Understanding Pell Network: The Remarkable Debut with $190 Million TVL — What Makes This Bitcoin Restaking Star So Special?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Pell Network: The Remarkable Debut with $190 Million TVL — What Makes This Bitcoin Restaking Star So Special?
Pell Network is committed to advancing BTC restaking, delivering more secure and efficient solutions for the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Author: Xingxing
In 2024, the restaking market has witnessed a tremendous shift from an emerging narrative to a breakthrough reality. Meanwhile, Bitcoin's decentralized value and the rising popularity of innovations like Ordinals have redirected attention back to the Bitcoin ecosystem, signaling the arrival of a "BTCFi Summer."
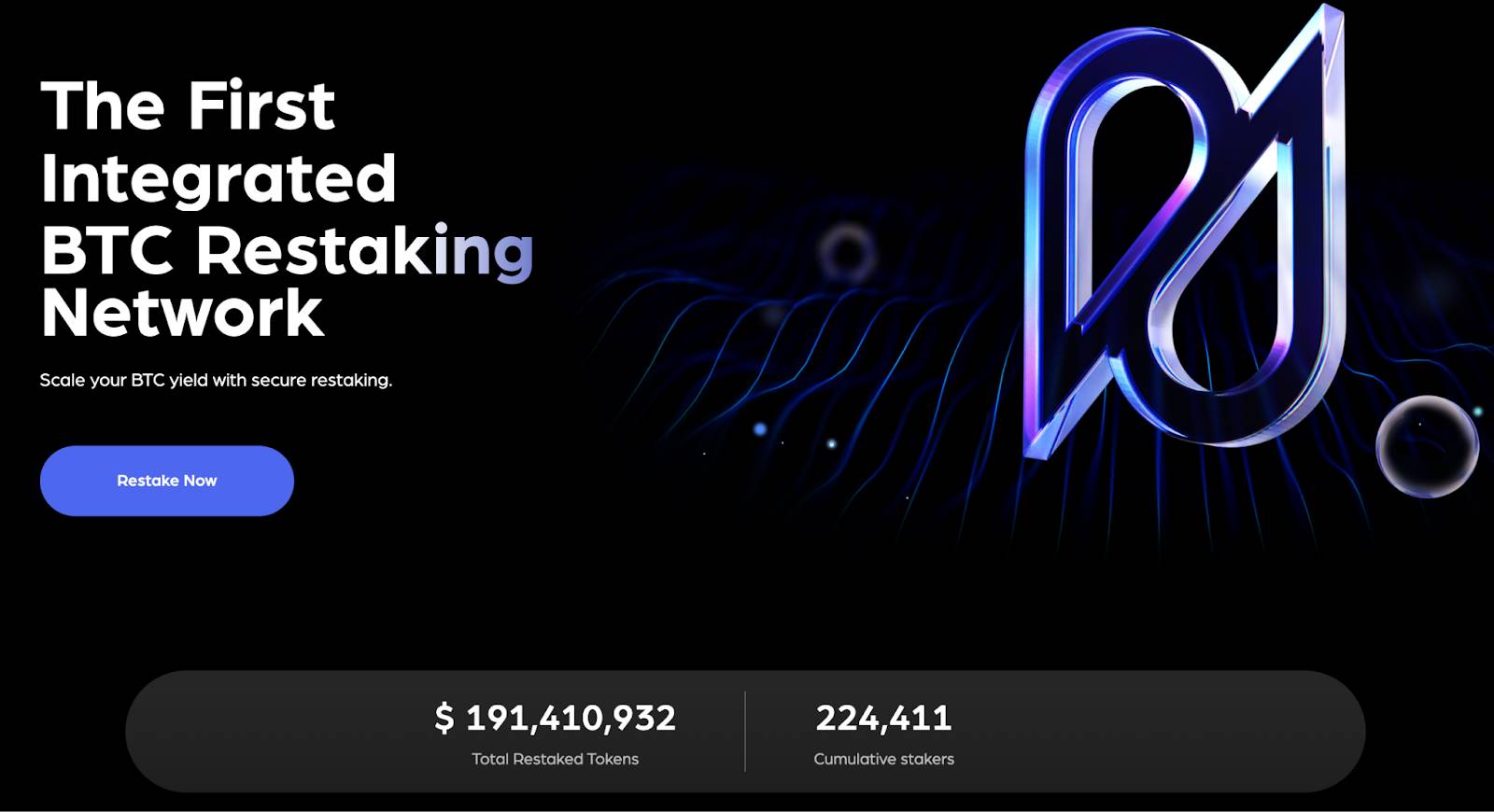
Pell Network, as the first AVS (Actively Validated Services) network in the BTC ecosystem built on restaking, achieved a TVL of $190 million within three weeks of its pre-launch, attracting participation from 220,000 unique addresses. These impressive figures not only highlight Pell Network’s market appeal but also reflect strong user interest in understanding or engaging with the protocol.
