VanEck Research: Deconstructing the Premium, Leverage, and Capital Structure of U.S. Equity Strategies
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

VanEck Research: Deconstructing the Premium, Leverage, and Capital Structure of U.S. Equity Strategies
MSTR's premium acts as a "crypto reactor," where this premium fuels MSTR's equity value through a recursive loop.
Authors: Patrick Bush,Matthew Sigel
Translation: TechFlow
We conducted an in-depth analysis of MicroStrategy (MSTR), treating it as a structurally leveraged Bitcoin (BTC) investment vehicle, focusing on its net asset value (NAV) premium, regulatory positioning, and capital structure flexibility—factors that collectively drive its investment opportunities and risks.
Please note that VanEck holds positions in Bitcoin, MSTR, STRK, and STRF.
Four Key Takeaways:
-
MSTR stock is aleveraged proxy for Bitcoin: MSTR stock behaves similarly to a call option on Bitcoin. The company’s strategy involves issuing equity and debt to purchase more BTC when prices rise. This structure creates asymmetric upside potential and high sensitivity to BTC price volatility, making MSTR a popular alternative to direct Bitcoin ownership.
-
MSTR trades at a significant premium to its net asset value (NAV): We estimate that MSTR trades at a +112% premium to the combined fair value of its Bitcoin holdings and core software business. This premium stems from market expectations of future BTC accumulation, regulatory advantages, and speculative positioning.
-
The MSTR premium acts as a “crypto reactor”: This premium fuels MSTR’s equity value through a recursive cycle: volatility and BTC exposure attract investor capital, enabling further BTC accumulation, which in turn amplifies the premium.
-
Convertible securities add flexibility but increase risk: MSTR’s convertibles and preferred shares (notably STRK and STRF) offer varying levels of yield and BTC exposure, but also introduce complexity, asymmetric downside risk, and heightened sensitivity to volatility. The convertible due March 15, 2030, offers the greatest exposure to MSTR, yet even these instruments remain highly dependent on BTC performance and the sustainability of the premium.
Strategy (MSTR) accounts for nearly one-third of pure crypto-equity market capitalization and represents 10% of the Market Vector Global Digital Assets Equity Index (MVDAPP). As such, inclusion in portfolios becomes a critical consideration for investment managers seeking alpha through digital asset transformation.
Ongoing debate continues over the merits of holding MSTR versus direct Bitcoin (BTC) or leveraged BTC exposure, with the company’s complex capital structure further fueling discussion. This complexity includes convertible and equity-linked instruments issued by Strategy, such as high-yield convertible preferred shares (STRK) and even higher-yielding non-convertible preferred shares (STRF).
In this report, we analyze Strategy’s capital structure and assess the pros and cons of holding positions within its equity or debt ecosystem. We conclude that common shares of MSTR represent the superior investment choice relative to other options, based on the following reasons:
-
Maximum exposure to Bitcoin
-
Simplicity of investment strategy
-
Optimal risk/reward profile
What Is Strategy?
Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) is an enterprise analytics software provider and the pioneer of the “corporate Bitcoin treasury” concept. In August 2020, Strategy evaluated its large cash reserves as vulnerable to inflation in the prevailing low-interest-rate environment. It then launched its Bitcoin treasury initiative, deploying $250 million to purchase 21,454 BTC.
By December 2020, Strategy formalized its goal of acquiring BTC via financial instruments by issuing $650 million in convertible debt. Since then, Strategy has transformed from a pure-play enterprise software company into a leveraged Bitcoin financial instrument. Through leverage and various forms of equity issuance, Strategy now holds 2.7% of the total Bitcoin supply, valued at approximately $61 billion as of this writing.
Strategy’s core objective is to maximize the MSTR stock price by increasing the amount of Bitcoin “backing” each common share. By issuing debt or equity, Strategy increases the BTC per-share metric, a dynamic it refers to as “Bitcoin Yield.” During periods of rising Bitcoin prices and strong investor demand, Strategy seizes opportunities to increase leverage or issue additional equity. Thus, Strategy’s BTC exposure and leverage are recursive, expected to grow over time.
When Bitcoin appreciates, the value of Strategy’s BTC reserves rises, enabling it to re-leverage via debt issuance to buy more Bitcoin. On the equity side, Bitcoin bull markets boost MSTR common stock performance in capital markets, allowing Strategy to raise funds through stock issuance to purchase additional BTC. Ultimately, MSTR stock provides accelerated exposure aligned with Bitcoin price appreciation, with price dynamics resembling a call option on Bitcoin.
Understanding the Source of MSTR Equity “Premium”
Currently, MSTR common stock trades above the combined sum of its Bitcoin net asset value (BTC NAV) and the value of Strategy’s underlying software business. This excess is known as the “premium.” As of this writing, MSTR common stock trades at a +112% premium to the fair value of its underlying assets (BTC holdings + core business). Mathematically, we define it as:

Source: VanEck Research (as of March 25, 2025)
There is much debate about the origin of the MSTR premium, but we believe it is primarily driven by four factors:
-
Market expectations of Strategy’s future Bitcoin holdings
-
Limited investor access to direct Bitcoin exposure
-
Leveraged BTC exposure and perceived advantage of Strategy’s leverage
-
Speculative behavior
The primary source of the MSTR premium lies in market expectations of Strategy’s future Bitcoin accumulation. Three key variables can be used to estimate the future value of Strategy’s Bitcoin holdings:
-
Terminal number of BTC held
-
Future expected Bitcoin price
-
Discount rate applied to those holdings
The premium on MSTR stock largely reflects market recognition of the company’s ongoing commitment to purchasing Bitcoin. A positive premium indicates that the market expects the value per BTC to continue growing, reflecting the discounted present value of future Bitcoin prices.
The second factor can be described as a “regulatory premium,” arising from structural constraints in the investment landscape. Many institutional and individual investors cannot directly purchase Bitcoin due to regulatory restrictions, investment mandates, distribution bottlenecks, or lack of secure custody solutions.
Faced with limited access to capital-efficient, leveraged Bitcoin instruments, they instead invest in MSTR. Additionally, unfavorable tax treatment and capital holding requirements for Bitcoin in many jurisdictions make listed equities like MSTR a more attractive alternative. As common stock, MSTR also enjoys financial advantages as collateral. These investor constraints make MSTR an appealing proxy for Bitcoin exposure, particularly for those unable to access the asset class directly.
The third component of the MSTR premium reflects market confidence in Michael Saylor’s (Strategy’s founder) ability to deploy financialleverage. Saylor has demonstrated an ability to raise massive amounts of capital at low interest rates, while the corporate structure has shown resilience during Bitcoin market downturns. Unlike typical margin traders, Saylor is able to withstand drawdowns and maintain long-term positions. At times during 2022 and 2023, despite equity deficits reaching hundreds of millions of dollars, MSTR’s market cap remained in the billions, reflecting investor confidence in Strategy’s long-term leverage structure.
MSTR’s unique dynamics have driven its 30-day historical volatility to ~113%, far exceeding Bitcoin’s ~55%. Overall, MSTR stock provides investors with convenient access to leveraged Bitcoin exposure through public equity markets. The premium is a major contributor to MSTR stock’s returns and volatility. By decomposing the weights, correlations, and volatilities within the MSTR portfolio (Bitcoin + core business + premium), we find that the premium contributes 96.5% to total returns and approximately 87.5% to volatility.
