From mNAV Premium to Trillion-Dollar Vision: Michael Saylor's Bitcoin Credit Empire
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

From mNAV Premium to Trillion-Dollar Vision: Michael Saylor's Bitcoin Credit Empire
This experiment challenges the traditional logic of corporate valuation, and its success or failure will influence the financing paradigm and regulatory direction of the digital asset industry.
Author: Lesley, MetaEra
In the history of financial innovation on Wall Street, few have transformed personal conviction into corporate strategy—and in turn reshaped an entire industry’s funding model—like Michael Saylor. The chairman of Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) is driving an unprecedented financial experiment: replacing traditional equity and debt financing with perpetual preferred stock to continuously fund its aggressive Bitcoin accumulation strategy.
According to Bloomberg, Strategy has raised approximately $6 billion from the market this year through four rounds of perpetual preferred stock offerings, with the latest issuance—“Stretch” (STRC)—amounting to $2.5 billion. Michael Saylor described STRC as Strategy’s “iPhone moment,” emphasizing its potential to open a scalable and low-volatility capital market access channel for its Bitcoin treasury.
This once-obscure business intelligence software company has leveraged nothing more than unwavering belief in Bitcoin to mobilize massive capital leverage. As of August 18, Strategy holds 629,400 bitcoins, having invested a total of $33.139 billion, with a current market value exceeding $72 billion.
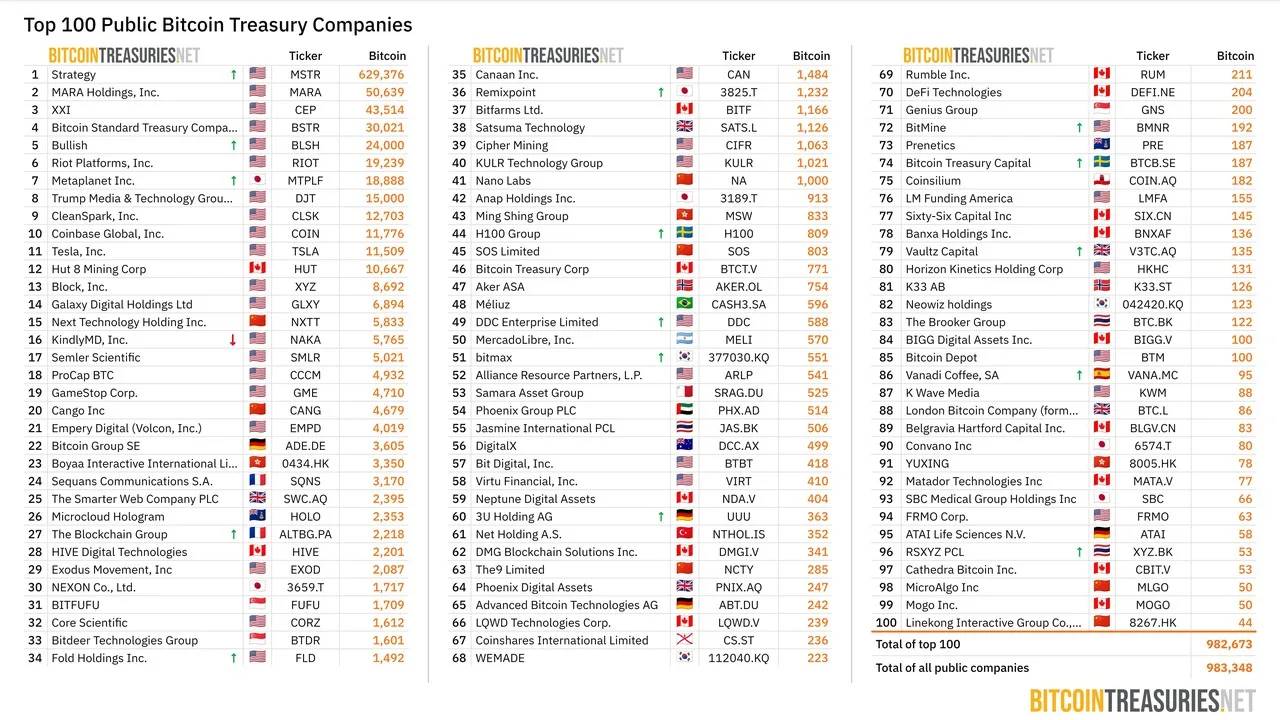
Top 100 Publicly Listed Companies Holding Bitcoin (Source: bitcointreasuries.net)
More strikingly, retail investors accounted for nearly a quarter of participation in the latest perpetual preferred stock offering—a proportion almost unimaginable in traditional corporate preferred stock markets. Behind this financial engineering stands a radical evangelist who once urged fans to “sell a kidney to buy Bitcoin,” and a legion of retail investors willing to follow his conviction.
