A Deep Dive into Arweave: Pay Once, Data Stored Forever
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

A Deep Dive into Arweave: Pay Once, Data Stored Forever
As demand for blockchain technology and decentralized storage continues to grow, Arweave is poised to become a leader in this field in the future.
Author: Chain Teahouse
1. Project Overview
Arweave is a decentralized data storage solution that provides permanent and immutable data storage services through its Blockweave technology and native cryptocurrency, the AR token. Users pay a one-time fee to store data permanently and are rewarded for contributing unused storage space.

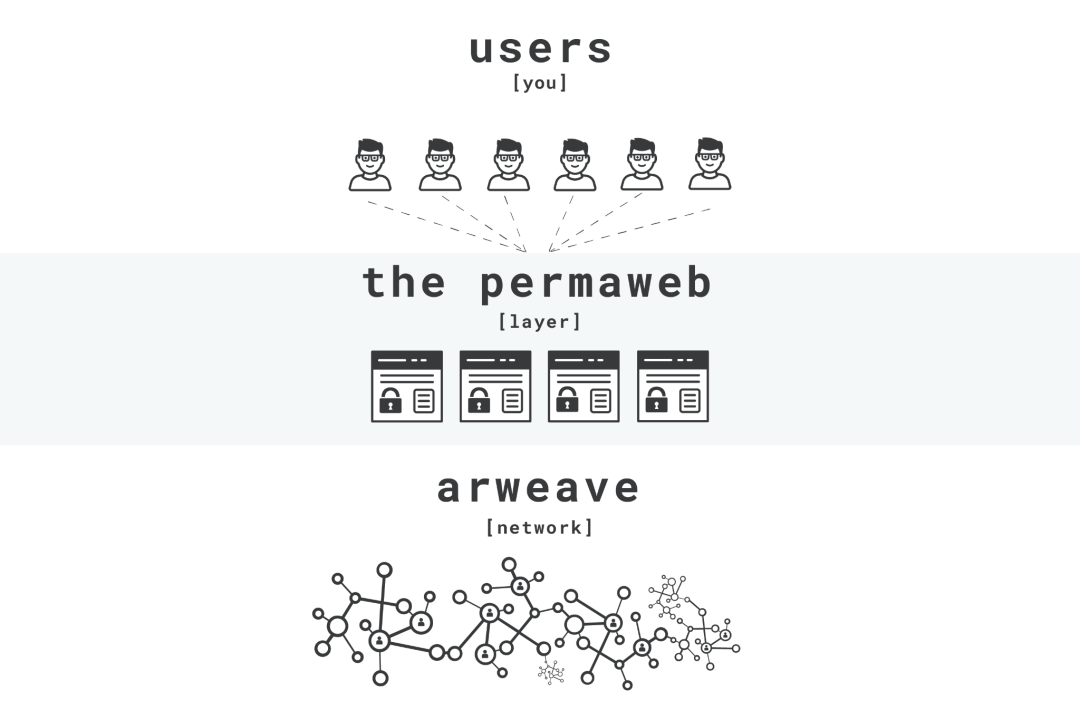
As a tool helping anyone store data permanently, Arweave works by distributing information across a network of computers known as nodes or miners. This differs from the traditional internet, where today’s web is controlled by servers owned by a few companies that may fail at any time or quietly alter content.
Arweave powers a parallel internet (known as the Permaweb) via an extensive network of nodes. All these nodes earn money by providing long-term storage of existing data and storing new data upon client request. Arweave uses its native cryptocurrency, AR, to operate the service: when people spend tokens to store data, they pay AR to miners, and part of the AR is placed into an endowment fund to ensure infinite permanent storage.
2. How It Works
Arweave operates using an innovative data structure called Blockweave, which links each block not only to the previous block but also to a randomly selected historical block (called a recall block). Before adding a new block, miners must provide Proof of Access (PoA), ensuring the integrity and immutability of all data. Users pay a one-time fee to store data permanently, with part of the fee covering initial storage costs and another portion going into an endowment fund for future storage expenses. Succinct Proofs of Random Access (Spora) further enhance network efficiency and security. Bundling technology improves data upload efficiency and network performance by combining multiple transactions into one large transaction. Through these mechanisms, Arweave achieves a decentralized, permanent data storage network.
