ROMA: The Central Framework of Open-Source Meta-Agent
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

ROMA: The Central Framework of Open-Source Meta-Agent
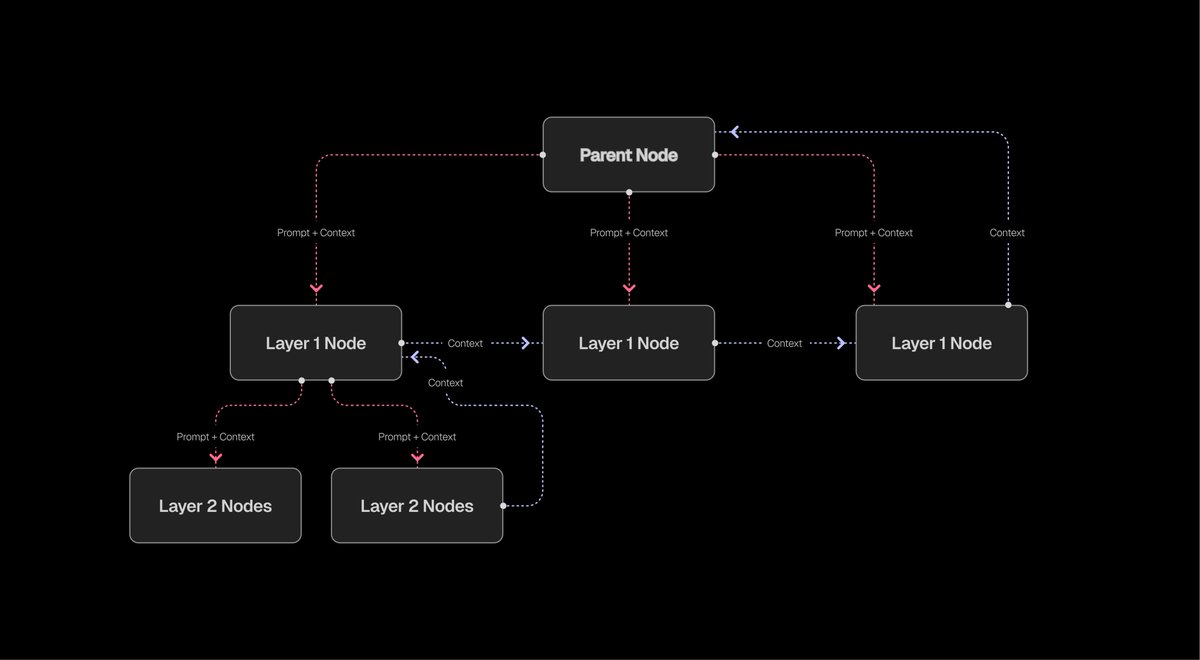
The core of ROMA is a structure designed for multi-agent systems: a hierarchical recursive task tree.
Author: Sentient China Chinese
Introducing ROMA (Recursive Open Meta-Agent)
ROMA (Recursive Open Meta-Agent) is an open-source meta-agent framework for building high-performance multi-agent systems. It coordinates multiple simple agents and tools to collaboratively solve complex problems.
The core of ROMA is a structure designed for multi-agent systems: a hierarchical recursive task tree.
In this system, the root node breaks down complex goals into multiple subtasks and passes context to child nodes for execution; once subtasks are completed, results are aggregated back to the root node. Through this context flow mechanism, ROMA simplifies and stabilizes the construction of agents capable of handling medium-to-long-range, multi-step tasks.
Example
For instance, you want an agent to help you write a report on climate differences between Los Angeles and New York.
In ROMA:
-
The top-level root node decomposes the task into multiple subtasks:
Subtask 1: Research the climate of Los Angeles.
Subtask 2: Research the climate of New York.
-
Each subtask can invoke specialized agents and tools, such as AI search models or weather APIs.
-
After both research tasks are complete, the root node generates a "comparative analysis" task to synthesize the results into a complete report.
This structure makes task decomposition and result aggregation clear and transparent.
Advantages of ROMA
ROMA makes building multi-agent systems more straightforward and transparent.
