Binance Research: Exploring the OP Stack Ecosystem and Superchain
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Binance Research: Exploring the OP Stack Ecosystem and Superchain
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the OP Stack and the theory of hyperchains, as well as the OP Stack ecosystem, including Base, Zora Network, and DeBank Chain.
Author: Shivam Sharma, Binance Research
Translation: HuoHuo, Baishu Blockchain
The era of L2 rollups is approaching, with activity on Ethereum L2s reaching all-time highs. The average transactions per second (TPS) on L2s has exceeded that of Ethereum since the end of 2022.
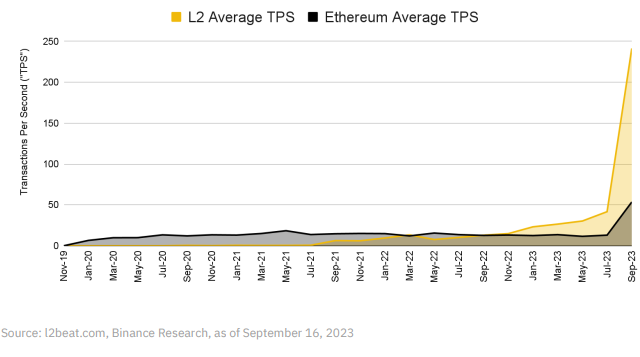
In the latest wave of L2 launches, many are built using the OP Stack—an open-source software development toolkit supporting Ethereum L2s, including OP Mainnet and new entrants such as Base and Zora Network. Optimism envisions a future where these rollups, combined with numerous others, form a decentralized network of L2 chains known as the Superchain.
This article dives deep into the OP Stack and the Superchain vision, then explores the evolving OP Stack ecosystem, including Base, Zora Network, DeBank Chain, and more. It also examines infrastructure solutions making this suite of OP Stack chains accessible to developers and builders from all backgrounds.
About Optimism
Optimism is the company behind OP Mainnet, an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible Optimism Rollup that has been operational since 2021 and is one of the leading Ethereum Layer 2 solutions. At the time of writing, OP Mainnet has a total value locked (TVL) exceeding $2.6 billion and holds the second-largest market cap among all Ethereum Layer 2 solutions, with over 25% market share.
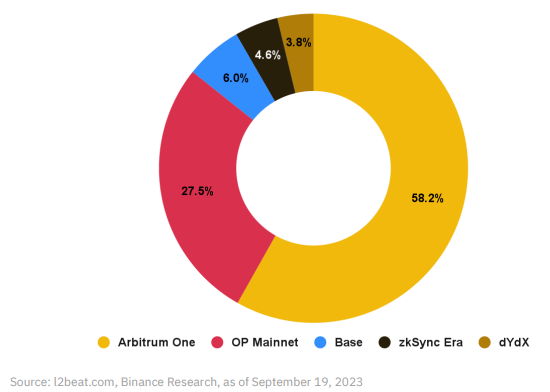
In October 2022, Optimism introduced the OP Stack—a “highly scalable, highly interoperable modular open-source blueprint” for various types of rollups. It also unveiled the concept of the “Superchain,” referring to a highly integrated and unified group of Layer 2 blockchains built on the OP Stack. The next major milestone was migrating their L2 rollup to Bedrock.
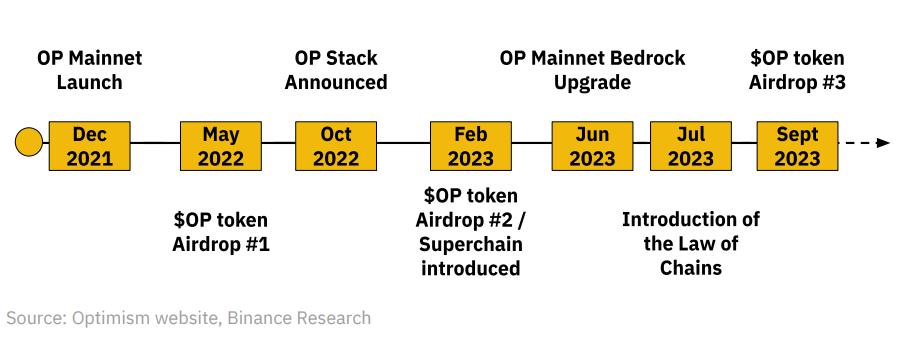
A brief timeline of Optimism so far
The OP Stack is the standardized, shared, and open-source development framework powering OP Mainnet, composed of various software components that build Optimism’s L2 rollup to create a shared, interoperable, and collaborative network of L2 blockchains. The OP Stack aims to simplify the construction of L2 blockchains—akin to a “supermarket for building L2s”—enabling builders to easily modify or create modules to meet their specific needs.
