How to Achieve 220x Returns Using a Hyperliquid Market-Making Bot?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

How to Achieve 220x Returns Using a Hyperliquid Market-Making Bot?
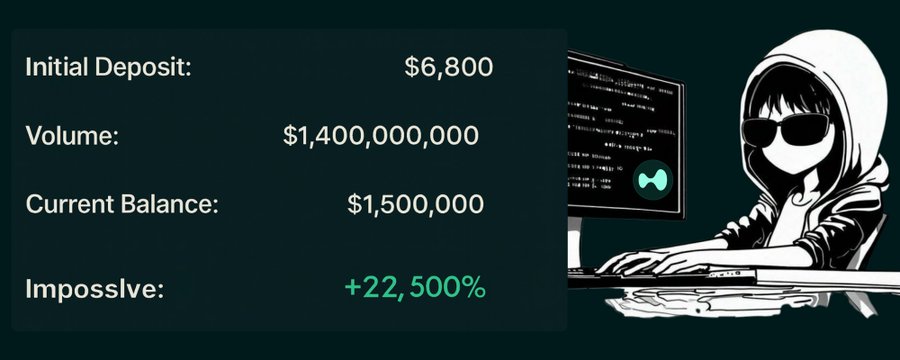
🤔Grow $6,800 to $1.5 million within two weeks.
By: The Smart Ape
Translated by: Saoirse, Foresight News
This is a perfect case demonstrating the importance of "learning to code" — with programming, you can grow $6,800 into $1.5 million in just two weeks on the cryptocurrency exchange Hyperliquid.
Not long ago, a Hyperliquid trader achieved exactly that.
Even more astonishing is that this trader took almost no risk. He didn't bet on market direction or chase trending assets; instead, he relied solely on a sophisticated market-making strategy centered around "maker rebates," combined with automation and strict risk management.
Hyperliquid's Market-Making Mechanism
Before diving into the strategy, we need to understand how market making works on Hyperliquid. Hyperliquid is an order-book-based exchange where users can place two types of orders:
-
Bid orders: "buy orders" (e.g., "I want to buy SOL tokens at $100")
-
Ask orders: "sell orders" (e.g., "I want to sell SOL tokens at $101")
These pending orders collectively form the "order book." Traders placing bid or ask orders are known as "makers."
-
The core role of makers is to "provide liquidity": by placing limit orders in advance, they add tradable depth to the market.
-
In contrast, "takers" are traders who immediately execute against existing orders in the book (e.g., "market buy" a token at the best available ask price).
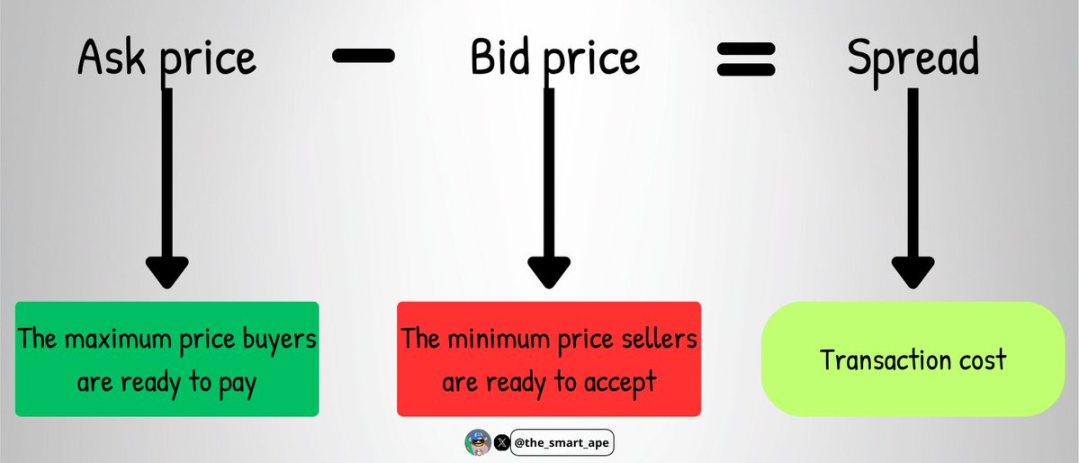
Makers are crucial to market health: their presence keeps bid-ask spreads low; without them, traders could face "unfair pricing" and large slippage.
