Fuel: An L2 Protocol Yet to Launch Its Mainnet—What’s Behind Its Scalability, Parallelization, and Cross-Chain Solutions?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Fuel: An L2 Protocol Yet to Launch Its Mainnet—What’s Behind Its Scalability, Parallelization, and Cross-Chain Solutions?
A monolithic L1 architecture is like an ancient country road, no longer able to handle the growing volume of vehicles and pedestrians.
Fuel is a permissionless, trust-minimized Layer 2 modular execution protocol within Ethereum, optimized for low-cost, high-throughput value transfer transactions.

Currently, traditional monolithic Layer 1 blockchain architectures perform poorly when handling large volumes of concurrent transactions, easily encountering bottlenecks that lead to transaction delays and high fees. In addition, traditional architectures face technical challenges and limitations in achieving cross-chain interoperability.
More vividly, the general-purpose computing systems or monolithic L1 architectures currently in use resemble an ancient country road. While once sufficient for a small village's traffic needs, as the village rapidly grows into a bustling city, this narrow path can no longer handle the increasing volume of vehicles and pedestrians. Today, not only does congestion frequently occur on this road, but maintenance and expansion have also become increasingly difficult.
This complex environment is akin to a modern urban transportation system. Facing ever-growing traffic flows, pedestrian movements, and diverse mobility demands, what’s needed is no longer simply widening roads, but rather constructing an efficient, multi-layered transportation network—including highways, subways, bus systems, and pedestrian walkways—that seamlessly interconnect to ensure smooth operations.
Solutions like Fuel aim to address scalability while ensuring efficient parallel processing, state management, and cross-chain interoperability by designing a more modern transportation system—one capable of flexibly adapting to the evolving traffic demands of a city, ensuring every user reaches their destination quickly and securely.
Therefore, to realize a rollup-centric future, a new architecture specifically designed for Ethereum rollup requirements is needed. Fuel combines Bitcoin’s UTXO model, Solana’s parallelization, Ethereum’s security, Move’s asset-oriented design, and Cosmos’ interoperability with customizable virtual machines to create the ultimate Ethereum rollup operating system.
In simple terms, Fuel adopts a unique approach distinct from existing blockchain design paradigms, focusing on modularity at the execution layer and achieving long-term scalability by minimizing state growth. Fuel also introduces FuelVM and a new programming language called Sway, overcoming the limitations of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Fuel is fundamentally designed to provide an execution environment for highly configurable rollups, powered by a highly optimized rollup architecture.
Core Features:
-
FuelVM: Fuel introduces a completely new FuelVM that supports efficient transaction processing and built-in security mechanisms, surpassing EVM limitations. FuelVM uses a globally shared memory architecture where all contract calls can access shared global memory, enabling cross-contract data transfers without requiring storage space. FuelVM allows users to specify which contracts are involved in a transaction, enabling the virtual machine to process other transactions simultaneously during non-contentious state access, thus achieving full parallelization. Additionally, FuelVM supports a native asset system that allows minting UTXO-based native assets via opcodes and employs a multidimensional resource pricing model to optimize block utility and promote network decentralization.
-
Modular Blockchain Architecture

As an execution layer, Fuel can be combined with other blockchain layers such as Ethereum and Celestia, offering flexible configurations—for example, operating as an Optimistic Rollup on Ethereum. This modular integration across multiple blockchains enhances its flexibility and scalability.
-
UTXO Model
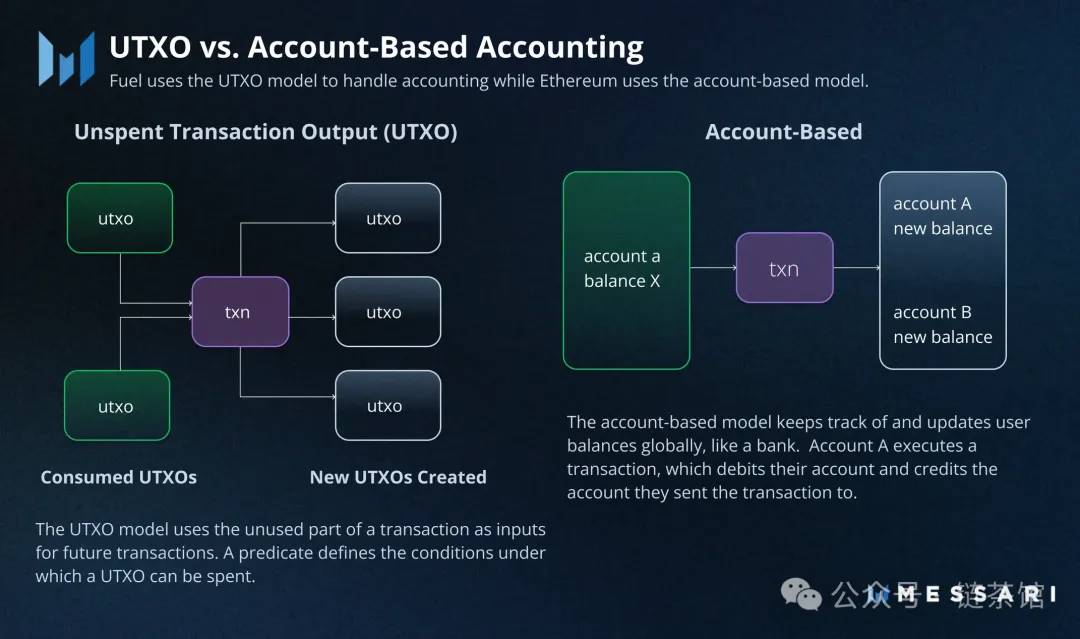
Fuel adopts Bitcoin’s Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model, differing from the traditional account model. Fuel inherits Bitcoin’s UTXO model as its accounting framework. In this model, there are no concepts of wallets or accounts; each UTXO represents a certain amount of tokens, and transactions serve to consume previously created UTXOs and generate new ones. Fuel’s UTXO model is more generalized—beyond representing token transfers, it can also represent smart contract states. Each contract UTXO carries both the contract state and balance, uniquely identified by a contract ID. This model enables parallel transaction execution, using strict access lists to ensure transaction execution order complies with specifications, thereby improving transaction processing efficiency.
-
Parallel Processing: Through strict access lists, Fuel enables parallel execution of independent transactions, significantly increasing throughput.
-
Sway Programming Language: The Fuel team developed the Sway programming language. Built on Rust and incorporating features of Solidity, Sway offers a clean development experience tailored for Fuel’s high-performance computing environment. Sway inherits Rust’s syntax, allowing developers to write secure and efficient smart contract code, with built-in top-level contract storage and blockchain mechanisms that provide a safer programming environment. The Fuel team has also developed Forc, the Sway toolchain, including a package manager, VSCode extension, testing infrastructure, and block explorer, supporting developers building with Sway.
-
Scripts and Predicates: Fuel supports scripts and predicates, allowing multiple contracts to be invoked within a single transaction and enabling conditional checks on UTXO availability, thus reducing state bloat.
-
Account Abstraction: Through UTXOs and predicates, Fuel achieves stateless account abstraction, enabling programmable definition of transaction validation conditions.
Leveraging these developer-friendly technologies, numerous teams are already building projects on Fuel.