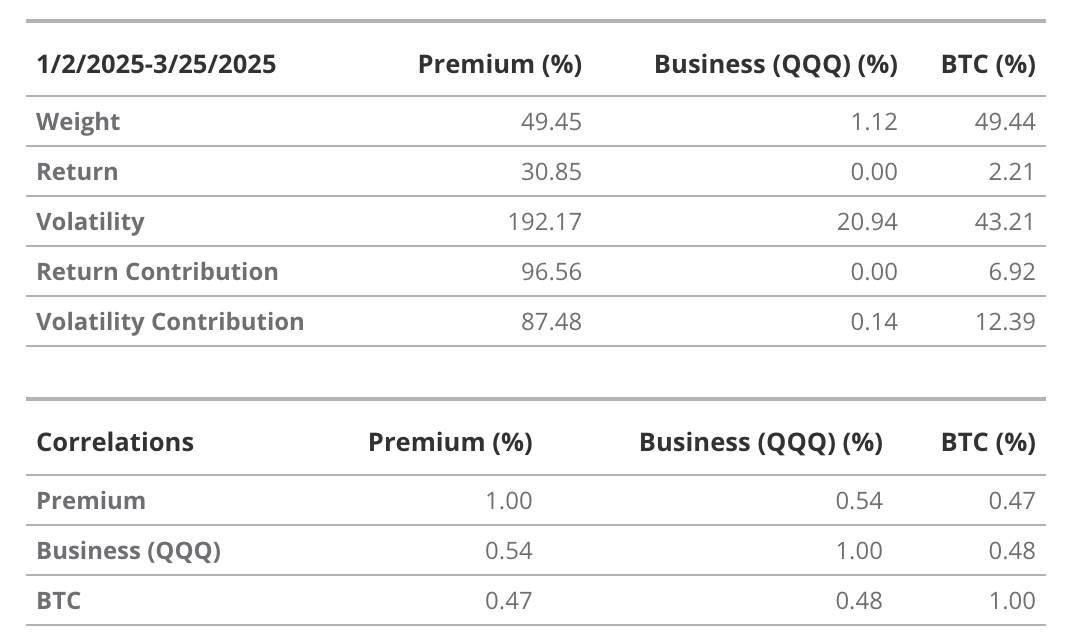
We use QQQ (Invesco’s Nasdaq 100 ETF) as a proxy for technology exposure, specifically large-cap software and cloud computing companies, to reflect the characteristics of MSTR’s core business.
Source: VanEck Research (as of March 26, 2025). Past performance does not guarantee future results. Information, valuation scenarios, and price targets in this article are not financial advice and do not constitute any call to action, buy/sell recommendation, or prediction of Bitcoin’s future performance. Bitcoin’s actual future performance is unknown and may differ significantly from the assumed outcomes presented herein. Furthermore, the scenarios listed may not cover all risks or other factors that could hinder performance. These are simulated results based solely on our research and are for illustrative purposes only. Please conduct your own research and reach your own conclusions.
The fourth component of the MSTR premium arises from speculative trading dynamics tied to its volatility and capital structure. Because the premium contributes so significantly to MSTR’s returns and volatility, any disruption to core drivers will negatively impact MSTR’s stock price. This is because Saylor uses MSTR’s volatility to fund BTC purchases. As detailed below, Saylor’s preferred financing hierarchy for BTC purchases is: preferred stock, convertible preferred stock, convertible debt, and finally common stock. This order is based on “BTC Yield” available to common shareholders, driven by BTC per common share. For example, selling preferred stock causes dilution but converts proceeds directly into BTC yield for common shareholders.
These securities issued by Strategy are popular among investors because MSTR’s high volatility creates abundant opportunities across layers of its capital structure and in MSTR options trading. Indeed, Strategy is able to maintain low interest rates on its convertible debt precisely because MSTR’s volatility makes the embedded option highly valuable. One could argue that Strategy prices these option values relatively cheaply to attract relative-value trading entities. These sophisticated arbitrageurs engage in relative-value trades across Strategy’s various securities based on volatility differentials.
Ultimately, there is a circular relationship between Strategy’s premium and its ability to finance further BTC purchases. The premium is the main source of MSTR’s volatility, and the premium itself depends heavily on Strategy’s ability to raise funding for BTC acquisitions. The market is willing to buy Strategy’sstock precisely because its capital structure generates volatility, and Strategy arguably sells this volatility at a discount. During Q1 2025 earnings call, Saylor described this reinforcing dynamic as a “crypto reactor” capable of sustaining itself for a long time.
The MSTR premium shows a clear positive correlation with Bitcoin price. Over the past year, its correlation coefficient with BTC was 0.52 (T-Stat = 9), with an approximate beta to BTC of 1.77. This indicates that as Bitcoin prices rise, the premium tends to expand, further enhancing MSTR’s stock performance. The linkage between BTC price, speculation, financing capability, and MSTR valuation forms a self-reinforcing loop central to the company’s strategy.
Correlation Between Premium and Bitcoin Price
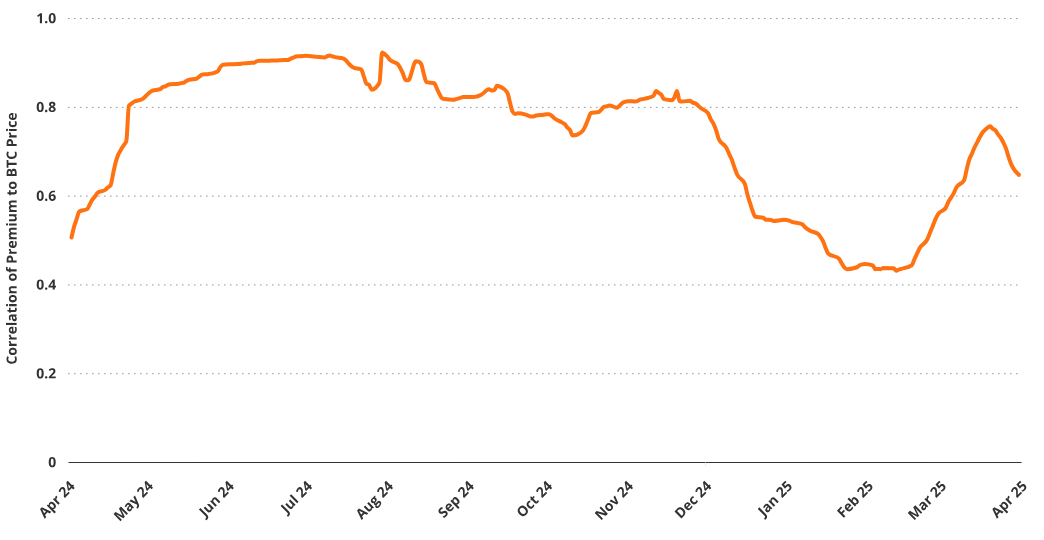
Source: VanEck Research (as of March 26, 2025). Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
Financing the Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
In October 2024, Strategy announced an ambitious “21/21” capital plan aiming to raise $42 billion by 2027—$21 billion from MSTR stock sales and $21 billion from fixed-income securities—for Bitcoin (BTC) purchases. Under the original plan, Strategy intended to sell $5 billion, $7 billion, and $9 billion in stock in 2025, 2026, and 2027 respectively. Fixed-income issuances were to follow the same schedule. The debt issuance target is to maintain leverage between 20%–30%. Strategy’s leader, Michael Saylor, termed this “Intelligent Leverage,” emphasizing it is not for speculation but for strategic acquisition of the “dominant digital asset.”
