AI + Web3: Exploring the Convergence of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

AI + Web3: Exploring the Convergence of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain
How can ZKML bridge AI and blockchain?
Author: zf857.eth
Recently, NVIDIA released its first-quarter earnings report, with revenue reaching $7.19 billion, surpassing the market expectation of $6.52 billion. The gross margin stood at 64.6%, while adjusted earnings per share were $1.09, higher than the expected $0.92. Driven by this strong performance, U.S. chip stocks surged after hours, with NVIDIA’s stock price rising as much as 29.35% post-market, hitting a record high of $395. Its market capitalization approached the "trillion-dollar" mark, increasing by $184 billion in a single trading session—an amount equivalent to the total market cap of three Bitcoins—highlighting unexpectedly robust demand for AI chips.
During the earnings release, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang highlighted the vast potential of AI applications, stating that the computing industry is undergoing two simultaneous transformations: accelerated computing and generative AI. Enterprises are racing to integrate generative AI into their products, services, and business processes. The global installed base of data centers, valued in the trillions of dollars, is transitioning from general-purpose computing to accelerated computing.
Currently, nearly all major U.S.-based venture funds and institutions are closely monitoring the AIGC sector, rapidly building investment frameworks to avoid missing out on this transformative trend. Data shows that in the first quarter of 2023, the global AIGC industry raised a total of $3.811 billion across 17 funding rounds. The rise of one technological wave often signals the decline of another. Increasing skepticism toward Web3 has emerged: “Capital is shifting to AI; Web3 faces tighter regulation and lacks compelling narratives,” and “AI seems more practical and offers a clearer path to unicorns.”
Since the dawn of human history, collective storytelling has shaped our cultures and deepened our understanding of the world—the importance of narrative cannot be overstated. Today, the narrative around artificial intelligence is gaining momentum, even permeating the Web3 space. Industry insiders have begun asserting that “Web3 without AI lacks soul,” and over half of Web3 companies are already pivoting toward AI. So how will AI and Web3 converge? Recently, ZKML—a novel fusion of zero-knowledge proofs and machine learning—has gained traction. How might it bridge AI and Web3 to build a trustworthy, decentralized future?
I. AI Needs Web3, and Vice Versa
Michael Casey, Chief Content Officer at CoinDesk, said: “Viewing cryptocurrency and artificial intelligence as unrelated technologies is a mistake. They are complementary, each enhancing the other.”
Web3, cryptocurrencies, and blockchain address long-standing societal challenges since the birth of the internet—specifically, how to securely maintain valuable information within decentralized environments. These technologies tackle issues of trust in information through new systems based on distributed ledgers and incentive mechanisms. Such systems enable communities composed of mutually untrusting strangers to collectively maintain open data records, allowing them to distribute and share valuable or sensitive information without intermediaries.
We are now rapidly advancing into a full-scale AI era, bringing formidable challenges. These include protecting copyright in large language model (LLM) inputs, avoiding biased outputs, and addressing the so-called “liar's dividend”—our current inability to reliably distinguish real content from AI-generated fakes. Ensuring humanity remains protected from AI’s negative impacts has no simple solution. No approach relying on outdated 20th-century regulatory and technical frameworks can adequately address these issues. We urgently need a decentralized governance system to meet the challenges of producing, verifying, and sharing information in this new age.
Regardless of whether today’s Web3 can fully deliver these solutions, blockchain technology already plays a role in addressing such problems. Immutable ledgers allow us to trace the origin of images and other content, helping prevent deepfakes. This technology can also verify the integrity of datasets used in machine learning AI products. Cryptocurrencies offer borderless digital payments, enabling compensation for individuals worldwide who contribute to AI training—for example, projects like Bittensor are working to build tokenized blockchain-governed communities that incentivize developers to create human-friendly AI models. In contrast, privately owned AI systems typically prioritize shareholder interests over user rights.
