From zkVM to Open Proof Market: RISC Zero and Boundless Explained
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

From zkVM to Open Proof Market: RISC Zero and Boundless Explained
ZK technology is evolving from a single scaling tool into a universal foundation for blockchain trusted computing.
Author: 0xjacobzhao
In the blockchain domain, cryptography is the core foundation of security and trust. Among its innovations, zero-knowledge proofs (ZK) can compress arbitrarily complex off-chain computations into short proofs that are efficiently verified on-chain—without relying on third-party trust—and can selectively hide inputs to protect privacy. With its unique combination of efficient verification, universality, and privacy preservation, ZK has become a key solution for scaling, privacy, cross-chain, and other application categories. Despite current challenges such as high proof generation overhead and complex circuit development, ZK's engineering feasibility and real-world adoption have far surpassed alternative approaches, making it the most widely adopted trusted computing framework.
1. Evolution of the ZK Landscape
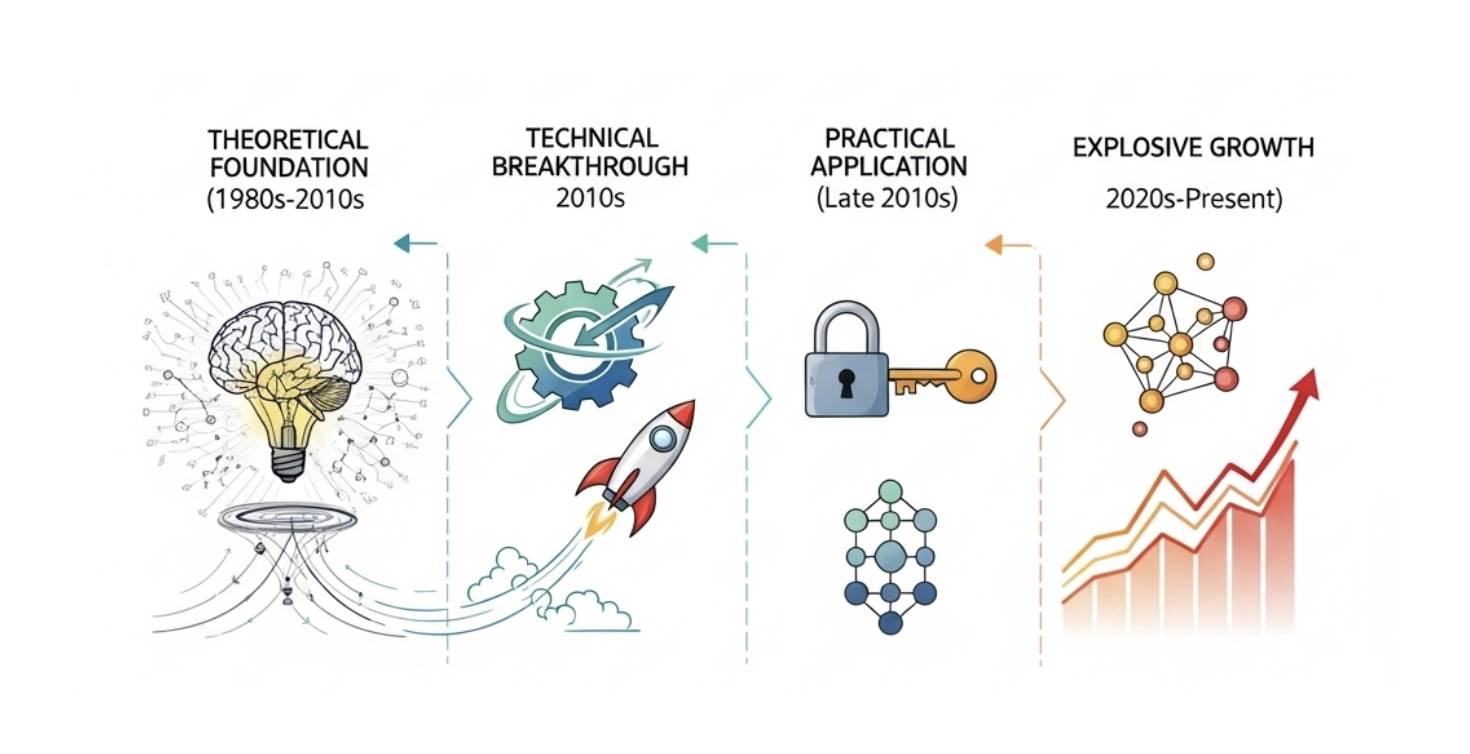
The development of zero-knowledge proof (ZK) technology has not been instantaneous but rather the result of decades of theoretical accumulation and engineering exploration. It can be broadly divided into the following key phases:
1. Theoretical Foundations and Technical Breakthroughs (1980s–2010s): The concept of ZK was introduced by MIT researchers Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff, initially remaining within interactive proof theory. In the 2010s, the emergence of non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (NIZK) and zk-SNARKs significantly improved proof efficiency, though early versions still relied on trusted setups.
2. Blockchain Applications (Late 2010s): Zcash brought zk-SNARKs into privacy-preserving payments, achieving the first large-scale blockchain deployment. However, due to high proof generation costs, practical use cases remained limited.
3. Explosive Growth and Expansion (2020s–Present): This period marks ZK’s full entry into mainstream industry adoption:
-
ZK Rollup: By batching computation off-chain and submitting proofs on-chain, ZK rollups achieve high throughput while inheriting security, becoming a core Layer 2 scaling path.
-
zk-STARKs: StarkWare introduced zk-STARKs, eliminating the need for trusted setup and enhancing transparency and scalability.
-
zkEVM: Teams like Scroll, Taiko, and Polygon work toward EVM bytecode-level proving and seamless migration of existing Solidity applications.
-
General-purpose zkVM: Projects like RISC Zero, Succinct SP1, and Delphinus zkWasm support verifiable execution of arbitrary programs, expanding ZK beyond scaling into the role of a “trusted CPU.”
-
zkCoprocessor packages zkVM as a co-processor, enabling outsourcing of complex logic (e.g., RISC Zero Steel, Succinct Coprocessor).
-
zkMarketplace commercializes proof computation power, forming decentralized prover networks (e.g., Boundless), advancing ZK into a universal computing layer.
To date, ZK technology has evolved from an obscure cryptographic concept into a core module of blockchain infrastructure. It not only supports scaling and privacy protection but also demonstrates strategic value in cutting-edge areas such as cross-chain interoperability, financial compliance, and artificial intelligence (ZKML). As toolchains, hardware acceleration, and proof networks continue to improve, the ZK ecosystem is rapidly moving toward scale and ubiquity.