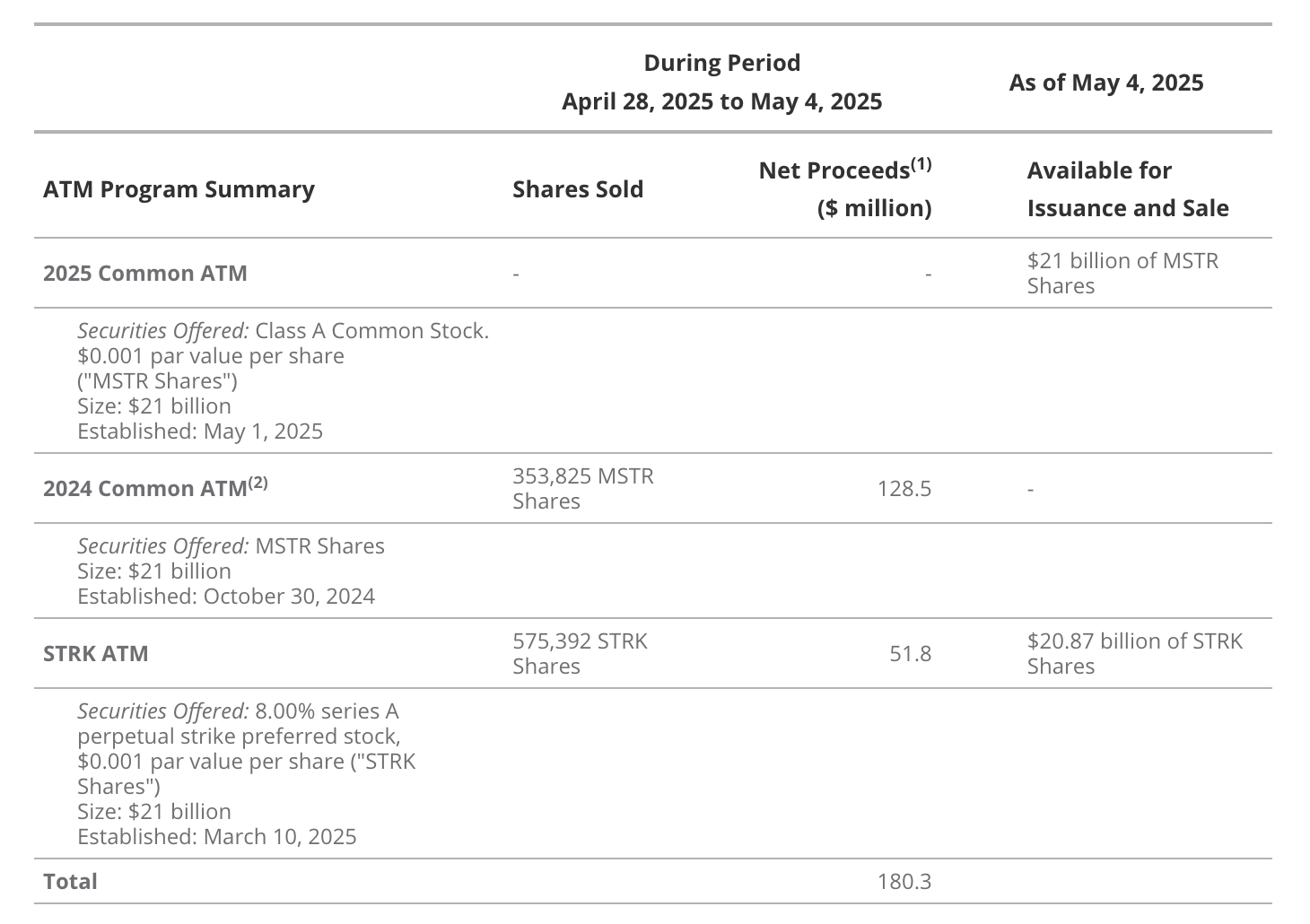
Thanks to an unprecedented crypto bull market following the launch of the 21/21 plan, by May 2025, Strategy had already sold the full $21 billion worth of MSTR stock under its “at-the-market” (ATM) program. On the fixed-income side, Saylor has sold $5 billion in convertible bonds, $875 million in STRK convertible preferred shares, and $850 million in non-convertible preferred stock. On May 1, 2025, the company announced an expansion of its financing plan to $84 billion, including a new $21 billion MSTR ATM program, the existing $21 billion STRK ATM, and an additional $14 billion in convertible debt issuance.
32% Completion of 42/42 Financing Plan

Source: Strategy, as of May 7, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
With Bitcoin currently priced around $95,000, Strategy holds 555,450 BTC. Calculations show Saylor’s leverage ratio ((debt + preferred stock) / market cap) is 9%, the lowest level Strategy has carried since 2020. Given Saylor’s current below-average leverage and preference for “convertible, unsecured, and non-recourse” debt, it is reasonable to expect future fundraising through convertible debt.
Financing BTC Purchases Through Volatility
Source: Strategy, as of March 25, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
Since MSTR stock is linked to Bitcoin, it exhibits extreme volatility, and its leverage may increase further as Strategy finances additional BTC purchases. Most investors view leveraged investments in highly volatile assets like BTC unfavorably and typically demand higher interest rates. Strategy addresses this by issuing convertible bonds and convertible preferred shares, whose embedded optionality constitutes most of their value.
Sophisticated investors favor these instruments because they enable strategies such as convertible arbitrage. In this high-risk, complex trading strategy, experienced investors profit from discrepancies between realized volatility, implied volatility, and other components of option pricing models by buying convertible bonds while shorting MSTR stock and/or MSTR options.
This trading dynamic helps Strategy solve its cash flow needs while ensuring low interest payments on its debt. Due to strong market demand for high-volatility convertible securities, Strategy can promise investors very low future interest rates. A complex balancing act thus emerges between Strategy’s capital markets strategy and the demand from potential investors.
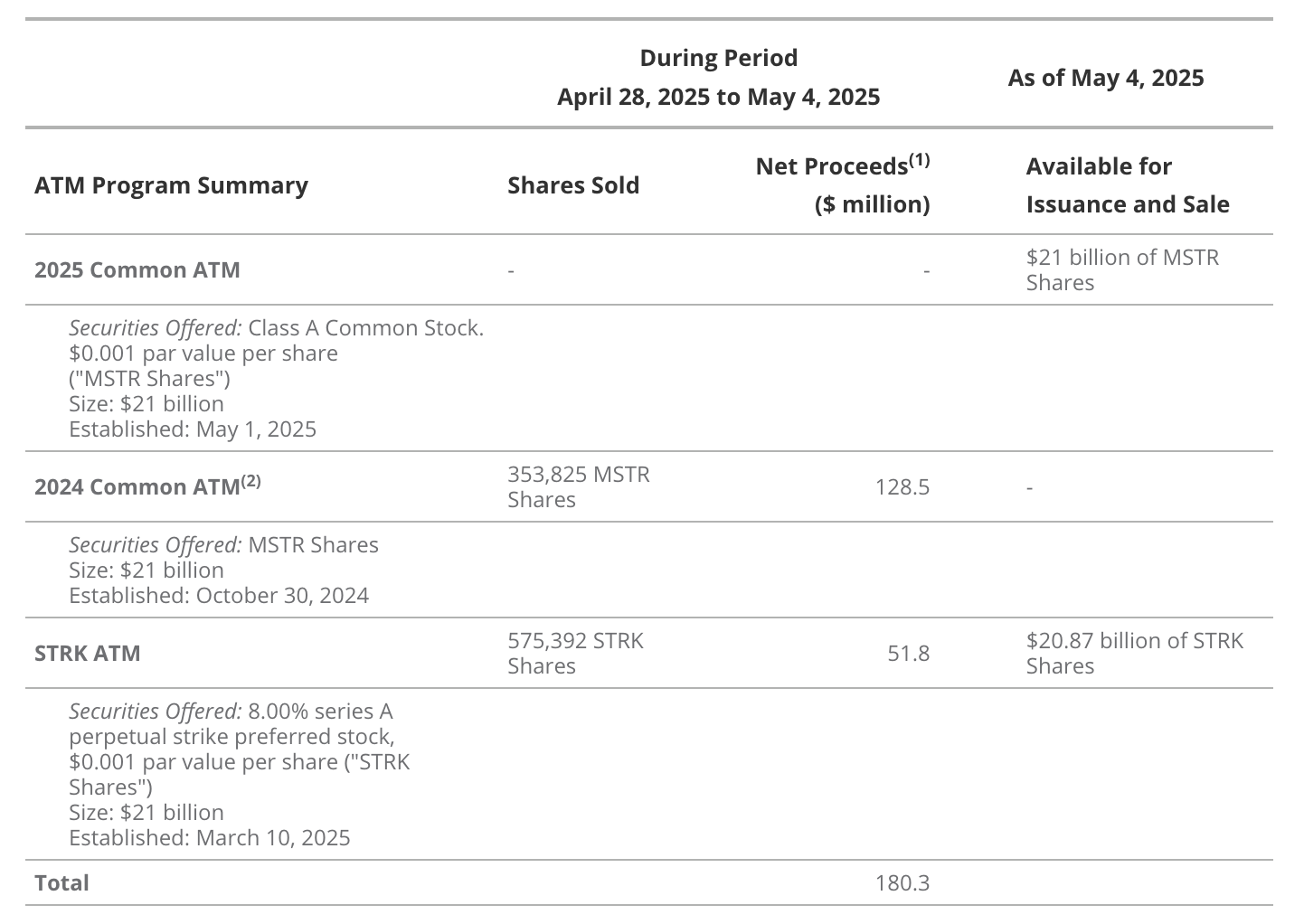
Source: Strategy, as of May 5, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
-
Net proceeds are after sales commissions.
-
The 2024 common stock ATM program has been largely exhausted, and its sales agreement has been terminated per terms.
