
Tiger Research: A Detailed Explanation of World Network and World ID
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Tiger Research: A Detailed Explanation of World Network and World ID
World Network has the potential to evolve from a simple human verification system into a global identity infrastructure.
Author: Tiger Research Reports
Translation: TechFlow
Key Takeaways
-
As artificial intelligence advances rapidly, distinguishing between humans and AI in digital environments has become increasingly difficult. This growing need to prove human identity has driven Tools for Humanity to develop relevant technologies and infrastructure.
-
World ID is a digital identity infrastructure designed to verify users as human beings. It leverages zero-knowledge proof technology to confirm identity without exposing personal information.
-
Beyond basic authentication, World ID functions as a flexible digital identity platform. With SDK integration and optional verification features, it enables effective applications across multiple industries.
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence is advancing at a pace surpassing Moore's Law, impacting nearly every industry. OpenAI recently raised $6.6 billion, the largest single investment ever made in a private company. This influx of capital highlights the rapid growth of the AI market and the global race to develop advanced AI technologies.
However, we must also recognize the dual nature of rapid technological advancement—AI being no exception. As the boundary between humans and AI blurs, new forms of crime are emerging. These changes distort markets and undermine fair trade, affecting the business world. While such issues have existed since the dawn of the internet, they have grown more complex and harder to manage with the rise of AI. Distinguishing sophisticated bots from real users has now become a major challenge, threatening trust and security in digital environments and posing serious societal risks. Efforts to address these problems are underway, and Tools for Humanity’s “World Network” stands as a prime example.
2. World Network: Human Identity Verification in the Age of AI

Source: World Network
World Network is a project aimed at identifying and protecting real humans in digital environments—an increasingly critical task amid advancements in artificial intelligence. Founded by physicist Alex Blania and AI pioneer Sam Altman, both bring deep expertise in AI research and development. Blania focuses on deep learning and its applications in quantum computing, while Altman, as co-founder and CEO of OpenAI, has been at the forefront of AI innovation.
The founders maintain a balanced perspective on AI progress, fully aware of its potential challenges. Their goal is to preserve human uniqueness in a future saturated with advanced AI. To achieve this, they established Tools for Humanity (TFH) and launched the World Network project. At its core, World Network revolves around “human identity verification,” with a mission to identify and protect real humans in complex digital spaces while promoting responsible technology use.
To accomplish this, World Network uses the iris as the most reliable biometric identifier. Every individual’s iris is unique, with an extremely low false match rate, ensuring secure authentication. Even identical twins have different iris patterns, which remain stable over time. World Network has developed a system that leverages these characteristics, using anonymized iris codes to verify human identity.
3. The Human Identity Verification Process of World Network
The human identity verification process in World Network works as follows: First, users install the World App on their smartphones and create a World ID. Then, at designated verification locations, users scan their World ID’s QR code using an Orb device, which verifies whether the individual is a unique human.
