Changes and Outlook for the Crypto Market Landscape Following the Passage of the Stablecoin Bill
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Changes and Outlook for the Crypto Market Landscape Following the Passage of the Stablecoin Bill
This article systematically outlines the ten-year growth trajectory of compliant dollar-backed stablecoins and their reconstructive impact on public blockchain ecosystems by analyzing the core frameworks of two major bills and incorporating quantitative forecasts.
By Jeffrey Ding, Chief Analyst at HashKey Group
Originally published in Wen Wei Po
With the recent passage of stablecoin-related legislation in both the United States and Hong Kong, the global digital asset market has officially entered a new cycle of regulation-driven growth. These regulations not only fill critical gaps in the oversight of fiat-collateralized stablecoins but also provide a clear compliance framework—including segregated reserve assets, redemption guarantees, and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements—effectively reducing systemic risks such as bank runs or fraud.
This article analyzes the core frameworks of these two landmark bills, combines them with quantitative projections, and systematically outlines the 10-year growth trajectory of compliant U.S. dollar-backed stablecoins and their transformative impact on public blockchain ecosystems.
1. Growth Drivers and Quantitative Projections for USD Stablecoins Under the GENIUS Act
The U.S. "GENIUS Act" (Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act) was passed by the Senate in May 2025, marking a pivotal step in U.S. stablecoin regulation. The act establishes a comprehensive regulatory framework for stablecoin issuers, mandating that each issued token must be backed 1:1 by highly liquid assets such as U.S. dollars, short-term U.S. Treasury securities, or government money market funds. Issuers are required to undergo regular audits and comply with AML and Know Your Customer (KYC) standards. Additionally, the law prohibits stablecoins from offering interest-bearing features, restricts foreign entities from issuing dollar-pegged stablecoins in the U.S., and explicitly classifies stablecoins as neither securities nor commodities—providing much-needed legal clarity within the digital asset landscape. This legislation aims to strengthen consumer protection, mitigate financial risks, and foster innovation under a predictable regulatory environment.
The implementation of the GENIUS Act is expected to significantly reshape the global crypto market. First, the requirement to invest in non-interest-bearing, high-quality U.S. dollar assets will directly benefit U.S. Treasury issuance, turning stablecoins into a major distribution channel for Treasuries. This mechanism not only alleviates pressure on U.S. fiscal deficit financing but also reinforces the dollar’s position in international settlements through digital currency channels. Second, the clear regulatory framework may attract more traditional financial institutions and tech companies into the stablecoin space, accelerating payment system innovation and efficiency. However, the bill has sparked debate—such as potential conflicts of interest linked to former President Trump’s family involvement in crypto—and concerns over restricted access for foreign issuers potentially complicating international regulatory coordination. Nonetheless, the GENIUS Act provides institutional support for stablecoin development, positioning the U.S. at the forefront of global digital asset regulation.
According to Citigroup, under a scenario of clarified regulation, the global stablecoin market cap is projected to grow from $230 billion in 2025 to $1.6 trillion by 2030. This forecast hinges on two key assumptions: first, compliant stablecoins will accelerate the replacement of traditional cross-border payment systems, saving approximately $40 billion annually in remittance costs; second, stablecoin total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols will surpass $500 billion, establishing stablecoins as the foundational liquidity layer in decentralized finance.
2. Hong Kong’s Differentiated Approach to Stablecoin Regulation
The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region government’s recently released “Stablecoin Ordinance” marks a significant advancement in its systematic strategy for Web3.0. The ordinance introduces a licensing regime for stablecoin issuers, requiring approval from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), along with strict compliance in areas such as reserve asset management, redemption mechanisms, and risk controls. Furthermore, Hong Kong plans to introduce dual licensing for over-the-counter (OTC) trading and custody services within the next two years, further strengthening end-to-end supervision across the virtual asset ecosystem. These measures aim to enhance investor protection, improve market transparency, and solidify Hong Kong’s status as a global hub for digital assets.