To understand this financial experiment that could reshape the digital asset industry landscape, we must start from the beginning.
The Story and Mechanics of Perpetual Preferred Stock
Perpetual preferred stock is a hybrid financial security without a fixed maturity date, combining the income certainty of bonds with the perpetual nature of equities. Issuing companies are not required to repay principal but only pay scheduled dividends periodically, allowing them indefinite use of investor capital.
From an investor's perspective, purchasing perpetual preferred stock is akin to acquiring a "permanent income right"—returns primarily come from ongoing dividend income rather than the principal repayment typical of traditional bonds.
The table below compares perpetual preferred stock, convertible bonds, and common stock across several key dimensions:
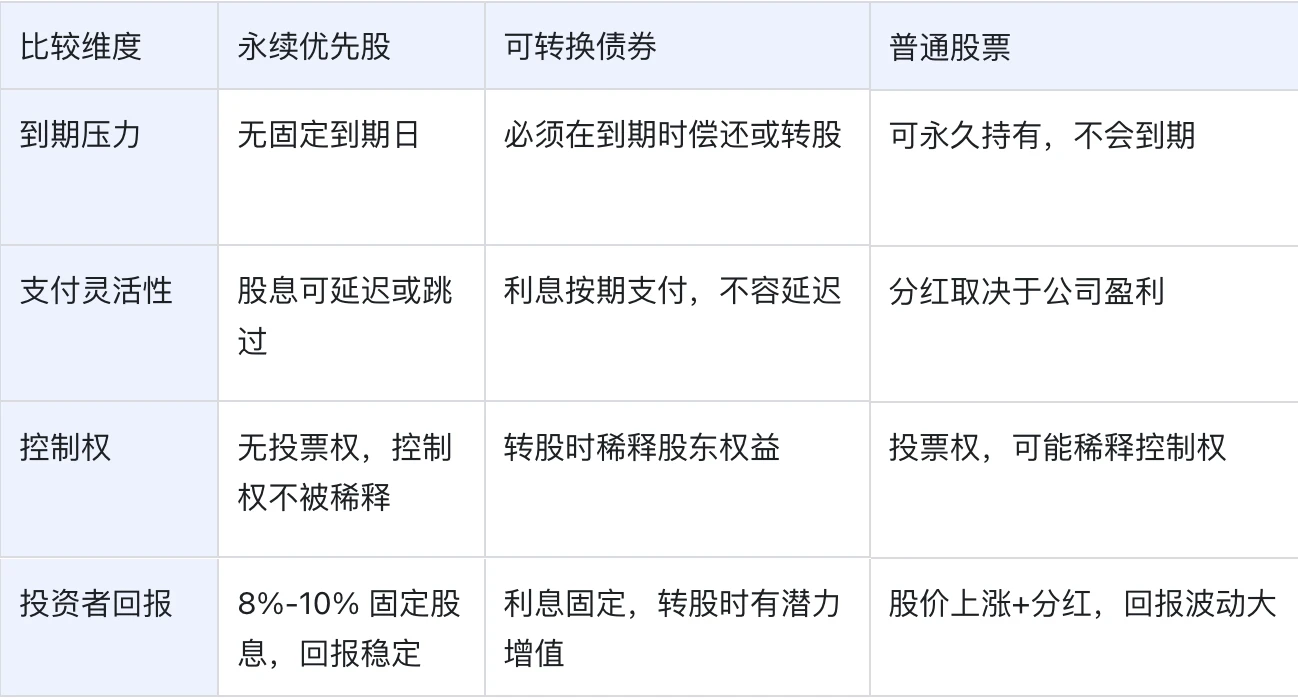
In summary, perpetual preferred stock serves as a "third type of financing instrument" between debt and equity:
-
For companies, it enables long-term capital lock-up without principal repayment, reduces cash flow pressure through flexible dividend arrangements, and avoids equity dilution caused by common stock issuance;
-
For investors, although subordinate to debt in the capital structure, perpetual preferred stock typically offers higher and more secure returns, and ranks ahead of common stock in liquidation proceeds.
Because of this, it combines flexibility on the financing side with stable returns on the investment side, becoming an increasingly important option in corporate capital operations.
While perpetual preferred stock provides Strategy with a flexible financing method, its market volatility, liquidity, and structural risks cannot be ignored.
-
Market Volatility and Liquidity Risk: Bitcoin price volatility directly affects Strategy’s ability to meet dividend obligations and refinance; increasing financing scale intensifies dividend payment burdens; and under Saylor’s “HODL” strategy, selling Bitcoin further limits the company’s access to cash flows.