So, what exactly is Pell Network? This article will analyze this emerging protocol by exploring the market potential of BTC restaking, Pell Network’s technical architecture, use cases, and ecosystem, helping users gain deeper insights into the latest developments in Bitcoin restaking.
The BTC Restaking Sector: A Boon for BTC Stakers
For a long time, BTC holders have faced a key challenge: how to maximize their asset yields. Traditional BTC holding is limited to custody and trading, offering relatively few revenue streams. While liquid staking has enabled BTC holders to earn passive income by staking their assets—thereby increasing capital efficiency—this still falls short of meeting current user demands.
The restaking sector aims to fully address this issue. EigenLayer has already proven the viability of restaking within the Ethereum ecosystem, amassing $15 billion in total value locked (TVL), equivalent to 4% of Ethereum’s market cap ($370 billion). EigenLayer not only leveraged LSD assets to create a vast restaking ecosystem but also evolved into a consensus layer securing Ethereum itself.
These successes were quickly adopted by the Bitcoin ecosystem. Babylon, a protocol focused on native BTC staking, was among the first to launch. By staking native BTC into Babylon, users enable the protocol to help secure PoS chains and validate transactions on those chains. In return, PoS chains provide security rewards to both Babylon and BTC holders. Babylon transformed previously non-stakable BTC into a stakable asset, achieving the critical transition from zero to one.
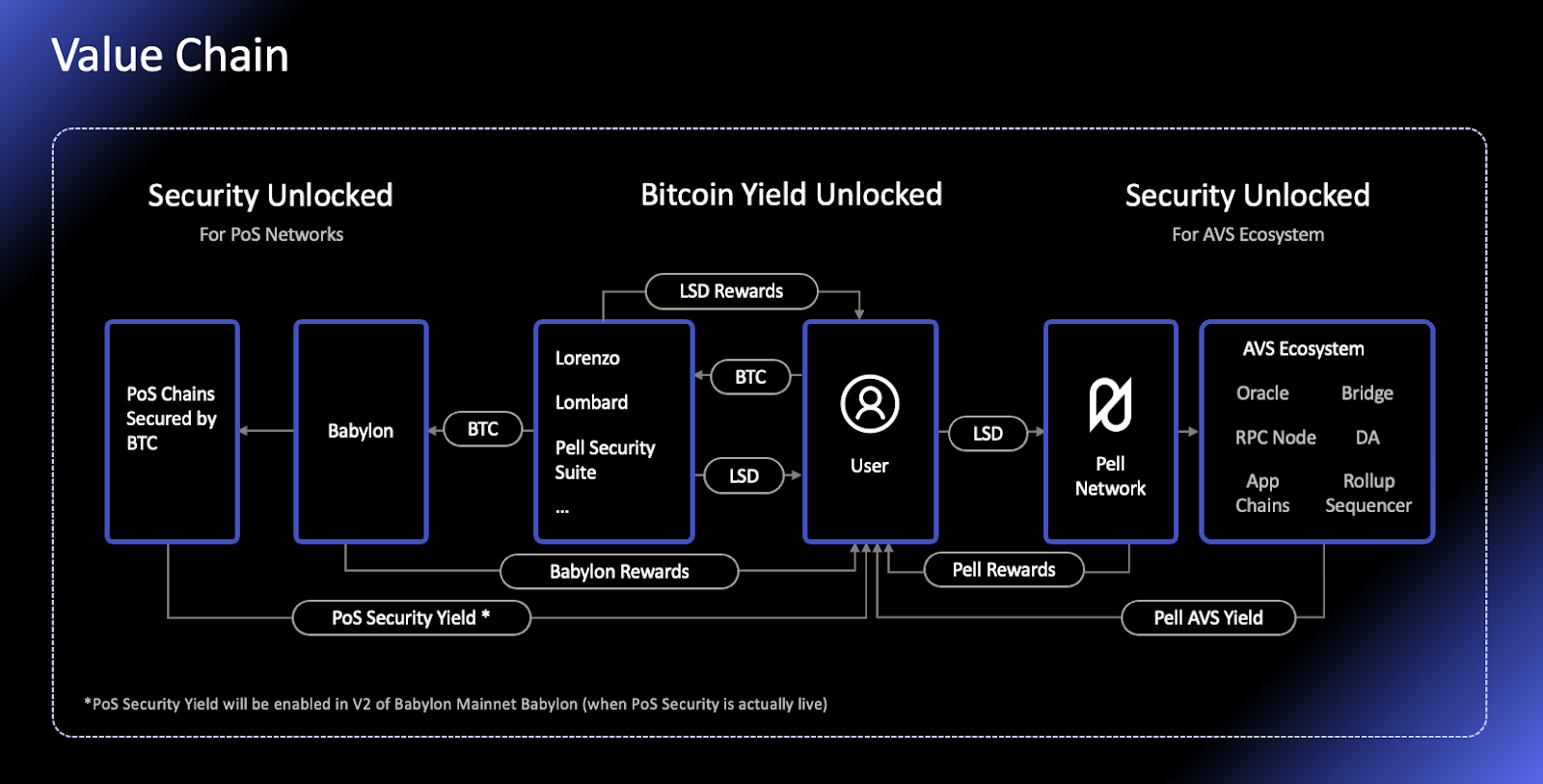
Pell Network builds upon Babylon by enabling BTC LSD holders to restake their tokens while introducing cross-chain interoperability and programmable trust, thereby extending the security of BTC assets across the broader Bitcoin ecosystem and even to other major public blockchains. Seamlessly integrating with Babylon, Pell Network drives the evolution of Bitcoin’s staking ecosystem from one to one hundred. Preliminary estimates suggest that the BTC restaking sector could produce unicorn protocols exceeding $45 billion in TVL, positioning Pell Network as one of the leading contenders.
Pell Network Technical Architecture
Pell Network is the first omnichain AVS (Actively Validated Services) network, providing cryptographic-economic security for decentralized infrastructure through restaked BTC LSD (Liquid Staking Derivatives) assets.