Builders can customize existing modules or create new ones to suit their requirements, as the OP Stack deconstructs different L2-building components into independent modules. Ultimately, Optimism expects highly compatible L2s, known as OP chains, to become part of a unified Superchain.
The Superchain vision represents Optimism’s ambition to evolve its ecosystem into a Superchain. The Superchain is envisioned as a decentralized network of L2 chains (OP chains) that share security, a communication layer, and an open-source tech stack (the OP Stack). These chains will be standardized and used as interchangeable resources to enhance cross-chain interoperability.
This standardization will allow builders to develop applications targeting the entire Superchain, rather than just individual base-layer chains. It should be noted that the Superchain remains a conceptual framework currently under continuous refinement.
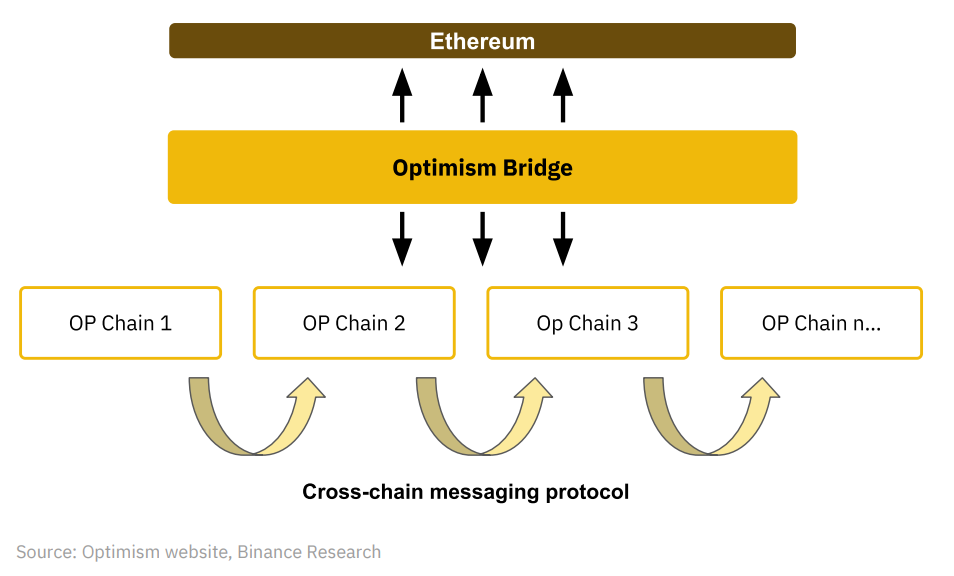
Illustration of the Superchain
The Growing OP Stack Ecosystem
Since the launch of Bedrock in June 2023, we’ve seen a surge of OP Stack-based rollups. Next, we’ll take a closer look at some standout projects and key infrastructure initiatives.
A quick glance at the table below shows Base significantly outpacing others in growth. In fact, Base’s cumulative number of unique addresses even exceeds that of OP Mainnet. Base’s Onchain Summer campaign and integration with Coinbase—providing access to its vast user base—are likely key drivers behind these high figures.
Note that only OP Mainnet, Base, Zora Network, and Public Goods Network are live on mainnet, while the other three projects covered here remain in testing phases.