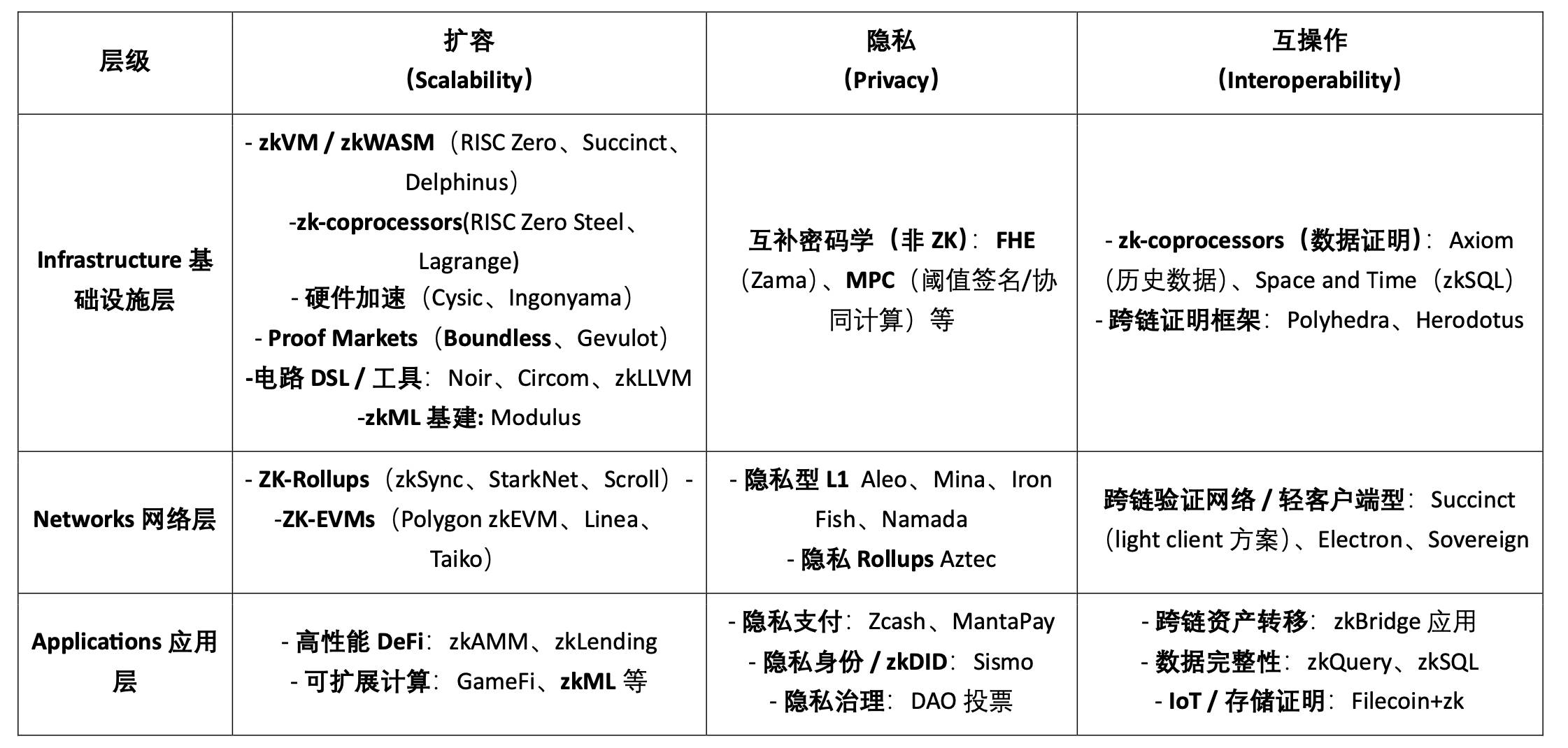
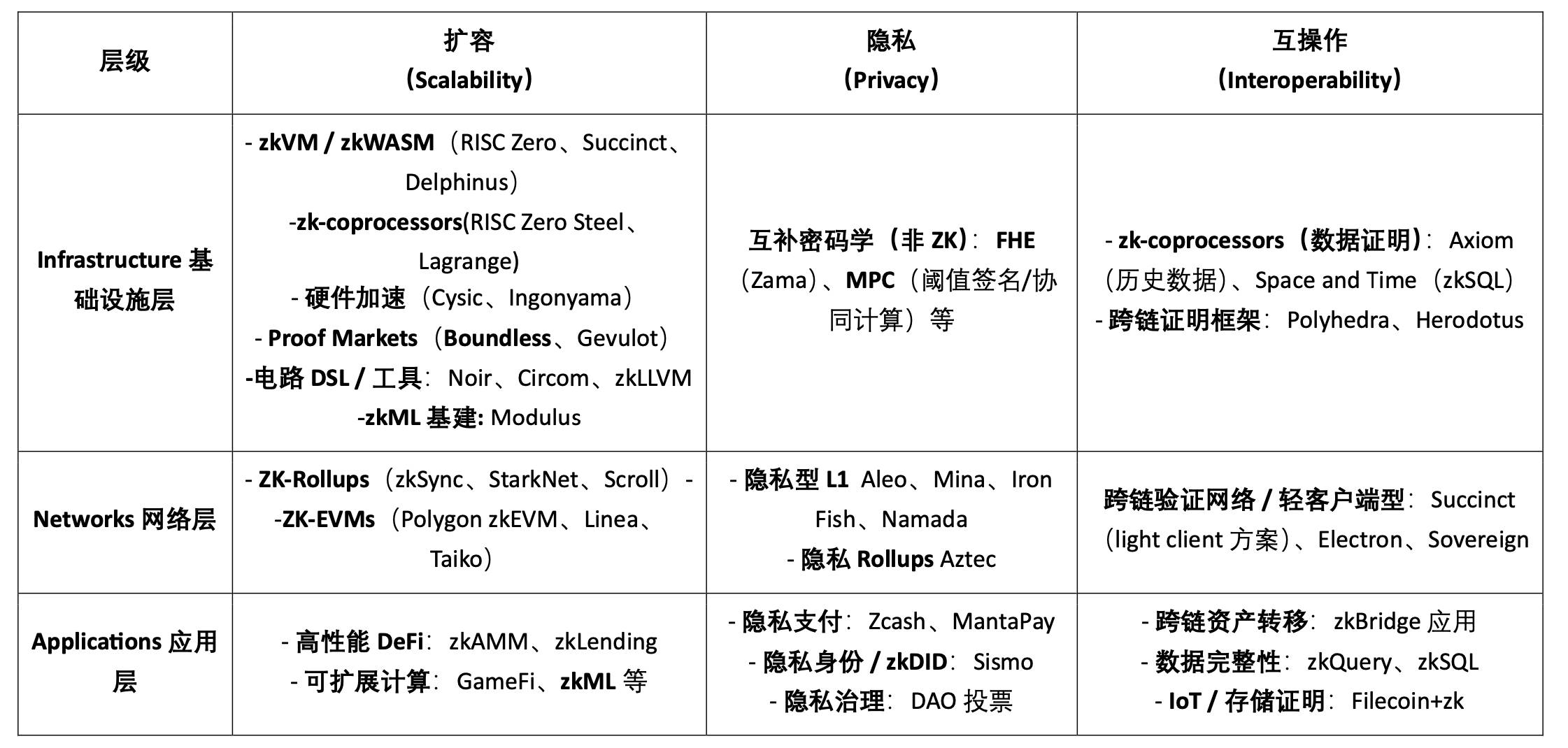
2. ZK Technology Application Landscape: Scaling, Privacy, and Interoperability
Scalability, Privacy, and Interoperability & Data Integrity represent the three foundational scenarios of ZK "trusted computing" today—addressing native pain points of blockchain including performance bottlenecks, lack of privacy, and multi-chain trust issues.
-
Scalability is the earliest and most widespread application of ZK. The core idea is to move transaction execution off-chain and verify it on-chain via compact proofs, significantly increasing TPS and reducing costs without sacrificing security. Key approaches include zkRollup (zkSync, Scroll, Polygon zkEVM) for transaction batching; zkEVM, which builds circuits at the EVM instruction level for Ethereum-native compatibility; and more general zkVMs (RISC Zero, Succinct) supporting verifiable outsourcing of arbitrary logic.