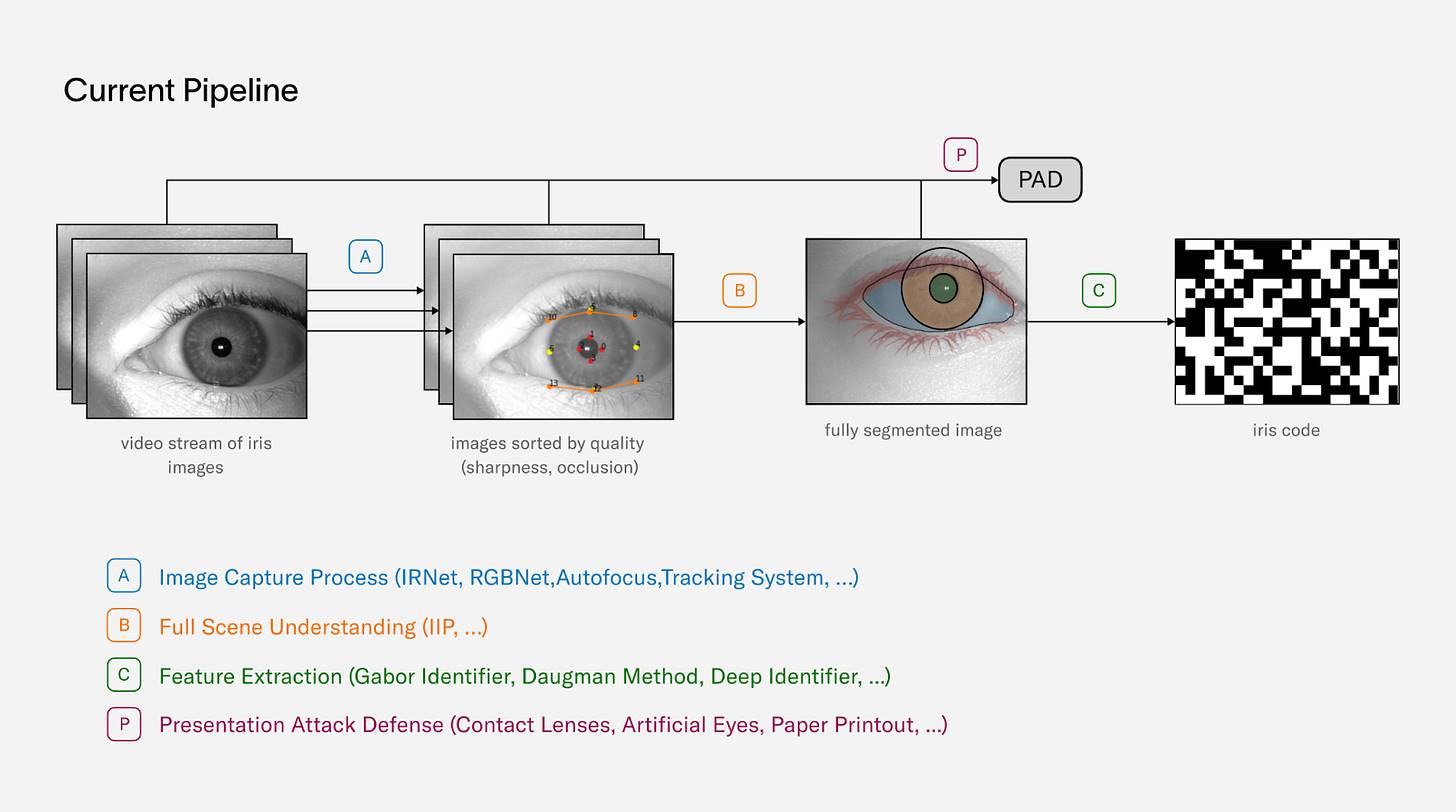
Source: World Network
Next, the Orb captures images of the user’s iris and face, generating an iris code for integrity verification. After verification, the original iris image is immediately deleted. During the World ID certification process, the iris code is securely transmitted end-to-end to the user’s smartphone via public-key encryption. Only when combined with the private key stored on the phone can the iris code be decrypted, completing the identity verification. This method ensures data security and gives users full control over their information.

Decentralized database of World ID managed by independent trusted organizations (October 2024), Source: World Network
The iris code is split into fragments and stored anonymously using secure multi-party computation (SMPC). These fragments are distributed among trusted organizations in locations such as the United States and Germany, each having access only to their specific fragment. This structure significantly enhances data anonymity and security. As more universities and non-profit organizations join, this system is expected to grow even stronger. Once all steps are completed, users can prove their unique identity online through a verified World ID. For more details, visit World Network’s “Private by Design” page.
4. World ID: A New Standard for Digital Identity
Through World Network, proving human identity has evolved beyond just a “certificate.” Building on this foundation, World ID is becoming a versatile digital identity platform. It integrates seamlessly with various services via SDKs and allows additional identity information to be added as needed.
Source: World Network
World ID has already verified over 7 million users across more than 160 countries and integrated with major platforms like Shopify, Telegram, and Reddit. Users may optionally link government-issued IDs (such as passports or driver’s licenses) to their World ID. This feature enables selective verification of specific attributes—like age or nationality—when required. These capabilities allow access to age-restricted services, region-specific products, and authenticated verifications.
Besides scalability, World ID employs blockchain and zero-knowledge proof technologies to safeguard user privacy. This setup allows users to share only necessary information without revealing personal details. For instance, age-restricted services can confirm adulthood without accessing exact birth dates. These features position World ID as a new standard for digital identity verification in the AI era.
5. Use Cases of World ID
With the widespread adoption of AI, the risk of manipulation and fraud via bots and fake accounts is rising—especially in commercial settings. World ID holds strong potential to counter these threats. Thanks to its scalability, it can be applied across diverse environments to solve various problems. Below, we explore concrete examples of how World ID is being used across industries and services.
5.1. World ID in Social Networking Services
Source: @elonmusk
Social networking services are facing a crisis as AI-generated content becomes more sophisticated and cheaper to produce. Elon Musk reported that fake and spam accounts account for approximately 20% of all users on X (formerly Twitter). These accounts manipulate public opinion through ads and spam, promote scams, and damage platform credibility.
As AI technology advances, this risk is expected to grow. World ID aims to address this issue through a biometric-based unique identity verification system. By limiting one account per person, World ID can effectively prevent fake accounts and reduce platform abuse.