This involves Strategy pricing implied volatility, setting strike prices, and increasing redemption prices to maximize tradability of each issuance. For instance, setting a redemption price close to the market allows Strategy to cap the option component of its bonds. The result is derivatives that behave more like “capped calls,” with delta potentially lower than standard call options. Choosing strike prices far out-of-the-money can also reduce the option’s value and thus lower delta. Lower delta means fewer MSTR shares (or options) are needed to hedge the option embedded in convertible bonds. Many convertible arbitrage players prefer low-delta issuances as they require less capital on trading balance sheets.
Evaluating the Sustainability of Strategy’s Financing
While Strategy’s core business generates some operating income, its BTC purchases funded via financing will create substantial cash demands. Based on Strategy’s filings and statements, we project total debt to reach $13 billion by end-2025 (up from ~$8 billion in April 2025) and $19 billion by end-2026. We also expect preferred stock to grow to $7.5 billion in 2025 and $15.5 billion in 2026.
By end-2025, we estimate annual interest payments will reach $48 million, rising to $87 million in 2026. Meanwhile, preferred stock (STRK) dividend payments are projected to increase from $217 million in 2025 to $904 million in 2026. We base these estimates on market expectations for coupon rates on MSTR bonds and preferred dividends. While Strategy retains the option to pay STRK dividends in common stock, doing so would dilute existing MSTR holders by reducing BTC per share.
With projected 2025 revenue of $475 million, Strategy relies on financing to cover its fixed-income obligations. Of course, the ability to raise new capital depends on Bitcoin’s price. If Bitcoin continues to rise, raising new capital becomes easier. From August 2024 to May 2025, Strategy increased its holdings from 226,000 BTC to 555,450 BTC through fundraising. However, during the crypto downturn from June 2022 to December 2022, Strategy raised only $49 million from stock sales and $11 million from debt sales. Bear markets may pose challenges for Strategy due to increased cash outflows from new fixed-income securities issuance.
MSTR as a Convex Bet on BTC Price
Investing in MSTR resembles investing in a call option on BTC, given MSTR’s leveraged sensitivity (or “torque”) to BTC price volatility. However, it more closely resembles dynamically replicating a BTC call option by increasing leverage exposure as prices rise. Strategy increases its BTC position as financing becomes available, which typically occurs when BTC prices are rising. The risk of this strategy lies not only in price declines but also in the collapse of premium due to failed BTC purchase financing. Additionally, this strategy deploys capital at BTC peaks, which could be seen as poorly timed.
"Naive" Purchase Net Gains Outperform Strategy's Purchases
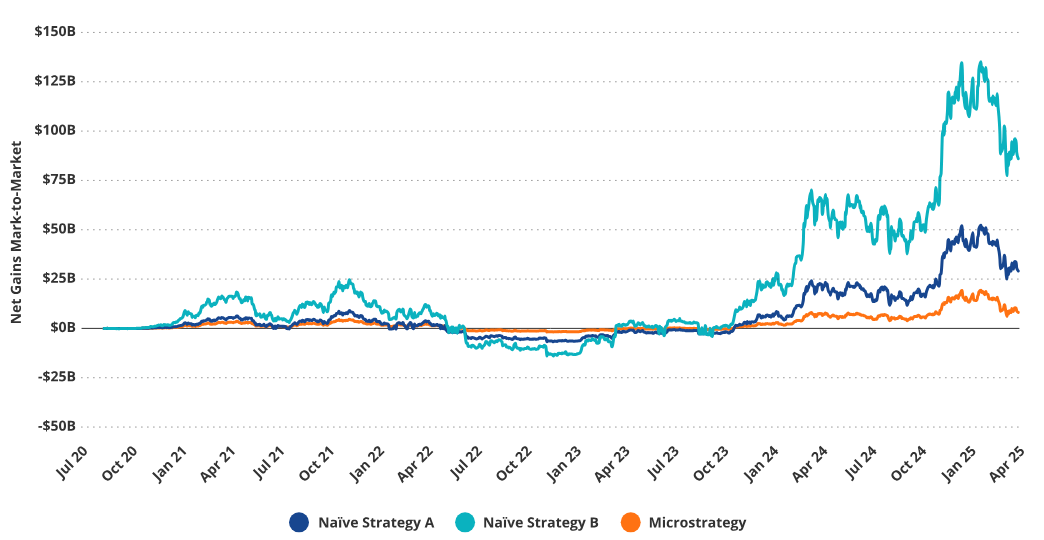
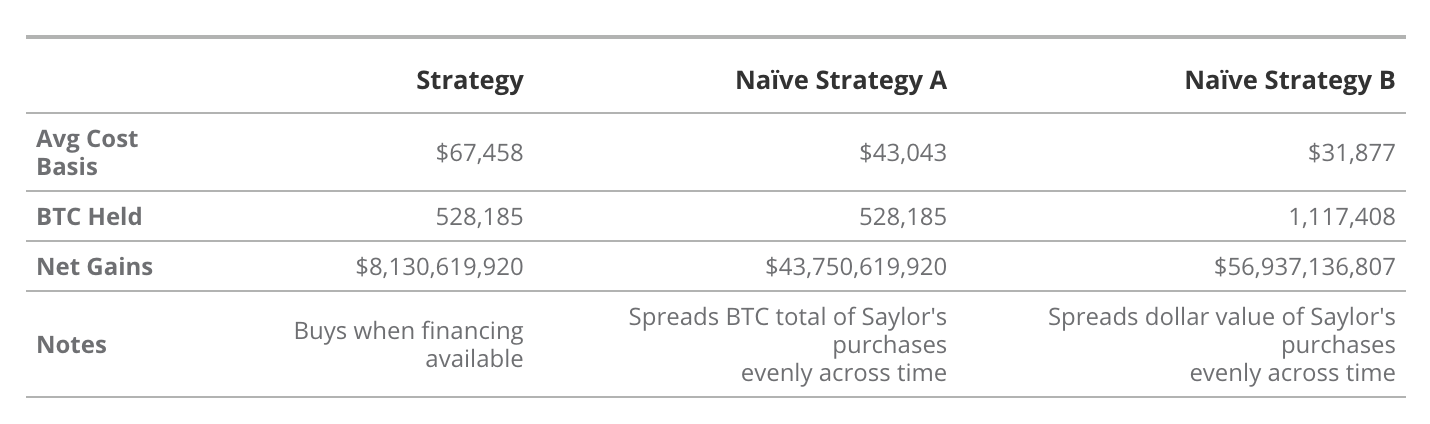
Source: VanEck Research, Strategy, as of March 26, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
Strategy’s BTC purchases at local highs generate “losses” relative to other strategies, as this results in a higher average BTC purchase price compared to random purchases. Whether Strategy’s buying activity actually caused these local “peaks and troughs” is another question. Regardless, compared to a “naive,” randomly implemented BTC purchase strategy, this peak-buying approach results in losses for shareholders. On the other hand, due to MSTR’s “positive convexity,” changes in Bitcoin’s price lead to significant increases in the dollar value of BTC per share, and new financing also increases BTC held per share. Thus, investors gain greater BTC exposure as BTC prices rise.
As individual investors, it is nearly impossible to replicate Saylor’s strategy without a corporate “shell.” Although investors can see their margin balances grow when BTC rises through BTC futures, they cannot “patiently” hold such leveraged positions during price declines. Futures contracts are marked-to-market daily, meaning gains and losses are settled regularly, and margin calls must be met immediately during market pullbacks. If BTC’s price retreat exceeds their margin balance, leveraged traders face forced liquidation.
Therefore, even a savvy trader attempting to mimic Saylor’s strategy—incrementallyaccumulating as BTC rises—could faceforced liquidation from even moderatepullbacks, wiping out their position. These daily margin requirements make it difficult for individual investors to replicate Strategy’s long-term BTC accumulation strategy usingfutures. Thus, Strategy holds a significant financial advantage enabling it to run a leveraged BTC strategy more effectively.
MSTR’s Capital Strategy and Bitcoin Yield
Strategy’s financial engineering increases BTC exposure per common share by adding debt and shares. This is because Strategy’s core goal is to increase common stock exposure to BTC price movements. Saylor refers to the increase in BTC per share as “BTC Yield.” This key performance indicator (KPI) is calculated by comparing BTC held per common share across different periods. As of May 2025, BTC Yield year-to-date is approximately 14% (based on issued common shares) and about 13% on a fully diluted basis. Strategy’s minimum BTC Yield target for 2025 is 25%. This means the BTC amount per 1,000 MSTR common shares will increase from approximately 1.79 BTC on May 8, 2025, to about 1.99 BTC by year-end.