The HKMA also intends to publish operational guidelines on real-world asset (RWA) tokenization in 2025, promoting the on-chain representation of traditional assets such as bonds, real estate, and commodities. By leveraging smart contracts to enable automated dividend payouts and interest distributions, Hong Kong seeks to build an innovative ecosystem integrating traditional finance with blockchain technology, opening broader application pathways for Web3.0. Under this regulatory architecture, stablecoin issuance is expected to flourish across multiple currencies and use cases, reinforcing Hong Kong’s role as a fintech nexus.
While drawing inspiration from U.S. regulatory principles, Hong Kong’s draft Stablecoin Bill exhibits notable differences in implementation details (see Table 1):
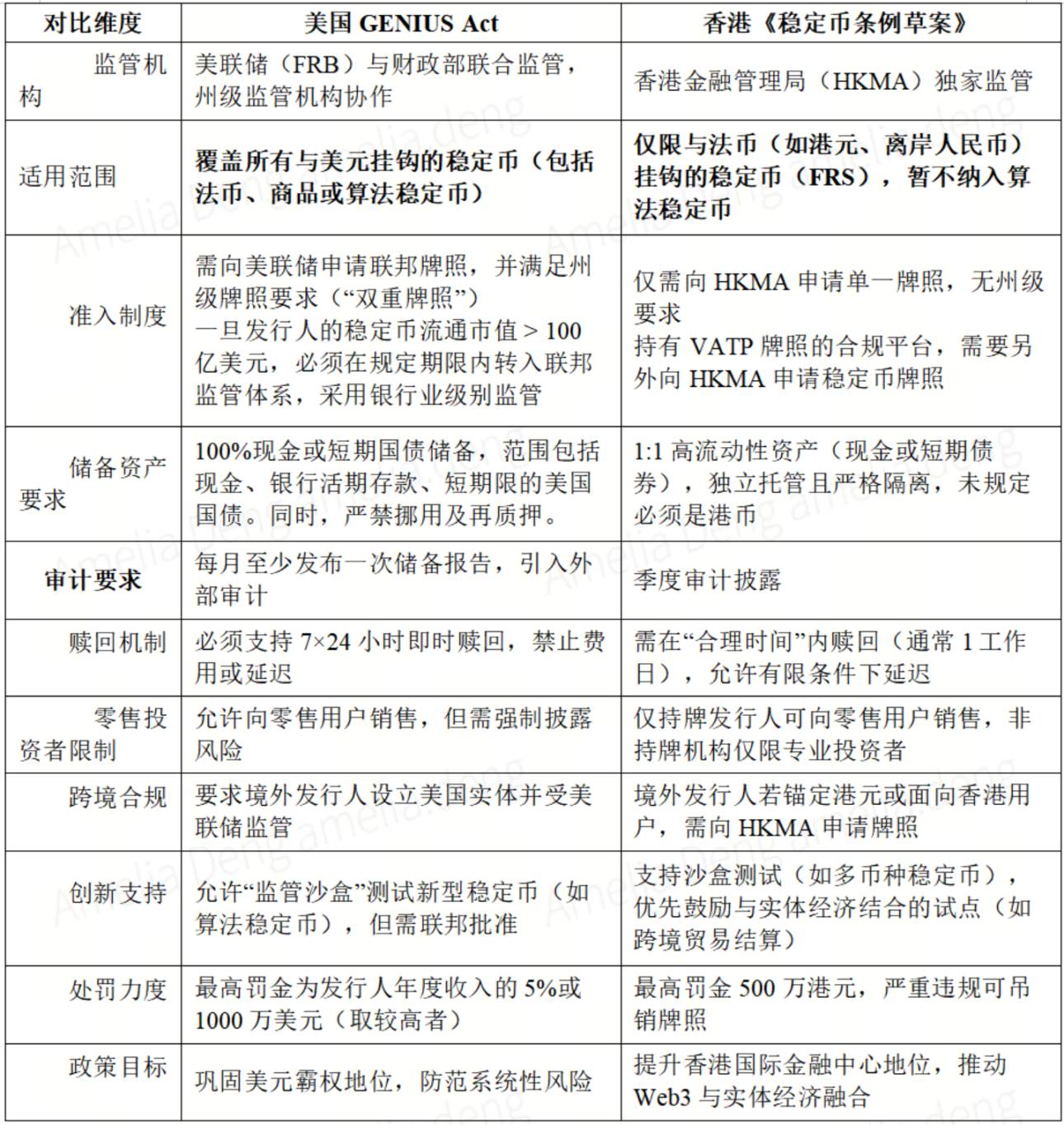
Table 1: Comparison of U.S. and Hong Kong Stablecoin Regulatory Frameworks
3. Evolution of the Global Stablecoin Landscape Amid Regulatory Competition and Cooperation
(a) Reinforcement of the U.S. Dollar’s Role as a Global Reserve Currency
Under the regulatory framework established by the GENIUS Act, payment-focused stablecoins must hold U.S. Treasury securities as reserve assets—a rule that elevates dollar-backed stablecoins beyond mere digital currencies to instruments of strategic significance. In essence, these stablecoins have become a new distribution channel for U.S. debt, creating a unique global capital recycling mechanism: when users worldwide purchase dollar-denominated stablecoins, the proceeds are channeled into U.S. Treasury holdings. This facilitates capital inflows back to the U.S. Treasury while silently expanding the global footprint of the U.S. dollar—an extension of America’s financial infrastructure onto a global scale.