-
Privacy Protection aims to prove the legitimacy of transactions or actions while avoiding exposure of sensitive data. Typical applications include private payments (Zcash, Aztec), ensuring fund transfers are valid without revealing amounts or counterparties; private voting and DAO governance, enabling governance without disclosing vote content; and private identity/KYC (zkID, zkKYC), proving "eligibility" without revealing additional information.
-
Interoperability & Data Integrity is the key path for ZK to solve trust issues in a multi-chain world. By generating proofs of another chain's state, cross-chain interactions can bypass centralized relays. Common forms include zkBridge (cross-chain state proofs) and light client verification (efficiently verifying source chain block headers on target chains), with representative projects like Polyhedra and Herodotus. Additionally, ZK is widely used for data and state proofs, such as Axiom’s and Space and Time’s zkQuery/zkSQL, or integrity verification in IoT and storage scenarios, ensuring off-chain data can be trusted when brought on-chain.
Beyond these three core scenarios, ZK technology holds promise for broader industry applications: AI (zkML), where proofs validate model inference or training for "trusted AI"; financial compliance, such as exchange reserve proofs (PoR), clearing, and auditing to reduce trust costs; and gaming and scientific computing, ensuring authenticity of logic and experimental results in GameFi or DeSci. Fundamentally, these are all extensions of "verifiable computation + data proof" across different industries.
3. Beyond zkEVM: The Rise of General-Purpose zkVM and Proof Markets
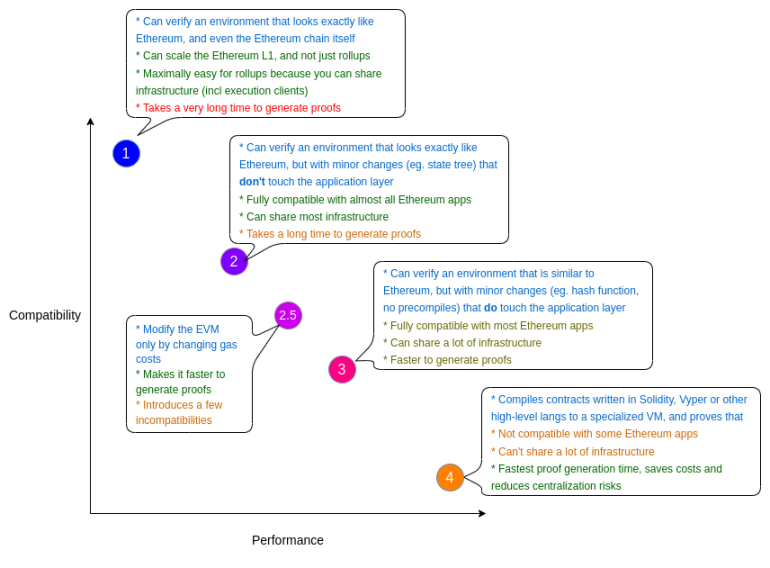
Ethereum founder Vitalik’s 2022 classification of four types of ZK-EVM (Type 1–4) revealed the trade-off between compatibility and performance:
-
Type 1 (Fully Equivalent): Bytecode identical to Ethereum L1, lowest migration cost, but slowest proofs. Representative project: Taiko.
-
Type 2 (Fully Compatible): High EVM equivalence with minimal底层 optimizations, strongest compatibility. Representative projects: Scroll, Linea.
-
Type 2.5 (Quasi-Compatible): Minor modifications to EVM (e.g., gas costs, precompile support), sacrificing slight compatibility for performance gains. Representative projects: Polygon zkEVM, Kakarot (EVM running on Starknet).
-
Type 3 (Partially Compatible): More fundamental底层 changes, capable of running most apps but unable to fully reuse Ethereum infrastructure. Representative project: zkSync Era.
-
Type 4 (Language-Level Compatibility): Abandons bytecode compatibility, compiles directly from high-level languages to zkVM, best performance but requires rebuilding the ecosystem. Representative project: Starknet (Cairo).
This phase centered on the "zkRollup wars," aiming to alleviate Ethereum’s execution bottleneck. However, two major limitations emerged: high difficulty and inefficiency in EVM circuitization, and the realization that ZK’s potential extends far beyond scaling—to cross-chain validation, data proof, and even AI computation.
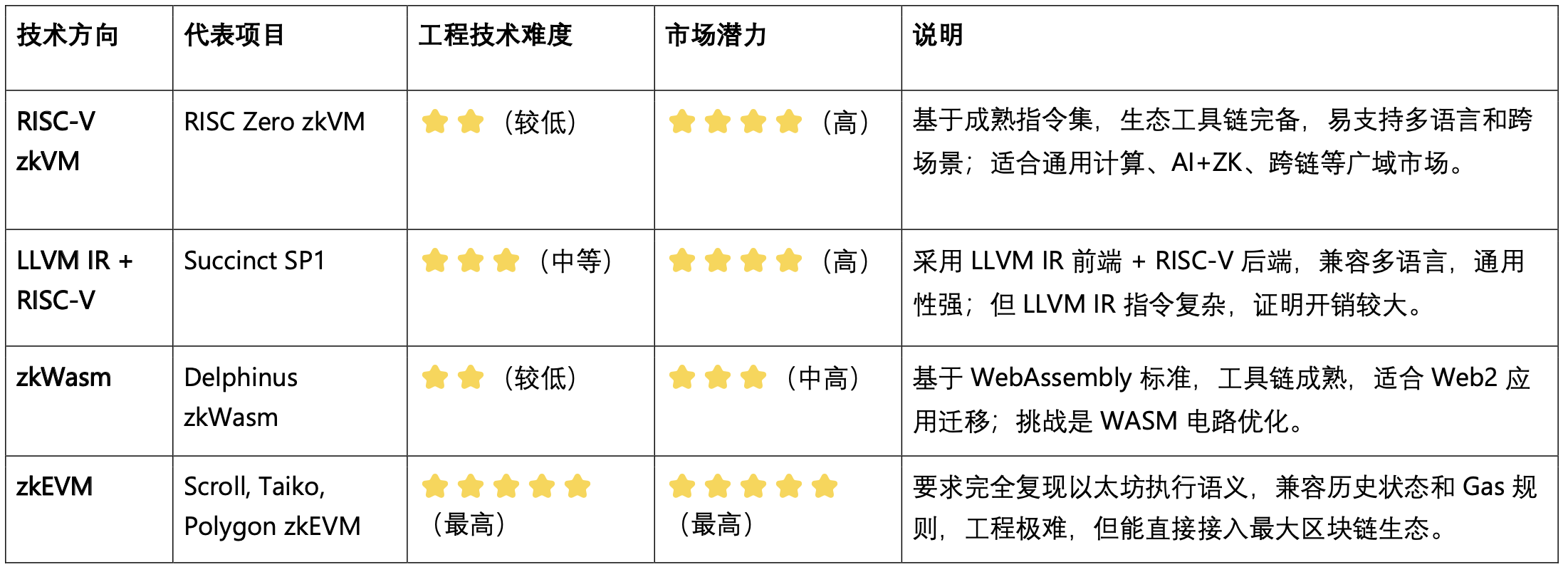
Against this backdrop, general-purpose zkVMs have risen, replacing the zkEVM's "Ethereum compatibility mindset" with a vision of "chain-agnostic trusted computing." Based on universal instruction sets (e.g., RISC-V, LLVM IR, Wasm), zkVMs support languages like Rust and C/C++, allowing developers to build any application logic using mature ecosystem libraries, then generate proofs for on-chain verification. RISC Zero (RISC-V) and Delphinus zkWasm (Wasm) are typical examples. Their significance lies in transforming zkVM from merely an Ethereum scaling tool into the "trusted CPU" of the ZK world.