5.2. World ID in Subscription Services
Subscription platforms frequently face abuse from multiple accounts. Companies like YouTube and Netflix find increasing numbers of users creating extra accounts to exploit free trials or resell access. This not only makes it hard to identify genuine users but also raises customer acquisition costs and reduces industry efficiency.
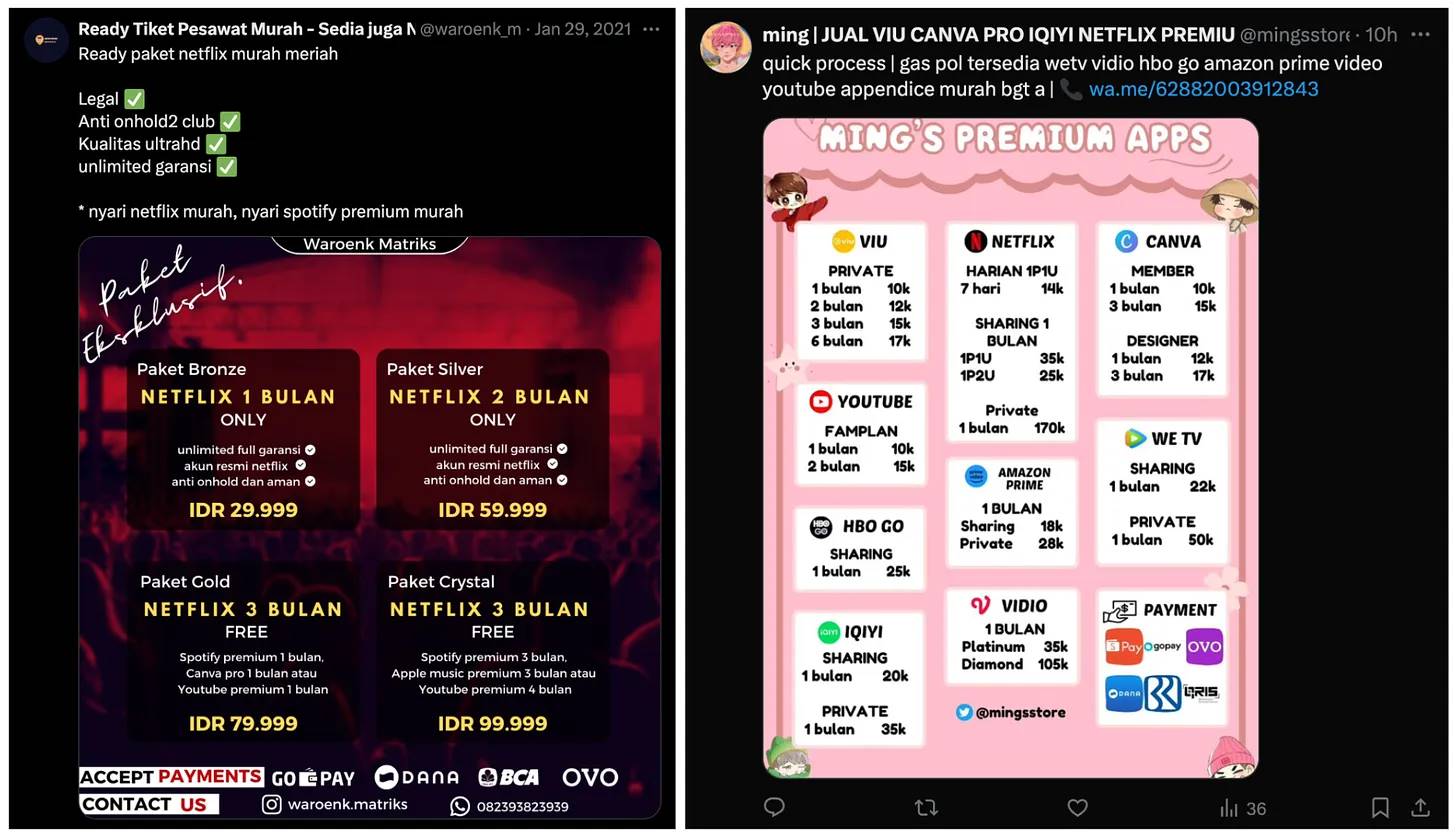
Resale of free trial accounts for Netflix, Spotify, YouTube, etc., on X platform. Source: respective X accounts
World ID’s unique identity verification system resolves these issues by confirming each user as a real human and preventing duplicate accounts. This solution could significantly improve cost efficiency in the subscription service industry.
5.3. World ID in the Concert Ticketing Market
World ID has significant implications for the concert industry, which long suffers from unfair ticketing practices, black-market sales, and long venue queues. World ID offers solutions to these challenges and promises to streamline the entire process—from purchase to entry.