Strategy’s Bitcoin Yield Faces Challenging Comparison Outlook
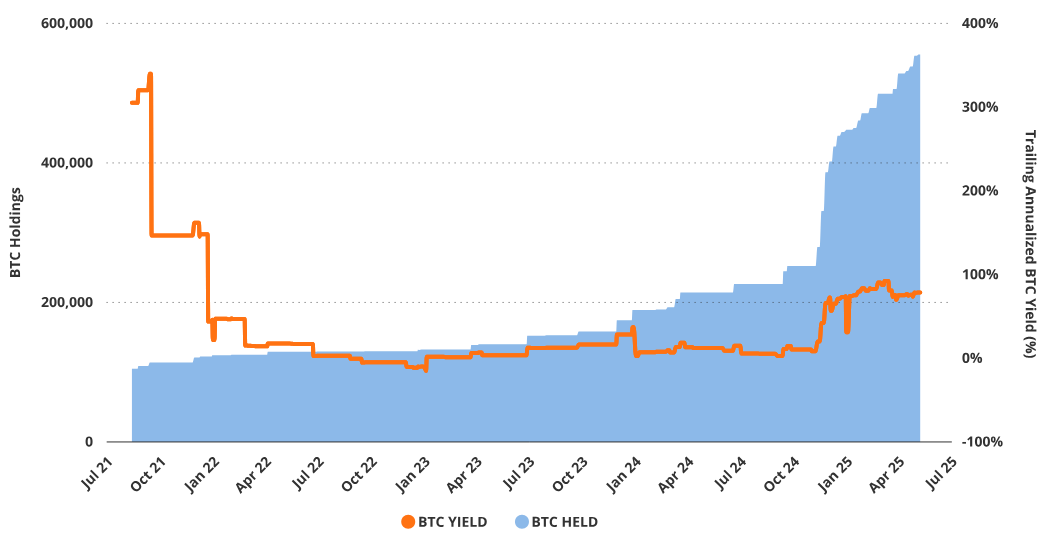
Source: Strategy, as of May 8, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
Strategy’s management team has multiple options for creating Bitcoin Yield. They can acquire Bitcoin by selling various financial products, thereby increasing the numerator (BTC holdings); or repurchase common stock to reduce the denominator (the base for calculating BTC per share). Given MSTR trades at a premium, selling “expensive stock” or issuing debt to acquire Bitcoin appears rational.
Selling common stock via ATM (At-the-Market) to buy Bitcoin may be the simplest method, but it is also the most dilutive and requires purchasing the most Bitcoin. During Q1 2025 earnings call, Saylor referenced this dynamic and noted a preference for selling permanent, non-convertible equity to acquire Bitcoin.
Example of BTC KPIs from $100 Million Issuance Across Different Securities
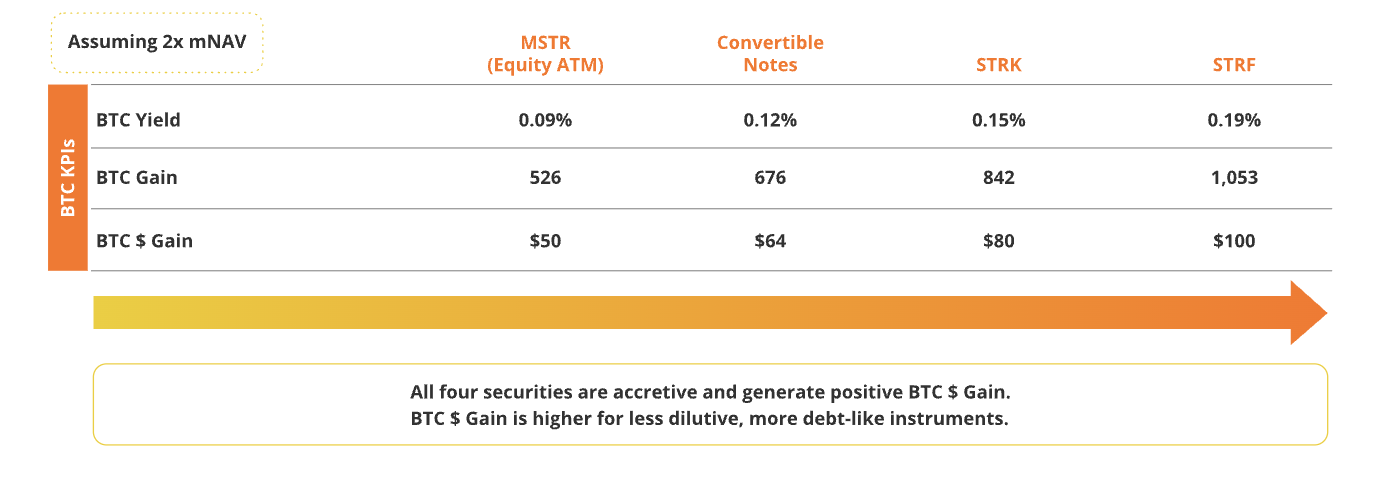
Source: Strategy, as of May 8, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
If Saylor does not achieve Strategy’s yield target by increasing common shares, he would need to purchase 58,312 BTC, costing approximately $5.9 billion at current prices. Alternatively, if he only issues common stock to increase exposure, he would need to issue about 25.8 million shares to buy $10.83 billion worth of Bitcoin, or about 108,305 BTC. Given strong market demand for Strategy’s capital structure, Strategy is likely to easily achieve its 25% yield target for 2025.
High BTC Yield Is Difficult to Sustain
Funding Required per Basis Point Increase in MSTR Yield (Millions USD, 90-Day Moving Average)
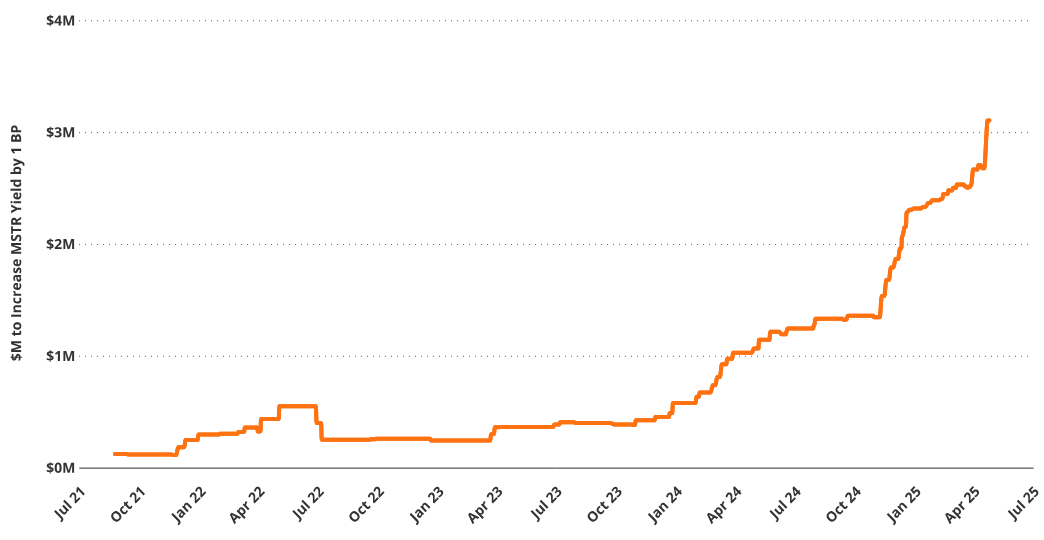
Source: VanEck Research, as of April 11, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
The reality facing Saylor’s Bitcoin strategy is that high Bitcoin yields are difficult to sustain due to diminishing returns. As Strategy accumulates more BTC, generating significant incremental Bitcoin yield becomes increasingly difficult. This is because, as the total BTC base grows, the amount of BTC required to produce each additional basis point of yield increases disproportionately.
For example, in August 2021, MicroStrategy needed only 2.6 BTC to generate one basis point of Bitcoin yield. By May 2025, this number had surged to 58 BTC. In monetary terms, the funding required to generate the same unit of yield increased from approximately $126,000 to $5.5 million. This reflects a fundamental mathematical reality: as Strategy’s BTC base grows, the marginal contribution of each additional BTC to yield decreases, while the funding required grows exponentially. This compounding inefficiency leads to a continuously declining ceiling for sustainable yield.