-
Elix is a DEX focused on delivering efficient trades with low slippage. Drawing inspiration from proven mechanisms like Curve’s concentrated liquidity pools, Elix aims to enable optimal trading conditions for users. By leveraging Fuel, Elix benefits from parallel processing, resulting in faster transaction speeds and enhanced security.
-
Spark is a DeFi super app built on the Fuel network, aiming to revolutionize financial services through its comprehensive service suite. Spark v1 introduces a multi-collateral cross-margin system, supporting deposits of various assets and implementing sophisticated liquidation protocols to ensure trading flexibility and risk management. Spark supports up to 2000 TPS for both long- and short-term perpetual contracts and provides integrated SDKs and APIs that support non-custodial interactions with order books, promoting seamless integration and innovation. Fuel’s network enables Spark to leverage high throughput and security for delivering complex financial services.
-
Acumen Protocol is a non-custodial interest rate protocol that uses algorithmically determined rates to power open financial applications. It bridges cryptocurrency and traditional finance, enabling DeFi users to access attractive, stable, and uncorrelated yields, while creating a fair environment where small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and entrepreneurs can thrive. As a modular execution layer, Fuel provides the blockchain infrastructure for Acumen, ensuring performance and security when handling large volumes of debt and asset tokenization transactions.
-
Thunder is an NFT marketplace that enables bulk transactions within a single transaction at minimal fees. For experienced NFT traders, this marketplace offers a more seamless trading experience, with fast execution enabled by parallelization.
In preparation for the upcoming mainnet launch of Fuel, the team launched the Fuel Points Program on July 8.

Participants can deposit eligible assets into a pre-deposit smart contract via the Fuel Points Program portal. These assets will remain secured in a Fuel pre-deposit smart contract on Ethereum until the Fuel mainnet launches. After depositing assets, participants earn Fuel Points daily based on the USD value of deposited assets.
Participants can earn between 1.5 and 3 points per dollar of deposited asset value per day, depending on the asset type. For example, when depositing ETH, users receive 1.5 points per dollar deposited per day. The USD value of assets is determined hourly by price oracles (such as DeFiLlama API), and points are calculated accordingly. For instance, if a user deposits 1 ETH when the ETH price is $3,500, they will earn 3500 × 1.5 / 24 = 218.75 points per hour.
Points can be monitored through the portal, and early depositors receive more points. Currently accepted assets include ETH, WETH, EETH, rETH, rsETH, WBETH, USDT, USDC, USDE, sUSDE, ezETH, and stETH. Point multipliers for different assets may change, with updates published by FuelNetwork on X. After the Fuel mainnet launch, participants must bridge their pre-deposited assets to the mainnet within 14 days, or their points will be forfeited.
Overall, Fuel stands out as a project worthy of attention from long-term investors, especially given strong capital backing, the application of next-generation Layer-2 token models, and the positive momentum surrounding its mainnet launch. Fuel’s ecosystem development and ongoing grant programs have fostered a vibrant environment filled with innovative ideas and creativity—even at this early stage, its ecosystem appears relatively robust. However, Fuel’s mainnet has yet to launch, and its performance in the competitive rollup landscape remains to be seen. Let’s continue to monitor its future development.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