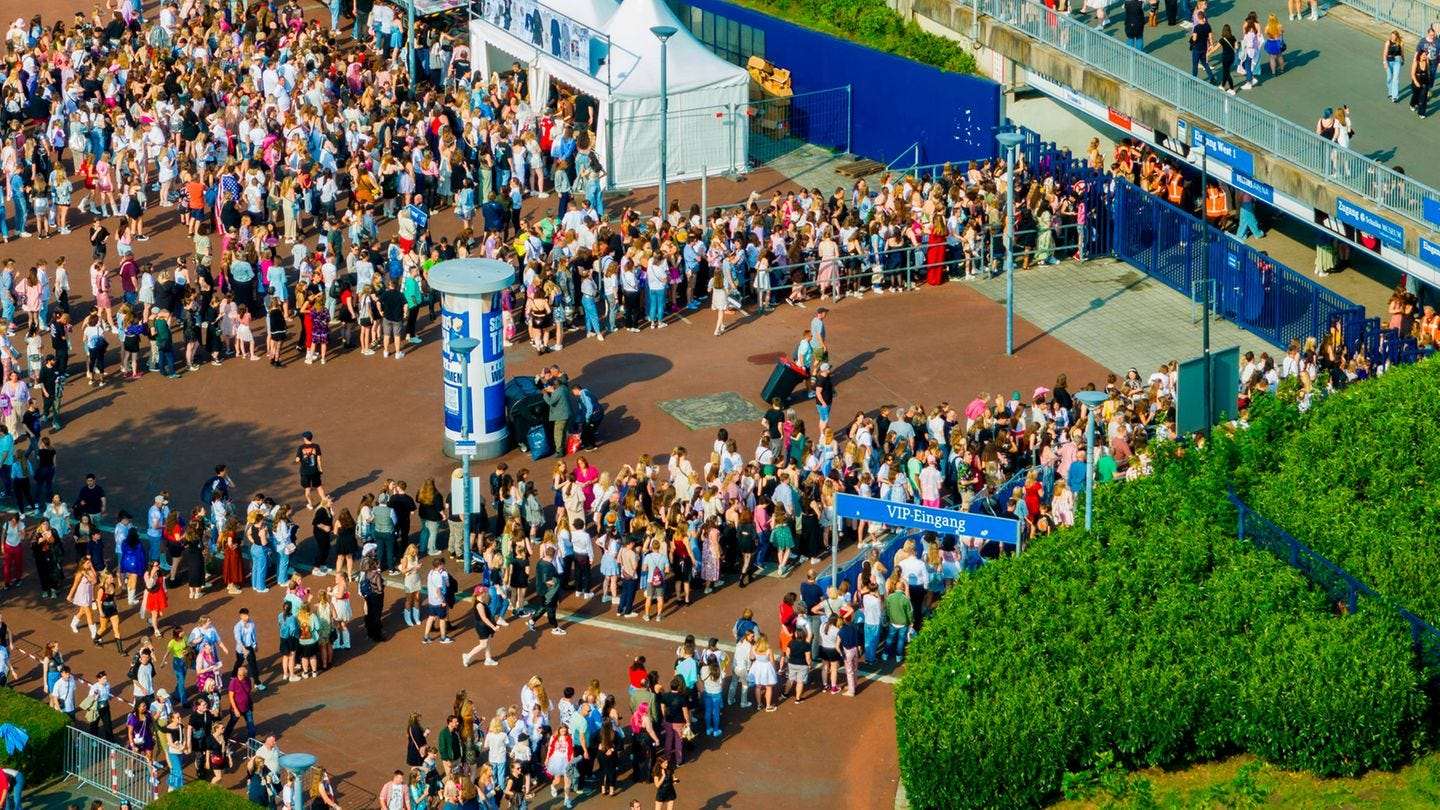

Long lines for Taylor Swift concert entry. Source: Christoph Reichwein/dpa
During ticket purchasing, World ID prevents bulk account usage and pre-verifies identities, ensuring fairness and giving genuine fans better access. At venue entrances, World ID, paired with the newly piloted Face Auth feature, enables fast and accurate identity checks. This method is more efficient and reliable than manual verification, reducing wait times and inconvenience for attendees.
This improvement also benefits event organizers. Streamlined entry reduces operational costs and improves audience management efficiency. Thus, World ID is poised to enhance overall operations and boost attendee satisfaction.