-
Uses Pydantic for structured input/output, ensuring clear and traceable context flow;
-
Developers can precisely observe the reasoning process, making it easier to debug, optimize prompts, and replace agents;
-
System transparency enables rapid iteration of "context engineering" instead of black-box operations;
-
Modular design allows insertion of agents, tools, or models at any node, including LLM-based specialized agents or "human review" steps;
-
The tree architecture natively supports parallelization, balancing flexibility and high performance, ideal for large and complex tasks.
Performance Validation: ROMA Search
To validate the framework's effectiveness, Sentient built ROMA Search — a web search agent based on the ROMA architecture (without domain-specific optimization).
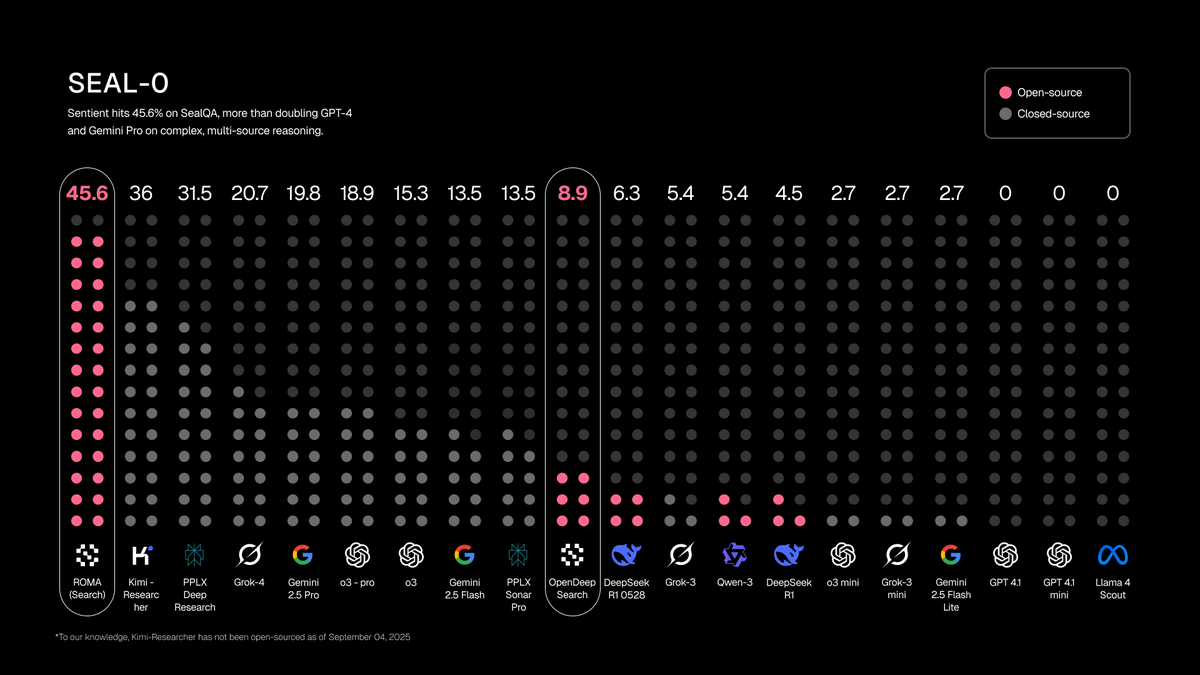
On SEALQA's most challenging subset, Seal-0 (testing complex multi-source reasoning), ROMA Search achieved 45.6% accuracy, setting a new record.
-
Outperforms the previous leader Kimi Researcher (36%);
-
Nearly twice as accurate as Gemini 2.5 Pro (19.8%);
-
In the open-source category, ROMA Search vastly surpasses Sentient’s own Open Deep Search (8.9%).