3. Core Mechanisms
3.1 Blockweave
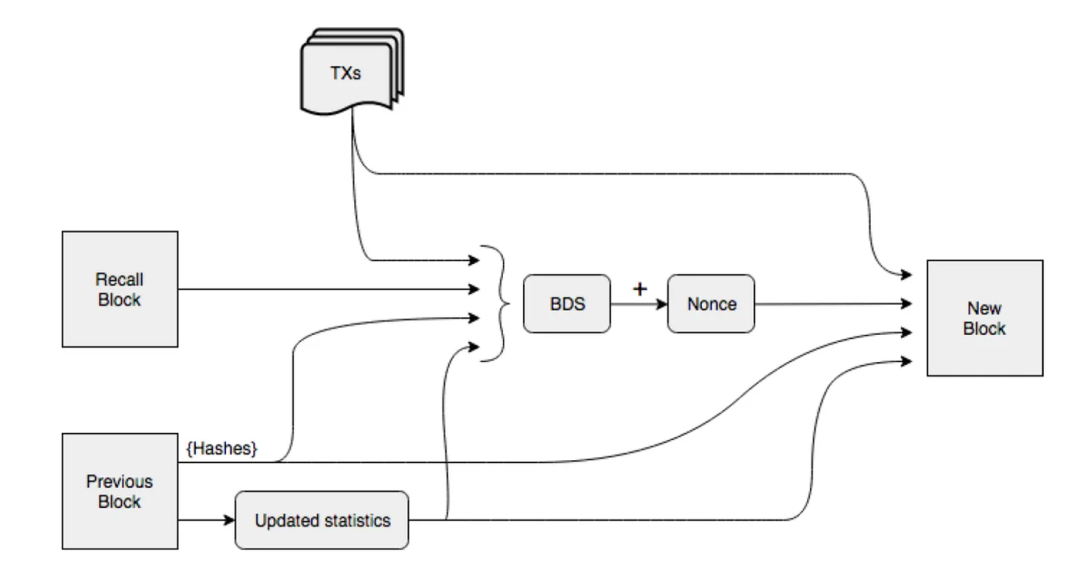
Blockweave is Arweave's core data structure, improving upon traditional blockchain designs to enable efficient, reliable, and permanent data storage. Below is a detailed analysis of Blockweave:
3.1.1 Basic Structure
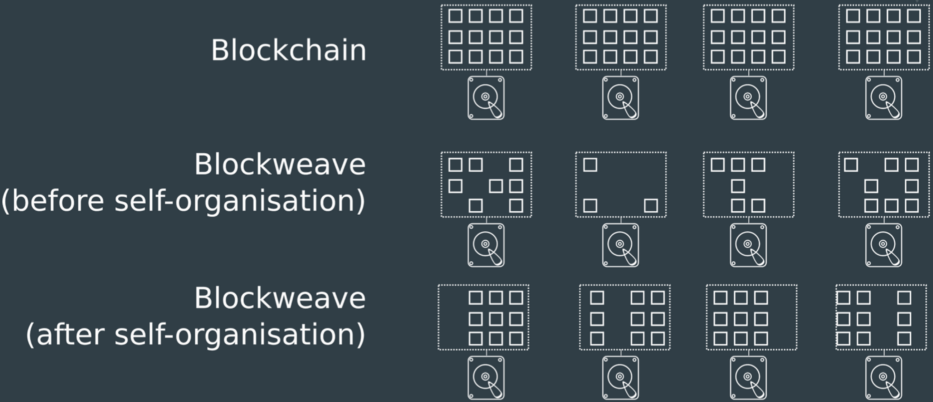
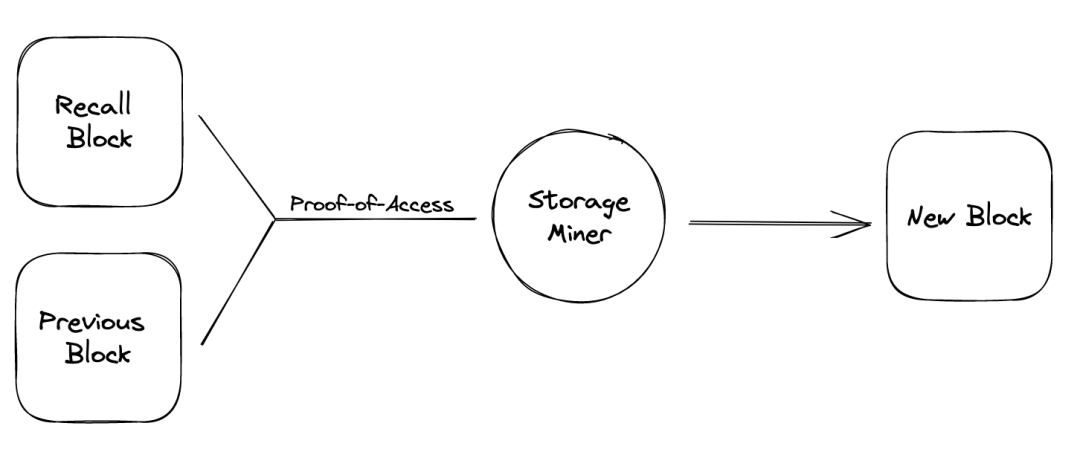
The main difference between Blockweave and traditional blockchains lies in their linking structure. In traditional blockchains, each block links only to the previous block, whereas in Blockweave, each block links not only to the previous block (parent block) but also to a randomly selected historical block (recall block). This dual-linking structure increases data redundancy and security.