Before these ideas can be realized and scaled, we still have a long journey ahead. We will need to integrate various other technologies, including zero-knowledge proofs (ZK), homomorphic encryption, secure computation, digital identity, decentralized credentials (DID), IoT, and more. Additionally, we must address numerous challenges such as privacy protection, penalizing malicious behavior, encouraging human-centric intelligent innovation, and achieving multi-party legislative oversight.
II. How ZKML Bridges AI and Blockchain
Recently, ZKML—a nascent convergence of zero-knowledge proofs and machine learning—has become widely discussed. Currently, deploying machine learning (ML) models is becoming increasingly complex. Many enterprises rely heavily on service providers like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft to deploy sophisticated ML models. However, these services are growing harder to audit and understand. As consumers of AI services, how can we trust the validity of predictions provided by these models?
ZKML serves as a bridge between AI and blockchain, solving privacy concerns related to AI models and inputs while ensuring verifiability of inference processes. It enables scenarios where public models can validate private data, or public data can validate private models. By integrating machine learning capabilities, smart contracts become more autonomous and dynamic, capable of processing decisions based on real-time on-chain data rather than static rules. This enhances flexibility, allowing smart contracts to adapt to diverse and even unforeseen use cases beyond their original design.
One major obstacle preventing widespread adoption of machine learning algorithms on blockchains is their high computational cost. Millions of floating-point operations cannot be directly executed on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), making on-chain execution challenging. Furthermore, trust issues plague ML models because both model parameters and training datasets are typically proprietary, and the algorithmic process operates as an opaque “black box,” potentially eroding trust between model owners and users. ZKML overcomes these hurdles by allowing anyone to run a model off-chain and generate a succinct, verifiable proof that the model indeed produced a specific result. This proof can then be published on-chain and validated by a smart contract. Thus, users can verify outcomes without accessing internal model details or sensitive data, resolving key trust barriers.
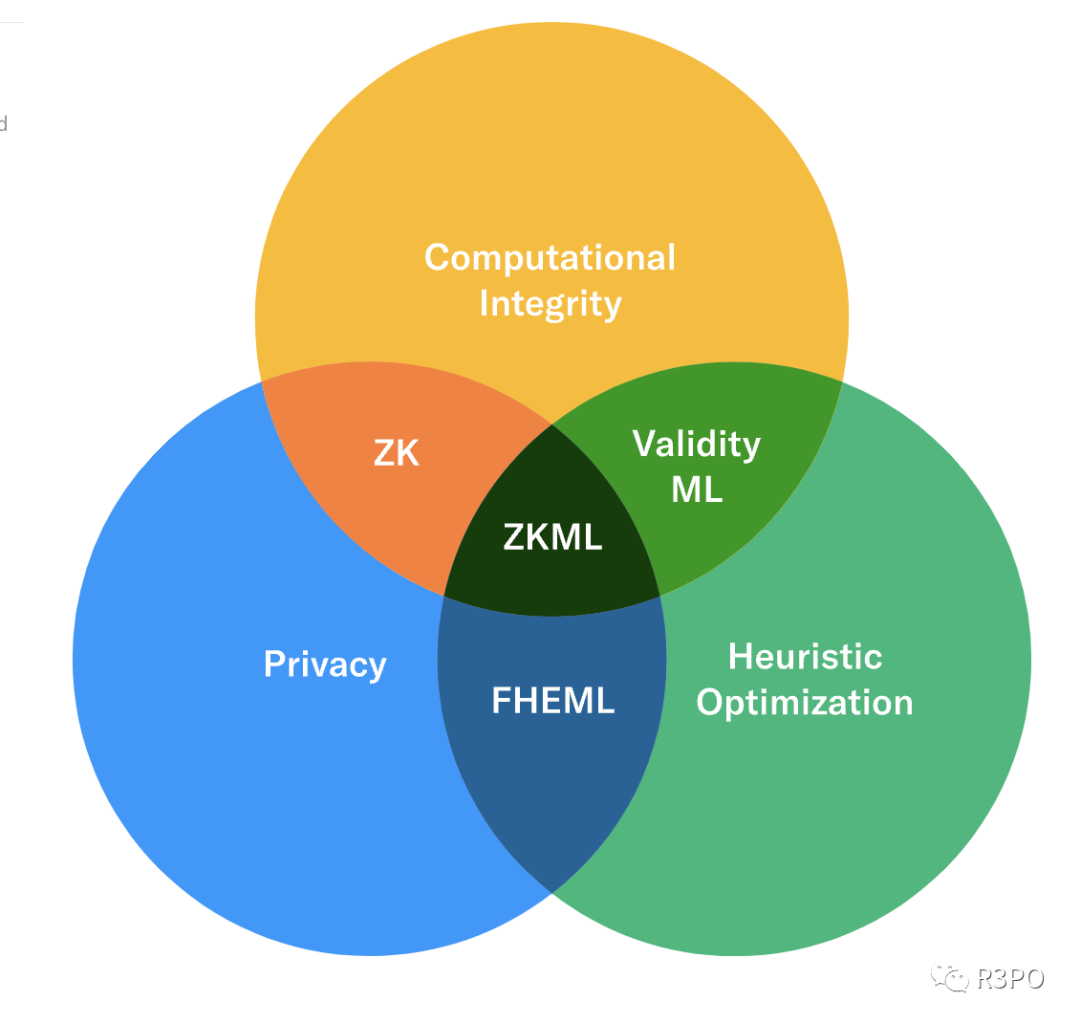