Beyond filling a critical security gap in the ecosystem, Pell Network significantly reduces the cost of building decentralized applications while offering BTC holders new avenues for passive income.
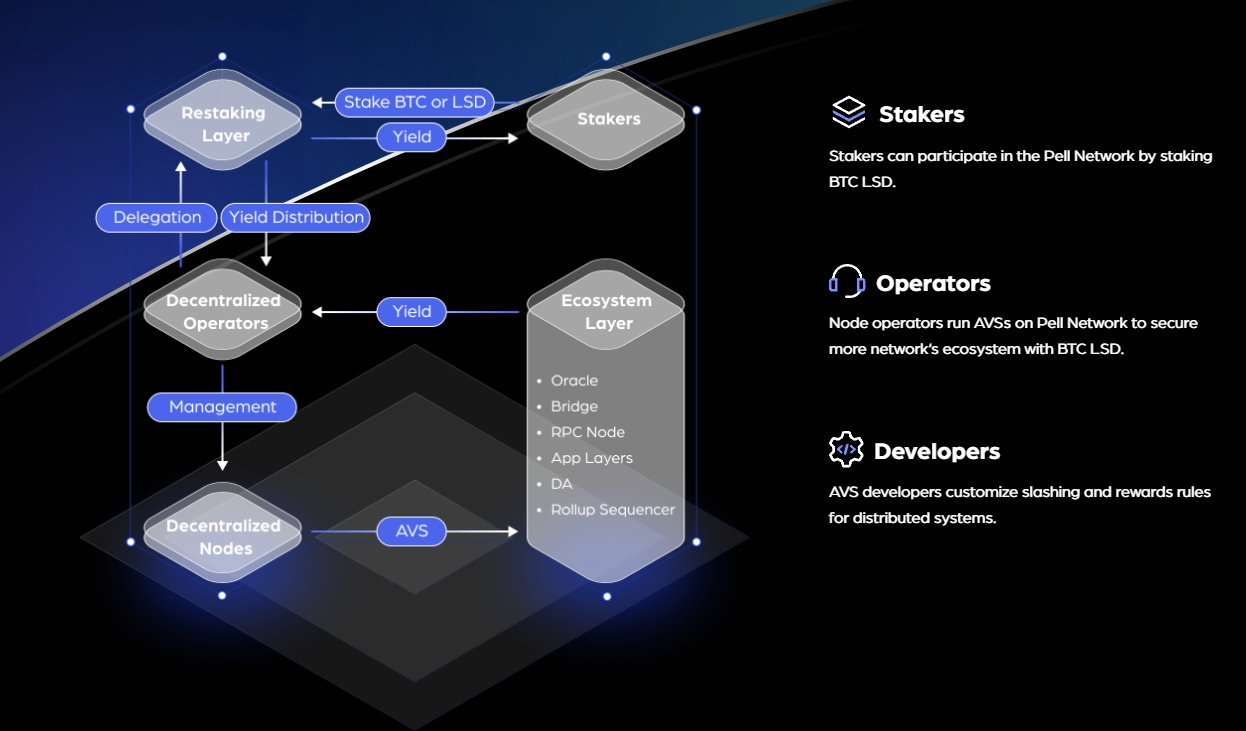
In short, Pell Network’s ecosystem consists of three primary roles: stakers, operators, and developers. Stakers participate by depositing BTC LSD into Pell Network. Operators manage and run AVS networks within Pell Network, using BTC LSD to enhance network security. Developers focus on designing and tuning slashing and reward mechanisms for decentralized systems.
1. Pell Network Restaking Assets
Pell Network offers multiple yield pathways, allowing stakers to earn additional income by securing new AVS (Actively Validated Services). Broadly speaking, these assets can be linked to three different blockchain layers: core protocols, AVS, and DeFi. Liquid staking can be seen as moving first into core protocols and then into DeFi to accumulate returns. Within Pell Network, there are several forms of restaking:
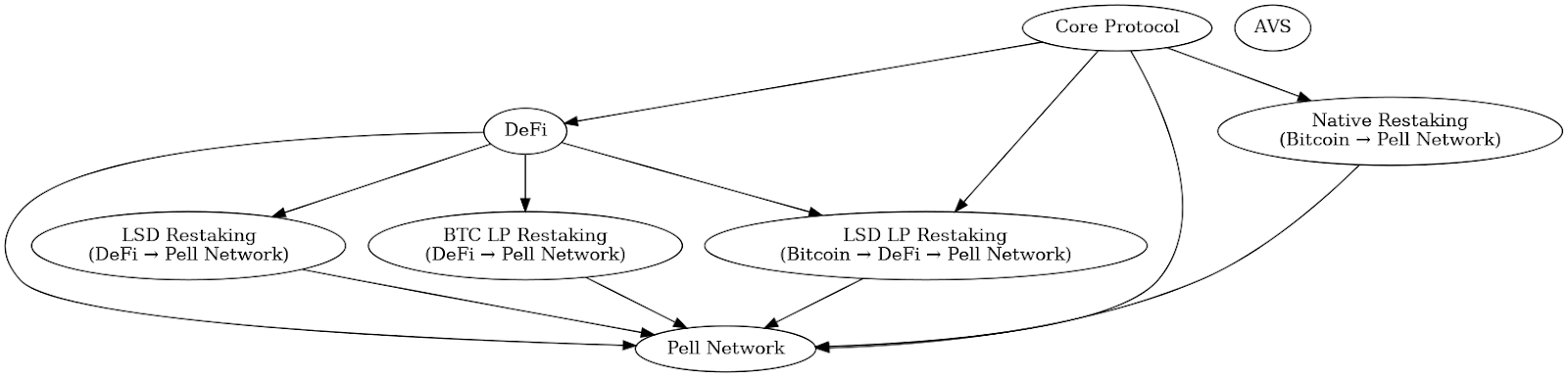
Pell Network Restaking Asset Flow
Native Restaking Assets: Validators can restake their BTC by directing withdrawal credentials to the Pell Network contract. This corresponds to BTC → Pell Network revenue stack.
