gamma
Gamma is built on Stacks’ BTC Layer 2 network. Currently, the Stacks ecosystem is dominated by NFTs, with almost no DeFi applications. Users can purchase Gamma NFTs using sBTC and STX. A Hiro wallet is required, which also allows users to mint their own Ordinal NFTs.
-
Bitcoin Punks
Bitcoin Punks are primarily traded via Ordinalmarket, which offers a one-click verification Vault feature to confirm authenticity. Currently, listings from OpenSea can also be purchased directly on Ordinalmarket.
Currently, there is no secondary NFT marketplace on Bitcoin equivalent to OpenSea. Minting requires running a full node, while buying, selling, and transferring relies on Bitcoin address transactions. Users lack intuitive interfaces. Given this gap, existing NFT platforms like BitKeep NFT Marketplace are integrating Bitcoin NFT trading functions to support BRC-20 ecosystem growth and provide easier access.
4.2 Opportunities in the BTC Ecosystem
-
BTC Ecosystem Scaling
Since the launch of the Ordinals protocol, Bitcoin’s average daily block size has exceeded two million bytes—a three-year high. Recently, someone even embedded a 3.9MB image, nearing Bitcoin’s current 4MB block limit. If demand persists, calls for Bitcoin scaling—a long-dormant debate—may resurface.
-
NFT Marketplaces
There is currently no OpenSea-like secondary marketplace for Bitcoin NFTs. Minting requires running a full node, while trading depends on Bitcoin address transfers, with no user-friendly interface. In response, platforms like BitKeep NFT Marketplace are integrating Bitcoin NFT trading to enhance liquidity and accessibility.
-
Domains and Other Infrastructure
Locating Bitcoin NFTs involves navigating complex, lengthy addresses. Similar to Ethereum, Bitcoin addresses are hard to remember. Services like ENS are needed. Projects like btc.us now offer .btc domain names, registered using STX tokens. If Bitcoin NFTs gain traction, demand for display and access tools like domain services will grow accordingly.
Building Bitcoin Layer 2 infrastructure is crucial. It enables Bitcoin to scale to more users, handle more transactions, and support diverse applications. Due to block size and throughput constraints, Bitcoin faces high fees and slow confirmation times. Layer 2 protocols aim to build scalable architectures atop Bitcoin, enabling fast, efficient processing of large-scale transactions and apps without compromising Bitcoin’s security or decentralization.
Technologies like State Channels, Lightning Network, and Sidechains can process massive transaction volumes without affecting the Bitcoin main chain. As BTC NFT popularity grows and miner revenue centralization intensifies, demand for Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions is increasing. This development is vital not only for Bitcoin’s growth and adoption but also for unlocking BTC’s liquidity. Combining BTC’s massive market cap and liquidity with native DeFi ecosystems opens vast possibilities.
5. Future and Development
The Ordinals protocol enables the Bitcoin network to process more transactions, enhancing speed and efficiency. NFTs and the BRC-20 token standard bring more decentralized application scenarios to the Bitcoin ecosystem, spanning digital art, gaming items, and DeFi. These new technologies and standards better meet user needs and open participation opportunities to a broader audience.
5.1 Current Pain Points in the BTC Ecosystem
The community holds sharply divided views on BRC-20: some believe it will spark another wave of FOMO on Bitcoin, while others see it as meaningless. Key concerns include:
-
Network Congestion Leading to High Costs:
Bitcoin’s public blockchain can store large amounts of data, leading to potential abuse—users may flood the network with irrelevant information, bloating blocks and increasing storage and transfer costs. However, the Bitcoin community has implemented mitigations such as SegWit and the Lightning Network to reduce network load.
-
On-chain inscription storage raises full-node operating costs, potentially leading to mining centralization:
As a decentralized system, every Bitcoin node stores the entire blockchain, so storage and computation costs rise with data growth. The community is addressing this through software upgrades and more efficient technologies. For example, the Schnorr signature upgrade aims to improve transaction efficiency and reduce node burden.
-
Poor scalability, lack of smart contract support, difficulty building a robust ecosystem:
Bitcoin was designed as digital cash, not a smart contract platform. While highly stable and secure—ideal for reliability-critical applications—its Layer 2 networks already host promising apps like hot wallets, exchanges, and NFT markets, supporting Bitcoin’s usability and expansion.
5.2 Looking Ahead
New narratives always face skepticism. The clash between old and new consensus indicates the BTC ecosystem is still in its early stages, where rewards and risks are equally high. BTC NFTs aren’t new this year, and their market liquidity remains underdeveloped. Compared to ETH and BTC market caps, any new technical breakthrough could unlock unimaginable growth. According to a Galaxy Research report, the rapidly growing Bitcoin NFT market could reach $4.5 billion by 2025.
6. Conclusion
As technology and markets evolve, new cultural layers and use cases will emerge. With the Bitcoin block reward halving approaching, Ordinals and BRC-20 offer fresh perspectives and directions for the crypto ecosystem. Going forward, Ordinals will find broader applications, driving progress in the Bitcoin ecosystem. In the digital world, identity verification and authentication are increasingly important. Wider adoption of Ordinals in NFTs and other crypto applications will make the ecosystem more secure and reliable.
The emergence of these technologies and standards is no accident. For the Bitcoin ecosystem, these innovations carry profound significance and demonstrate vast untapped potential. The future of the Bitcoin ecosystem remains promising. These technologies and standards will continue evolving, delivering more stable and superior performance.
Disclaimer
BitKeep has no affiliations with any third parties mentioned in this report that could affect the objectivity, independence, or impartiality of the content. All data and references cited in this report come from compliant sources; BitKeep makes no guarantees regarding their accuracy, truthfulness, or completeness.
The conclusions and opinions expressed in this article do not constitute investment advice for any related digital assets. BitKeep assumes no liability for losses incurred from the use of this report. Digital asset contract trading involves innovative products with high risk and complexity. Please rationally assess your investment capability and make cautious decisions. The information, opinions, and forecasts contained herein reflect the researchers' judgment at the time of publication and may change as industry dynamics and data evolve.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News