-
Parent Block: Like traditional blockchains, each block in Blockweave links to its immediate predecessor, forming a basic chain structure.
-
Recall Block: Each block also links to a randomly selected historical block. This random linkage aims to increase data redundancy and accessibility.
3.1.2 Data Validation Process
In Blockweave, miners must validate a randomly selected historical block before generating a new block. This validation mechanism is known as Proof of Access (PoA). PoA ensures that all stored data blocks can be accessed and verified. To increase their chances of earning mining rewards, miners store more historical data blocks, thereby increasing data redundancy.
-
Random Selection: By randomly selecting historical blocks for validation, miners cannot predict which specific data blocks will need verification, forcing them to store large amounts of historical data.
-
Data Integrity: This mechanism ensures data integrity and tamper resistance, enhancing overall data security.
3.1.3 Data Storage Redundancy
The dual-linking structure of Blockweave greatly increases data redundancy. Since each block links to multiple others, even if some nodes fail or lose data, other nodes can still recover the data via redundant links. This design enhances data durability and fault tolerance.
-
Multiple Links: The dual linkage of parent and recall blocks ensures highly redundant data storage across the network.
-
Data Recovery: When nodes fail or data is lost, other nodes can use redundant links to restore data, ensuring high availability.
3.1.4 Blockweave Construction and Mining
Miners on the Arweave network earn rewards by generating new blocks. To generate a new block, miners must be able to access and verify a designated historical block. This mechanism incentivizes miners to store more historical data, increasing the network’s overall data storage capacity and security.
-
Mining Process: Miners validate randomly selected historical blocks, generate new blocks, and receive AR token rewards.
-
Incentive Mechanism: This encourages miners to store more data, increasing redundancy and network security.
3.1.5 Data Immutability and Security
Because each block in Blockweave links to multiple blocks and is validated via PoA, once data is stored it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability provides high security, preventing malicious tampering or deletion.
-
Immutability: Once data is stored in Blockweave, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring data integrity.
-
Security: Multiple linkages and random validation mechanisms enhance data security, preventing malicious attacks.
