Crypto Development Guide: Web3 Security Technologies and Security Mechanisms
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Crypto Development Guide: Web3 Security Technologies and Security Mechanisms
A Guide to Web3 Account Abstraction, Reversible Transactions, and Other Popular Security Technologies and Mechanisms
In 2022, losses caused by security issues in the Web3 industry—such as smart contract vulnerabilities, bridge hacks, and phishing attacks—reached an all-time high. According to data from SAFEIS Security Research Institute, the total amount involved in blockchain security incidents last year exceeded $75.3 billion, making the security challenges facing Web3 more severe than ever before.
On one hand, these staggering security losses deter many who wish to enter the Web3 space. On the other hand, security is a primary and essential requirement for any high-quality blockchain project. To encourage broader participation in the development and growth of Web3, cryptocurrency security urgently needs improvement.

It's no surprise that 2023 will be a landmark year for breakthroughs in crypto security technology. These emerging technologies will directly enhance user safety in Web3 and increase the developmental value of projects. The following analysis will explore progress in cryptographic security technologies and the establishment of security mechanisms. We welcome your comments below—let’s discuss security together!
Web3 Security Technologies
As is widely known, Web3 security should not rely on centralized mechanisms. However, due to the early-stage development of cryptographic technology, many Web3 projects either adopt centralized off-chain security measures or suffer from technical vulnerabilities. As more participants join Web3, security issues have become increasingly apparent. Cryptographic security is one of the key cornerstones for the long-term development of Web3. Below are some cryptographic security technologies expected to gain attention this year.
Account Abstraction
Account Abstraction is seen as a pivotal technology for safeguarding crypto assets and driving Web3 adoption. Specifically, account abstraction decouples signers from accounts, allowing accounts to define their own logic for valid transactions without relying on ECDSA private-key signature algorithms. It aims to simplify the complexity of current wallet usage, enabling ordinary users to interact with crypto wallets more easily and securely. Avatar is currently the first crypto wallet on the market to implement account abstraction. By integrating OAuth protocols, users can log in with their Google accounts in one click, eliminating the need to install browser extensions, download DApps, or re-register wallets.
Additionally, Social Recovery functionality can be built atop account abstraction, allowing wallet owners to designate a group of trusted individuals who can move funds under specific circumstances—such as when the original owner loses their keys. For example, Argent Wallet is a decentralized wallet leveraging Social Recovery; its enhanced security has made it one of the most popular “smart contract wallets.” Further technical advancements remain for Web3 developers to explore. For deeper insights into this technology, refer to “The Future of Ethereum Account Abstraction—EIP-4337”.
Reversible Transactions
The irreversibility of blockchain transactions is a double-edged sword. Frequent crypto thefts occur, yet there is no “undo” button to cancel a transaction, leaving many victims unable to recover lost funds. Reversible transaction-enabled crypto assets could potentially reverse such thefts. In the second half of last year, building upon Vitalik Buterin’s 2018 proposal for a DAO-governed reversible ERC-20 standard, researchers at Stanford University introduced two new standards: ERC-20R and ERC-721R.
This technology allows funds to be returned to their rightful owners post-transaction through a decentralized judicial voting process, without deleting the original transaction from the blockchain. It introduces a “decentralized court” mechanism: when assets are stolen, victims can request asset freezing, and the “court” votes on whether to proceed. After freezing, the court evaluates evidence from both sides to determine rightful ownership and resolve disputes.
However, shifting from irreversible to reversible transactions raises significant trust-related challenges. Who can initiate a dispute? What if malicious false accusations lead to fund blockages? Who qualifies as a judge? How to prevent corrupt or bribed judges? Moreover, if disputed funds have already been used in cross-transactions, reversing them would trigger lengthy dispute periods. For decentralized exchanges (DEXs), waiting for fund resolution would inevitably hurt liquidity and hinder application development. Therefore, numerous technical hurdles around reversible transactions remain unresolved.
Cross-Chain Technology
Cross-chain security remains crucial for breaking down blockchain data silos. Several projects have already made progress in this area. For instance, Stargate Finance is the first DApp built on the LayerZero protocol. Using its proprietary “Delta (∆) algorithm,” it claims to “perfectly” solve the “impossible trinity” problem. Leveraging LayerZero’s interoperability features, it connects liquidity across different public chains, enhancing capital efficiency while maintaining security. It has established the first fully composable native asset bridge, making cross-chain liquidity transfers seamless, unified, and secure.

