Bitlight Labs: Unlocking the Potential of the Lightning Network Ecosystem
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Bitlight Labs: Unlocking the Potential of the Lightning Network Ecosystem
Bitlight Labs closely follows the development of the BTC ecosystem.
Author: Howe
Summary
-
From the beginning of last year to autumn, the surge in inscriptions fueled growth in Bitcoin (BTC) ecosystem traffic and consensus expansion, while once again exposing shortcomings such as insufficient BTC ecosystem infrastructure and transaction limitations. Due to Bitcoin's non-Turing-complete nature, more complex ecosystem infrastructure and functional products can only be built on scalability solutions.
-
The RGB protocol is a client-side validation protocol built atop Bitcoin’s base layer (LNP/BP) and the Lightning Network, introducing smart contracts into the Bitcoin ecosystem via the Lightning Network. Its design breaks from previous approaches by separating the roles of contract issuer, state owner, and state evolution. Smart contract data is stored off-chain and verified by clients, with Bitcoin scripts used as the ownership control system.
-
Bitlight Labs seized the opportunity presented by BTC ecosystem development, rapidly rising to prominence by building products based on the RGB protocol and Lightning Network, filling critical infrastructure gaps and advancing the BTC ecosystem. It holds a significant advantage within the RGB ecosystem and provides essential support for the future of the BTC ecosystem.
Introduction
The recent boom in inscriptions has ignited rapid development in the Bitcoin ecosystem. At the same time, this surge has brought long-standing issues within the BTC ecosystem back into public view, accelerating ecosystem development at the capital level.
First, infrastructure in the BTC ecosystem remains inadequate. Bitcoin’s extremely low throughput and high gas fees severely limit the issuance and trading of inscriptions. Second, due to Bitcoin’s non-Turing-complete nature, we cannot run complex logic on the BTC ecosystem—such as introducing DeFi to provide greater liquidity and utility for existing inscriptions.
Therefore, despite Bitcoin being currently the most decentralized and secure blockchain, building more applications and use cases on its ecosystem presents an incredibly promising narrative. However, because Bitcoin itself lacks Turing completeness and cannot natively support smart contracts, attention must turn to Bitcoin’s scaling solutions—currently dominated by three main directions: the Lightning Network, sidechains, and Bitcoin Layer 2s.
Among these, the Lightning Network serves as a Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin, originally included in Bitcoin’s early codebase. It aims to enable faster, lower-cost microtransactions while reducing congestion on the main blockchain. While primarily designed to solve Bitcoin’s scalability challenges, it also offers developers a platform to experiment with new functionalities.