3.2 Succinct Proofs of Random Access (Spora)
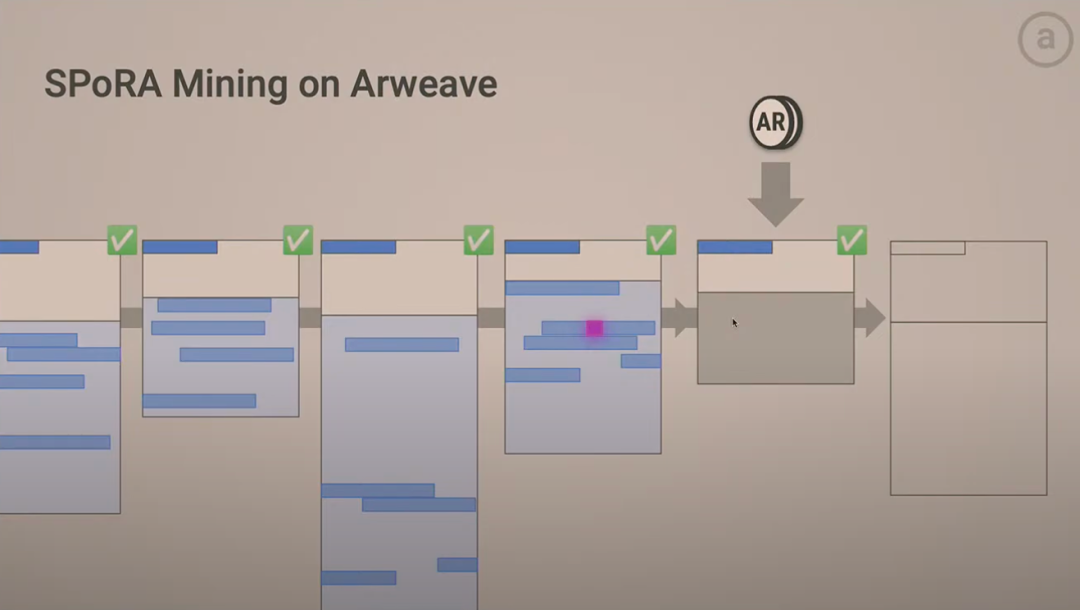
Succinct Proofs of Random Access (Spora) is a key consensus mechanism used by Arweave to improve network efficiency and security. With Spora, Arweave enhances data storage and access efficiency while maintaining data integrity and security. Below are key aspects of Spora:
3.2.1 Basic Principle
Spora (Succinct Proofs of Random Access) is an improved version of Proof of Access (PoA). Its core idea is to verify new data blocks by randomly selecting historical data blocks, thus ensuring data integrity and security. This randomness reduces the possibility of miner cheating while increasing network security and data redundancy.
3.2.2 Data Validation Process
In Spora, miners must validate a randomly selected historical data block before adding a new block. This random selection prevents miners from predicting which specific data blocks require validation, making selective data storage impossible. As a result, Spora forces miners to store large volumes of historical data to increase their mining success probability, thereby improving data redundancy and overall network security.
3.2.3 Enhanced Miner Incentives
Spora strengthens miner incentives. Because miners must store more historical data blocks to increase their chance of successful mining, they are motivated to invest more resources in data storage and maintenance. Miners not only earn mining rewards through validation and storage but also enhance their competitiveness within the network by increasing their data storage volume.
3.2.4 Improved Energy Efficiency
Compared to traditional Proof of Work (PoW) mechanisms, Spora is much more energy-efficient. PoW requires miners to perform complex computations to validate transactions, leading to massive energy consumption. In contrast, Spora verifies historical data blocks through random access, significantly reducing computational resource usage and improving network energy efficiency. This efficient validation process not only lowers energy costs but also reduces environmental impact.
3.2.5 Security and Attack Resistance
Spora enhances network security and resistance to attacks through its randomness and data redundancy. Because miners cannot predict which data blocks will be validated, targeted attacks become extremely difficult. Additionally, the large volume of historical data stored by miners increases the amount of data attackers would need to compromise, thereby strengthening overall network security.
3.3 Bundling Technology