Key Insight: Maker Rebates
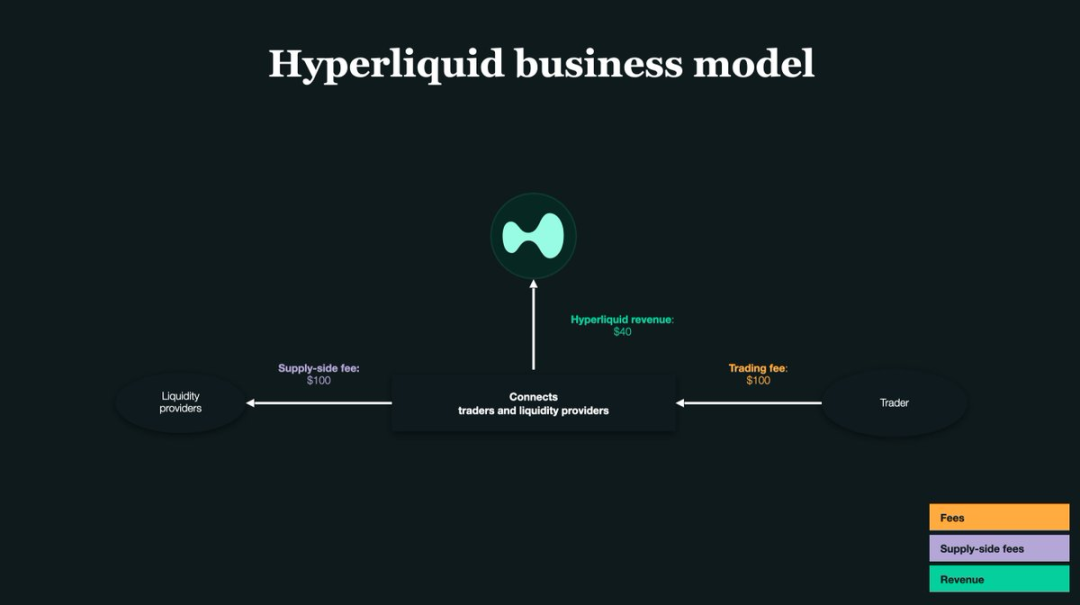
Liquidity is the lifeblood of exchanges — to incentivize users to act as makers and provide liquidity, Hyperliquid offers "trading rebates": whenever a maker’s order is filled, the platform pays back a small rebate.
On Hyperliquid, the rebate rate is approximately 0.0030% per trade — meaning for every $1,000 traded, the maker earns $0.03 in rebate.
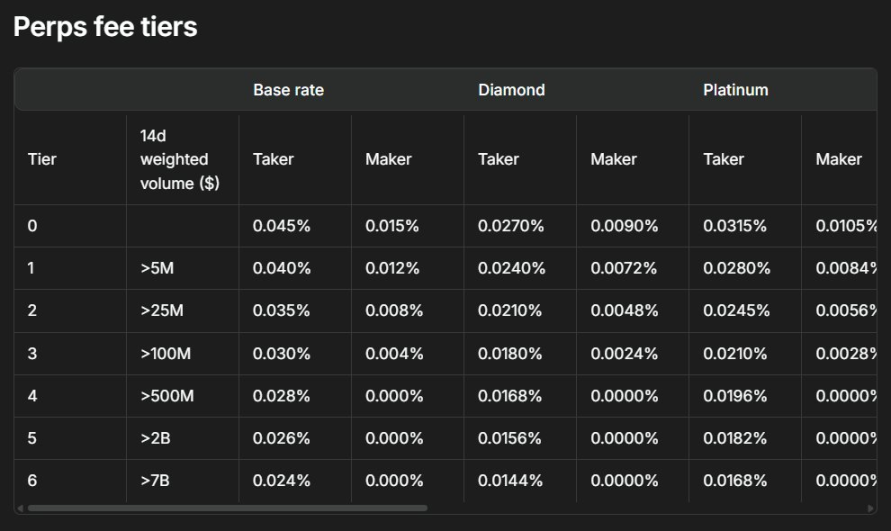
It was precisely this seemingly tiny rebate that enabled the trader to turn $6,800 into $1.5 million. His core strategy was "one-sided quoting": placing limit orders on only one side of the order book (either bids or asks), and quickly canceling or switching sides as prices moved.