RGB builds upon the Lightning Network to introduce smart contracts to Bitcoin, enabling more advanced features. It allows users to create and manage non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and other complex assets without compromising the stability and security of Bitcoin’s main chain.
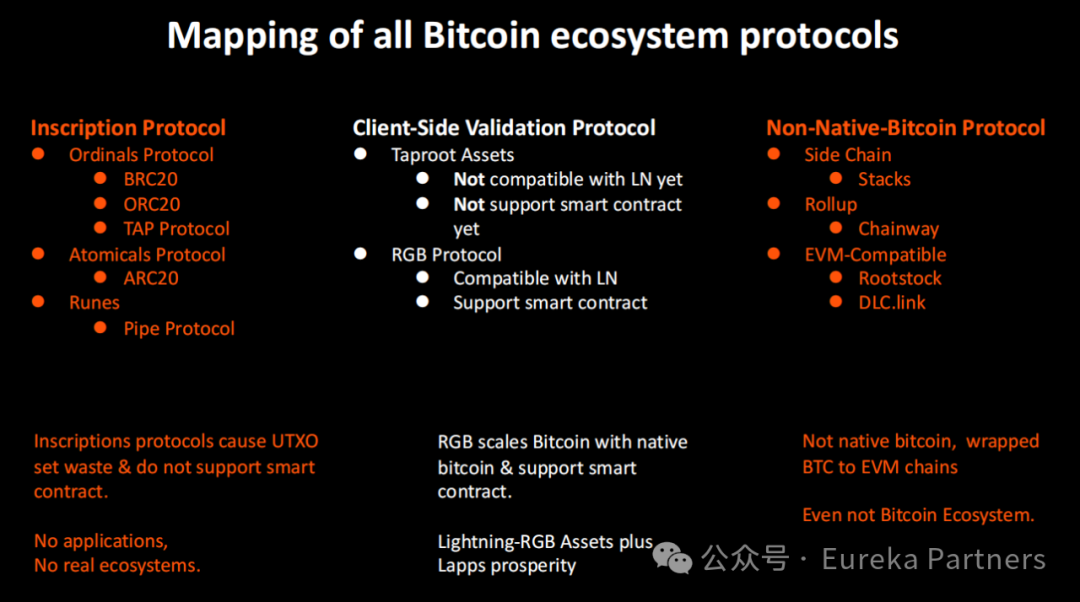
This means RGB unlocks greater possibilities for the Bitcoin ecosystem, bringing Bitlight Labs into focus. Committed to unlocking the potential of the Lightning Network ecosystem, Bitlight Labs has launched or is developing a suite of functions including a decentralized non-custodial wallet, AMM, and Launchpad—laying the foundation for a complete DeFi ecosystem and providing robust infrastructure for the development of RGB and Lightning Network assets.
Overview of the RGB Protocol
Historically, the concept of smart contracts originated with Nick Szabo, yet it has continued to inspire generations of innovators. However, the promise of smart contracts as a technically guaranteed foundation for free markets, free capitalism, and decentralized governance has never been fully realized—because all existing systems claiming to be "smart contract platforms" have so far failed to deliver the three essential characteristics required:
-
Scalability
-
Sufficient programmability (nearly equivalent to a universal Turing machine)
-
Decentralization and censorship resistance
Over the past decade, collaborative efforts among cryptographers and cypherpunks have led to new technological and theoretical foundations that make this goal achievable. These include Peter Todd’s concepts of client-side validation and single-use seals, along with Giacomo Zucco’s development of client-validated “colored coins” capable of serving as a scalable layer on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network. In this proposal, these ideas are combined with strong privacy-preserving technologies (such as Confidential Transactions proposed by Blockstream, enhanced with Bulletproofs++ range proofs), as well as novel concepts developed by the proposal authors at UBIDECO Research Institute—including partial replicated state machines, functionally restricted type systems, and registry-based virtual machines—to create a new programmable, secure, privacy-preserving, censorship-resistant, and scalable smart contract system called RGB.
Since mid-2019, Dr. Maxim Orlovsky and Pandora Core AG have been the primary contributors to the project. Following standards set by the Swiss nonprofit LNP/BP Standards Association, co-founded by Dr. Orlovsky and Dr. Zucco in 2019, the RGB protocol has matured through contributions from numerous individuals and industry organizations, officially launching on the mainnet in June 2023.
How It Works
In any given RGB contract, genesis tokens belong to a Bitcoin UTXO (either pre-existing or temporarily created). To transfer these tokens, you must spend this UTXO. When doing so, the Bitcoin transaction must include an additional output containing a commitment to a message—the RGB payment information—which defines the inputs, the destination UTXO for the tokens, the asset ID, amount, spending transaction, and other relevant data.