LSD Restaking Assets: Validators can restake their LSD (BTC already staked via other protocols) by transferring LSD tokens to the Pell Network smart contract. This corresponds to DeFi → Pell Network revenue stack.
BTC LP Restaking Assets: Validators stake a liquidity pair (LP) token containing BTC. This also corresponds to DeFi → Pell Network revenue stack.
LSD LP Restaking Assets: Validators stake an LP token pair that includes a liquid-staked BTC derivative. This represents the BTC → DeFi → Pell Network revenue stack path.
2. AVS Network (Actively Validated Services)
Pell Network’s AVS network is one of its core competitive advantages. This innovative system utilizes restaked assets to provide cryptographic-economic security for diverse audiences, supporting customizable slashing conditions and reward thresholds.
To address challenges such as whether AVS expected revenues can cover operator costs and whether operators possess sufficient computational resources to participate in AVS validation, Pell Network proposes two solutions through modular design:
-
Large-Scale AVS
In large-scale AVS, the total computational workload is evenly distributed across all participating operator nodes—a concept known as horizontal scaling in distributed computing. For example, in a large-scale data availability protocol, data is split into N chunks, each sized at 2/N of the original, making total storage costs comparable to being stored by just two nodes. In such AVS, per-node data processing demands may be low, but the system achieves high throughput by aggregating performance across multiple nodes.
Additionally, compared to traditional blockchain systems, large-scale AVS reduces reliance on centralized validators, as verification costs can be fully shared among operators in non-horizontally scalable blockchains.
-
Lightweight AVS
Lightweight AVS involves tasks that are replicated by all operators but incur very low costs. Examples include verifying information via light clients, validating zero-knowledge proofs, running lightweight nodes for other blockchains, and executing oracle price feeds. These tasks require minimal computation and infrastructure, making them ideal for deployment on Pell Network.