-
Structural Risks of the Financing Model: Dividend payments on non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock are at the issuer’s discretion, which may lead to refinancing difficulties if market confidence wavers; overreliance on retail investors poses challenges should their enthusiasm fade, especially regarding institutional investor appeal.
-
Market Bubble and Systemic Risk: The crypto treasury company model may exhibit bubble characteristics; once market demand dries up, firms relying on such financing models may face broken funding chains, potentially triggering broader market volatility.
Since early 2024, Saylor has cumulatively raised over $40 billion via stock and bond financings. This year alone, Strategy has raised about $6 billion through four perpetual preferred stock issuances. Saylor even claims theoretically raising as much as $100–200 billion is possible. These four issuances reflect clear strategic evolution and distinct market positioning.
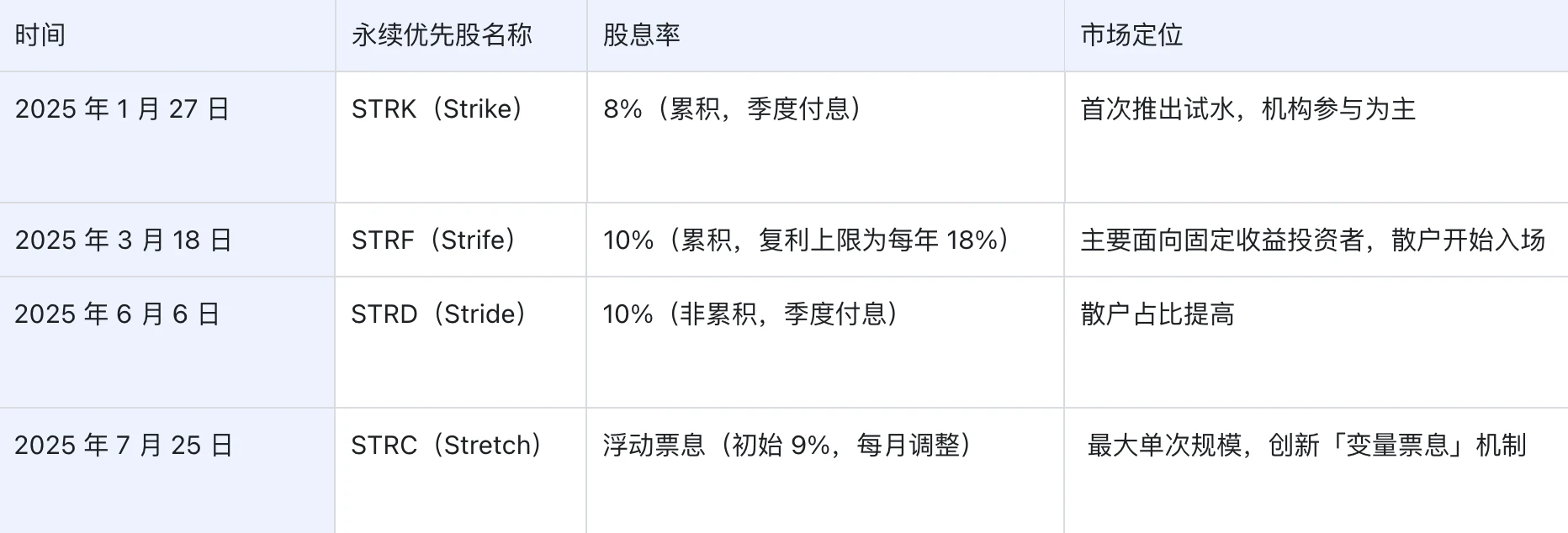
Last month, Strategy launched STRC (Stretch), a floating-rate perpetual preferred stock designed to offer stable pricing and high returns for income-seeking investors looking for indirect Bitcoin exposure. With a par value of $100 per share, STRC pays monthly dividends, starting with an annualized yield of 9%.
Saylor’s core objective in launching STRC (Stretch) is accessibility. Unlike earlier instruments he promoted—STRK, STRF, and STRD—which were seen as innovative but overly complex or volatile, STRC resembles an enhanced-yield savings account. By focusing on short-term investments and low price volatility, it eliminates risks associated with long-term fluctuations while offering higher returns than bank deposits. Backed by Bitcoin as over-collateralization, it ensures that even amid Bitcoin price swings, STRC’s trading price remains close to its $100 par value, providing investors with a more stable and attractive option.
Why Perpetual Preferred Stock? A Fundamental Shift in Business Model
As bottlenecks emerge in traditional financing models, perpetual preferred stock becomes a pivotal choice for Strategy’s fundamental business transformation amid shrinking mNAV premiums and the search for new funding sources.