In simple terms, his logic was: provide liquidity on one side only to earn rebates, while using bots to dynamically adjust order direction in real time, avoiding directional exposure and risk. Ultimately, massive trading volume generated through automated high-frequency trading turned minuscule per-trade rebates into substantial profits.
The Core Problem with Traditional Market Makers
Most market makers place orders simultaneously on both the "bid" and "ask" sides of the order book.
For example: you place two orders — a bid to buy 1 SOL at $100, and an ask to sell 1 SOL at $101.
If both orders fill, you profit $1 from the spread ("buy low, sell high").
But this model has a critical flaw: inventory risk.
-
If the bid fills but the ask doesn’t: you’re left holding SOL tokens;
-
If the ask fills but the bid doesn’t: you’re left holding stablecoins (e.g., USDT).
If the market then moves against your position, these unintended holdings can lead to significant losses.
This is why the Hyperliquid trader chose "one-sided quoting": by placing orders on only one side, he could tightly control his inventory and avoid holding unwanted assets. However, this approach comes at a cost — higher vulnerability to "adverse selection."
What Does "Getting Arbitraged" Mean?
Consider this scenario: you place a bid to "buy SOL at $100." Suddenly, negative news causes SOL’s price to drop instantly to $90.
-
Your "$100 buy" order remains active in the book, not yet canceled;
-
Faster traders immediately sell SOL to you at $100 (executing against your bid);
-
Result: you overpaid by 10% for SOL, and despite earning the rebate, suffer a large loss.
This is called "adverse selection," commonly referred to as "getting arbitraged."
Therefore, when using a "one-sided quoting" strategy, precision and speed are critical — the entire strategy hinges on the bot’s reaction speed and accuracy.
High-Frequency Trading Infrastructure
To avoid being arbitraged, the trader built an "ultra-fast execution system," including:
-
Co-location: hosting his trading server physically close to Hyperliquid’s servers to minimize network latency;
-
Automation: the bot adjusts quotes thousands of times per second, enabling real-time price tracking;
-
Real-time risk control: automatically closing or adjusting positions before inventory risk spirals out of control.
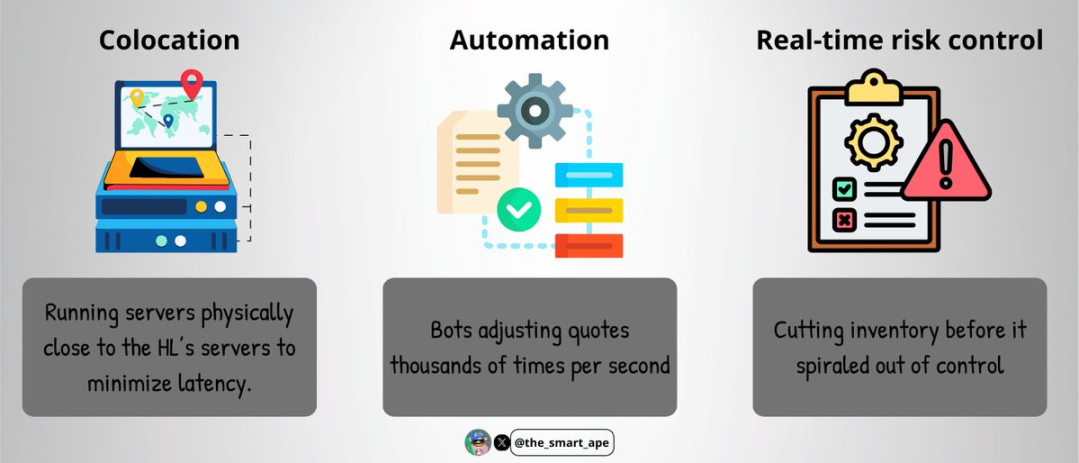
Building such infrastructure requires both high costs and extreme technical complexity — which is why only a few professional market makers can deploy such systems.
Technically, his trading bot was likely written in C++ or Rust (languages known for "high speed" and "low latency"), and hosted near Hyperliquid’s "matching engine" to ensure priority order matching.
The bot uses WebSocket or gRPC protocols to receive real-time order book data, completing "place order - cancel - switch side" operations within milliseconds — ensuring continuous rebate earnings while avoiding stale orders due to price changes.
How to Maintain "Delta Neutrality"?