From the perspective of international settlement, stablecoins represent a paradigm shift in the dollar-clearing system. Traditionally, cross-border dollar flows rely heavily on interbank networks like SWIFT. In contrast, blockchain-based stablecoins operate as “on-chain dollars,” seamlessly integrated into various compatible distributed payment systems. This technological leap frees dollar settlement capabilities from exclusive dependence on legacy financial institutions. It not only broadens the dollar’s international usage but also represents a modernization of dollar settlement sovereignty in the digital age, further cementing its central role in the global monetary system.
(b) Regulatory Coordination Challenges Between Hong Kong and Singapore in Asia
Although Hong Kong has taken the lead in establishing a stablecoin licensing regime, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has concurrently launched a “stablecoin sandbox,” allowing experimental issuance of tokens pegged to fiat currencies. Such divergent approaches create opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, prompting issuers to engage in “regulatory shopping.” To address this, ASEAN financial regulators should establish unified reserve audit standards and AML information-sharing mechanisms through forums like the ASEAN Financial Regulators Forum.
Despite similar objectives, Hong Kong and Singapore differ markedly in their implementation strategies. Hong Kong adopts a cautious and tightening regulatory approach, with the HKMA planning to establish a statutory licensing regime that positions stablecoins as “virtual banking alternatives” strictly governed under traditional financial regulations. In contrast, Singapore embraces an experimental philosophy, permitting pilot programs for fiat-pegged digital tokens and preserving flexibility for technological and business model innovation—adopting a tolerance-for-error regulatory stance.
These regulatory disparities could incentivize issuers to selectively register in jurisdictions with looser oversight or exploit gaps between standards, undermining the integrity of fiat-backing verification. Over the long term, without coordination, such fragmentation risks eroding regulatory fairness and policy coherence, potentially triggering a race-to-the-bottom in regional regulation and leading to self-defeating competition. Moreover, inconsistent standards may weaken Asia’s voice in the global stablecoin system, affecting the competitiveness of both Hong Kong and Singapore as international financial centers.
To enhance Asia’s collective influence in global digital financial governance, regulators in both regions must strengthen policy alignment, striking a better balance between mitigating systemic risks and encouraging financial innovation.
Conclusion: Regulatory Clarity Ushers in a Golden Decade for Stablecoins
The joint implementation of the U.S. GENIUS Act and Hong Kong’s draft Stablecoin Ordinance signifies a transition in digital asset regulation—from fragmented oversight to a structured, systemic framework. Compliant U.S. dollar stablecoins are poised for exponential growth over the next decade, serving as the core bridge between traditional finance and the crypto ecosystem. Meanwhile, the technical evolution of public blockchain infrastructure will determine whether maximum value capture can be achieved within these regulatory boundaries. For stablecoin issuers, building multi-chain, multi-currency, and multi-jurisdiction-compliant stablecoin systems will be the key strategic imperative for winning the next decade of competition.
(Note: The data models in this article are based on Citigroup's April 2025 report, U.S. Senate Banking Committee hearing records, and publicly available documents from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority. Growth projections have factored in macroeconomic volatility and technological risk variables.)
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News