From the diagram above, we see that ZKML combines computational integrity, heuristic optimization, and privacy preservation. This technology holds broad application potential in Web3 and is developing rapidly. An increasing number of teams and individuals are entering the space, driving innovation across promising ZKML projects.
III. Analysis of ZKML Projects
Below are several promising ZKML projects.
1. Worldcoin
Worldcoin is applying ZKML to develop a privacy-preserving proof-of-personhood protocol. Users with World ID will store biometric data (such as iris scans) securely on their mobile devices, download the ML model used to generate IrisCode, and locally create zero-knowledge proofs. On-chain smart contracts can then verify that the IrisCode was correctly generated.
This capability enables useful applications such as membership verification and voting. Currently, they use trusted execution environments (TEEs) with secure enclaves to authenticate camera-signed iris scans. Their ultimate goal, however, is to employ ZKPs to prove correct neural network inference under cryptographic-grade security, ensuring that ML model outputs do not leak personal user data.
2. Modulus Labs
Modulus Labs is one of the most diversified projects in the ZKML space, actively conducting research while building on-chain AI application prototypes. Through projects like RockyBot (an on-chain trading bot) and Leela vs. the World (a chess game where players compete against a verified instance of the Leela Chess engine), they demonstrate practical use cases for zkML. The team also contributes to research, publishing works such as *The Cost of Intelligence*, which benchmarks the speed and efficiency of various verification systems across different model sizes.
3. Giza
Giza is a protocol enabling fully trustless deployment of AI models on-chain. Its tech stack includes the ONNX format for ML models, the Giza Transpiler to convert models into Cairo program format, the ONNX Cairo Runtime for verifiable and deterministic model execution, and the Giza Model smart contract for deploying and running models on-chain. Overall, Giza functions as an on-chain compiler from machine learning models to proofs, offering an alternative pathway for on-chain AI development.
4. Zkaptcha
Zkaptcha focuses on the bot problem in Web3, providing captcha services for smart contracts to protect against automated attacks. It uses zero-knowledge proofs to create Sybil-resistant smart contracts. Currently, end users generate proof-of-human-work by completing captchas, which are verified on-chain and accessible via a few lines of code in smart contracts. In the future, Zkaptcha plans to incorporate zkML to offer Web2-like captcha services, potentially analyzing behavioral patterns such as mouse movements to determine if a user is human.