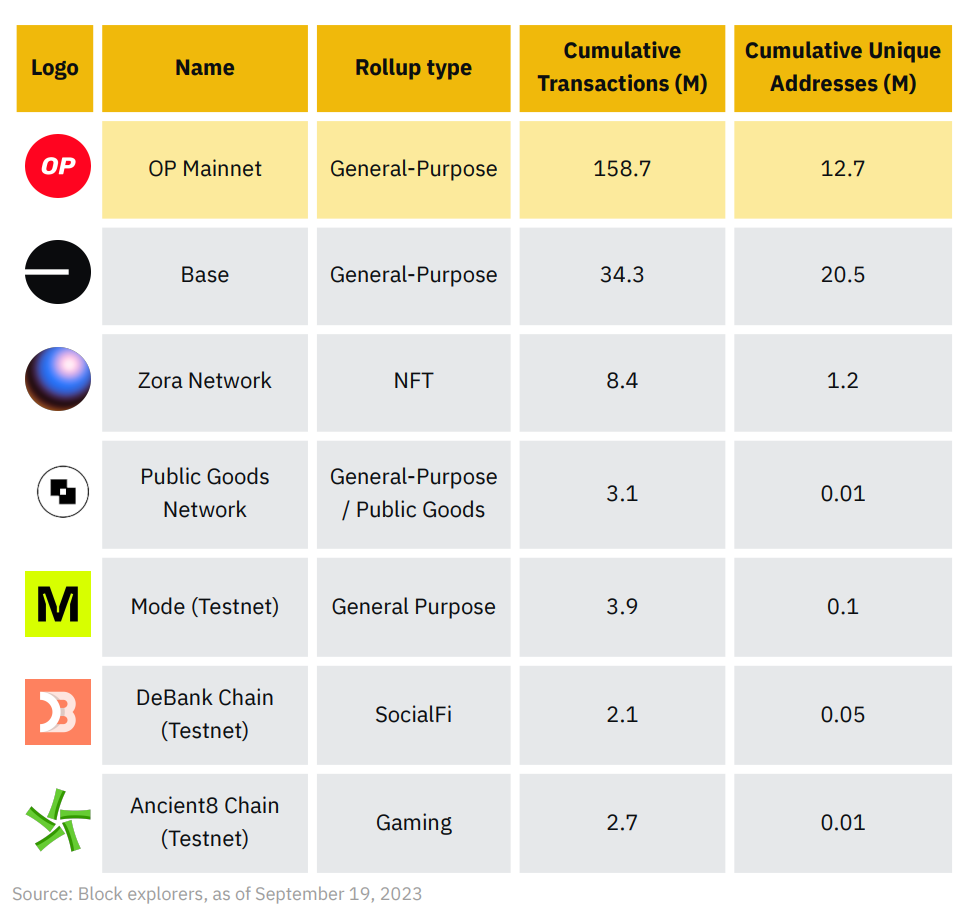
(1) Notable Projects
-
Base
Base was one of the first announced OP Stack L2s (initially in February 2023) and launched its public mainnet on August 9. A general-purpose L2, Base is the most popular OP Stack chain after OP Mainnet.
Onchain Summer, a month-long launch event coinciding with Base’s release, attracted multiple partners—including Coca-Cola—to mint NFTs. The campaign drew over 268,000 unique wallets from 75 distinct collections, generating more than 700,000 mints. Close integration with Coinbase enables seamless access for Coinbase users. Base has also launched over 100 dApps, with its ecosystem rapidly expanding.
Additionally, friend.tech, a prominent SocialFi platform allowing users to trade tokenized “keys,” has attracted significant user engagement and trading volume. However, it remains in test mode, and future growth may depend on attracting non-crypto and Web2 users.
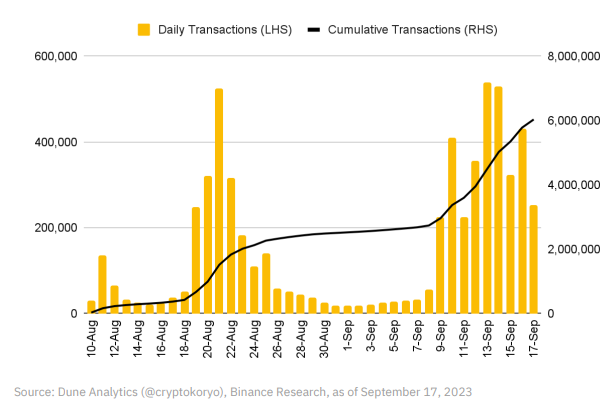
After initial excitement in mid-August, daily transactions on friend.tech slowed significantly until recently picking up again
The Base Ecosystem Fund, led by Coinbase Ventures, focuses on supporting early-stage projects in DeFi, fiat on/off ramps, and creator platforms. Additionally, the Base team released Pessimism, an open-source monitoring system designed to enhance the security of OP Stack and other EVM-compatible chains by detecting protocol threats and mitigating security risks.