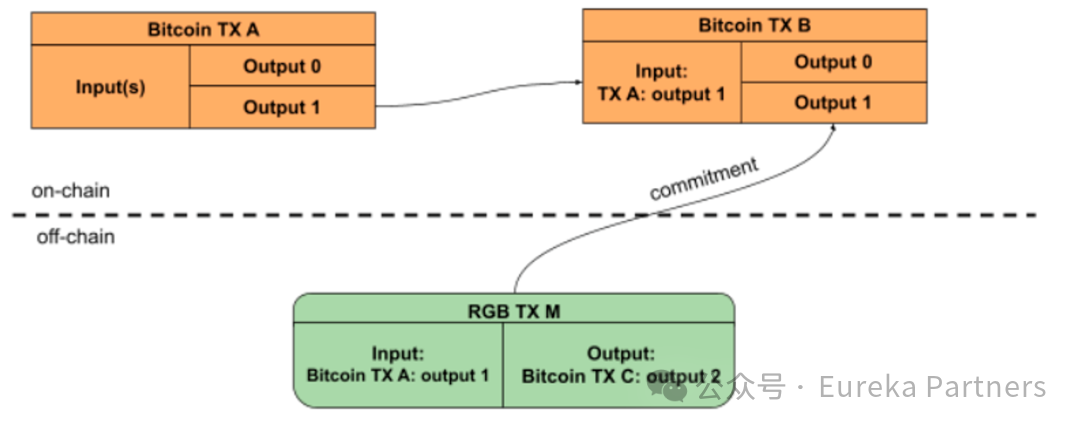
If you hold tokens assigned to output #1 of Bitcoin transaction A, transferring them requires creating both an RGB transaction and a Bitcoin transaction that spends output #1 of transaction A, with the latter committing to the RGB transaction. As shown, the RGB transaction transfers tokens from output #1 of Bitcoin transaction A to output #2 of Bitcoin transaction C (not depicted), rather than to transaction B. Typically, output #0 of transaction B serves as a change address, returning remaining funds (after miner fees) to the original owner, while output #1 commits to the RGB transaction to prevent double-spending.
Scalability
Thanks to its “client-side validation” model and batch processing capabilities, RGB uses the blockchain more efficiently, as the vast majority of data is stored off-chain. Moreover, RGB is compatible with the Lightning Network—you can even create dedicated asset channels—and can leverage any future Bitcoin scalability upgrades.
Strong Ownership Model
The strong ownership model introduced by the RGB ecosystem means that smart contracts manage an “ownership state” with clearly defined owners. Only these designated owners can update the contract state. Contracts define various rights as sets of operations executable on the contract, categorizing them as either “public” or “owned,” and assign them using right-specific validation logic. This design ensures contract security and transparency, allowing only authorized owners to perform critical state updates. The smart contract operates under an “ownership state” with one or more clearly defined owners; no one else can alter the state. Rights are always defined as operation sets applicable to the contract, divided into “public” or “owned,” and allocated using right-specific validation rules.
Programmability
The RGB protocol not only enables token and asset issuance on Bitcoin but also gives issuers flexibility to write custom issuance contracts. Issuers can define different asset types and apply distinct validation rules during transfers. Furthermore, RGB can issue broader forms of rights, enabling non-financial use cases (e.g., decentralized identity, proof of publication).
Privacy Protection
To transfer RGB tokens tied to a Bitcoin transaction, a Bitcoin transaction must be initiated. However, the outputs of the RGB transfer do not need to match those of the Bitcoin transaction. As in the earlier example, the output of the RGB transaction (output #2 of Bitcoin transaction C) may have no connection to the Bitcoin transaction (transaction B) that commits to it. This means RGB tokens can be “teleported” from one UTXO to another without leaving any trace on the Bitcoin transaction graph, greatly enhancing privacy.
In this design, Bitcoin UTXOs serve as disposable containers for RGB assets. Transferring assets simply involves opening a new container and closing the old one.
Specific RGB payment details are transmitted off-chain through dedicated communication channels—from the payer’s client to the recipient’s client—for verification against RGB protocol rules. As a result, blockchain observers gain no insight into RGB user activity.
Closed Validation Loop
However, verifying received payment data alone isn’t enough to confirm that the sender actually owns the assets. To ensure finality, you must also receive the full transaction history of these tokens—from the current transaction back to their initial issuance. By validating the entire history, you can confirm that no inflation occurred and that all spending conditions attached to the assets have been satisfied.
This design also benefits scalability, as you only need to validate the portion of history relevant to you—not the entire asset history. Additionally, since transactions aren’t broadcast to a global ledger, privacy improves because fewer parties become aware of your transaction.