Evaluation of Strategy’s Convertible Bonds
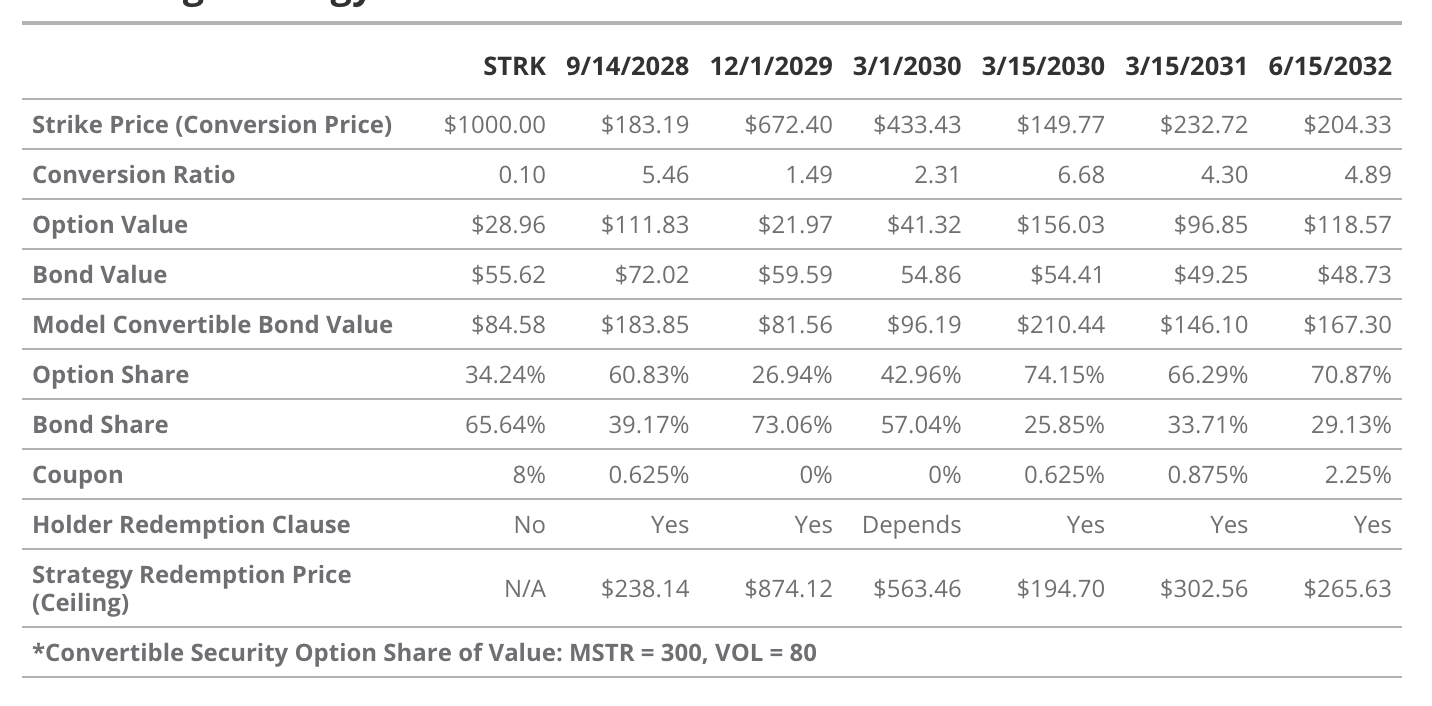
Source: VanEck Research, Strategy, as of April 2, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Information, valuation scenarios, and price targets in this article are for reference only, do not constitute financial advice, any action recommendation, or buy/sell advice, nor do they constitute predictions of Bitcoin’s future performance. Bitcoin’s actual future performance is unknown and may differ significantly from the hypothetical results depicted here. Risks or other factors not considered in the scenarios may hinder performance. These are simulation results based on research, for illustrative purposes only. Please conduct your own research and draw your own conclusions.
Convertible bonds are hybrid securities combining fixed-income features with equity upside potential. Specifically, they consist of a traditional bond and an embedded call option, allowing holders to convert the bond into common shares of MSTR under specific conditions. The total value of a convertible bond equals the bond value plus the conversion option value. Therefore, investors in convertible bonds allocate part of their principal to the corporate bond and another part to the call option. Consequently, convertible bond prices are sensitive to option pricing variables (such as underlying price, delta, gamma, etc.) and bond pricing factors (such as interest rates and credit spreads).
Strategy’s convertible notes include special provisions that cap the upside of the embedded option while offering some principal protection to investors. Strategy embeds a “call option,” allowing the company to redeem the notes at par plus accrued unpaid interest after the call date. The most common provision in Strategy’s convertibles is that the company can redeem the bonds if MSTR’s trading price reaches 130% of the conversion price. This clause limits the upside of the bond’s option value after the call date. Additionally, except for the March 1, 2030, issuance, Strategy allows convertible bondholders to put the bonds back to the company at par after the put date, serving as a price floor in case of financial distress.
The March 15, 2030, convertible bond is the most leveraged to MSTR price due to its large option component
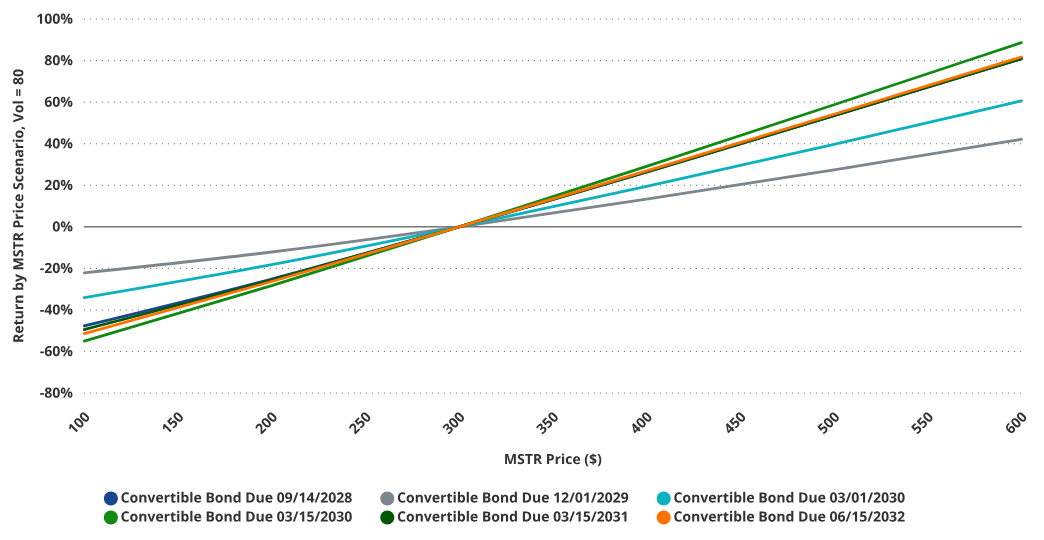
Source: VanEck Research, as of April 2, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
Due to the extreme volatility of the underlying stock, MicroStrategy’s convertible bonds contain significant embedded option value. Depending on the issuance, up to 74% of the bond’s total value may be attributed to the option. The higher this percentage, the greater the investor’s exposure to MSTR stock price volatility. This exposure can shift dramatically as MSTR’s volatility changes and as options move in or out of the money.
Among all outstanding convertible bonds, the Class B bond due March 2030 has risk characteristics closest to MSTR stock. Under high volatility scenarios (e.g., when MSTR volatility > 80), this bond exhibits the highest sensitivity to MSTR price regardless of whether the stock rises or falls. Conversely, the December 2029 bond shows the lowest sensitivity to MSTR price because its embedded option is deeply out-of-the-money. This results in a smaller contribution of the option to overall bond value, weakening its impact on bond price volatility.