5.4. World ID in E-commerce
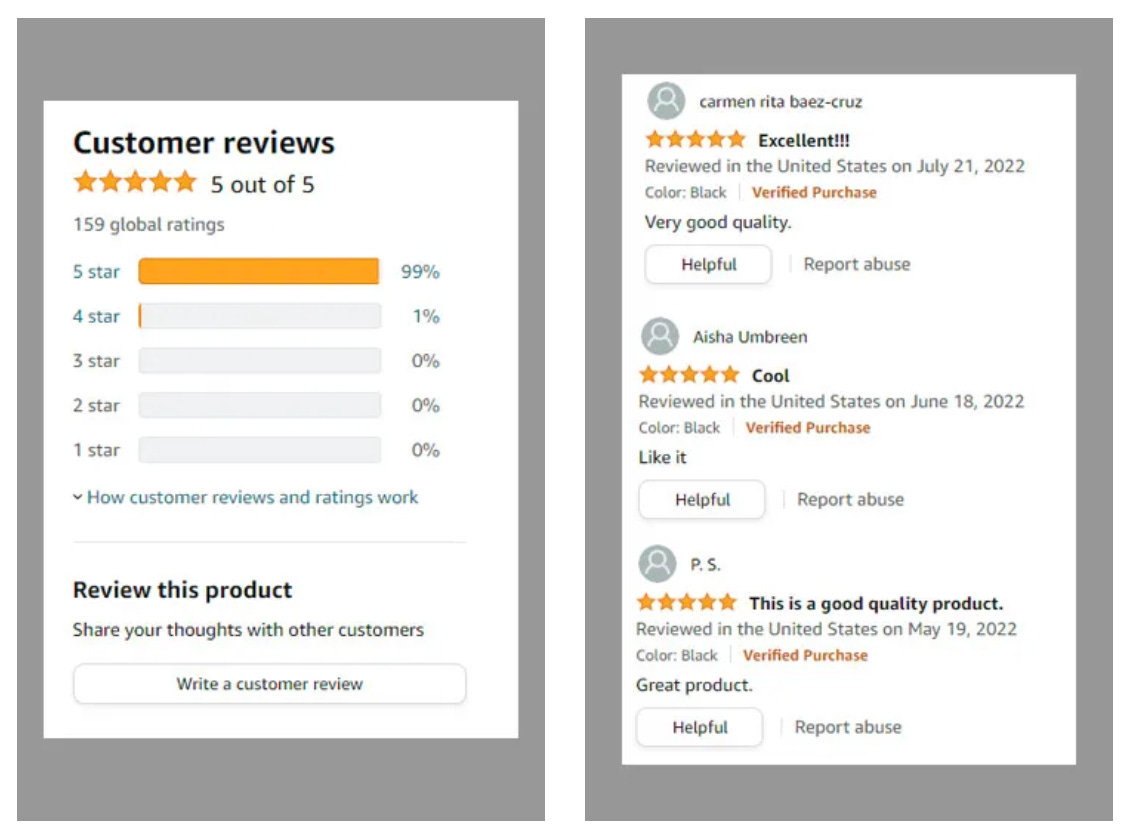
Example of fake reviews. Source:WIRED
World ID holds substantial potential in e-commerce. While the sector has grown rapidly, AI advancements bring new challenges. A major concern is the reliability of review systems, which heavily influence buyer decisions. AI makes it easier to generate fake reviews at scale, undermining rational consumer choices.
According to UK government research, 11–15% of product reviews for common items in the UK e-commerce market may be fake. Even large platforms like Amazon struggle with this, leading to increased user complaints. Most e-commerce platforms typically react after problems arise, whereas World ID offers a proactive solution. By allowing only verified World ID users to post reviews, AI-generated fake reviews can be significantly reduced. This helps buyers make informed decisions and strengthens the integrity of the entire e-commerce ecosystem.