-
RISC-V Path: Represented by RISC Zero, this approach uses the open, general-purpose RISC-V instruction set as the zkVM execution core. Advantages include an open ecosystem, simple instruction set, and ease of circuitization, capable of handling compiled outputs from mainstream languages like Rust and C/C++, ideal for a "general zkCPU." The drawback is no native compatibility with Ethereum bytecode, requiring integration via coprocessor models.
-
LLVM IR Path: Represented by Succinct SP1: Frontend uses LLVM IR for multi-language compatibility, backend remains based on RISC-V zkVM—essentially "LLVM frontend + RISC-V backend"—more universal than pure RISC-V but incurs higher proof overhead due to LLVM IR complexity.
-
Wasm Path: Represented by Delphinus zkWasm. WebAssembly has a mature ecosystem and high developer familiarity, with inherent cross-platform support, but its instruction set is relatively complex, limiting proof performance.
In further evolution, ZK technology is moving toward modularity and marketization. First, zkVM provides a general-purpose trusted execution environment—akin to the "CPU/compiler" of zero-knowledge computing—supplying foundational verifiable computation capabilities to applications. On top of this, zk-coprocessors package zkVM as auxiliary processors, enabling chains like EVM to outsource complex computations off-chain and verify them back on-chain via zero-knowledge proofs. Examples include RISC Zero Steel and Lagrange, analogous to "GPU/coprocessor" roles. Further still, zkMarketplace decentralizes the distribution of proof tasks through a network where global prover nodes compete via bidding to complete jobs—such as Boundless, building a computational marketplace for zero-knowledge proofs.
Thus, the zero-knowledge tech stack is gradually evolving along a chain: zkVM → zk-coprocessor → zkMarketplace. This progression marks the transformation of zero-knowledge proofs from a single Ethereum scaling tool into a universal trusted computing infrastructure. Within this evolution, RISC Zero—using RISC-V as the zkVM core—achieves optimal balance among openness, circuitization efficiency, and ecosystem adaptability. It delivers low-barrier development experiences while enabling extensions like Steel, Bonsai, and Boundless to evolve zkVM into a zk-coprocessor and decentralized proof market, unlocking broader application possibilities.
4. RISC Zero’s Technical Approach and Ecosystem Map
RISC-V is an open, royalty-free instruction set architecture not controlled by any single vendor, possessing inherent decentralized characteristics. Leveraging this open architecture, RISC Zero builds a zkVM compatible with general-purpose languages like Rust, breaking free from the constraints of Solidity within the Ethereum ecosystem. This allows developers to directly compile standard Rust programs into applications that generate zero-knowledge proofs. This path expands the scope of ZK applications from blockchain contracts to broader domains of general-purpose computing.
RISC0 zkVM: A Universal Trusted Computing Environment
Unlike zkEVM projects that must accommodate the complex EVM instruction set, RISC0 zkVM is based on the RISC-V architecture, designed to be more open and universal. Its applications consist of Guest Code compiled into ELF binary files. The Host runs and records the execution process (Session) via an Executor, and the Prover subsequently generates a verifiable Receipt containing public output (Journal) and encrypted proof (Seal). Third parties need only verify the Receipt to confirm computational correctness, without re-executing the entire process.
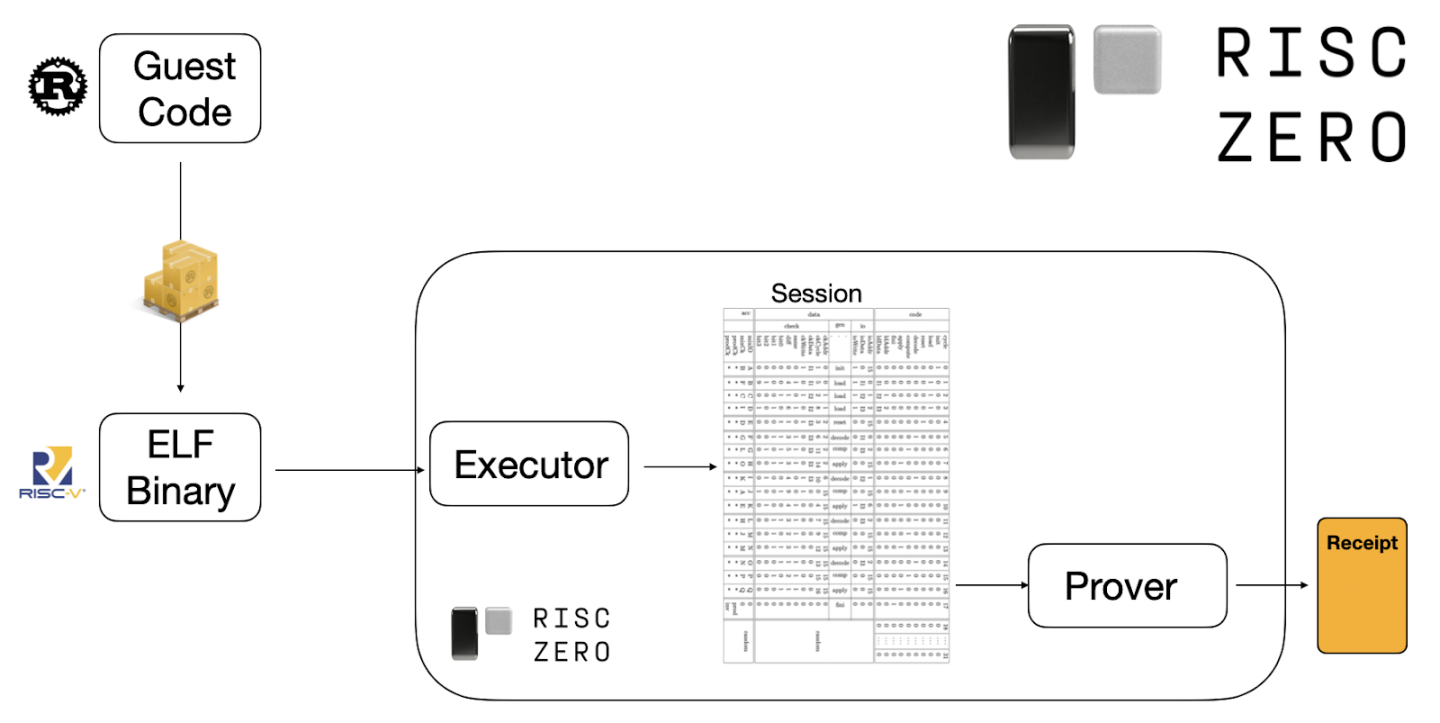
The release of R0VM 2.0 in April 2025 marked the entry of zkVM into the real-time era: Ethereum block proof time reduced from 35 minutes to 44 seconds, costs lowered up to 5x, user memory expanded to 3GB, supporting more complex applications. Two critical precompiles—BN254 and BLS12-381—were added, covering mainstream Ethereum needs. More importantly, R0VM 2.0 introduced formal verification for enhanced security, completing deterministic verification for most RISC-V circuits, with the goal of achieving the first block-level real-time zkVM (<12 second proofs) by July 2025.
zkCoprocessor Steel: Bridging Off-Chain Computation
The core idea of zkCoprocessor is to offload complex computations from on-chain to off-chain execution, then return results via zero-knowledge proofs. Smart contracts only need to verify the Proof, not recompute the entire task, significantly reducing gas costs and overcoming performance bottlenecks. For example, RISC0’s Steel provides external proof interfaces for Solidity, enabling outsourcing of large-scale historical state queries or batch cross-block computations—even verifying dozens of Ethereum blocks with a single Proof.