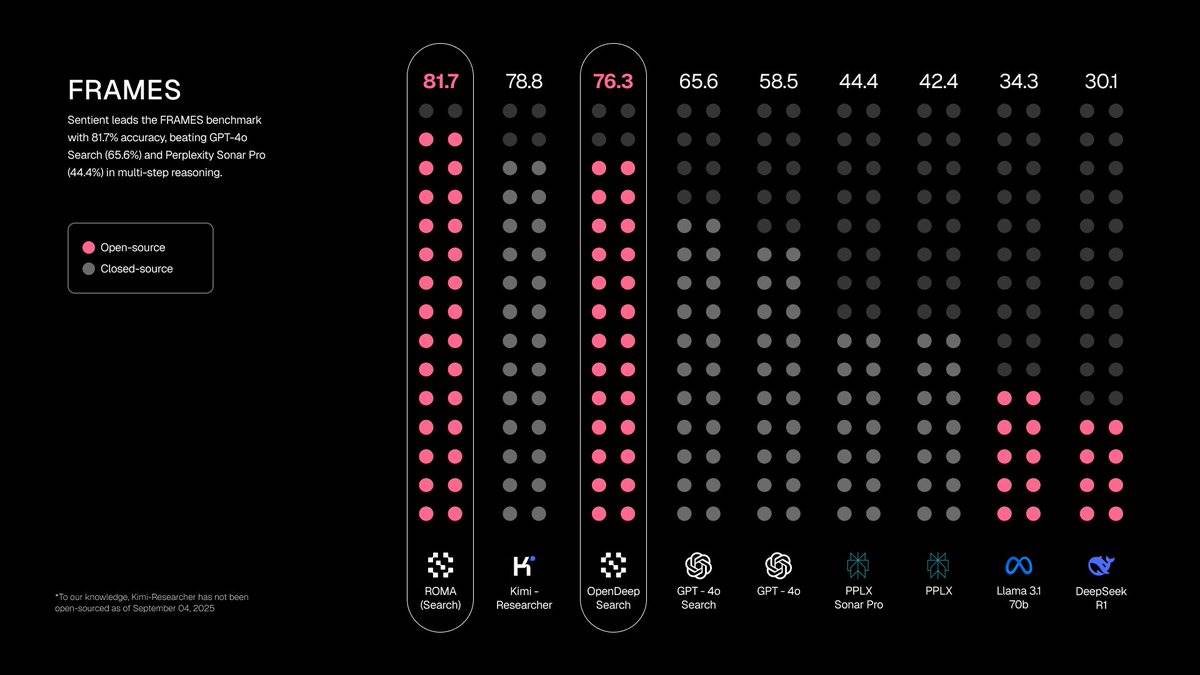
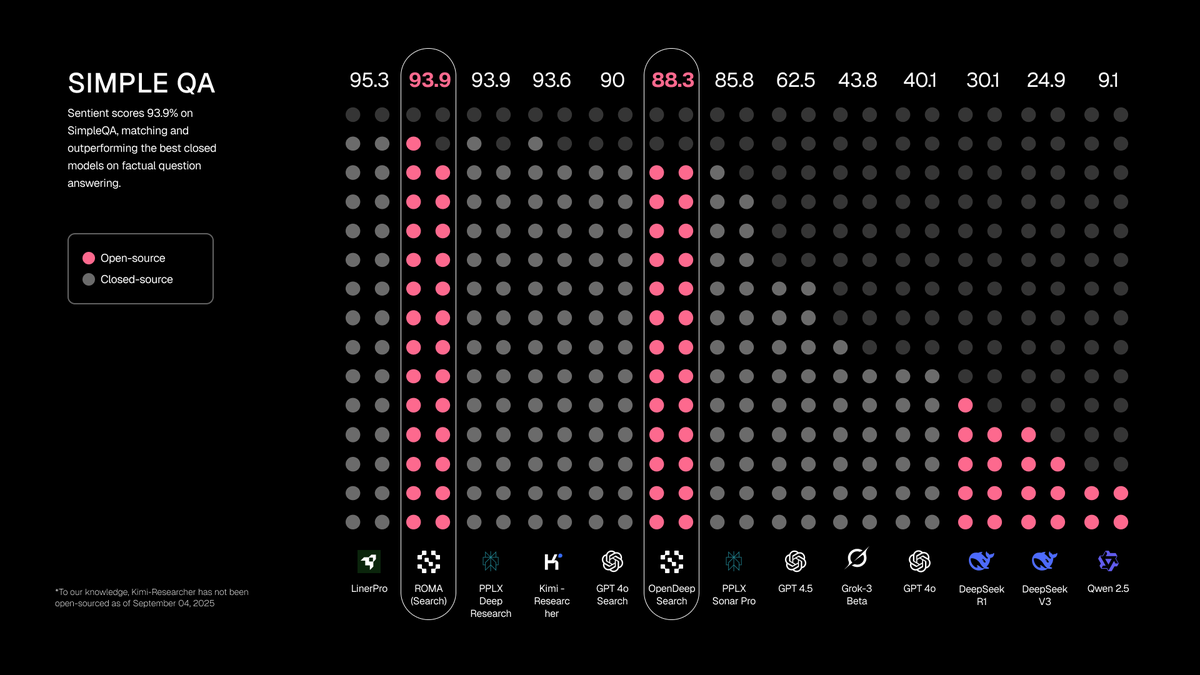
Additionally, ROMA Search achieves state-of-the-art performance on FRAMES (multi-step reasoning) and near-top-tier performance on SimpleQA (fact retrieval), demonstrating strong cross-task generalization.