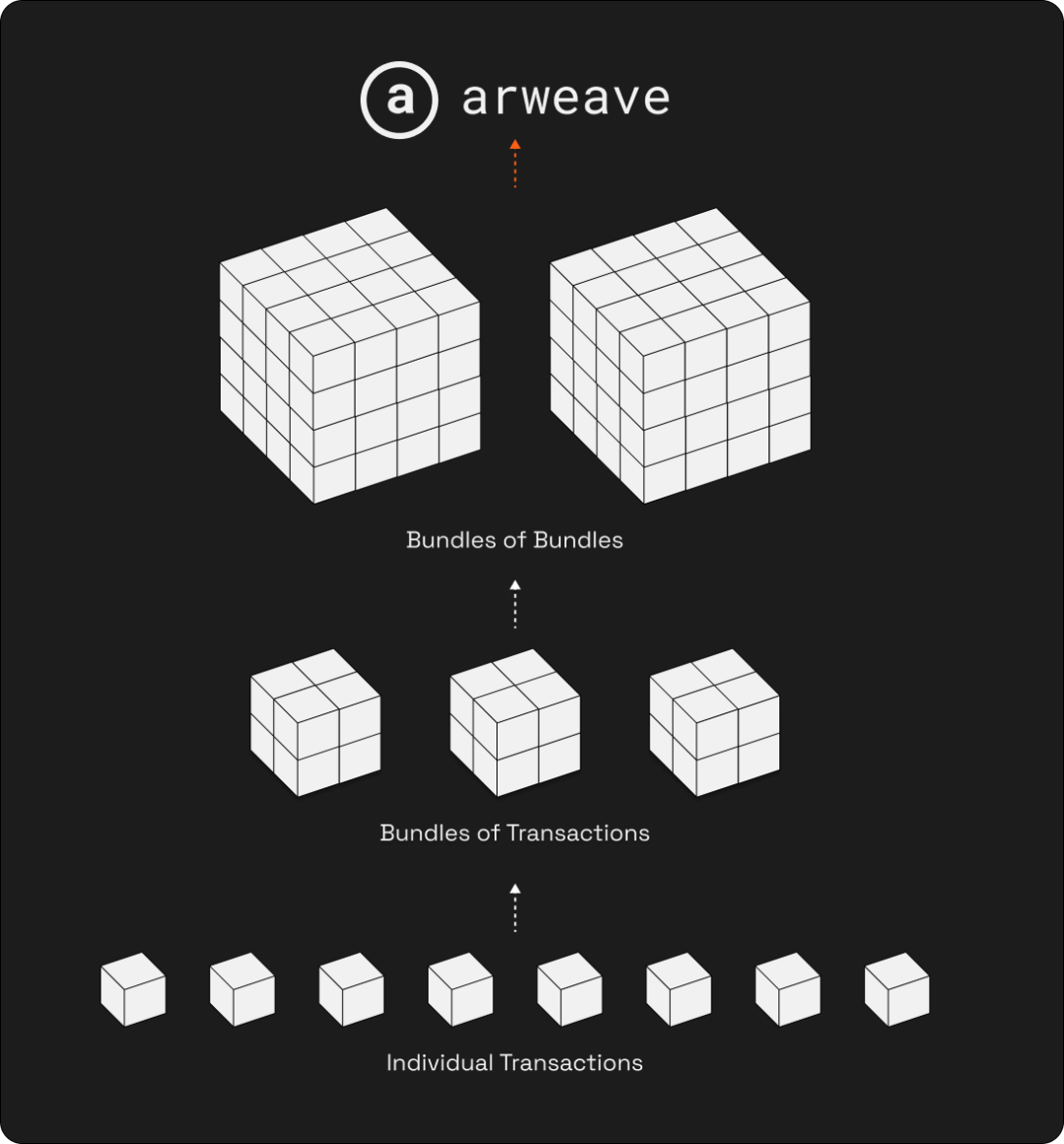
Arweave’s Bundling technology is one of its key innovations for improving data upload efficiency and network scalability. This technology enables Arweave to efficiently handle large-scale data uploads, enhancing user experience and network performance. Below is a detailed analysis of Bundling:
3.3.1 Basic Principle
The core idea of bundling is to combine multiple small transactions into one large transaction and then upload this single large transaction to the Blockweave. This reduces frequent individual upload operations, alleviating network congestion and improving data transmission efficiency.
3.3.2 Improved Data Upload Efficiency
Without bundling, each transaction upload must be processed and recorded separately, increasing blockchain load and causing inefficiencies. With bundling, multiple small transactions are packaged into one large transaction before upload, reducing the number of on-chain transactions and significantly improving upload efficiency.
3.3.3 Network Scalability
Bundling significantly improves the scalability of the Arweave network. In large-scale upload scenarios—such as NFT projects and media file storage—bundling effectively handles numerous concurrent upload requests, avoiding network congestion and performance bottlenecks. For example, Arweave successfully uploaded 47 GB of data in a single bundle operation, a feat difficult to achieve with traditional on-chain storage solutions.
3.3.4 Transaction Finality and Developer Experience
With bundling, developers and users gain greater certainty about upload outcomes, as the success rate of uploading one large transaction is higher than uploading many small ones individually. This predictability improves developer experience, allowing them to focus on application development without worrying about the complexities of underlying data storage.
3.3.5 Cost Efficiency
Bundling not only improves upload efficiency but also delivers significant cost savings. In traditional on-chain storage models, every transaction incurs a fee. By merging transactions, bundling reduces the total number of transactions and thus lowers overall costs. This is particularly advantageous for users needing to store large volumes of data.
3.3.6 Data Integrity and Security
Bundling ensures data integrity and security. Even though multiple transactions are merged into one, each individual transaction remains intact and tamper-proof. Thus, if issues arise during upload, data can be re-bundled and re-uploaded to ensure safety and completeness.