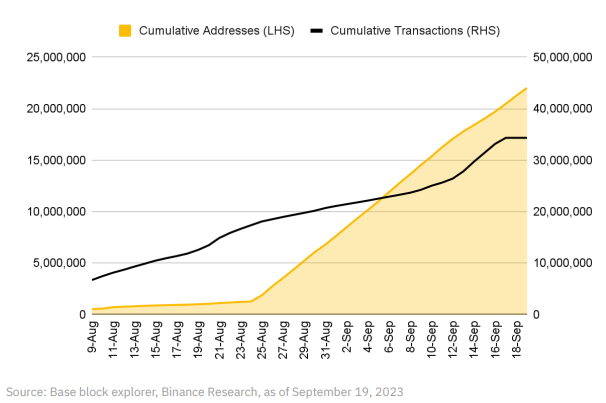
Since its mainnet launch in early August, Base's user metrics have shown strong growth throughout September
Through a collaboration between Optimism and Base, they established an economic agreement whereby Base will donate either 2.5% of sequencer gross revenue or 15% of net profits to Optimism, with the potential to earn up to $118 million in OP tokens over the next six years. Although not officially confirmed, other OP Stack chains may have similar revenue-sharing agreements with Optimism, highlighting the importance of collectively contributing to shared Superchain infrastructure.
-
Zora Network
Zora Network is a decentralized, permissionless protocol enabling anyone to buy, sell, and create NFTs. Additionally, they launched their own OP Stack Layer 2 network to support users and reduce platform costs.
They launched their mainnet on June 21, 2022, offering a better user experience for NFT trading, with NFT creation costing less than $0.50 and providing numerous free mint options. Compared to Ethereum, OP Stack offers a block interval of just two seconds, allowing transactions on Zora Network to be confirmed within seconds.
Furthermore, Zora Network successfully completed three funding rounds, raising a total of $60 million, including a $50 million round led by Haun Ventures in 2022, valuing the company at $600 million. These funds will help drive Zora Network’s development and expansion in the NFT space.
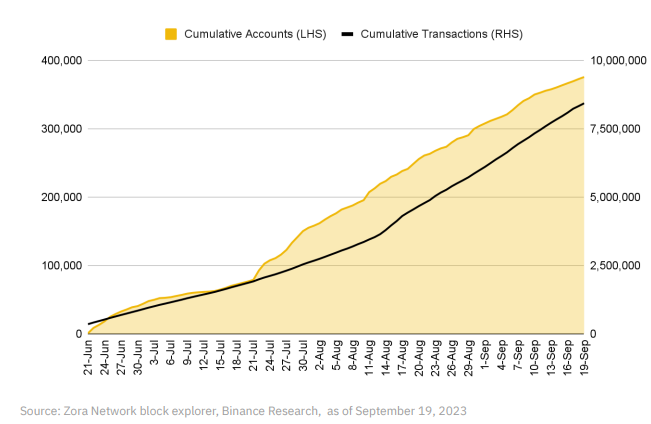
Since late July, Zora user metrics have been steadily increasing
-
Public Goods Network
The Public Goods Network (PGN) is an L2 protocol specifically designed to support public goods. Public goods are non-excludable and non-rivalrous products or services—such as parks, libraries, and road infrastructure—and in the digital realm include open-source software, permissionless data, and AI models. PGN is developed by Gitcoin and SuperModular, backed by multiple public goods advocates forming the Public Goods Coalition responsible for managing and organizing PGN.
According to PGN documentation, the vast majority of net sequencing fees will be allocated to fund public goods projects, meaning increased L2 activity leads to more funding for public benefit initiatives. PGN aims to attract diverse dApps to deploy on its L2, not limited to those directly related to public goods. PGN plans to evaluate and distribute its fees to public goods projects within six months prior to January 2024, with further details to be announced in the coming weeks.
Additionally, PGN plans to implement Contract-Sourced Revenue (CSR) after October 2023, which will allow developers to collect a portion of transaction fees generated by their contracts, supporting sustainable business models. CSR could become part of broader L2 networks, and there is already an Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) suggesting introducing CSR on EVM-based L2s.
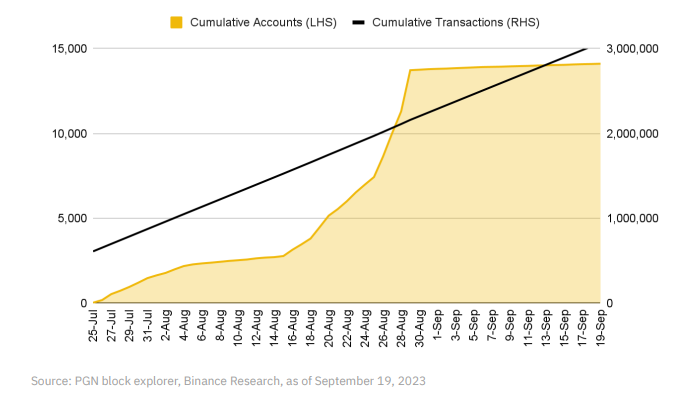
PGN’s user metrics showed steady growth in August. Although new account growth slowed in September, transaction volume continues to climb.