Bonsai: High-Performance SaaS Proof Service
To meet industrial-grade application demands, RISC Zero launched Bonsai, an officially hosted Prover-as-a-Service platform that distributes proof tasks via GPU clusters, allowing developers to access high-performance proving without building their own hardware. Meanwhile, RISC Zero offers the Bento SDK to enable seamless interaction between Solidity and zkVM, greatly reducing integration complexity for zkCoprocessor. In contrast, Boundless achieves decentralized proving through an open market, forming a complementary relationship.
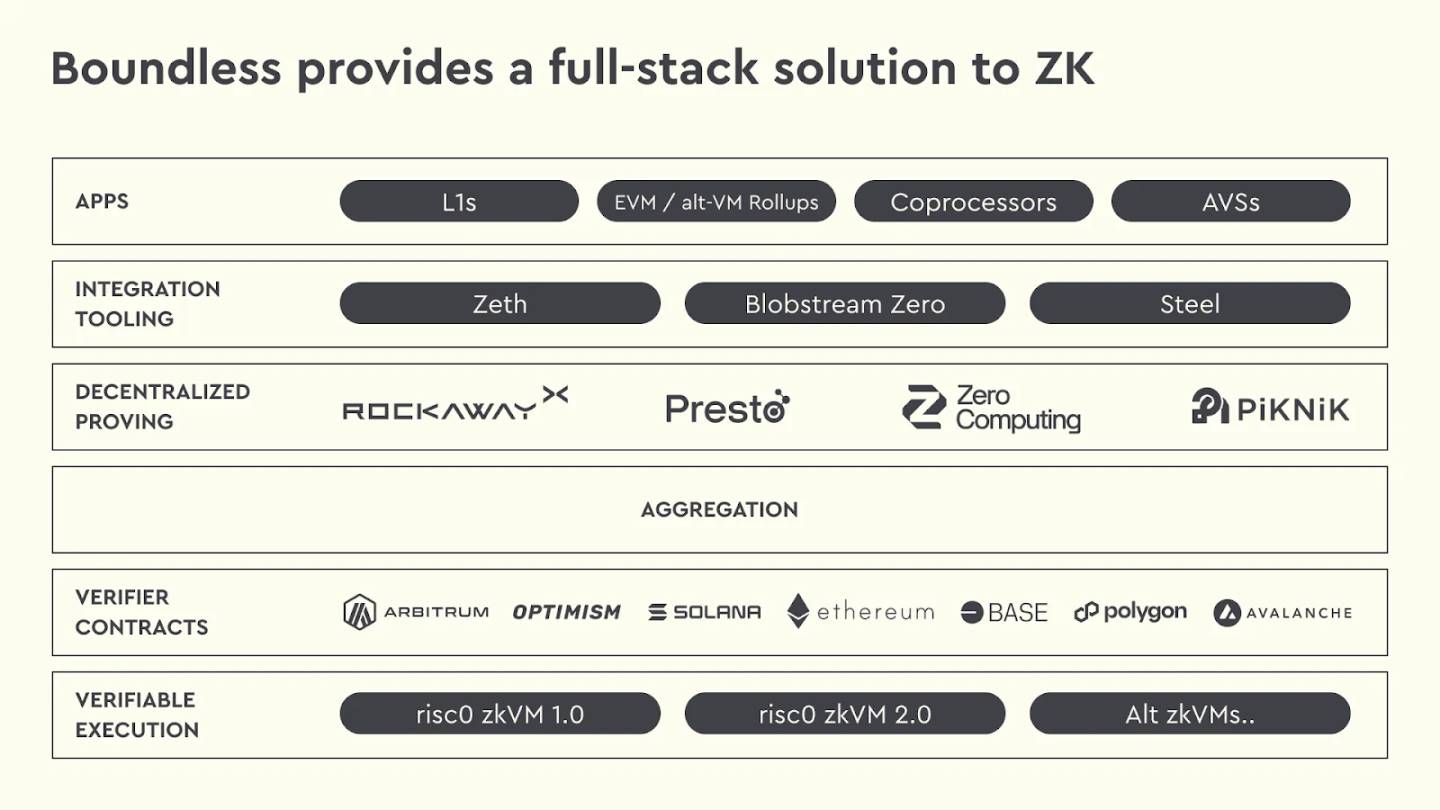
RISC Zero’s Full Product Matrix
RISC Zero’s product ecosystem extends upward from zkVM, gradually forming a comprehensive matrix spanning execution, networking, markets, and application layers:
5. The ZK Market: Decentralized Commoditization of Trust Computation
The zero-knowledge proof (ZK) market decouples the expensive and complex proof generation process, transforming it into a decentralized, tradable computational commodity. Through a globally distributed prover network, computational tasks are outsourced via bidding, dynamically balancing cost and efficiency, and continuously attracting GPU and ASIC participants through economic incentives—forming a self-reinforcing cycle. Boundless and Succinct are leading representatives in this space.
5.1 Boundless: A General-Purpose Zero-Knowledge Computing Market
Concept and Positioning
Boundless is a general-purpose ZK protocol launched by RISC Zero, aiming to provide scalable verifiable compute capabilities for all blockchains. Its core innovation is decoupling proof generation from blockchain consensus and distributing computational tasks via a decentralized market mechanism. After developers submit proof requests, prover nodes compete to execute them under a decentralized incentive model and are rewarded based on "Proof of Verifiable Work." Unlike traditional PoW’s meaningless computation, Boundless transforms computational power into ZK results for real applications, giving computational resources actual value.
Architecture and Mechanism
The workflow of the Boundless market includes:
-
Request Submission: Developers submit zkVM programs and inputs to the market;
-
Node Bidding: Prover nodes evaluate tasks and bid, gaining execution rights upon locking the task;
-
Proof Generation and Aggregation: Complex computations are broken into subtasks, each generating a zk-STARK proof, which are then recursively compressed into a unified final proof via aggregation circuits, drastically reducing on-chain verification costs;
-
Cross-Chain Verification: Boundless provides unified verification interfaces across multiple chains, enabling one-time construction and cross-chain reuse.
This architecture allows smart contracts to avoid re-executing complex computations, confirming validity simply by verifying short proofs—thus overcoming gas limits and block capacity constraints.
Ecosystem and Applications: As a market-layer protocol, Boundless complements other RISC Zero products:
-
Steel: EVM’s ZK Coprocessor, enabling off-chain migration and on-chain verification of complex Solidity executions;
-
OP Kailua: Provides ZK upgrade paths for OP Stack chains, delivering higher security and faster finality.
Boundless aims to achieve sub-12-second real-time proofs on Ethereum through FRI optimization, polynomial parallelization, and VPU hardware acceleration. As node count and demand grow, Boundless will form a self-reinforcing computational network—not only reducing gas costs but also enabling new applications like on-chain verifiable AI, cross-chain liquidity, and infinite computation.
5.2 Boundless for Apps: Breaking Gas Limits
Boundless for Apps aims to provide Ethereum and L2 applications with "infinite compute," offloading complex logic to a decentralized proof network for execution and returning results via ZK proofs. Key advantages include infinite execution, constant gas cost, Solidity/Vyper compatibility, and native cross-chain support.