3.4 Wildfire Mechanism
Wildfire is an incentive mechanism within the Arweave network designed to optimize data propagation and enhance network performance, thereby improving overall user experience. Below is a detailed analysis of Wildfire:
3.4.1 Basic Principle
Wildfire incentivizes nodes to quickly respond to and fulfill data requests through a ranking system. Nodes are ranked based on their speed and efficiency in propagating data across the network. Higher-ranked nodes receive more requests and rewards. This ensures rapid data dissemination and improves overall network performance.
3.4.2 Data Propagation Efficiency
The core of Wildfire is improving data propagation efficiency. After receiving new data, nodes quickly relay it to other nodes. Fast and responsive nodes achieve higher rankings, gaining more request-handling opportunities and corresponding rewards.
-
Rapid Propagation: Nodes rapidly relay new data to others, ensuring fast data flow across the network.
-
Efficiency Priority: The ranking system encourages nodes to optimize propagation efficiency, enhancing overall network performance.
3.4.3 Node Ranking System
Wildfire incentivizes efficient data propagation by ranking node performance. The ranking system scores nodes based on their speed and reliability in responding to data requests. High-scoring nodes enjoy higher priority in the network, receiving more request opportunities and rewards.
-
Response Speed: A node’s response speed to data requests is a key ranking metric—the faster the response, the higher the rank.
-
Data Reliability: The stability and consistency of data provided by a node also affect its ranking—the more reliable the data, the higher the rank.
3.4.4 Incentive and Reward Mechanism
Wildfire motivates nodes to improve data propagation efficiency by rewarding high-ranking nodes. Nodes earn higher ranks and more rewards by quickly and reliably disseminating data. This reward system ensures active participation, boosting overall network performance and data availability.
-
Rank-Based Rewards: High-ranking nodes receive more request-handling opportunities and corresponding rewards.
-
Economic Incentives: Nodes earn economic returns by providing fast and reliable data propagation, encouraging continuous performance optimization.
3.4.5 Network Health and Robustness
Wildfire not only improves data propagation efficiency but also enhances network health and robustness. By incentivizing rapid responses and data dissemination, Wildfire ensures stable and efficient network operation under high load and demand.
-
High-Load Adaptation: Under heavy loads, Wildfire ensures data propagates quickly and efficiently across the network.
-
Enhanced Robustness: By optimizing node performance, Wildfire strengthens overall network resilience and reliability.
4. AR Token
The AR token is the native cryptocurrency of the Arweave network, playing multiple critical roles—from incentivizing miners and paying for data storage to maintaining economic balance across the ecosystem.

Below is a detailed analysis of the AR token:
4.1 Basic Functions of the AR Token
-
Pay for Data Storage: Users must pay AR tokens as a one-time fee to store data on the Arweave network. These fees guarantee permanent data storage.
-
Incentivize Miners: Miners earn AR tokens as rewards for storing and validating data. This mechanism encourages active participation in data storage and maintenance, ensuring network security and reliability.
4.2 One-Time Payment Model
Unlike traditional subscription-based services, Arweave’s business model allows users to pay a one-time fee for permanent data storage. Part of this fee covers initial storage and access costs, while another portion goes into an Endowment Fund to cover future storage expenses.
-
Initial Storage Cost: Fees are immediately used to cover initial data storage and access.
-
Endowment Fund: Approximately 86% of the fee goes into the Endowment Fund, which provides long-term incentives for miners and ensures data persistence.
4.3 Storage Endowment Fund

The Endowment Fund is designed similarly to traditional financial endowments, aiming to use interest and appreciation to cover future storage costs. Interest generated from users’ initial payments funds long-term miner compensation, ensuring data remains preserved indefinitely.
-
Fund Operation: Accumulated funds and interest ensure miners receive ongoing economic incentives for years to come.
-
Expected Cost Decline: As data storage costs are expected to continue declining over time, the interest income from the Endowment Fund should suffice to cover long-term storage expenses.
4.4 Token Supply
-
Initial Supply: 66 million AR tokens.
-
Circulating Supply: 55 million AR tokens.
-
Gradual Halving: Similar to Bitcoin’s halving mechanism, ensuring token scarcity and long-term value. However, unlike Bitcoin, AR uses gradual halving, meaning token issuance decreases incrementally over short cycles.