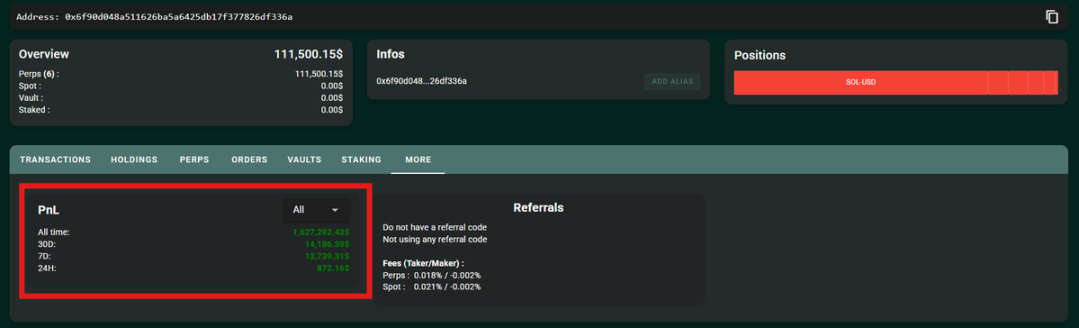
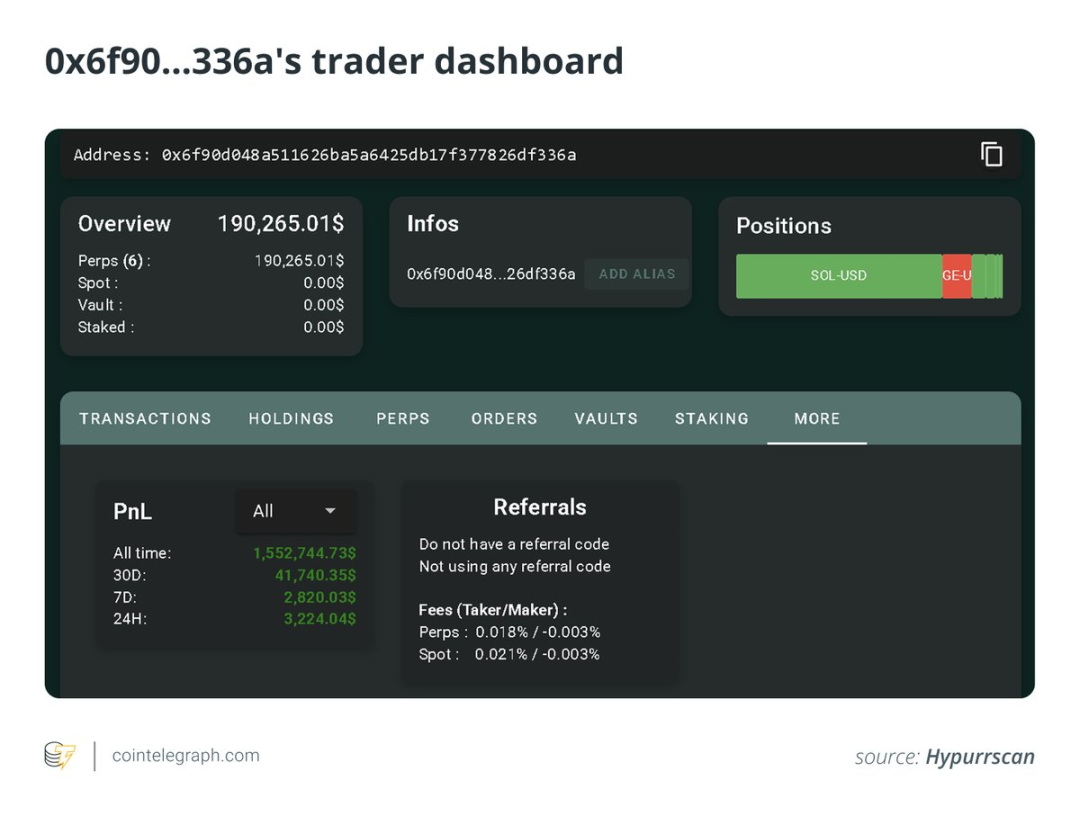
Most impressively, the trader maintained "delta neutrality" throughout: despite total trading volume reaching several billion dollars, his net exposure remained under $100,000.
How did he achieve this?
-
The bot continuously monitors changes in SOL inventory;
-
A strict risk ceiling is set (net exposure never exceeds $100,000);
-
Once exposure approaches the limit, the bot immediately stops trading on the current side and switches to the opposite side, rebalancing via reverse trades.