Steel, as EVM’s ZK Coprocessor, enables developers to implement large-scale state queries, cross-block calculations, and event-driven logic within Solidity contracts, using R0-Helios light clients for cross-chain data verification between ETH and OP Stack. Projects like EigenLayer are already exploring integration, showcasing its potential in DeFi and multi-chain interactions.
Steel: A Scalable Computing Layer for EVM
Steel’s core goal is to overcome Ethereum’s limitations in gas caps, per-block execution, and historical state access by moving complex logic off-chain and verifying it back on-chain via zero-knowledge proofs. It delivers near-infinite compute support at constant verification cost while maintaining security.
In Steel 2.0, developers gain three new capabilities to expand contract design:
-
Event-driven logic: Directly uses Event logs as input, avoiding reliance on centralized indexers;
-
Historical state queries: Accesses storage slots or account balances from any block since the Dencun upgrade;
-
Cross-block computation: Executes operations across multiple blocks (e.g., moving averages, cumulative metrics) and submits results via a single on-chain proof.
This design dramatically reduces costs. Steel enables previously EVM-constrained applications—such as high-frequency computation, state rollback, or cross-block logic—to become viable, gradually establishing itself as a key bridge between off-chain computation and on-chain verification.
5.3 Boundless for Rollups: ZK-Powered Rollup Acceleration
Boundless for Rollups leverages a decentralized proof network to deliver faster, more secure settlement for OP Stack and other Layer 2 chains. Core advantages include:
-
Accelerated Finality: Reduces 7-day settlement time to ~3 hours (Hybrid mode) or <1 hour (Validity mode);
-
Stronger Security: Offers cryptographic-grade security through progressive upgrades from ZK Fraud Proof to Validity Proof;
-
Decentralization Roadmap: Leverages distributed prover networks and low collateral requirements to rapidly advance toward Stage 2 decentralization;
-
Native Scalability: Maintains stable performance and predictable costs even on high-throughput chains.
OP Kailua: ZK Upgrade Path for OP Chains
As the core solution of Boundless for Rollups, OP Kailua—launched by RISC Zero—is specifically designed for Optimism-based rollups, enabling teams to surpass traditional OP architectures in both performance and security.
Kailua offers two modes for gradual upgrades:
-
Hybrid Mode (ZK Fraud Proof): Replaces multi-round interactive fault proofs with ZK Fraud Proof, greatly reducing dispute resolution complexity and cost. Malicious actors bear proof fees, finality shortened to ~3 hours.
-
Validity Mode (ZK Validity Proof): Transitions directly to a ZK Rollup, using zero-knowledge validity proofs to eliminate disputes entirely, achieving <1 hour finality and the highest security level.
Kailua enables smooth upgrades for OP chains—from optimistic → hybrid → ZK Rollup—meeting Stage 2 decentralization requirements, lowering upgrade barriers, and improving economics for high-throughput scenarios. While preserving continuity of existing applications and toolchains, the OP ecosystem gradually gains fast finality, lower staking costs, and stronger security. Eclipse has already used Kailua to implement ZK Fraud Proof for accelerated upgrades; BOB has completed its transition to a ZK Rollup.
5.4 The Signal: A ZK Signal Layer for Cross-Chain Interoperability
Positioning and Mechanism
The Signal is a core application launched by Boundless—an open-source ZK consensus client. It compresses Ethereum beacon chain finality events into a single zero-knowledge proof, which any chain or contract can directly verify—enabling trust-minimized cross-chain interactions without multisig or oracles. Its value lies in granting Ethereum’s final state "global readability," laying the foundation for cross-chain liquidity and logic interaction, while significantly reducing redundant computation and gas costs.
Operation Mechanism
-
Boost The Signal: Users can "amplify the signal" by submitting proof requests, with all ETH directly funding new proofs to extend signal duration, benefiting all chains and applications.
-
Prove The Signal: Anyone can run a Boundless Prover node to generate ZK proofs of Ethereum blocks and broadcast them, replacing traditional multisig verification and forming a cross-chain consensus layer based on "math instead of trust."
-
Expansion Path: Initially generate continuous proofs for finalized Ethereum blocks ("Ethereum Signal"), then extend to other public chains for unified multi-chain signals, and ultimately interconnect on a shared cryptographic signal layer—"shared wavelength"—enabling asset-free, non-custodial cross-chain interoperability.
Over 30 teams are now involved in advancing The Signal, with over 1,500 Prover nodes aggregated on the Boundless market competing for 0.5% token incentives. Any GPU-equipped user can join permissionlessly. The Signal has launched on the Boundless Mainnet Beta and supports production-grade proof requests based on Base.
6. Boundless Roadmap, Mainnet Progress, and Ecosystem
Boundless follows a clear phased development path:
-
Phase I – Developer Access: Early developer access with free proof resources to accelerate application exploration;
-
Phase II – Public Testnet 1: Open testnet launch introducing bilateral market mechanisms, enabling real-world interaction between developers and prover nodes;
-
Phase III – Public Testnet 2: Introduces market incentives and full economic mechanisms to test a self-sustaining decentralized proof network;
-
Phase IV – Mainnet: Full mainnet launch providing universal ZK computing capabilities across all chains.

On July 15, 2025, the Boundless Mainnet Beta officially launched, entering production first on Base. Users can request proofs with real funds, while prover nodes join permissionlessly, supporting up to 100 GPUs per node and participating in bidding. As a showcase application, the team launched The Signal—an open-source ZK consensus client that compresses Ethereum beacon chain finality events into a single zero-knowledge proof, verifiable directly by any chain or contract. This grants Ethereum’s final state "global readability," serving as a foundation for cross-chain interoperability and secure settlement.
Network browser data shows rapid growth and strong resilience. As of August 18, 2025, the network has processed 542.7 trillion computation cycles, completed 399,000 orders, and covered 106 distinct programs. The largest single proof reached over 106 billion cycles (August 18), with peak network compute reaching 25.93 MHz (August 14), setting industry records. Daily order volume briefly exceeded 15,000 in mid-August, with daily compute peaks surpassing 40 trillion cycles—demonstrating exponential growth. Order fulfillment success rates consistently remain between 98%–100%, indicating a mature market mechanism. Notably, as prover competition intensifies, the cost per cycle has dropped close to 0 Wei, signaling the network’s entry into an era of efficient, low-cost large-scale computation.
Additionally, Boundless has attracted active participation from top-tier miners. Bitmain and other leading manufacturers are developing dedicated ASIC mining rigs; companies including 6block, Bitfufu, Yuanliqu, Intchain, and Nano Labs are converting existing mining pool resources into ZK proof computation nodes. Miner involvement is pushing Boundless’s ZK market further toward large-scale industrialization.
7. ZK Coin Token Economic Model Design
ZK Coin (ZKC) is the native token of the Boundless protocol and serves as the economic and security anchor of the entire network. Its design aims to build a credible, low-friction, sustainably scalable zero-knowledge computing market. The total supply of ZKC is 1 billion tokens, with an annual inflation rate that declines year-over-year: starting at ~7% in the first year, gradually decreasing to 3% by Year 8, and stabilizing long-term at that level. All newly issued tokens are distributed via Proof of Verifiable Work (PoVW), ensuring issuance is directly tied to real computational tasks.