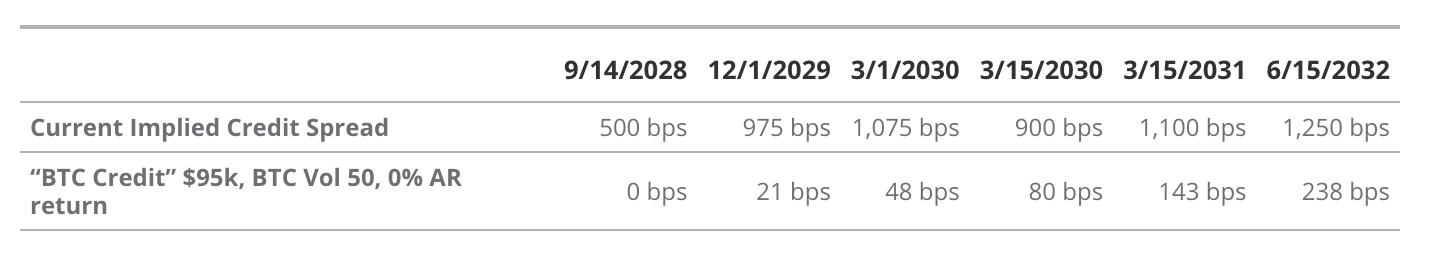
Implied Credit Spread vs. BTC-Adjusted Credit Valuation
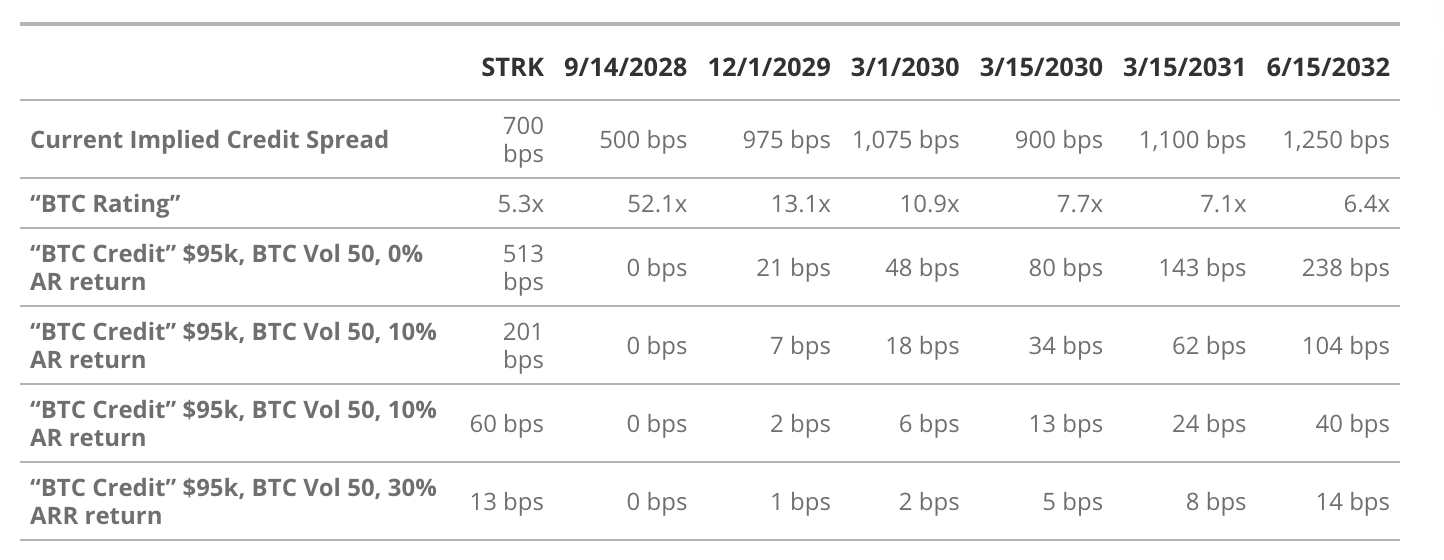
Source: VanEck Research, Strategy, as of May 7, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
The bond portion of Strategy’s convertible debt is controversial due to its wide credit spreads. Wide credit spreads reflect the market’s risk assessment of Saylor’s bonds, making these bonds priced as “cheap.” As Saylor mentioned on the Q1 2025 earnings call, credit spreads on Strategy’s fixed-income securities range from 500 to 1,250 basis points. This places Strategy’s bonds in the “double or triple junk bond credit spread” category.
Saylor argues these spreads are so wide because the market fails to properly value the BTC collateral backing the debt. Since rating agencies fail to adequately assess Strategy’s bonds, Saylor claims many long-term investors avoid them due to perceived risk. This depresses bond market prices and leads to excessively wide credit spreads.
Saylor conducts his own analysis of Strategy’s convertible bonds using option pricing models to demonstrate they are undervalued due to unappreciated collateral value. He introduces concepts of “BTC Rating” and “BTC Risk” to describe the potential risk of Strategy’s debt. “BTC Rating” is the multiple of BTC holdings to bond face value at current BTC market prices. This metric applies to all bonds, adjusted for seniority in case of Strategy’s BTC liquidation. For example, the September 14, 2028, bond has a BTC Rating of 52.1x, meaning Strategy’s BTC value is 52.1 times the bond’s face value at current BTC prices.
Saylor combines “BTC Rating” with option pricing models, using current BTC price and volatility to calculate the probability that BTC price falls below liquidation levels, ensuring bondholders do not incur losses. He calls this calculated probability “BTC Risk” and inputs it into bond pricing models to generate a new “credit spread,” which he terms “BTC Credit.” As shown in the table above, Saylor believes the market overestimates default probabilities for each bond, causing them to trade below “fair” valuations.
Implied Yield on Bond Component of MSTR Convertible Bonds
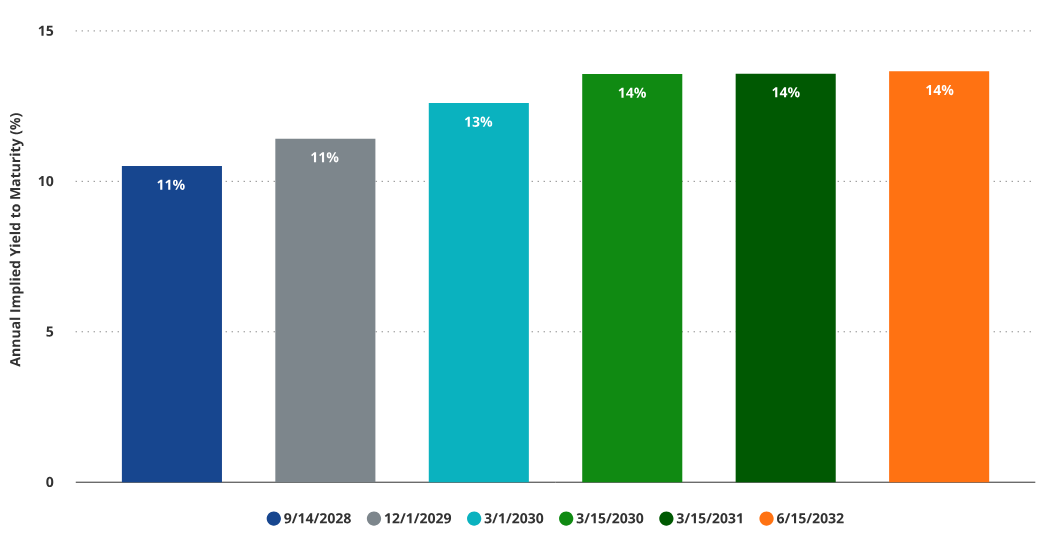
Source: VanEck Research, as of April 7, 2025. Past performance does not guarantee future results. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned. All forecasts are VanEck’s research-based results, for illustrative purposes only, valid until the date of publication and subject to change without notice.
A major issue with Strategy’s convertible bonds is the significant impact of the embedded option component on pricing. As a result, many bonds currently trade well above par, providing some downside protection. However, if option premiums weaken, a large portion of bond value could decline. For example, as of May 7, 2025, the 2028 convertible bond traded at $227.15. If MSTR’s stock price falls below the conversion price of $183.19 at maturity, the bond’s value would fall to $100 (assuming other factors unchanged). This reflects the significant embedded option premium in these instruments.
Another notable risk is sensitivity to changes in option pricing factors like volatility. We estimate that if volatility drops from 85 to 50, bond values would decline by approximately (-13%) on average; if volatility further drops from 85 to 30, average price declines would reach about (-20%).
MSTR stock performance is significantly influenced by the “premium,” which accounts for 87% of its volatility and 96% of total returns. We believe this indicates that investors in MSTR convertible bonds are not just buying stock options—they are effectively buying options on the persistence of the “premium.” And this premium is largely driven by Bitcoin price. As Bitcoin rises, the company gains greater financing capacity, increasing expected asset value and supporting speculative behavior toward MSTR stock.