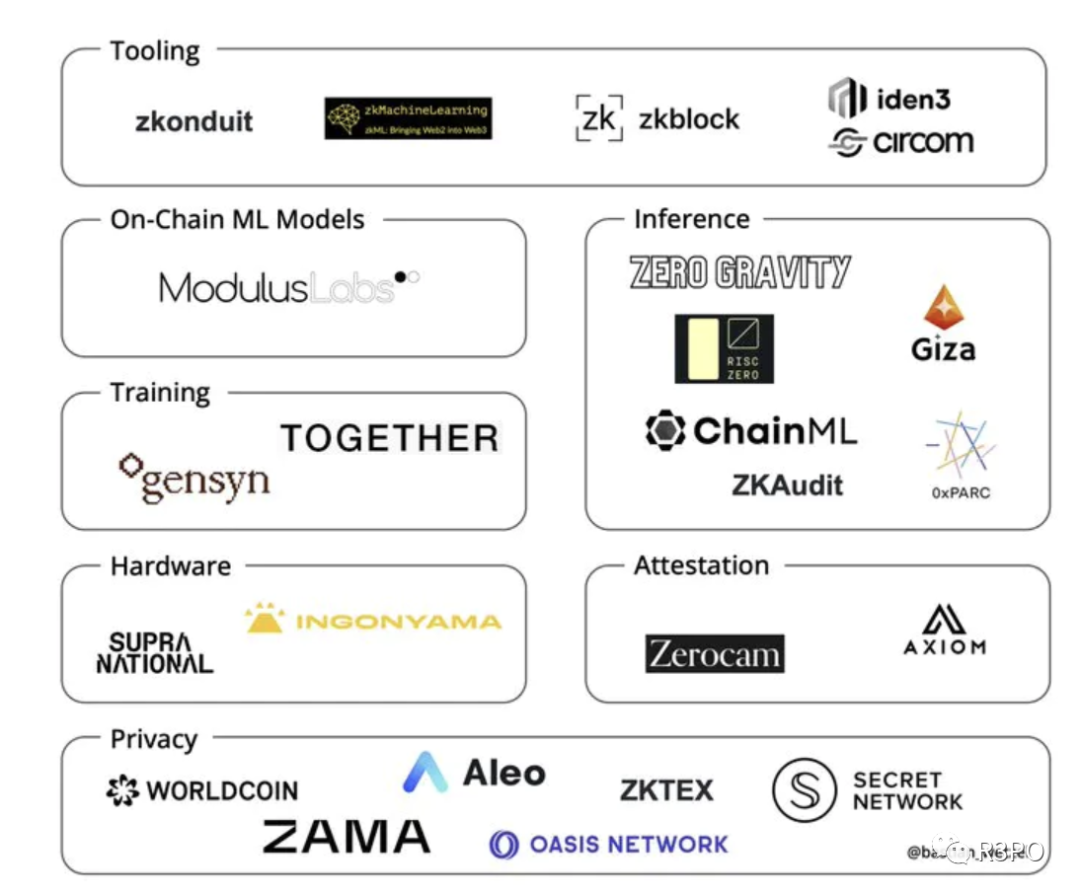
For now, the zkML field remains in its early stages. Nevertheless, there is strong reason to believe that zkML can bring brighter prospects and advancements to crypto. We look forward to seeing greater product diversity emerge in this domain. zk technology and crypto provide secure, trustworthy environments for ML operations, and beyond product innovation, they may also catalyze new crypto business models—because in this wild, decentralized world of Web3, decentralization, crypto technologies, and trust are the most fundamental infrastructure.
Conclusion
Establishing trust in an increasingly complex and uncertain digital world remains a core challenge for both AI and Web3. Yet, the integration of artificial intelligence with Web3 offers immense promise for building a trustworthy, secure, decentralized future. For developers, technologists, policymakers, and society at large, shaping the joint evolution of AI and Web3 is crucial—we may yet create an intelligent internet age beyond imagination.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News