Proof of Verifiable Work (PoVW) is Boundless’s core innovation, transforming "verifiable computation" from a technical capability into a measurable, tradable commodity. Traditional blockchains rely on redundant execution by all nodes, constrained by individual node compute limits. PoVW enables single computation with network-wide verification via zero-knowledge proofs, introducing a trustless measurement system that turns computational work into a priceable resource. This allows computation to scale on demand, discover prices via markets, sign service contracts, and incentivize prover nodes—creating a demand-driven positive cycle. PoVW enables blockchains to transcend compute scarcity for the first time, supporting applications in cross-chain interoperability, off-chain execution, complex computation, and privacy protection—laying both economic and technical foundations for Boundless to become a universal ZK computing infrastructure.
Token Roles and Value Capture
ZK Coin (ZKC) is Boundless’s native token and the economic backbone of the entire network:
-
Staking Collateral: Provers must stake ZKC before accepting orders (typically ≥10× max request fee). Failure to deliver on time results in slashing (50% burned, 50% awarded to other provers).
-
Proof of Verifiable Work (PoVW): Provers earn ZKC rewards for generating zero-knowledge proofs, similar to mining. Rewards are split: 75% to provers, 25% to protocol stakers.
-
Universal Payment Layer: App developers pay proof fees in their native tokens (e.g., ETH, USDC, SOL), but provers must stake ZKC—meaning all proofs are backed by ZKC.
-
Governance Function: ZKC holders participate in Boundless governance, including market mechanisms, zkVM integrations, and fund allocations.
Token Distribution (Initial Supply: 1 Billion)
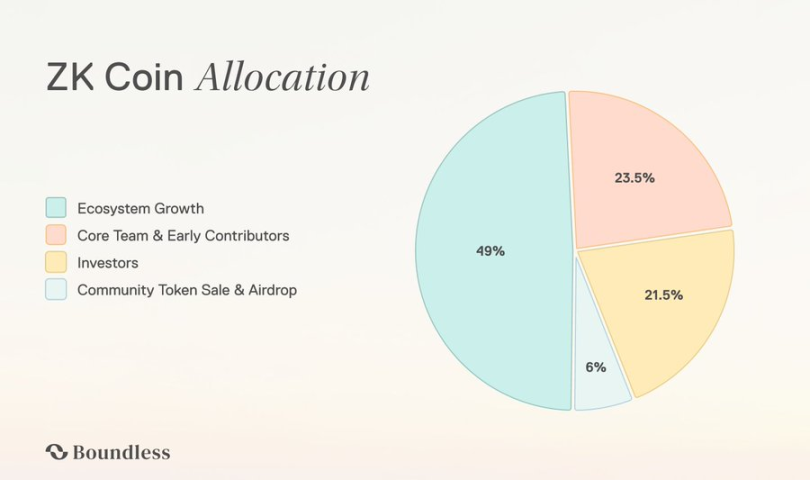
Ecosystem Growth (49%)
-
31% Ecosystem Fund: Supports app development, developer tools, education, and infrastructure maintenance; linearly unlocked over 3 years.
-
18% Strategic Growth Fund: For enterprise integrations, BD partnerships, and institutional prover cluster onboarding; unlocked gradually over 12 months, tied to partnership outcomes.
Core Team and Early Contributors (23.5%)
-
20% to core team and early contributors, with 25% cliff after one year and remainder linearly unlocked over 24 months.
-
3.5% allocated to RISC Zero for zkVM R&D and research funding.
Investors (21.5%): Strategic capital and technical supporters; 25% cliff after one year, remainder linearly unlocked over two years.
Community (~6%): Public sale and airdrops to enhance community participation; public sale: 50% unlocked at TGE, 50% after 6 months; airdrop: 100% unlocked at TGE.
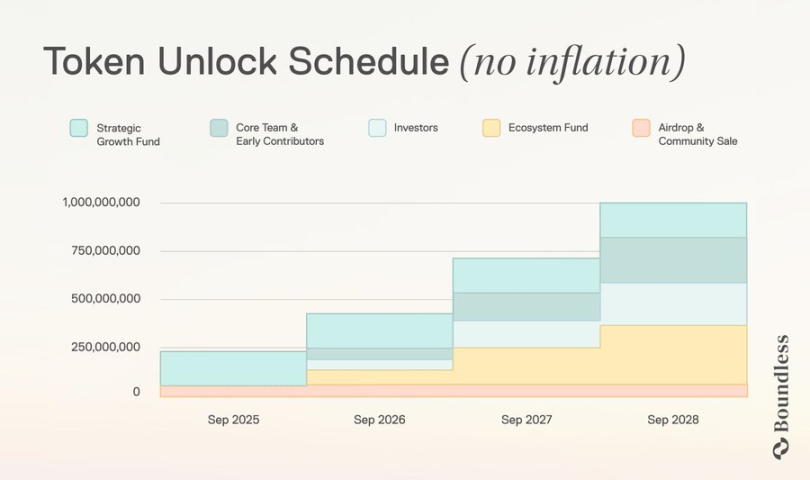
ZKC is the core economic and security anchor of the Boundless protocol—serving as collateral to ensure proof delivery, binding issuance to real work via PoVW, acting as a payment backing layer for cross-chain ZK demand, and empowering token holders in governance. As proof requests increase and penalty burn mechanisms take effect, more ZKC becomes locked and removed from circulation, creating long-term value support under dual pressure of rising demand and shrinking supply.
8. Team Background and Project Funding
RISC Zero was founded in 2021. The team comprises engineers and entrepreneurs from leading tech and crypto organizations including Amazon, Google, Intel, Meta, Microsoft, Coinbase, Mina Foundation, and O(1) Labs. They have built the world’s first zkVM capable of running arbitrary code and are now constructing a general-purpose zero-knowledge computing ecosystem around it.

Jeremy Bruestle – Co-founder & CEO, RISC Zero
Jeremy is a seasoned technical expert and serial entrepreneur with over twenty years of experience in system architecture and distributed computing. Former Principal Engineer at Intel and co-founder & Chief Scientist at Vertex.AI, he also served as co-founder and board member at Spiral Genetics. He founded RISC Zero in 2022 and serves as CEO, leading zkVM technology development and strategy, driving the adoption of zero-knowledge proofs in general computing.
Frank Laub – Co-founder & CTO, RISC Zero
Frank has deep expertise in deep learning compilers and virtual machine technologies, having worked on deep learning software at Intel Labs and Movidius, and accumulated extensive engineering experience at Vertex.AI and Peach Tech. Since co-founding RISC Zero in 2021, he has served as CTO, leading the development of the zkVM kernel, Bonsai network, and developer toolchain.
Shiv Shankar – CEO, Boundless
Shiv brings over fifteen years of technology and engineering management experience across fintech, cloud storage, compliance, and distributed systems. Since 2025, he has served as CEO of Boundless, leading product and engineering teams in advancing the marketization of zero-knowledge proofs and building cross-chain computing infrastructure.
Joe Restivo – COO, RISC Zero
Joe is a three-time successful entrepreneur and operations expert with extensive organizational management and risk control experience. Two of his companies were acquired by Accenture and GitLab. He teaches risk management at Seattle University School of Business. Joined RISC Zero in 2023 as COO, overseeing company-wide operations and scaling.
Brett Carter – VP of Product, RISC Zero
Brett has extensive product management and ecosystem experience. Previously Senior Product Manager at O(1) Labs. Joined RISC Zero in 2023 as VP of Product, responsible for product strategy, ecosystem application deployment, and market alignment with Boundless.

In terms of funding, RISC Zero closed a $40 million Series A round in July 2023, led by Blockchain Capital, with seed lead Bain Capital Crypto continuing participation. Other investors include Galaxy Digital, IOSG, RockawayX, Maven 11, Fenbushi Capital, Delphi Digital, Algaé Ventures, IOBC, Zero Dao (Tribute Labs), Figment Capital, a100x, and Alchemy.