4.5 AR Token Distribution
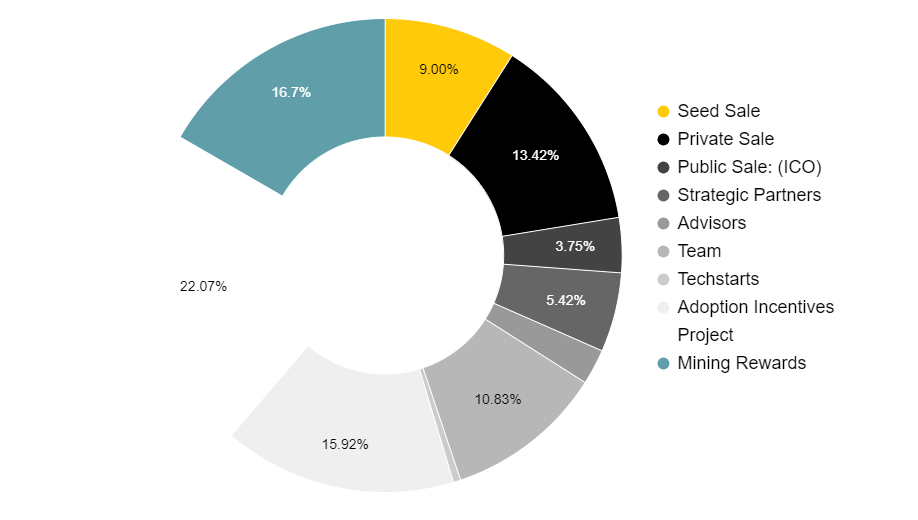
-
Seed Sale: 9%.
-
Private Sale: 13.42%.
-
Public Sale (ICO): 3.75%.
-
Strategic Partnerships: 5.42%.
-
Advisors: 2.42%.
-
Team: 10.83%.
-
Tech Startups: 0.5%.
-
Adoption Incentives: 15.92%.
-
Projects: 22.07%.
-
Mining Rewards: 16.67%.
4.6 Economic Incentives of the Token
The AR token incentivizes network participants in multiple ways:
-
Miner Rewards: Miners earn AR tokens for storing and verifying data, increasing their engagement.
-
User Payments: Users pay AR tokens to store data, ensuring permanent preservation.
-
Revenue Sharing: Arweave introduces Profit Sharing Tokens (PSTs), enabling developers building and operating applications to earn micro-dividends, fostering ecosystem growth and innovation.
4.7 Market Performance of the Token
The market performance of the AR token is influenced by various factors, including rising storage demand, ecosystem development, and market recognition of decentralized storage solutions. The value of the AR token increases alongside network growth and user demand.
-
Market Demand: As the Arweave network grows and user demand increases, the market value of the AR token rises accordingly.
-
Ecosystem Development: More developers and projects joining the Arweave ecosystem drive up demand and value for the AR token.
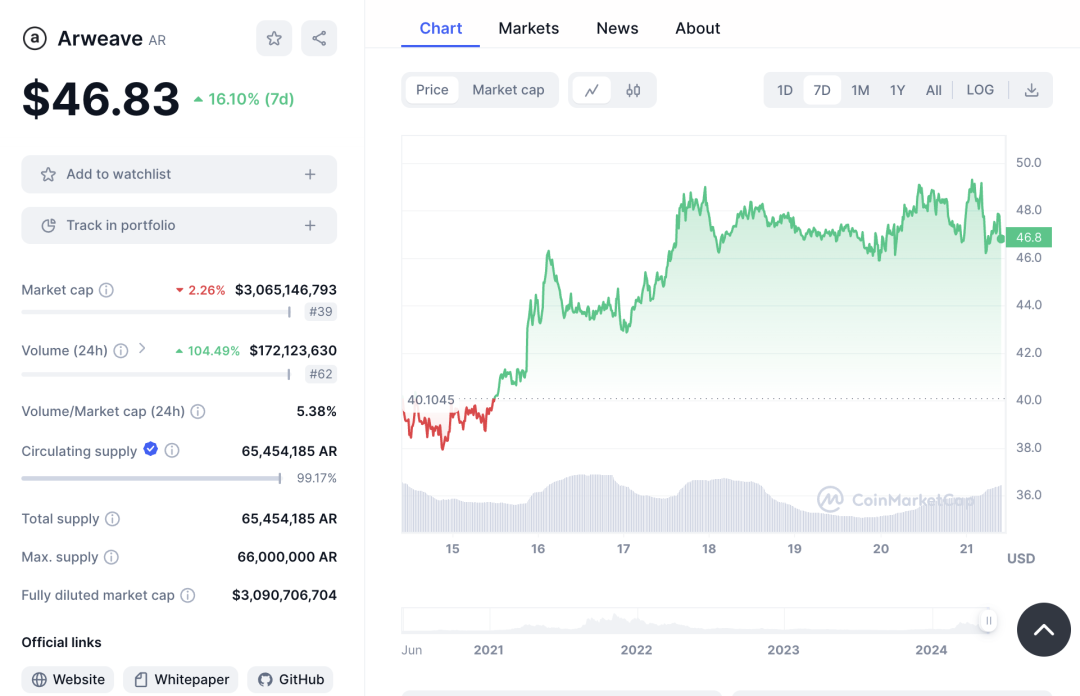
As of now, the AR token’s market performance is as follows:
-
Price: $46.83, up 16.10% over the past 7 days.