Blinded Secret Values
To further enhance privacy, RGB supports output blinding. When sending a payment request, you don’t need to reveal the UTXO where you’ll receive tokens. Instead, you ask the payer to send tokens to a hash derived from your target UTXO concatenated with a random secret blinding value. This way, the payer cannot determine which UTXO receives the tokens, preventing exchanges and service providers from knowing whether users are withdrawing to UTXOs blacklisted by regulators or tracking how these tokens are spent later. Note that when tokens are spent, the blinding secret must be revealed to the recipient so they can verify the Bitcoin-related portions of the transaction history. This means RGB users enjoy full privacy at the time of receipt and holding, but future holders will see all UTXOs involved in the token’s transfer history. Thus, while perfect privacy is achieved upon receiving and holding RGB tokens, the confidentiality of a user’s financial history degrades with each subsequent transfer, eventually converging toward the same level of privacy as regular Bitcoin transactions.
Current Status
Currently, the market widely views RGB, Taproot, and BitVM-based solutions as the leading scalability options. Most protocols aim to extend the BTC ecosystem without modifying Bitcoin’s core architecture. Compared to BitVM—which, despite strong institutional interest, faces major implementation hurdles due to Bitcoin’s still-limited infrastructure and uncertain rollout timeline—RGB is already gaining momentum and attracting increasing numbers of projects to its ecosystem.
Built on top of the Lightning Network, RGB inherits its advantages while leveraging client-side validation to enable smart contracts. Compared to other inscription protocols and non-native BTC protocols like Stacks and Rootstock, RGB uniquely supports native BTC assets and smart contracts, as well as Lightning Network assets and Lapps, paving the way for a vast BTC ecosystem.
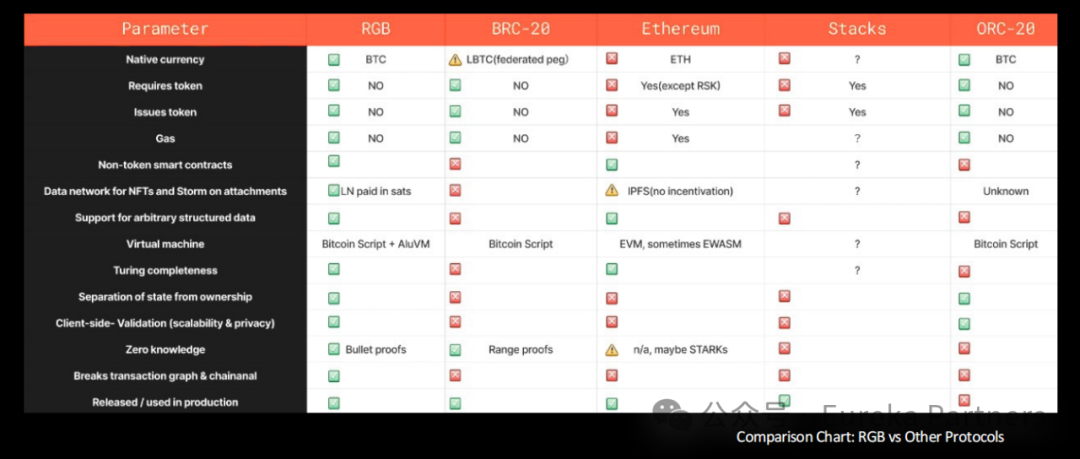
Nonetheless, the current RGB protocol still faces several challenges:
-
Slow Development Pace: Few developers are working on the protocol, and as it is maintained by a nonprofit, funding concerns slow overall progress.
-
Poor Compatibility Between Versions: Features developed on older versions (e.g., v0.10) may require rework in newer versions (e.g., v0.11), incurring high risk and cost. Though necessary for long-term planning and improvement, this poses short-term friction.
-
Limited Funding and Market Attention: The BTC ecosystem is currently dominated by the inscriptions narrative. Since RGB’s vision is longer-term, it remains less connected to current market trends, resulting in relatively low investment and attention.
-
Data Security Concerns: All RGB transaction data is stored off-chain, and the security of this data relies on individual projects or clients. Users can back up data to protect their assets, but there remains a risk of malicious behavior by project teams or client software.