5.5. World ID in Crime Prevention, Including Deepfakes
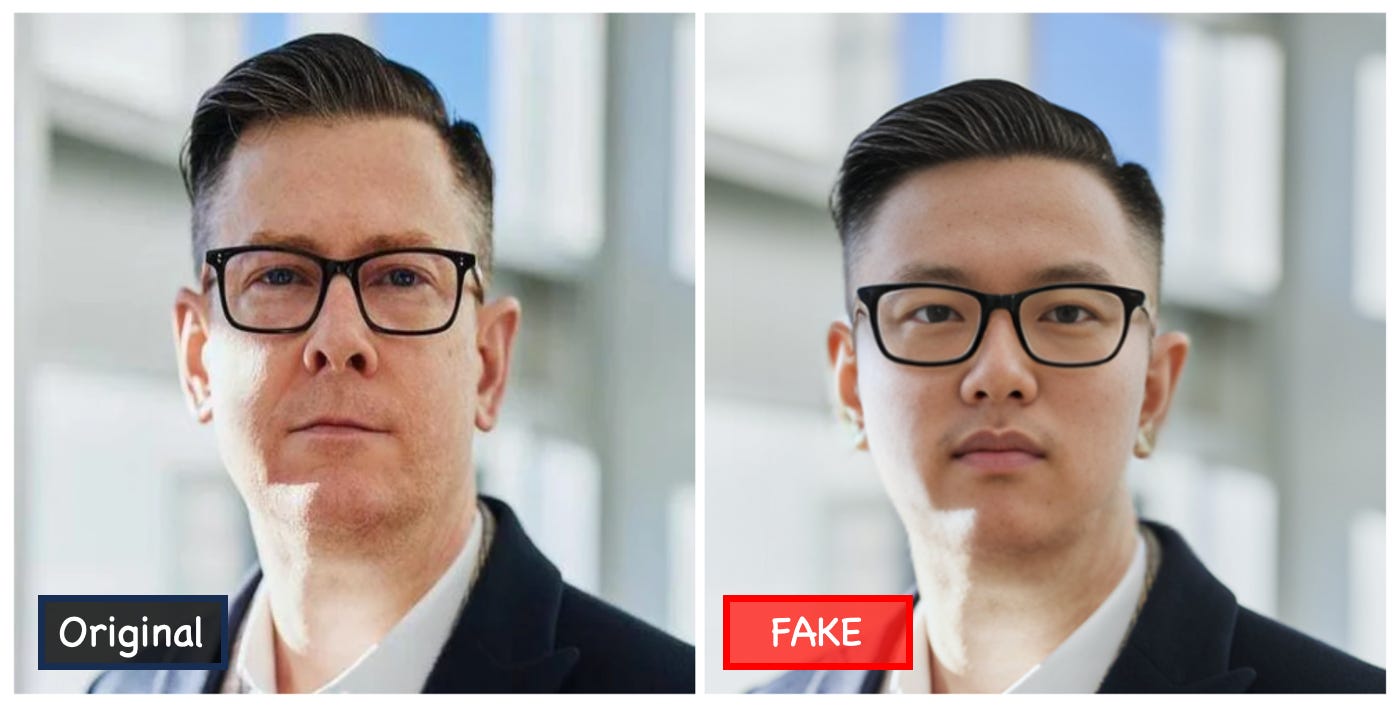

Source:KnowBe4
A notable case involves North Korean developers using deepfake technology to forge identities and gain employment. With the rise of remote work, such incidents are increasing. These developers were found participating in projects like Injective, Fantom, and SushiSwap under fake identities, using deepfakes during video interviews to impersonate legitimate candidates. Once hired, they attempted to infiltrate internal systems and steal funds.
In February this year, a security breach at multinational firm Arup highlighted the severity of this threat. Criminals impersonated the company’s CFO, using fake audio and visuals in a video conference to deceive employees and obtain sensitive information via phishing emails. This incident shows that AI-powered crimes are no longer theoretical—they are causing real damage.
These cases demonstrate that traditional identity verification methods are no longer sufficient. To address this, World Network introduced World ID Deep Face. This feature detects the presence of real humans during video calls and live streams, mitigating deepfake risks.

How World ID Deep Face works. Source: World Network
Accessible via the World app and desktop clients, and available as an SDK extension, World ID Deep Face can be seamlessly integrated into platforms like Google Meet, Zoom, Twitch, and YouTube, enhancing security and preventing identity fraud. It can also be deployed on recruitment platforms and other identity-sensitive services. World ID Deep Face is set to become a vital tool against AI-driven identity fraud.
6. Challenges Facing World ID and Their Solutions
With its high security and usability, World ID has the potential to become a core authentication tool in the AI era. However, several challenges remain: 1) Public resistance to biometric data usage, 2) Risks of World ID misuse, and 3) Physical accessibility of Orb devices.
6.1. Public Resistance to Biometric Data Usage
Despite the high authenticity of World Network’s human verification approach, public skepticism toward biometric data persists. Privacy concerns are the primary reason. To earn trust, World Network must implement robust security measures.
World Network addresses this through Anonymous Multi-Party Computation (AMPC). Iris codes are split into parts, stored in a decentralized and de-identified manner, and managed as numerical data rather than images. After verification, only the World ID—not the iris code—is used for subsequent logins. These safeguards aim to alleviate public concerns about biometric data usage.