1. Traditional Financing Hits a Wall: Compression of mNAV Premium
Strategy’s perpetual preferred stock experiment stems from a real-world challenge: the compression of the mNAV premium.
mNAV premium refers to the phenomenon where Strategy’s stock price trades persistently above its Bitcoin net asset value. This premium was once central to Saylor’s “financial magic”—enabling the company to raise capital at prices exceeding Bitcoin’s intrinsic value, achieving a “discount purchase” effect. However, Brian Dobson, Disruptive Technology Equity Research Analyst at Clear Street, noted: “The mNAV premium has compressed in recent weeks, and Strategy’s management is understandably concerned about creating too much dilution.”
This shift forces Strategy to seek alternative financing routes. Traditional common stock issuance becomes far less efficient when mNAV premium narrows; while convertible bond markets offer lower costs, they exclude retail investors—a critical source of capital. The emergence of perpetual preferred stock is thus a natural response under these constraints.
2. Unlocking New Capital Sources: The Retail Investor “Faith-Driven” Model
More importantly, Saylor has tapped into an unprecedented funding opportunity: converting personal influence directly into corporate capital.
Michael Saylor currently has 4.5 million X followers (Source: X platform)
Michael Youngworth, Head of Global Convertibles and Preferred Strategy at Bank of America, admitted: “To my knowledge, no company has ever harnessed retail enthusiasm like Strategy before.” In the latest STRC issuance, retail participation reached as high as 25%, nearly inconceivable in traditional corporate preferred stock markets.
These retail investors adopt a “faith-driven” investment approach toward Strategy, providing a relatively stable capital base. Compared to institutional investors, they are less sensitive to short-term market fluctuations and more willing to accept higher risk premiums. This unique investor composition has become a key competitive advantage distinguishing Strategy from traditional corporations.
3. Strategic Transformation: From Equity Financing to Hybrid Capital Structure
The introduction of perpetual preferred stock marks a fundamental shift in Strategy’s business model.
Under the old model, Strategy relied on rising stock prices to sustain fundraising capacity—an approach highly dependent on market sentiment and Bitcoin price swings. The new model creates a relatively stable “middle tier” via perpetual preferred stock: preferred shareholders receive relatively predictable dividend returns, common shareholders absorb greater volatility, and the company secures perpetually matched funding to hold Bitcoin—a perpetual asset.
This redesigned capital structure allows Strategy to better navigate market cycles. Even during Bitcoin price declines and loss of mNAV premium, the company can maintain fundraising capabilities through perpetual preferred stock.
4. Ultimate Goal: Building a Billion-Dollar BTC “Credit” Vision
Saylor’s ambition extends far beyond current achievements. He speculates that “theoretically, $100 billion…even $200 billion could be raised,” aiming to build a large-scale “credit” system backed by Bitcoin.
The core logic of this vision completely overturns traditional corporate finance: instead of relying on cash flows from products or services, it builds a self-reinforcing mechanism of “holding Bitcoin → generating stock premium → fundraising to buy more Bitcoin → forming a positive feedback loop.” Through layered financing tools like perpetual preferred stock and convertible bonds, Strategy attempts to transform volatile digital assets into stable income streams, leveraging mNAV premium to arbitrage “buying Bitcoin at a discount” and constructing a Bitcoin-centric financial empire.
Yet, this financial experiment carries significant risks. If successful, Bitcoin could transition from a speculative asset to a widely accepted financial collateral. But as short-seller Jim Chanos warns, during Bitcoin downturns, paying 8–10% perpetual dividends could become a heavy burden. Yuliya Guseva of Rutgers Law School bluntly states, “If market appetite vanishes, this model will no longer be sustainable.” Saylor is betting Strategy’s future on whether digital assets can redefine the foundational rules of modern finance.
Conclusion: Innovation or Gamble?
Strategy’s perpetual preferred stock experiment represents a major innovation in digital asset corporate financing. Michael Saylor has ingeniously combined personal influence, market sentiment, and digital asset investment through financial innovation, forging an unprecedented path for corporate development.
From a broader perspective, Strategy’s experiment signifies a fundamental reconfiguration of the relationship between enterprises and investors in the digital economy era. The traditional framework of corporate valuation—based on cash flows, profitability, and balance sheets—completely breaks down here, replaced by a new value creation mechanism rooted in asset appreciation expectations and market sentiment. This is not merely a financial innovation, but an extreme test of the boundaries of modern corporate theory.
Regardless of the final outcome, Strategy’s experiment has already provided a replicable blueprint for future digital asset companies, while sounding an alarm for regulators: when corporate financing increasingly depends on retail sentiment and asset bubbles, can traditional risk management frameworks still effectively protect investor interests? The answer to this question will determine the future trajectory of the digital asset industry.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News