-
Market Cap: $3,065,146,793, down 2.26% recently.
-
24-Hour Trading Volume: $172,123,630, up 104.49% recently.
-
Volume / Market Cap Ratio: 5.38%.
-
Circulating Supply: 65,454,185 AR, accounting for 99.17% of total supply.
-
FDV (Fully Diluted Valuation): $3,090,706,704.
5. Team / Partnerships / Funding
5.1 Team

Arweave is a decentralized data storage protocol whose core team consists of experienced technical experts and industry leaders. Founder and CEO Sam Williams graduated from the University of Nottingham and has deep expertise in blockchain technology. Chief Operating Officer (COO) Sebastian Campos Groth, a Georgetown University graduate, previously worked at Techstars and oversees daily operations. Legal lead Giti Said, a University of Vienna graduate, manages legal affairs. The team also includes several technology and business experts such as Richard Pardoe, co-founder of Liquity, and Andy Bell, engineering lead at Movement Labs, who collectively drive Arweave’s development and innovation.
5.2 Partnerships
1. KYVE
Overview: KYVE is a blockchain storage middleware built on Arweave, offering standardized validation and archiving frameworks.
Highlights:
KYVE launched its mainnet and uploaded over 2,000 TB of data.
KYVE established strategic partnerships with 19 projects and plans to host community growth events in 2024.
2. Irys (formerly Bundlr)
Overview: Irys is a scaling solution for Arweave that increases permanent data throughput via transaction bundling.
Highlights:
In September 2023, Irys processed 1 billion transactions.
In October 2023, Irys partnered with Solana Mobile to store DApp Store applications.
3. ArDrive
Overview: ArDrive is a decentralized cloud storage application, similar to Web3 versions of Dropbox or Google Drive.
Highlights:
In February 2023, ArDrive became fully decentralized and migrated all data onto Arweave.
In May 2023, ArDrive 2.0 launched, introducing dark mode, wallet generation, and large file upload features.
5.3 Funding

Since its inception, Arweave has raised $37.3 million through multiple funding rounds, with major investors including Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Union Square Ventures, Multicoin Capital, and Coinbase Ventures. Key funding events include:
1. Seed Round
-
Date: 2017
-
Amount: $5 million
-
Main Investors: Andreessen Horowitz (a16z)
2. Private Round
-
Date: 2019
-
Amount: $8.3 million
-
Main Investors: Multicoin Capital, Union Square Ventures, a16z, Coinbase Ventures, Arrington XRP Capital
3. Public Round (ICO)
-
Date: 2018
-
Amount: $15.7 million
-
Description: Conducted a public token sale (ICO), attracting numerous early investors.
4. Subsequent Funding
-
Date: 2020
-
Amount: $8.3 million
-
Main Investors: Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Union Square Ventures, Coinbase Ventures
5. Latest Funding
-
Date: 2023
-
Amount: $8.3 million
-
Main Investors: a16z, Coinbase Ventures, Multicoin Capital
6. Project Evaluation
6.1 Sector Analysis
Arweave belongs to the decentralized data storage sector, achieving permanent data storage through its innovative Blockweave technology. The project’s core goal is to provide an efficient, secure, and scalable data storage solution that ensures data permanence and immutability.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News