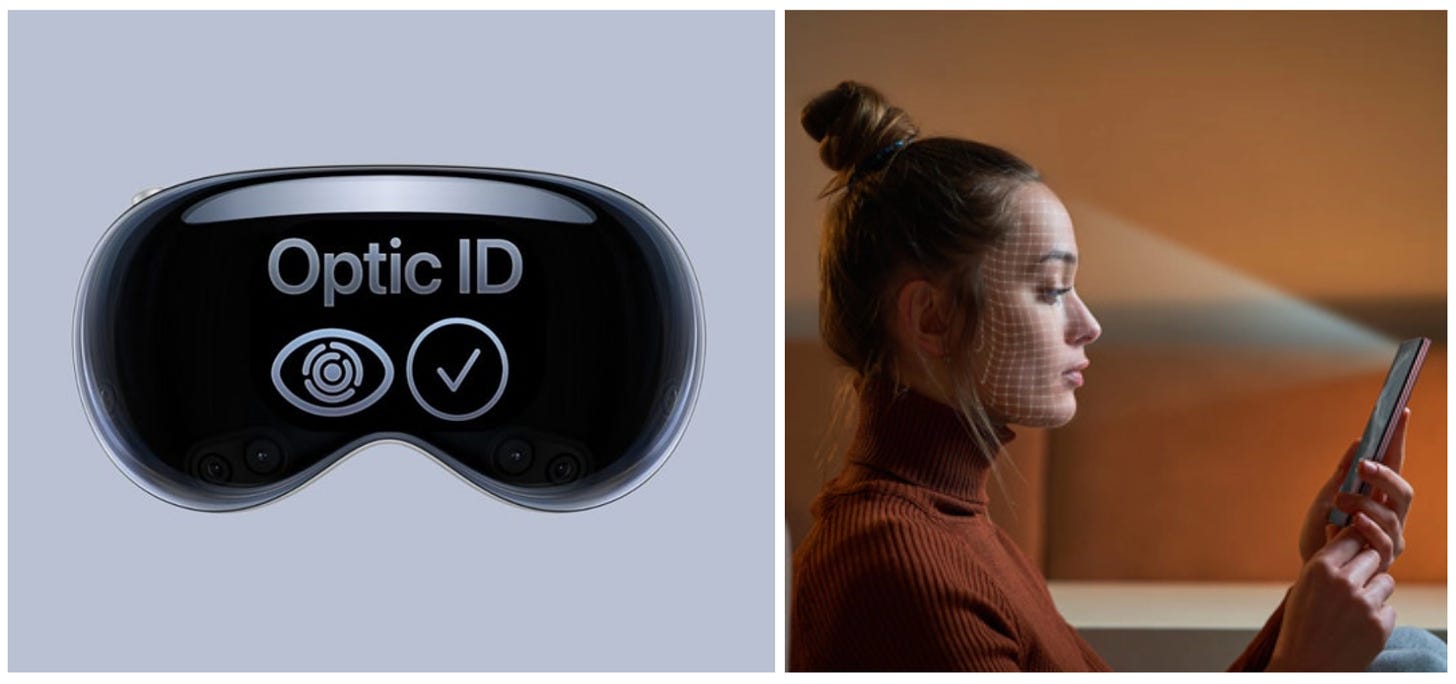

Source: Apple Optic ID (left), Samsung facial recognition (right)
Wider adoption of biometrics across industries plays a key role in boosting social acceptance. As technologies like Apple’s Optic ID and Samsung’s facial recognition become part of daily life, people may grow more comfortable with them. Gradual exposure helps raise awareness and accelerates the adoption of World ID.
6.2. Potential Misuse of World ID
Another challenge is the risk of abuse through account trading. In traditional sectors, ID resale is common, and World ID’s use of sensitive biometric data like iris scans could face similar exploitation. Such transactions threaten system integrity.
To combat this, World Network implements multiple safeguards. For instance, World ID authentication relies on facial image data stored locally on users’ smartphones. Additionally, if a user unknowingly sells their account, they can reclaim it using the World ID reset function. These protections aim to prevent account sales, loss, or theft, providing user security while increasing system flexibility and reducing abuse.
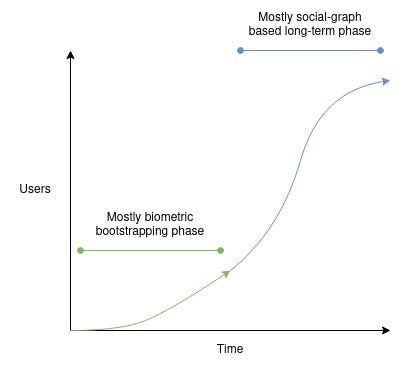
Source:Vitalik Buterin
Expanding the World ID ecosystem can naturally reduce misuse. Sold accounts lack authentic user behavior and exhibit distinct activity patterns. By first verifying via hardware-based biometrics and gradually incorporating social graph verification, authenticity can be better assessed. As user engagement grows, monitoring and detecting suspicious patterns becomes easier. Vitalik Buterin also suggests that combining biometric and social graph verification can help build long-term trust.