He avoided "spot-futures arbitrage" and operated entirely in the "perpetual futures" market — since all trades occur in the same market, hedging and risk control are simpler.
However, this strategy demands extreme discipline and precision: even the smallest operational error could result in massive losses.
The Underlying Math
The profit calculation behind the strategy is actually straightforward:
-
Within two weeks, the trader executed ~$1.4 billion in total volume;
-
Maker rebate rate: 0.003% per trade;
-
Rebate-only profit = $1.4B × 0.003% ≈ $420,000.
On top of this, he applied a "profit reinvestment" strategy — immediately recycling each rebate into new trades, amplifying returns via compounding. Ultimately, total profit reached $1.5 million.
All of this started with just $6,800 in initial capital.
Why You Can’t Simply Copy This Strategy
You might think: "If it works so well, why not just copy his trades?" But in reality, this strategy is nearly impossible to replicate, primarily because:
-
You lack his "execution speed": the combination of co-located servers and low-latency code is unattainable for retail traders;
-
You lack his "capital scale": although starting with only $6,800, compounding profits rapidly grew his trading size to institutional levels;
-
You lack "precise code and bots": his bot has been finely tuned to adapt to every minor order book fluctuation, which most developers cannot reproduce;
-
You lack "24/7 infrastructure and monitoring": crypto markets operate 24/7, requiring constant oversight to handle unexpected risks.
In short, this is a "professional-grade high-frequency trading system," far beyond what ordinary retail traders can easily replicate.
Potential Risks of This Strategy
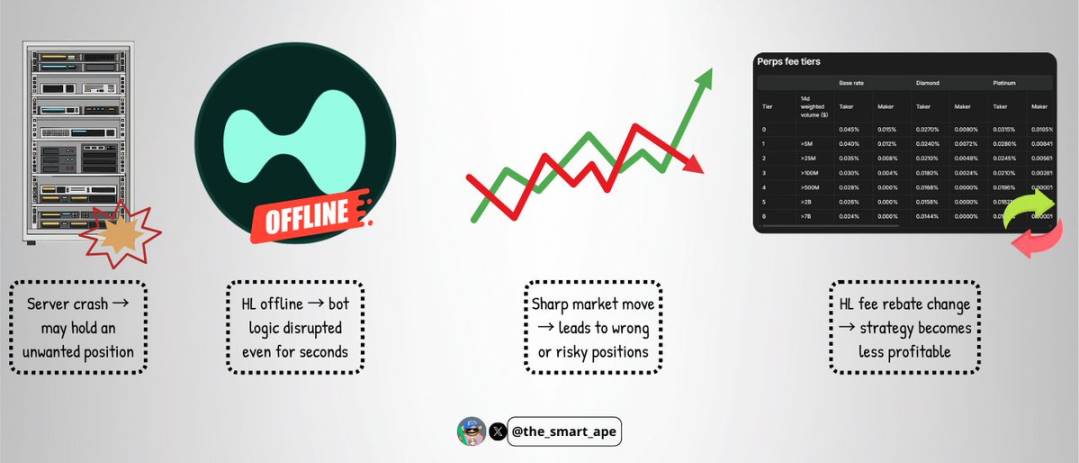
Even with such a sophisticated bot, non-trivial risks remain:
-
Server failure: if the server crashes, the bot may fail to cancel orders in time, leaving it exposed to large risky positions;
-
Exchange failure: though rare, if Hyperliquid experiences downtime or glitches, it could disrupt the bot’s logic within seconds;
-
Extreme market volatility: severe price swings could break the "one-sided quoting" balance, causing the strategy to fail and generate losses;
-
Fee structure changes: if Hyperliquid adjusts maker rebate rates or trading fees, the profitability of this strategy could collapse overnight.
While elegant, this strategy is not "foolproof."
Conclusion
Growing $6,800 into $1.5 million in two weeks may sound like "gambling on meme coins," but in reality, it reflects solid technical skills, strict discipline, and meticulous system design.
This is an excellent case study showcasing how to "scale maker rebates," "maintain delta neutrality," and minimize directional risk.
The key takeaway: trading isn’t just about "predicting prices." Sometimes, the most profitable strategies come from deeply understanding market mechanics and building systems that create value in corners others overlook.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News