Understanding Bitlight Labs
Bitlight Labs has developed a series of infrastructures focused on trading around the RGB protocol, targeting two main directions: from the RGB protocol to the Lightning Network ecosystem, and from BitcoinFi to Lapps. These offerings enrich both the broader Bitcoin ecosystem and the RGB-specific ecosystem.
In a prior interview, Bitlight Labs founder Valestin explained the team’s decision to fully commit to the RGB ecosystem based on several key factors:
-
Mature Technical Foundation: The RGB protocol demonstrates a robust technical foundation at both the client and smart contract levels. From code and documentation perspectives, it is already quite mature, requiring only further infrastructure development.
-
Bitcoin Lightning Network Integration: RGB leverages the Bitcoin Lightning Network for transactions, theoretically enabling up to 40 million TPS with near-zero fees. This allows RGB to meet diverse future payment needs and support large-scale user adoption and advanced application ecosystems.
-
Security via Bitcoin: By anchoring on Bitcoin—one of the most secure payment systems—RGB avoids the need for mainnet modifications or forks. This provides a strong security foundation while supporting high-performance smart contracts with theoretically infinite scalability.
-
Industry Support: The RGB protocol has gained backing from industry leaders such as Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino. Tether and Bitfinex have invested early in RGB ecosystem development and directly contributed to core code. Tether has announced plans to issue stablecoins on the RGB protocol, further accelerating its growth.
-
Mass Adoption Potential: Valestin sees strong potential for RGB to achieve mass adoption on Bitcoin. Features like efficient asset transactions, fragmented client execution, and highly customizable smart contracts suggest that future possibilities are limited only by imagination.
Currently, Bitlight Labs has launched two main products: Bitlight Wallet and BitSwap. Two additional products are planned (details not yet disclosed). Below, we focus on the two already released.
Bitlight Wallet
Bitlight Wallet is the first decentralized, non-custodial wallet specifically designed for the RGB protocol and Lightning Network assets. It is currently in Alpha testing and features five key attributes:
-
Pioneering: First decentralized non-custodial wallet tailored for RGB and Lightning Network assets
-
Multi-platform Design: Fully compatible across PC, iOS, Android, and hardware wallets
-
Enhanced Security: Self-custody solution ensuring user asset safety
-
Supports L1/L2 Cross-chain: Enables asset transfers between Bitcoin mainnet and Lightning Network
-
Asset Compatibility: Will gradually support more Bitcoin asset types, especially Lightning Network-compatible protocols such as Taproot Assets, Atomicals, and Runes

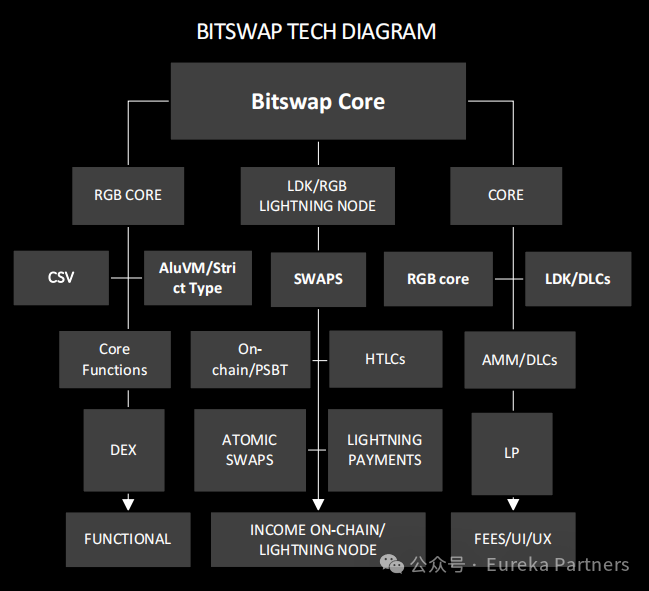
BitSwap
BitSwap is the first AMM DEX dedicated to RGB and Lightning Network assets. Currently, Bitlight Labs is the only team actively developing an AMM DEX for RGB assets. The team is also collaborating closely with Bitfinex and Tether to launch rgb20-USDT on the RGB protocol, making BitSwap the first marketplace to support USDT trading pairs on RGB.
