Interpreting the IMO: AI models can now be tokenized and issued—a new way for the crypto world to embrace AI
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Interpreting the IMO: AI models can now be tokenized and issued—a new way for the crypto world to embrace AI
Since everything can be tokenized, AI models can also be tokenized and issued as an asset.
Author: TechFlow
The crypto market never lacks new concepts.
But most of these new concepts are merely minor innovations built upon old mechanics; and it is precisely such incremental innovation that often sparks fresh waves of hype and speculation.
Nowhere is this more evident than in asset issuance methods.
From the ICO craze starting in 2017, to IEOs that followed, and now to today’s popular IDO or LBP (Liquidity Bootstrapping Pools)—each shift in asset issuance has ignited a wave of new projects and delivered profits to a segment of degens.
What changes is the form; what stays the same is the core.
Now, as we enter 2024 and AI becomes the “new backbone” of crypto narratives, launching assets around AI has emerged as a promising avenue for creating new concepts.
Take, for example, the recently introduced "IMO," which stands for "Initial Model Offering."
On March 2nd, an AI project named Ora Protocol first proposed the concept of IMO (Initial Model Offering) on its social media, drawing significant attention.
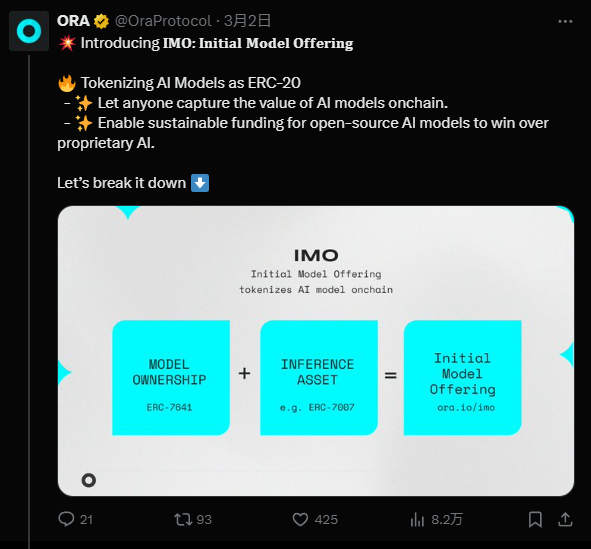
Put simply, if everything can be tokenized, then AI models should also be tokenizable—as assets ready for issuance.
But actually implementing IMO may not be so straightforward.
Quick Understanding of Tokenized AI Model Issuance
For any ICO and its variants, the core lies in creating a token—defining its supply, release schedule, utility, functionality—and ultimately forming a market price.
Here, the token does not necessarily correspond to anything in the real world—it can be created out of thin air, commonly known as “launching a coin.”
But IMO is different.
The essence of IMO lies in the monetization of real-world AI models.
Many open-source AI models face challenges in monetizing contributions, leading contributors and organizations to lack motivation due to insufficient revenue. This is why today's AI industry is largely dominated by closed-source, for-profit companies. For open-source AI models to thrive, the key lies in raising funds and building openly.
Thus, IMO aims to provide a new method of asset issuance, helping open-source AI models raise funds to support their development.
By analogy with previous IXOs: you back a token asset through investment, receive returns based on its market performance, and potentially share in revenues generated by the underlying protocol.

Under IMO, if you believe in a particular AI model, you can invest in its corresponding token. The AI model developer secures funding for further development, and as the model generates economic value through usage, you may share in those earnings.
How Does IMO Work in Practice?
To represent an AI model as a token and enable profit-sharing, several critical issues must be addressed:
-
How do we ensure a given AI model is genuine and truly linked to the token you hold?
-
How do we guarantee that token holders actually receive a share of the revenue generated from using the AI model?
Ora Protocol addresses these challenges using two distinct ERC standards—ERC-7641 and ERC-7007—combined with oracle and ZK technologies.
-
How do we verify that an AI model is real and not just an empty concept used to raise money via token sales?
First, it's important to know that Ora Protocol originated as an AI oracle solution, with its core product being the Onchain AI Oracle (OAO).
This oracle enables verification and execution of AI models on-chain, ensuring full transparency and verifiability of deployment and operation.