Through this layered AVS design, Pell Network captures most of the potential yield. This approach ensures even independently operated validators can achieve significant economic benefits from Pell Network, effectively reducing centralization pressures in staking.
Currently, Pell Network has successfully attracted over five AVS operators to sign letters of intent, thanks to its well-designed AVS network. The network enhances capital efficiency for BTC holders through restaking mechanisms while achieving an optimal balance between security, flexibility, and efficiency.
Pell Network Use Cases and Ecosystem
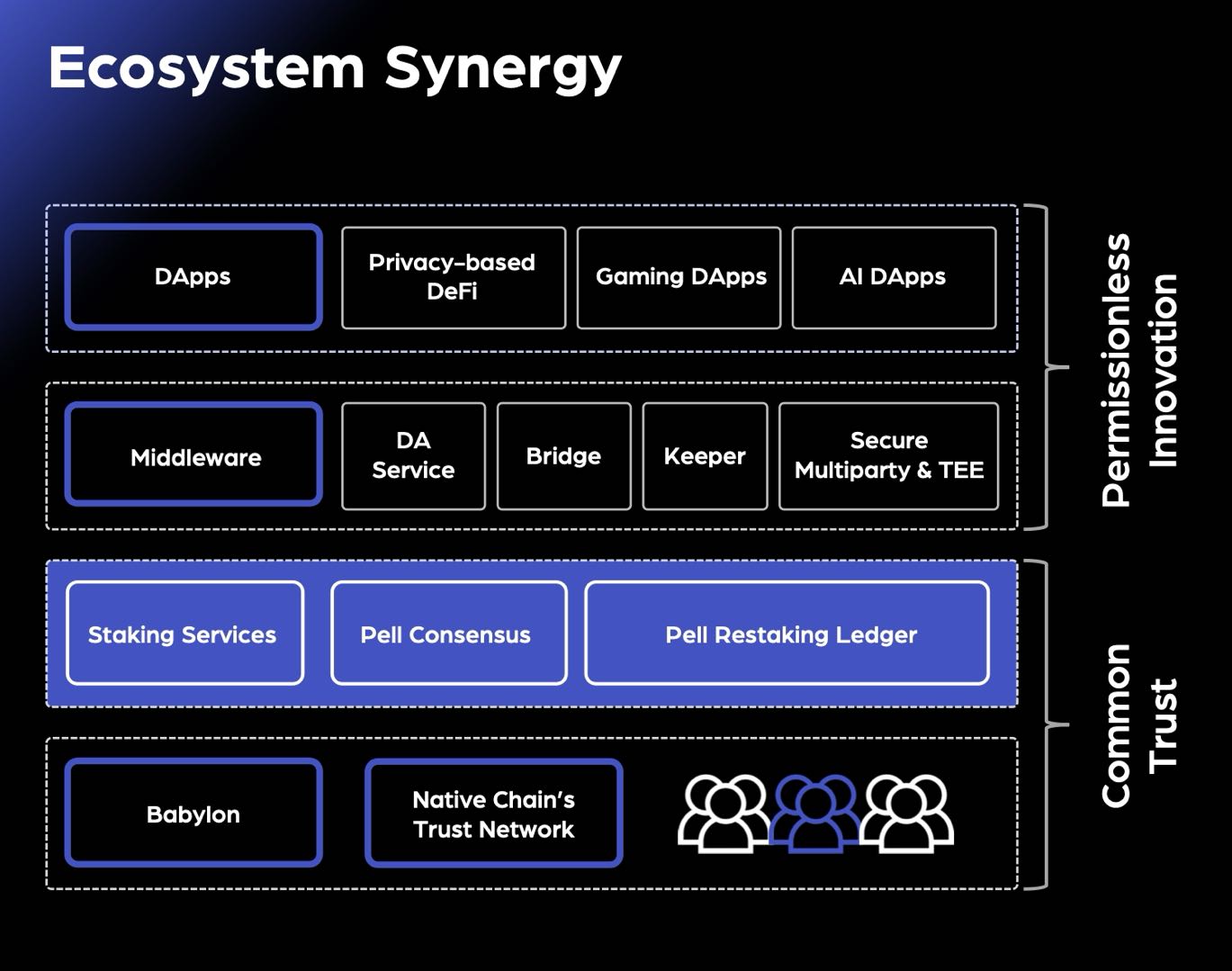
As a consensus layer for the ecosystem, Pell Network leverages advanced cryptography to enhance diversity and security, accelerating the adoption of innovative technologies. It provides a solid foundational service for a wide range of upper-layer applications.
By lowering developer costs for secure infrastructure, Pell Network allows teams to focus on business logic. This makes it highly suitable for building various novel Actively Validated Services (AVS), including new blockchains, middleware, and modular blockchain layers such as oracles and data availability layers. Below are some potential application directions:
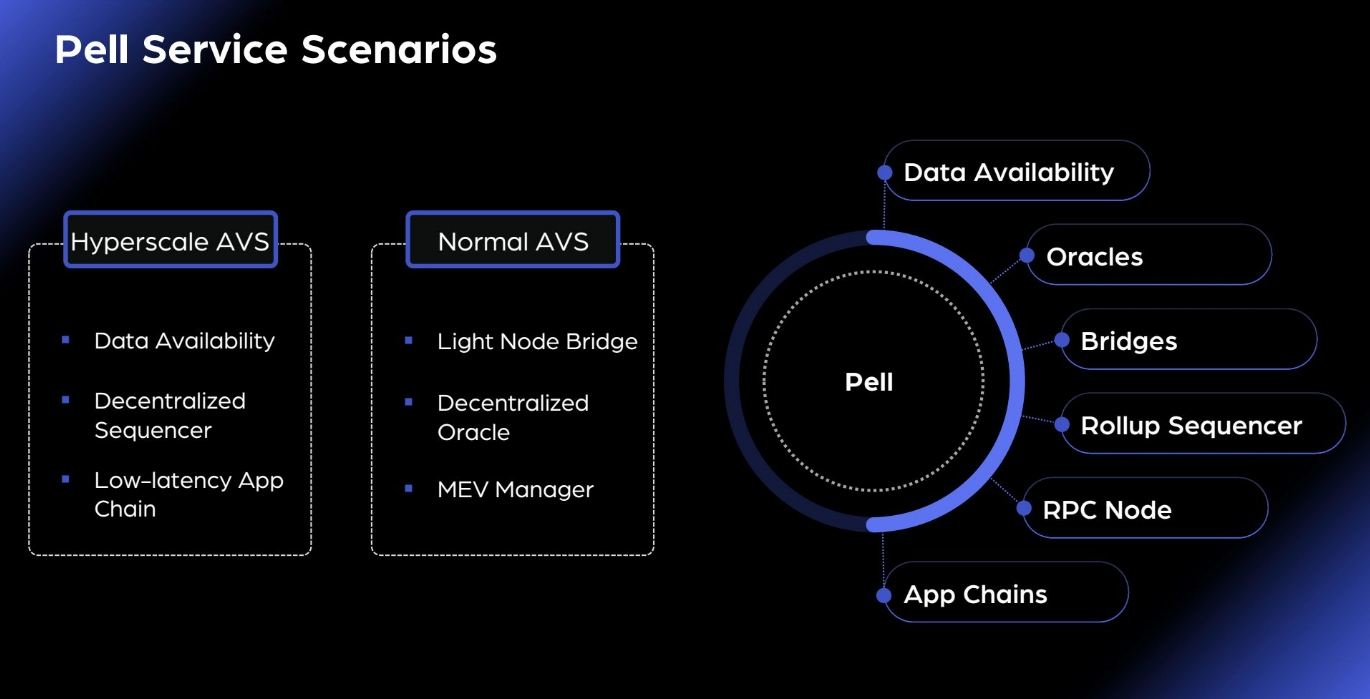
Oracles: Pell Network enables rapid construction of economically secure oracle networks, allowing developers to focus on data processing and feeds without investing heavily in building standalone AVS layers.
Large-Scale DA Layer: Leveraging restaking and community power within Pell Network, a highly efficient, low-cost large-scale Data Availability (DA) layer can be constructed.
Light-Node Cross-Chain Bridges: Building light-node cross-chain bridges based on Pell Network is straightforward. Stakers can verify cross-chain signatures off-chain. If a discrepancy is confirmed during a challenge event, validators in Pell Network will be slashed in a slow mode (non-optimistic).