-
Mode
Mode positions itself as a high-growth L2 network that empowers users and developers through direct incentives, enabling them to build world-class applications and scale their ecosystems. Revenue-sharing incentives play a central role in achieving this goal.
Operating an L2 requires maintaining a sequencer, which orders, processes, and submits L2 transactions to the L1 mainchain. Typically, transaction fees paid by users go to the DAO or the sequencer operator. Mode aims to redistribute these sequencing fees to developers and users across the network instead of concentrating them within a single company.
Developers building on Mode receive a share of Mode’s sequencer revenue based on the transaction fees collected in their deployed contracts. These payments are made in USD and settled every two weeks. This model allows developers to earn directly from their work, helping establish predictable and scalable Web3 business models.
Mode incentivizes users, developers, and protocols to refer new members, sharing a portion of transaction fee revenue. They also provide developer support and integrated tools. Mode is developing a developer dashboard to deliver key metrics and insights, helping developers scale more easily. They also plan to integrate multiple external tools and services to assist developers in building sustainable businesses. Finally, Mode adopts a minimal governance approach, requiring DAO votes only on a few critical issues, such as determining how sequencing fee revenue is distributed.
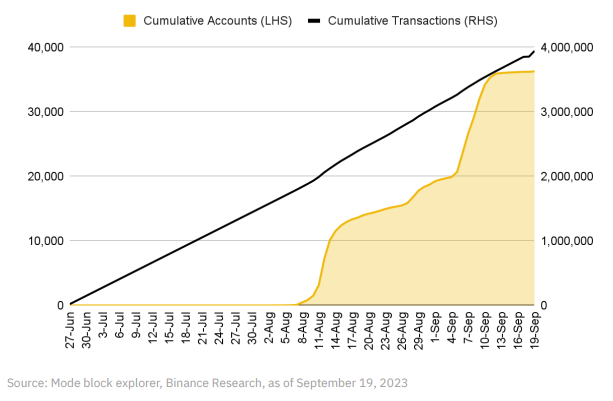
Mode approaches 4 million transactions with over 36,000 unique accounts
Mode is currently on public testnet, expected to continue through the end of September. The mainnet launch is anticipated in Q4 2023.
-
DeBank
DeBank is a Web3 portfolio tracking protocol offering multiple products, including portfolio tracking systems, social networking services, and NFTs. DeBank Chain is their OP Stack-based L2 testnet, expected to launch in 2024.
The core objective of DeBank Chain is to reduce transaction costs for user interactions within the DeBank ecosystem. Through modifications to the consensus mechanism, it has successfully lowered gas costs per transaction, better meeting the demands of high-frequency social interactions. Additionally, DeBank Chain features native account abstraction and generates protocol revenue. Since launching its testnet on August 11, DeBank Chain has recorded over 2.1 million transactions across more than 50,000 unique wallet addresses. Furthermore, DeBank has attracted over 250,000 registered users.
-
Ancient8 and Ancient8 Chain
Ancient8 has operated as a gaming guild and, through collaborations with over 100 games, aims to help gamers enter the Web3 world. They introduced Ancient8 Chain, an Ethereum L2 series focused on gaming. Its testnet launched on September 15. Ancient8’s vision is to build a complete gaming ecosystem encompassing NFT sales, gaming communities, game identity and credential creation, and project marketing. They have also formed the Ancient8 Collective, consisting of eight core partners, to jointly develop the Ancient8 Chain ecosystem. The project has raised $10 million in funding.
Although Ancient8 Chain’s testnet has only been live for a few days, it has already recorded over 2 million transactions involving nearly 5,000 unique accounts. These statistics indicate Ancient8 Chain’s popularity and momentum in the Web3 gaming space.