Openness and Extensibility of ROMA
ROMA is fully open-source and highly extensible.
Search is just the beginning—anyone can:
-
Insert new agents;
-
Extend the framework with custom tools;
-
Apply ROMA to financial analysis, scientific research reports, creative content generation, and more.
ROMA provides a solid central backbone; real breakthroughs will come from the ecosystem built by the community.
Why "Long-Horizon Tasks" Challenge Agents
AI has made significant progress on single-step tasks (e.g., summarizing articles, writing emails, arithmetic), but remains fragile when facing "long-horizon tasks"—goals requiring multi-step reasoning and continuous actions.
The key issue: error accumulation.
A model may have a 99% success rate per step, but when required to perform ten consecutive operations, the overall success rate drops sharply. One hallucination, misreading, or context loss can lead to total failure.
Therefore, building systems that reliably handle multiple subtasks and cross-source reasoning is extremely difficult.
Solving this requires overcoming two major challenges:
-
Architectural Level (Meta-Challenge): How to design systems that can reliably execute long-horizon reasoning even under error accumulation?
-
Task Level (Task-Specific Challenge): For specific goals, how to determine optimal task decomposition, tools, models, prompts, and validation steps?
Search tasks are ideal examples:
They are inherently multi-step (retrieve → read → extract → cross-validate → synthesize) and depend on real-time, complex external knowledge.
For example: "Among movies with a budget of $350 million or more, how many were not the highest-grossing movie of their release year?"
To answer, an agent must:
-
Decompose the question (find high-budget movies → find annual box office champions);
-
Retrieve up-to-date data from multiple sources;
-
Perform logical reasoning on results;
-
Synthesize a final answer.
During this process, hallucinations, mismatches, or inefficient loops can cause failure. Traditional agent architectures often hide internal reasoning paths, making tuning and improvement difficult.
ROMA's Solution
ROMA addresses long-horizon task challenges through a recursive, hierarchical system structure.
Each task is a "node":
-
Can be executed directly;
-
Or decomposed into subtasks;
-
Or aggregate sub-results.
The tree structure ensures transparent and traceable context flow, enabling step-by-step optimization.
On this backbone, developers only need to select appropriate tools, prompts, or validation mechanisms for each node to build robust multi-agent systems.