If Bitcoin prices fall, the premium may also decline. We estimate the beta of this relationship is about 1.77x, meaning the premium’s value could fall significantly relative to Bitcoin price. This decline would erode the value of the option component in convertible bonds.
The fixed-income component of convertible bonds is also affected by the premium. The straight bond value partly depends on the company’s future financing ability. However, Strategy’s revenues are insufficient to cover its fixed-income obligations, let alone repay principal at maturity. If the premium declines, Strategy’s financing ability weakens, potentially widening credit spreads and lowering the value of the corporate bond portion in convertible bonds. The main cause of premium decline could be falling Bitcoin prices. Additionally, lower Bitcoin prices reduce the probability of full recovery for bondholders in a Bitcoin liquidation scenario, further weakening the value of Strategy’s convertible bonds.
This downside scenario is not inevitable but serves to highlight that both components of convertible bonds—the option and the bond itself—are tied to the same underlying drivers: Bitcoin price and MSTR premium. While some investors may hedge these risks, many may struggle to understand, let alone manage, them effectively. MSTR convertible bonds may appeal to investors seeking yield and potential upside, but they involve numerous risks. These instruments may be better suited for sophisticated investors capable of executing dynamic hedging strategies and analyzing equity-linked debt behavior.
Rise in Convertible Bond Value from Tightening Credit Risk
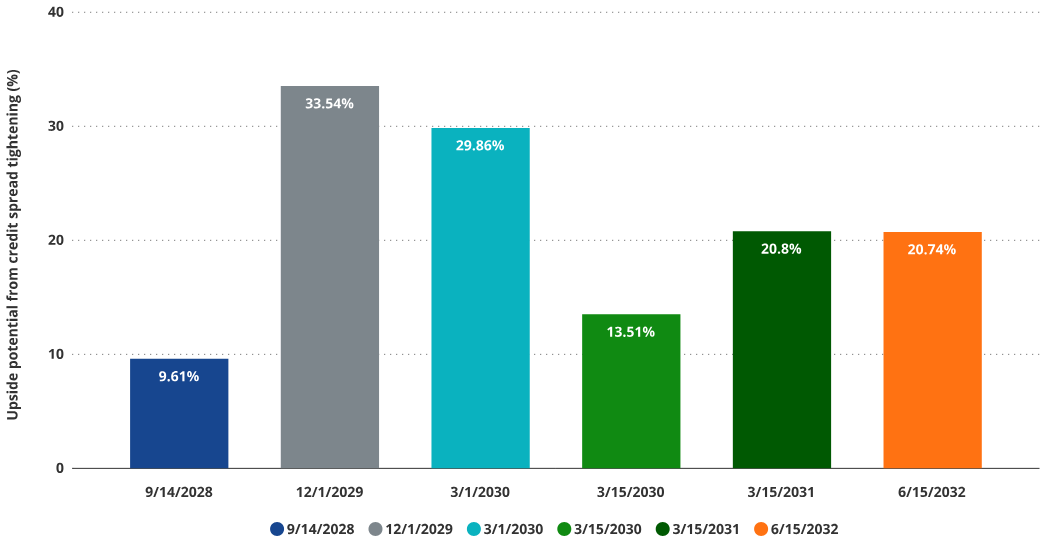
Source: VanEck Research, as of May 7, 2025. All forecasts are VanEck’s research-based results, for illustrative purposes only, valid until the date of publication and subject to change without notice.
Despite the risks, Strategy’s convertible bonds offer an exciting tool for speculating on progress in crypto accounting practices. If rating agencies adopt a more favorable view of Bitcoin as debt collateral, this could lead to a significant tightening of credit spreads. This would substantially increase the overall value of Strategy’s convertible bonds by boosting the bond component’s value. If Strategy’s bonds reached the lowest estimated “true” credit spread deemed fair by Saylor, we calculate the median convertible bond value would increase (+16%). In fact, convertible bonds with higher bond-value weighting may see the largest price gains.
The most attractive targets are the December 1, 2029 bond (+31% upside) and the March 1, 2030 bond (+26% upside). Given the March 1, 2030 bond is closer to being in-the-money, the combination of its credit spread converging to Saylor’s defined “BTC Credit” and its high option value could appeal to bold speculators. However, for traditional long-term investors, the risk exposures in these bonds may be too complex to manage. Relatively speaking, we find them less attractive than other parts of MSTR’s capital structure.
MSTR Price Simulation (BTC Price +/-80%, MSTR Volatility = 80)
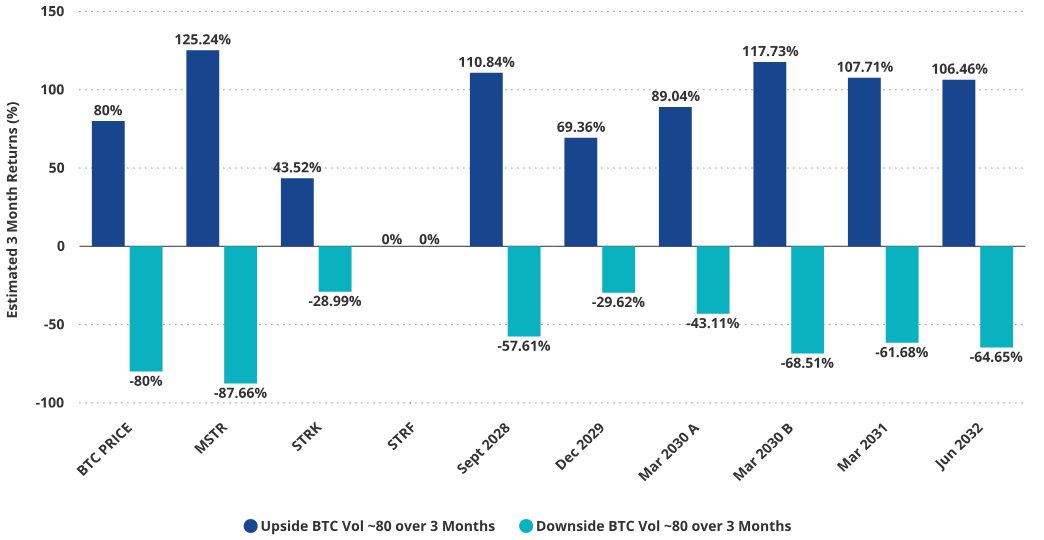
Assumes MSTR volatility of 80, BTC down 80% over 3 months.
Source: VanEck Research, as of April 2, 2025. All forecasts are VanEck’s research-based results, for illustrative purposes only, valid until the date of publication and subject to change without notice. This article does not constitute a buy/sell recommendation for any securities mentioned.
STRK Overview and Analysis
STRK, known as “Preferred Perpetual Convertible Equity,” integrates multiple concepts into a single security. It offers an 8% perpetual dividend at par, payable in cash or common stock. However, there are limitations on paying dividends in common stock; for example, if MSTR’s value falls below 35% of its January 27, 2025 price ($347.92), the total number of common shares issued as dividends will be capped.
STRK also provides a perpetual option on MSTR stock (i.e., no time decay on option value) and carries liquidation rights typically associated with preferred shares. Similar to convertible bonds but junior in priority, it is a fixed-income security with a deeply out-of-the-money call option, with a strike price of $1,000—2.5 times the current MSTR trading price (as of May 7, 2025).
Based on our calculations, about 36% of STRK’s current price comes from the call option, giving holders upside exposure to MSTR. Despite the option being deeply out-of-the-money, STRK’s option component trades at a delta close to 1 due to MSTR’s extremely high volatility and the perpetual nature of the option. This means STRK’s price movements are already tightly correlated with MSTR’s price movements in the option segment.
Prior to MSTR’s stock price approaching the conversion strike, we expect STRK’s sensitivity to volatility changes to exhibit pronounced asymmetry, skewed to the downside. For instance, if implied volatility increases from ~80% to 120%, we estimate STRK’s price would rise only slightly (+0.01%). However, if volatility drops from 80% to 40%, we expect STRK’s price to fall by about (-3%), and further dropping to 20% would result in approximately (-19%) loss.
The reason for this asymmetric risk lies in STRK’s embedded call option being deeply out-of-the-money and perpetual. In this state, increases in volatility beyond a certain level have minimal impact on the probability of the option eventually moving in-the-money, flattening the upside
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News