BitSwap integrates swap functionality, liquidity provision, and wallet integration (like Bitlight Wallet) to offer users a rich feature set:
-
Atomic swaps on-chain using PSBT
-
Swapping Lightning Network assets via Channels and Bifrost
-
Decentralized contracts (DLCs) providing independent price oracle checks
Roadmap
Looking ahead, Bitlight Labs plans to develop a suite of DeFi applications on the RGB protocol—including decentralized stablecoins, lending protocols, and LApps. As market conditions improve, these applications will inject renewed vitality into the BTC ecosystem.
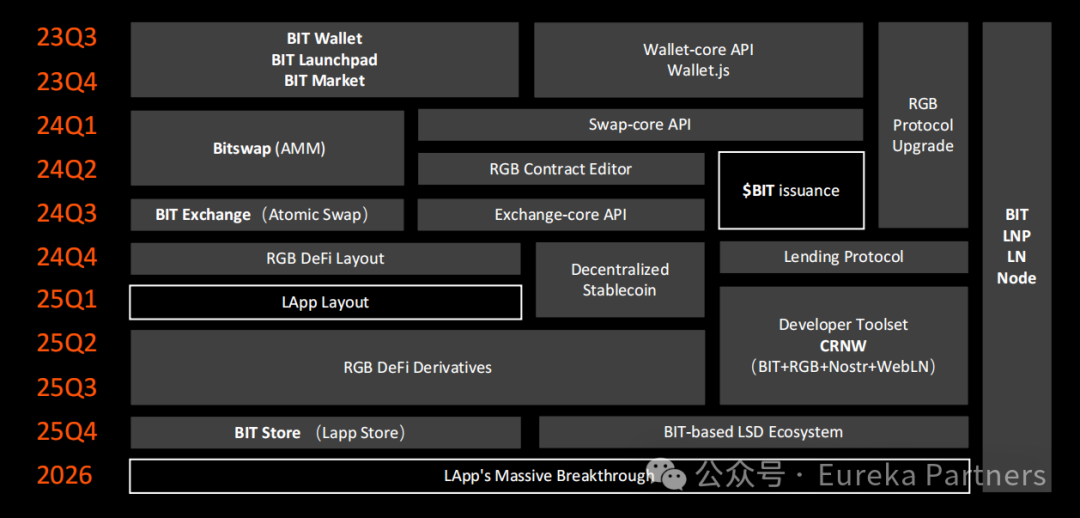
Conclusion
Whether considering market sentiment or the RGB protocol ecosystem itself, current BTC ecosystem users remain highly enthusiastic about Bitlight Labs, anticipating that its products will drive expansion of the RGB and BTC ecosystems.
Although RGB currently receives less attention compared to other scaling solutions, its ability to expand the ecosystem without altering Bitcoin’s core architecture makes it a crucial component of BTC ecosystem development. We look forward to seeing more innovative use cases emerge on the RGB protocol, adding vibrant color to the BTC ecosystem.
Bitlight Labs has closely followed the pace of BTC ecosystem development. Recognizing the unique strengths of the RGB protocol, the team decisively embraced it and swiftly developed a series of ecosystem applications, gaining a first-mover advantage.
This effort not only fills critical infrastructure gaps within the RGB ecosystem but also advances the broader BTC ecosystem—such as enhancing liquidity for RGB and Lightning Network assets. With few existing products in the RGB ecosystem, Bitlight Labs’ contributions are timely and impactful, establishing a clear first-mover edge.
Eureka Partners consistently treats the BTC ecosystem as a key strategic investment focus. We also look forward to the BTC network achieving better infrastructure and user experiences, driven by battle-tested protocols and products like RGB.
Asking travelers about the road ahead, lamenting the dim morning light. We await the next chapter of BTC’s ecosystem and narrative.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