Meanwhile, the DEX platform Chainge Finance uses DCRM technology to protect users’ cross-chain assets. DCRM splits a complete private key into multiple fragments, which never need to be reassembled during generation, storage, or use. These fragments are then distributed across different nodes. By applying this technology, Chainge automatically aggregates data from multiple DEXs to find optimal trading rates and splits orders across multiple chains, maximizing user benefits.
In summary, unlike mainstream cross-chain approaches such as custodial models, hash time-lock contracts, and relayer-based systems, many projects are now building security barriers through technological innovation. Whether these solutions truly meet Web3’s cross-chain security needs remains to be tested over time.
Web3 Security Mechanisms
Technology development takes time, and given the persistent threats to crypto security, many Web3 participants are turning to external security mechanisms to mitigate risks as much as possible.
Decentralized Auditing
Security audits are a critical step for Web3 projects to avoid risks. This year, audit services are expected to evolve toward greater accessibility and decentralization. On one hand, more projects are recognizing the importance of audits, leading to increased demand for professional auditing to identify potential vulnerabilities. Earlier this year, the TinTin Meeting series invited industry audit experts to discuss Web3 audit security, providing valuable knowledge for both project teams and users. For further details, see “Smart Contract Audits: The Most Important Line of Defense for Blockchain Security”.
On the other hand, auditing is moving toward decentralization and increasingly adopting DAO-like characteristics. Trends from security auditors like Code4rena and Immunefi.com suggest that blockchain security work will increasingly rely on small, agile, ad-hoc teams assembled to address the unique security needs of individual projects.

Take Code4rena as an example: it organizes audit competitions involving three roles—Wardens (security researchers), Sponsors (projects), and Judges (evaluators)—to conduct comprehensive audits. So far, Code4rena has partnered with major platforms including OpenSea, ENS, zkSync, Aave, Alchemix, and Nouns.
Decentralized Insurance
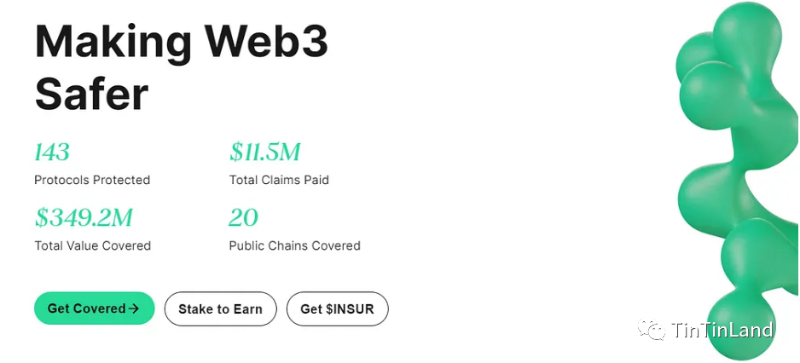
Following the LUNA and FTX collapses last year, many industry participants recognized the importance of safeguards, giving rise to demand for decentralized insurance. According to statistics, decentralized insurance services had already paid out $11.5 million by the end of 2022. Many investors are now turning to insurance to minimize risk and protect their assets.
Decentralized insurance can provide protection against inherent risks of crypto assets. As more users enter the crypto market, demand for risk insurance products is expected to grow. Premiums for these products range from 0.2% to 0.9% per month and are currently in short supply, with many services already sold out. Crypto insurance is still in its infancy, facing challenges in liquidity, capital efficiency, product usability, and cost—all areas expected to see improvements in 2023.
Overall, this year the Web3 industry will continue advancing on both cryptographic security technologies and security mechanisms. Moreover, due to Web3’s decentralized nature, innovations in crypto security occur in open, transparent, and open-source environments, allowing us to monitor progress and effectiveness in real time—enabling faster resolution of Web3 security issues. In many ways, the success of Web3 hinges on how effectively it innovates at the security layer to address new challenges posed by diverse application architectures—providing higher-level security for the application layer and greater peace of mind for ecosystem users.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