DApps: By aggregating Bitcoin’s security across all modules, Pell Network is especially well-suited for DApps reliant on data security, such as privacy-focused DeFi protocols, blockchain games, and Web3 AI applications.
RWA Systems: The RWA sector in DeFi typically follows a yield-driven development model. Combined with restaking, this integration is poised to become a market hotspot over the next 3–5 years. With its robust capability in handling and maintaining large volumes of underlying data, Pell Network is naturally positioned as a top choice for RWA platforms.
Through these use cases, Pell Network aims to deliver more diverse and efficient services to the blockchain ecosystem, driving industry-wide innovation and growth.
Conclusion
Pell Network’s vision is to build a decentralized free market for trust, enhancing Bitcoin’s economic and security utility through diversified equity options and restaking mechanisms. Stakers can either operate nodes directly or delegate to node operators, providing security validation services and earning extra income—maximizing capital efficiency for BTC holders.
Moreover, Pell Network supports the creation of both lightweight and large-scale decentralized components, delivering cost-effective, secure infrastructure solutions that fuel exponential growth and development across the Bitcoin ecosystem.
According to Pell Network’s roadmap, the platform will launch its testnet by the end of July, with mainnet expected in October. Additionally, Pell Network is developing its first official AVS oracle and will share token incentives with early participants who help build the network.
Looking ahead, Pell Network will continue advancing BTC restaking, delivering safer and more efficient solutions to the decentralized finance ecosystem. If you are a BTC holder or interested in decentralized finance, consider following Pell Network’s progress and joining this innovative platform to share in the substantial rewards brought by blockchain technology.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News