9. Competitive Analysis: zkVM and ZK Market Alternatives
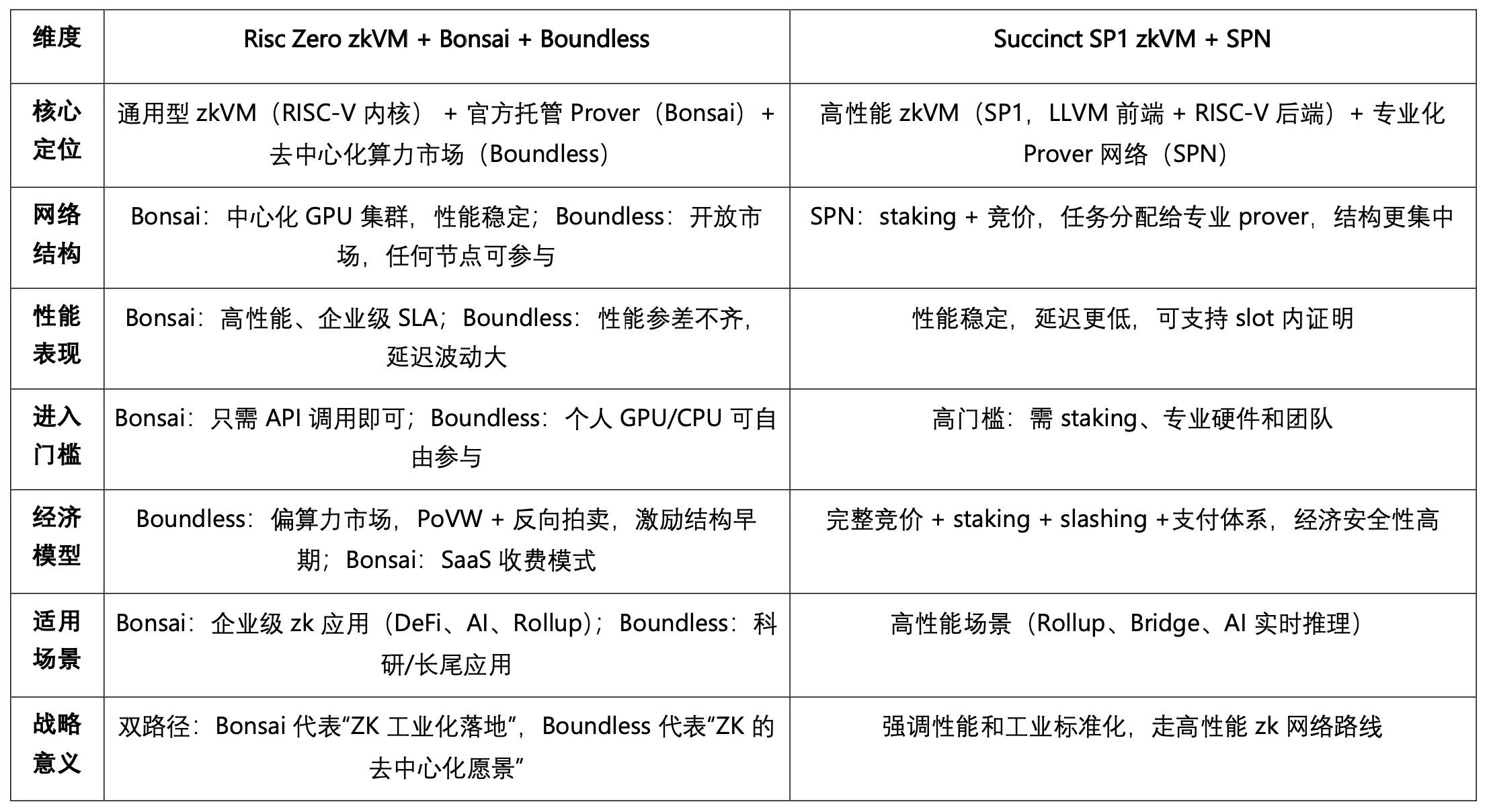
The primary competitor offering both zkVM and zkMarketplace is Succinct, composed of the SP1 zkVM and the Succinct Prover Network (SPN). SP1 is built on RISC-V and uses LLVM IR frontend for multi-language compatibility; SPN operates on Ethereum, allocating tasks via staking and bidding mechanisms, with the $PROVE token serving payment, incentive, and security functions. In contrast, RISC Zero adopts a "dual-engine" strategy: Bonsai provides official, hosted Prover-as-a-Service for high performance and stability, targeting enterprise applications; Boundless builds an open, decentralized proof market allowing any GPU/CPU node to join freely, maximizing decentralization and node coverage, albeit with relatively less consistency in performance.
RISC Zero balances openness with industrial deployment, whereas Succinct focuses more on high performance and standardization.
Differences and Positioning: Risc Zero (zkVM + Bonsai + Boundless) vs. Succinct (SP1 zkVM + SPN)
Comparison: RISC-V vs. Wasm
RISC-V and WASM are the two main paths for general-purpose zkVM. RISC-V is a hardware-level open instruction set with simple rules and mature ecosystems, favorable for circuit performance optimization and future verifiable hardware acceleration—but has limited integration with traditional web application ecosystems. WASM is a cross-platform bytecode, natively supporting multiple languages and web app migration with mature runtimes, but its stack-based architecture imposes lower performance ceilings than RISC-V. Overall, RISC-V zkVM is better suited for performance-focused and general computing expansion, while zkWasm excels in cross-language and web-centric scenarios.
10. Conclusion: Business Logic, Engineering Execution, and Potential Risks
ZK technology is evolving from a single scaling tool into a universal cornerstone of blockchain trusted computing. RISC Zero breaks free from EVM dependence using the open RISC-V architecture, extending zero-knowledge proofs into general off-chain computing, and catalyzing the emergence of zk-Coprocessors and decentralized proof markets (e.g., Bonsai, Boundless). Together, they form a scalable, tradable, and governable layer of computational trust, bringing blockchains higher performance, stronger interoperability, and broader application horizons.
That said, the ZK sector still faces short-term challenges: after peaking in 2023 with first-market hype around ZK concepts, 2024 saw mainstream zkEVM launches absorb secondary market interest. Moreover, top L2 teams mostly use proprietary provers, and use cases like cross-chain verification, zkML, and privacy computing remain in early stages, limiting available tasks. This means open proving marketplaces struggle to sustain large networks with current order volumes—their value lies more in pre-aggregating prover supply to seize opportunities during future demand surges. Meanwhile, although zkVM lowers technical barriers, it struggles to directly penetrate the Ethereum ecosystem. Its unique value may lie in supplementing off-chain complex computation, cross-chain verification, and non-EVM chain integration.
Overall, the evolution path of ZK technology is becoming increasingly clear: from zkEVM compatibility exploration, to the emergence of general-purpose zkVM, to decentralized proof markets exemplified by Boundless—zero-knowledge proofs are accelerating toward commoditization and infrastructural status. For investors and developers, this may still be a validation phase, but it harbors the core opportunities of the next industrial cycle.
Disclaimer: Some parts of this article were assisted by AI. The author has made every effort to ensure accuracy and reliability of the information. Any inaccuracies or omissions are regretted. This article is for research and reference only and does not constitute any investment advice, solicitation, or other form of financial service. Please note that token and related digital asset prices carry high risks and extreme volatility. Readers should exercise independent judgment and assume full responsibility for their investment decisions.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News