6.3. Accessibility of Orb Devices
While iris verification offers high security, the requirement for in-person validation via Orb presents a major barrier. Beyond geographical distance, there’s the challenge of mass-producing and distributing expensive Orb devices globally.

Orb 2.0 features. Source: World Network
To tackle this, World Network is opening up Orb designs to enable global manufacturing. They’re also collaborating with South Korea’s Chain Partners to jointly develop hardware through the second Orb program. The newly launched Orb 2.0 allows faster production, speeds up verification, and reduces component count by 30%, greatly improving manufacturing efficiency.

On-demand Orb availability. Source: World Network
Plans include placing Orbs in everyday locations like cafes to improve accessibility. In South America, a partnership with Rappi will launch an “On-Demand Orb” service, allowing users to complete World ID verification from home. Although expanded access brings new challenges—such as ATM-like management and security concerns—World Network’s efforts mark a crucial step toward building a global human identity verification infrastructure.
7. Conclusion
As AI advances rapidly, distinguishing humans from AI is becoming increasingly difficult. Consequently, the need to prove human identity has never been more urgent. Yet, this is no simple task. The challenge lies in verifying the humanity of approximately 8.1 billion people globally—a process that is both complex and massive.
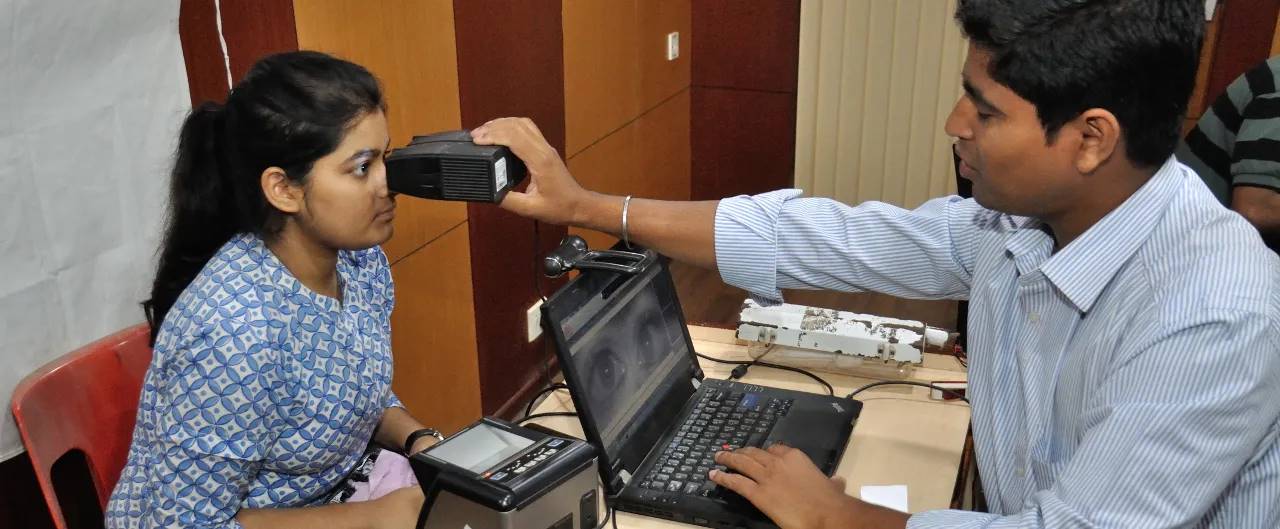

Source: Times of India
In many cases, biometrics are seen as the most effective solution. India’s Aadhaar system serves as a classic example. Using iris and fingerprint scanning, the Indian government successfully registered about 95% of its adult population. This system greatly simplified access to services like financial transactions. Successfully implementing such a large-scale biometric system in a country of over 1.4 billion people demonstrates the immense potential of biometric-based identity verification and supports the feasibility of global systems like World Network.
World Network builds on this model, integrating zero-knowledge proofs and blockchain technology to enhance security and privacy. Several real-world applications are already underway. For example, Malaysia’s government digital credential project uses World Network’s iris scanning technology. Additionally, WorldChain aims to boost global scalability by creating a permissionless system.
These technological advances suggest that World Network could evolve from a simple human verifier into a global identity infrastructure. Nevertheless, challenges remain. Low social acceptance, risks of abuse, and regulatory hurdles are key obstacles. How World Network navigates these challenges will be critical to its long-term success.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