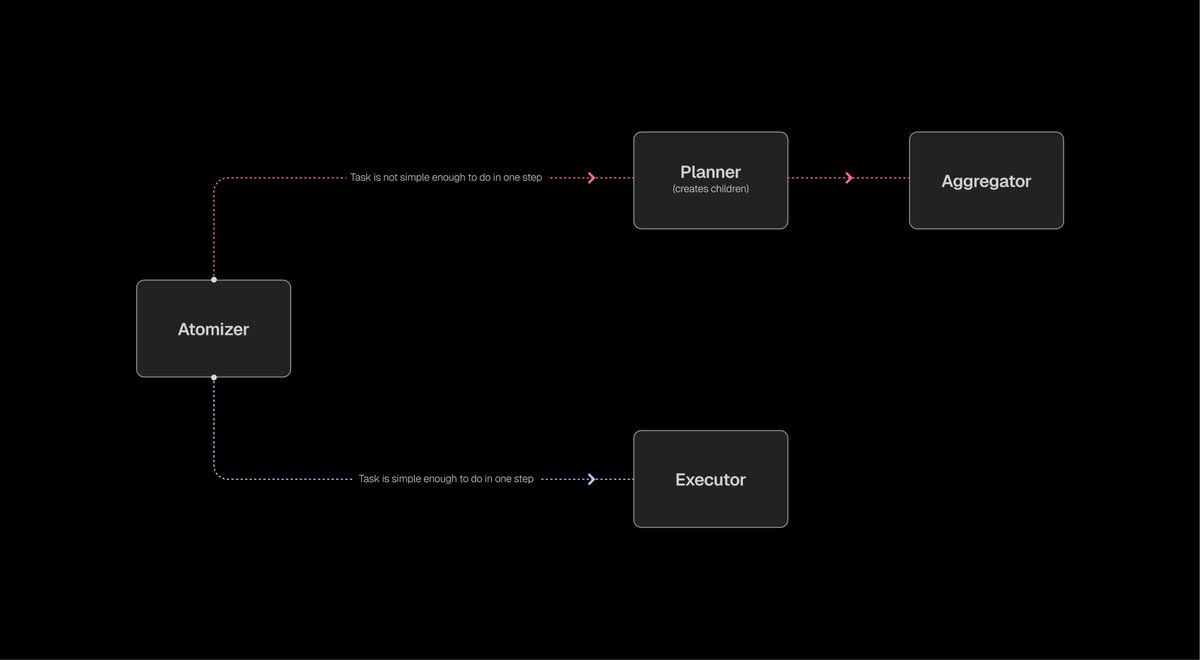
ROMA Execution Flow (using ROMA Search as example)
1️⃣ Atomizer — Assess Task Complexity
The system starts with the main task, determining whether it can be handled by a single agent or needs further decomposition.
2️⃣ Planner — Decompose Subtasks
If the task is complex, the node becomes a planner, breaking the goal into smaller tasks, e.g.:
-
Search for movies with budgets ≥ $350 million;
-
Search for the highest-grossing movies in corresponding years;
-
Analyze and generate a list of qualifying movies.
Each subtask creates a child node; nodes may depend on or run in parallel with others.
3️⃣ Executor — Execute Subtasks
When a subtask is simple enough, the node becomes an executor, invoking relevant tools or models (e.g., search API, information extraction model), then passing output to subsequent nodes.
4️⃣ Aggregator — Aggregate Results
After all executors finish, the root node becomes an aggregator, combining results, validating consistency, and generating the final answer.
Human-in-the-Loop & Stage Tracing
Humans can intervene at any node to verify facts or add context.
ROMA can also request user confirmation of subtasks during planning to avoid early misunderstandings.
Even without human input, the stage tracing system fully logs inputs and outputs at every node, helping developers quickly identify errors and optimize logic.
ROMA's Extensibility
The above example shows only single-layer decomposition.
In practice, ROMA supports recursive, multi-layer decomposition, forming deep task trees.
When subtasks are independent, the system automatically executes them in parallel, enabling efficient computation across hundreds or thousands of nodes.
Ready to Shape the Future of AI Agents?
ROMA Search is just the beginning.
We have fully open-sourced ROMA and invite global developers to explore together.
-
Builders: Try building agents in ROMA—swap models, test multimodal capabilities, or create generative tasks (e.g., comics, podcasts) and analytical tasks (e.g., research reports).
-
Researchers: Advance meta-agent architecture research using ROMA. Its transparent stage tracing offers unique insights into agent interaction and context flow.
Proprietary systems rely on single companies; ROMA evolves through the collective intelligence of the open-source community.
Join ROMA now:
GitHub repository:
https://github.com/sentient-agi/ROMA
Video introduction:
https://youtu.be/ghoYOq1bSE4?feature=shared
References:
¹https://arxiv.org/pdf/2506.01062
²https://moonshotai.github.io/Kimi-Researcher/
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