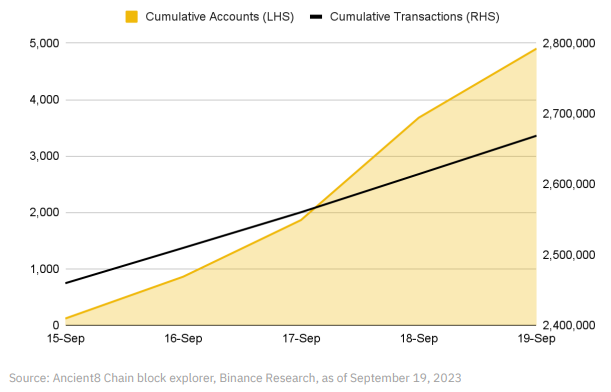
Ancient8 Chain’s testnet is still in early stages
(2) Infrastructure
-
Conduit
Conduit is a Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) platform that allows developers to easily launch their own OP Stack rollups. The Conduit team operates and maintains the rollups, enabling developers to focus on product development rather than infrastructure management.
Since its mainnet launch in March 2023, numerous OP Stack chains—including Zora Network, Public Goods Network, Ancient8 Chain, and Mode—have chosen to partner with Conduit for their rollup launches.

Conduit is a solution that simplifies launching and managing OP Stack L2 rollups. Developers can create their own L2 in minutes, complete with block explorers, transaction trackers, and auto-scaling RPCs. Additionally, Conduit automatically updates each partner’s L2, integrates with the Optimism Superchain, and contributes a portion of fees to the Optimism Collective Fund.
Conduit’s integrations allow partners to connect with other infrastructure projects like Zora Network and Axelar, enhancing its unified infrastructure and making it easier for rollups to grow their user bases.
Conduit has raised $7 million in seed funding led by Paradigm.
-
AltLayer
AltLayer is a RaaS protocol enabling developers to launch Optimism rollups. It supports a multi-chain, multi-virtual machine environment, including EVM, WASM, Solana VM, and Move VM. Unlike Conduit, AltLayer supports multiple different software development platforms. AltLayer is currently on testnet.
AltLayer’s offerings include a no-code dashboard allowing users to create custom L2 rollups in minutes, as well as a Rollup SDK for developers wishing to integrate rollup services directly into their own products. AltLayer also provides a shared sequencer set, enabling atomic cross-chain transactions and message passing between L2s launched with AltLayer.
AltLayer provides a core network called the Beacon Layer, acting as an intermediary between the execution layer and data availability layer for L2s. The Beacon Layer supports multiple rollup SDKs, data availability solutions, sequencer sets, and interoperability platforms, increasing rollup flexibility and interoperability.
Flash Layers are disposable, application-specific rollups ideal for high-traffic events such as NFT mints or mini-games. AltLayer also offers standard Optimism rollups as part of its platform, better suited for long-term applications like GameFi and SocialFi.
AltLayer raised $7.2 million in seed funding in 2022, led by Polychain Capital.
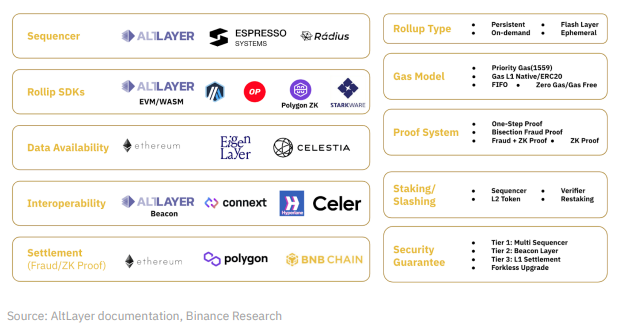
AltLayer’s universal OP Stack rollup supports multiple protocols
Conclusion
We are witnessing a surge in diverse rollup chains, including general-purpose L2s like Base and Mode, as well as specialized chains such as Zora Network, DeBank Chain, and Ancient8 Chain.
New capabilities such as Conduit integration are streamlining the deployment and scaling of OP Stack rollups, paving the way for even more L2 rollups built on this stack. The combination of Conduit and the OP Stack presents an interesting contrast to competing L2/L3 frameworks like Arbitrum’s Orbit or zkSync’s ZK Stack—specifically whether ecosystems will rely on dedicated RaaS providers for growth.
Ethereum rollup metrics continue to break historical records, with an increasing number of dApps choosing to deploy on L2s rather than L1. The era of rollups is indeed arriving. EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding) is expected to significantly reduce L2 rollup costs and boost competitiveness. High L2 adoption, easy deployment via infrastructure like OP Stack and Conduit, and the promise of EIP-4844 will further accelerate L2 development. The future remains exciting and full of possibilities.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News