Overview of the Hyperparallel Computer Arweave AO: Bringing AI Models into Smart Contracts, Planning Mainnet Launch in 2024
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Overview of the Hyperparallel Computer Arweave AO: Bringing AI Models into Smart Contracts, Planning Mainnet Launch in 2024
How does Arweave AO achieve the transition from a storage platform to a computing platform, and how is it building the narrative of an "Ethereum killer"?
By Nancy, PANews
Following last year's fork controversy, Arweave, the leading decentralized storage platform, has once again become a market focal point with the launch of its AO testnet—an ultra-parallel computer—driving its token AR to surge over 63% intraday. How does Arweave’s AO achieve the transformation from storage to a computing platform? And how is it building the narrative of an “Ethereum killer”?
According to Arweave, the team had been contemplating certain ideas since 2020—specifically, leveraging the Arweave data storage platform to support a highly scalable blockchain network. It wasn't until last year, when the team began developing plans to use tokens to represent content ownership, that active development commenced. Recently, they announced the launch of the AO testnet on February 27, sparking significant market anticipation.
The Arweave AO Launch
Transitioning from a decentralized data storage platform to a scalable network capable of supporting various smart contracts and blockchain protocols, AO was primarily inspired by the Erlang computing environment and its programming language. As a decentralized computing environment built atop the Arweave network, AO aims to support diverse applications such as social media and AI. Currently, AO has launched across a network of 220 machines, with multiple projects—including stablecoin protocol Astro Protocol and exchange Bark—already building on it. The mainnet is expected to go live this year following several audits.
Official documentation reveals that AO’s architecture consists of five core components: Processes (the computational units of the network), Messages (each interaction with a process is represented by a message), Scheduler Units (responsible for assigning slot numbers to messages sent to processes and ensuring data is uploaded to Arweave), Compute Units (nodes where users and message units compute the state of processes within AO), and Communication Units (nodes that relay messages across the AO network based on cranking processes, delivering messages to compute units and coordinating output calculations).
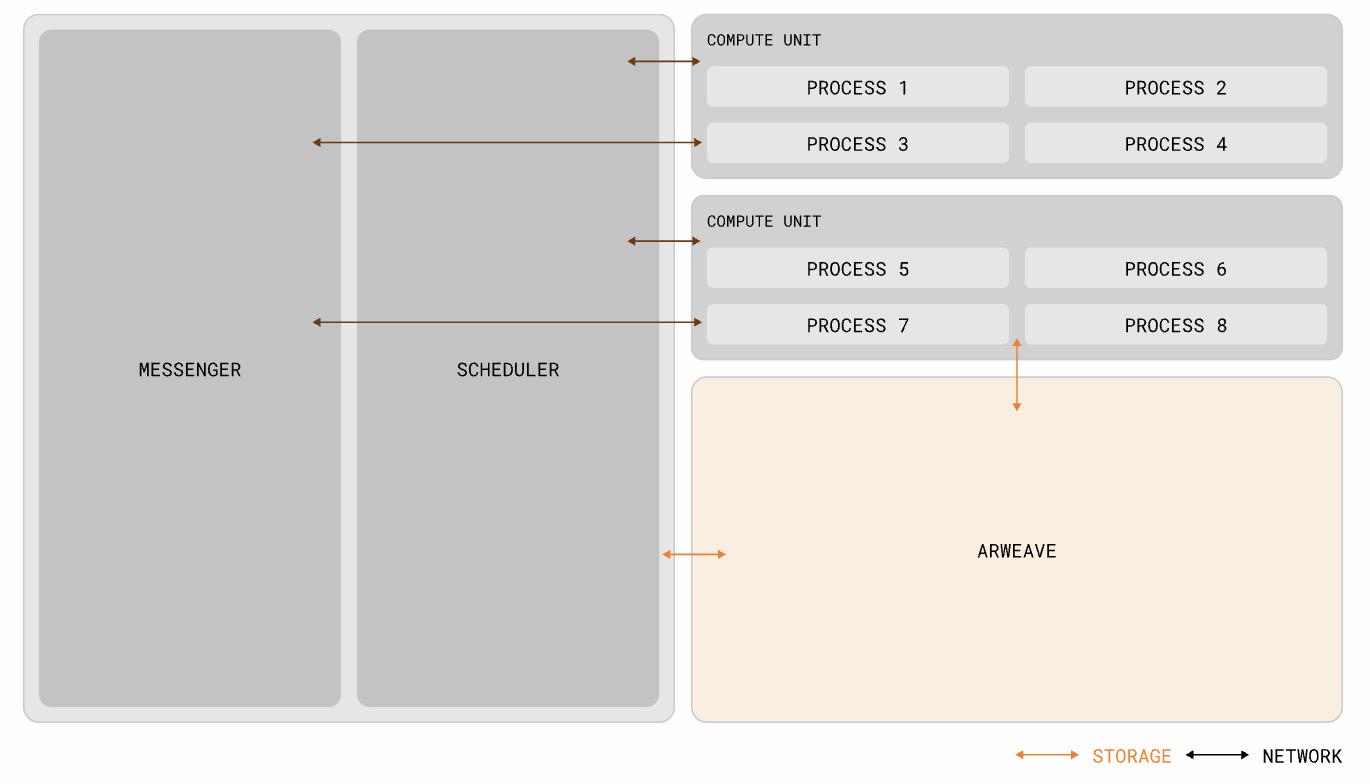
The product features five key capabilities: running an arbitrary number of processes in parallel, infinite resource utilization within processes, access to Arweave’s native infinite hard drive, automatic contract activation, and a modular architecture designed for scalability. This means AO differs from existing decentralized computing systems by enabling both large-scale computation and verifiable computation simultaneously. At its core, AO supports computational operations without protocol-enforced constraints on size or form, while maintaining the network’s own verifiability—thus achieving minimal trust assumptions.