However, since AI models are often core intellectual property, exposing them publicly would undermine competitive advantage. To address this, Ora Protocol incorporates another technology—opML (Optimistic Machine Learning).
In simple terms, opML may use zero-knowledge proofs or other cryptographic techniques to prove the correctness of a model’s output without revealing the model itself—ensuring both authenticity and confidentiality.

While we won't evaluate the technical merits behind opML or the research paper referenced above, understanding its functional outcome suffices.
Thus, through AI oracles and zero-knowledge proofs, we solve the problem of verifying the existence and integrity of an AI model.
-
Next question: How do we ensure ownership of the token tied to the AI model and enable revenue sharing?
Tokenizing an AI model is central to IMO. Ora Protocol introduces a new token standard called ERC-7641, compatible with ERC-20.

If an AI model developer believes their model has potential and wants to launch an IMO in the crypto market, here’s how it might work:
1. Link the AI model to an ERC-7641 asset and define the total token supply within the smart contract;
2. Crypto investors purchase the token, gaining proportional ownership of the AI model (akin to shareholders);
3. Once the AI model runs on-chain, any revenue generated—such as usage fees when the model is invoked, or royalties from NFTs created by the AI—is distributed automatically according to rules pre-defined in the ERC-7641 contract, based on each holder’s token stake.

Through this mechanism, ERC-7641 tokens serve as a bridge connecting AI models, their economic value, and token holders—enabling contributors and investors in open-source AI models to share in long-term value creation.
Hence, ERC-7641 tokens are also known as Intrinsic RevShare Tokens—an emerging standard designed specifically for distributing revenue generated by AI models.
The overall logic of IMO is now clear: AI model developers seeking funding bind their model to a token and launch an IMO; buyers acquire tokens and, per smart contract rules, gain rights to future revenue from the model’s usage and derivative creations.
Yet one crucial gap remains:
-
How can you verify that AI-generated works on-chain (e.g., NFTs, images, videos) truly originate from the specific AI model undergoing IMO, rather than being forged?
Ora Protocol’s solution: Tag all AI-generated content and implement this via ERC-7007.
Setting aside technical complexity, think of ERC-7007 as a token standard tailored for AI-generated content, ensuring authenticity and traceability of origin.
This standard records metadata of AI-generated content on-chain (such as the AI model used, generation time, input conditions, etc.) and uses smart contracts to enforce validation logic. Developers can leverage zkML or opML to verify whether a given NFT’s AIGC data genuinely stems from a specific ML model and input.
This enhances transparency regarding AIGC authenticity and, thanks to blockchain immutability, ensures records cannot be altered or falsified. Thus, within the ORA ecosystem, ERC-7007 is referred to as the “Verifiable AI-Generated Content Token.”
This standard is already open-sourced and publicly available—click here.
Now we fully understand the logic of IMO:
-
Bind an AI model to a revenue-sharing token and conduct an IMO
-
Investors earn revenue shares from the model’s future usage and derivative works based on their token holdings
-
Use a verifiable content attribution protocol to confirm authorship and distribute earnings accordingly
Still an Asset Game—Not Perfect
From ICO to IMO, as AI models become tokenizable, this year’s crypto frenzy is bound to revolve tightly around AI.
Yet the IMO framework pioneered by Ora Protocol is far from flawless.
-
Off-chain usage issue: Even if IMO enables on-chain tokenization and revenue sharing, it struggles to track and distribute earnings when models are used off-chain. When AI models power non-blockchain applications, capturing and allocating those revenues to token holders presents a complex challenge.
-
Uncertain market demand: While on-chain AI-generated content (like NFTs) opens new possibilities for creative industries, market demand remains highly uncertain. The value, liquidity, and pricing willingness for AIGC works are unknowns—making stable revenue sharing from AI models speculative at best.
-
Practical effectiveness of revenue sharing: In theory, profit distribution via ERC-7641 sounds appealing. But in practice, the mechanism’s viability awaits real-world testing. Given the high volatility of blockchain projects and tokens, actual returns for holders could vary dramatically.
In crypto, people can turn asset issuance into art—but rarely can they predict whether the asset will have utility or adoption.
Nevertheless, IMO offers an innovative framework enabling open-source AI models to secure funding and share value through tokenization.
This framework itself represents a timely and positively framed narrative.
In the world of imperfect asset games, latching onto the trending strength of AI often paves the easiest path to success.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