AO operates by separating the three primary components of blockchain execution into distinct modules that can communicate with each other and execute vast numbers of transactions concurrently, thereby achieving high-performance computing. According to Arweave founder Sam Williams, AO essentially takes the orchestration of a conventional blockchain, breaks it into modular components, and turns each into horizontally scalable subnets.
Compared to other high-performance blockchains like Aptos and Sui, AO can store massive datasets—such as AI models. Additionally, unlike Ethereum and similar chains that rely on a single shared memory space, AO enables an unlimited number of parallel processes that coordinate via open message passing, eliminating dependence on centralized memory.
Moreover, Arweave has developed AOS, a decentralized operating system built on AO using the Lua programming language. Functioning similarly to smart contracts, AOS allows developers to initiate command-line processes. These processes are not bound to any specific location, enabling seamless cross-network user interactions, with decentralized and trustless computing serving as its key advantages.
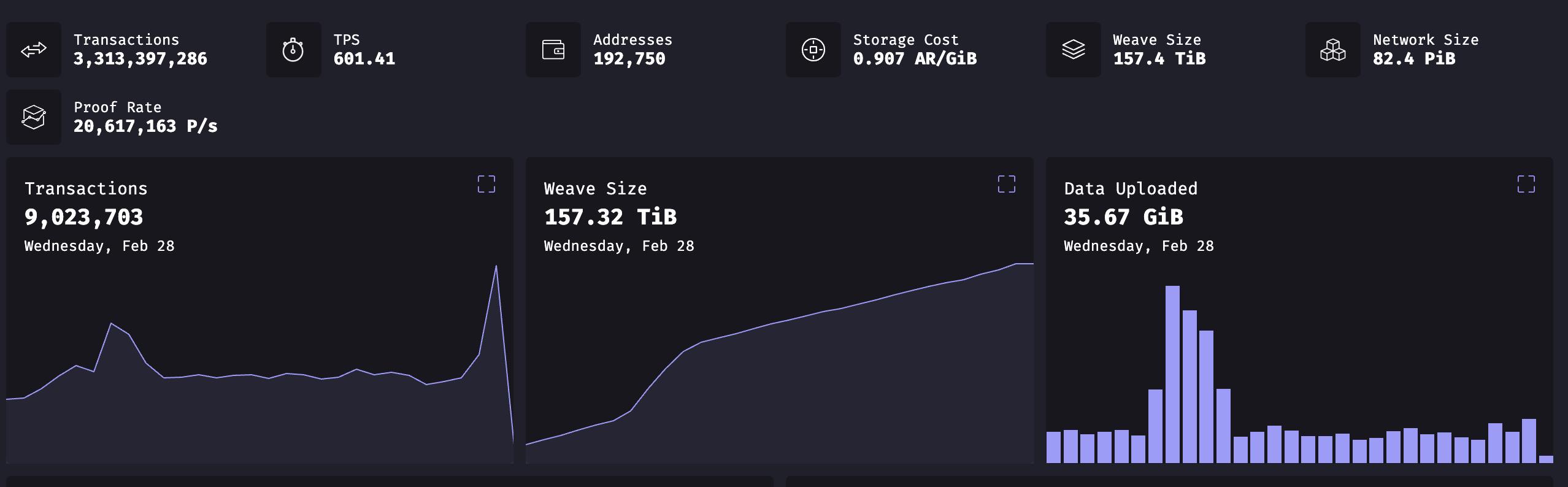
Following the release of the AO testnet, on-chain activity on Arweave has surged. Data from Viewblock shows that as of February 28, Arweave has processed over 3.3 billion transactions, with 1 billion occurring within the past two months alone. Meanwhile, Arweave’s TPS reached 601.41, significantly surpassing Solana, Polygon, Ethereum, and Arbitrum. CoinGecko data also indicates that the AR token has risen 166.3% over the past 30 days—the highest since May 2022—sparking a broad rally across the decentralized storage sector.
In summary, AO marks the beginning of a new era in decentralized storage and computing. While Williams confidently claims AO can rival Ethereum, the crypto space has seen no shortage of so-called “Ethereum killers.” For AO, which remains in the testnet phase, whether it can truly disrupt the current market landscape remains to be seen. PANews will continue to monitor AO’s progress.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News