In-Depth Analysis of the 7702 Phishing Attack Mechanism: How Should Wallets and Users Defend Themselves?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

In-Depth Analysis of the 7702 Phishing Attack Mechanism: How Should Wallets and Users Defend Themselves?
When signing with any wallet, carefully review the content before signing to avoid blind or mistaken approvals.
EIP-7702 grants addresses capabilities and flexibility similar to smart contracts, and an increasing number of 7702-based applications are being developed. This is crucial for bringing more people into Web3 and improving user experience.
However, the flexibility of 7702, combined with most users' lack of familiarity with it, is being exploited by fraud groups. Recently, we observed cases where users were drained by phishing group #InfernoDrainer, who leveraged MetaMask's 7702 batch execution capability to consolidate what should have been over a dozen separate authorizations into a single transaction, resulting in asset theft.
Note: MetaMask itself has no security vulnerabilities. When providing EIP-7702 functionality, MetaMask prioritizes user security and has implemented numerous protective measures. Users need to better understand the capabilities and associated risks of 7702 to prevent such security incidents from recurring.
1. MetaMask 7702 Delegator Signature Authorization Principle and Security Design
1. Technical Analysis
-
The user authorizes a deployed Delegator Contract, setting the code field of their account to point to this contract. Current official MetaMask Delegator Contract address: 0x63c0c19a282a1B52b07dD5a65b58948A07DAE32B
-
Authorization structure:
(chainId, delegatorAddress, nonce, signature)is written intoauthorization_list -
Signing method: MetaMask uses a unified signing logic at the底层 for EIP-7702-related authorization transactions—specifically the
signEIP7702Authorizationmethod. It performs ECDSA signing on the authorization datadigest7702 = keccak256(0x05 ‖ RLP(chainId, delegator, nonce)), generating a(v, r, s)signature structure appended to subsequent Type-4 transactions, enabling account authorization and upgrade. See implementation details at: https://github.com/MetaMask/eth-sig-util/blob/main/src/sign-eip7702-authorization.ts -
Verification method: The consensus layer verifies via
ecrecover(digest7702, sig) == tx.from. -
Security design: Websites cannot trick users into authorizing arbitrary Delegators because the
signEIP7702Authorizationmethod is only implemented internally within the MetaMask wallet and is not exposed to web pages viawindow.ethereum. Web-accessible signing methods likeeth_signTypedData_v4are not applicable for EIP-7702 authorization signatures, as their digest format differs:

While the signature format required by EIP-7702 is:

Since eth_signTypedData_v4 includes a fixed 0x1901 prefix and uses a completely different digest calculation process than 7702, it is virtually impossible—even with carefully crafted domainSeparator, primaryType, and message fields—to make digest712 == digest7702.
Therefore, websites cannot forge valid 7702 authorization signatures using this method. Additionally, MetaMask employs a whitelist mechanism for Delegator addresses, allowing by default—and only—the official Delegator (0x63c0...32B) and prohibiting DApps from injecting custom addresses, further preventing users from being tricked into signing malicious Delegator authorization data.
2. Usage Methods
Currently in MetaMask, upgrading an existing EOA to a 7702 Smart Account occurs in two ways: proactive upgrade and passive upgrade.
A proactive upgrade happens when the user manually clicks the "Switch" button in the wallet interface to authorize a specific Delegator Contract.
A passive upgrade occurs when interacting with certain DApps supporting 7702; MetaMask detects the action and automatically prompts the user to complete the upgrade.
2.1 Proactive Upgrade:
-
Transaction content: Only includes the action of upgrading the account, i.e., authorizing a specific Delegator Contract.
-
Upgrade process: Enter the account details page in the wallet and click the "Switch" button shown below to upgrade your Ethereum Mainnet account to a smart account. After clicking "Switch," a signature prompt appears for the upgrade transaction:
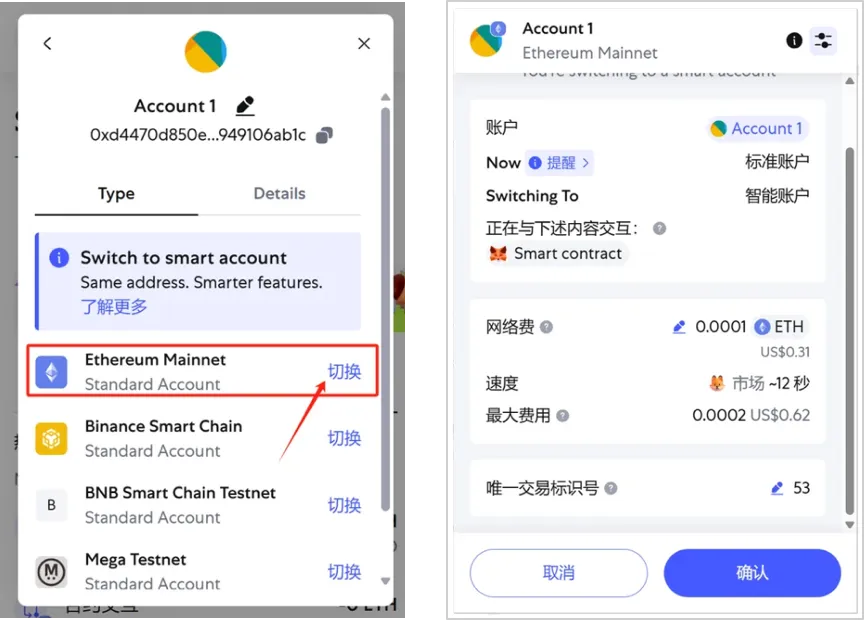
-
Authorization record: After confirmation, wait for the transaction to be confirmed on-chain. Once confirmed, the user successfully becomes a smart account. You can view the specific authorization transaction details under **
Authorizations (EIP-7702)** on the Etherscan page for the current wallet address.

2.2 Passive Upgrade
-
Transaction content: Includes both the account upgrade and batch interactions with on-chain contracts.
-
Upgrade process: When users interact with certain DApps on-chain, MetaMask may proactively suggest that the transaction can be completed via batch execution after upgrading to a smart account. For example, swapping tokens on Uniswap—clicking the "Use smart account" button upgrades the account, allowing token approval and swap to be executed in one transaction.
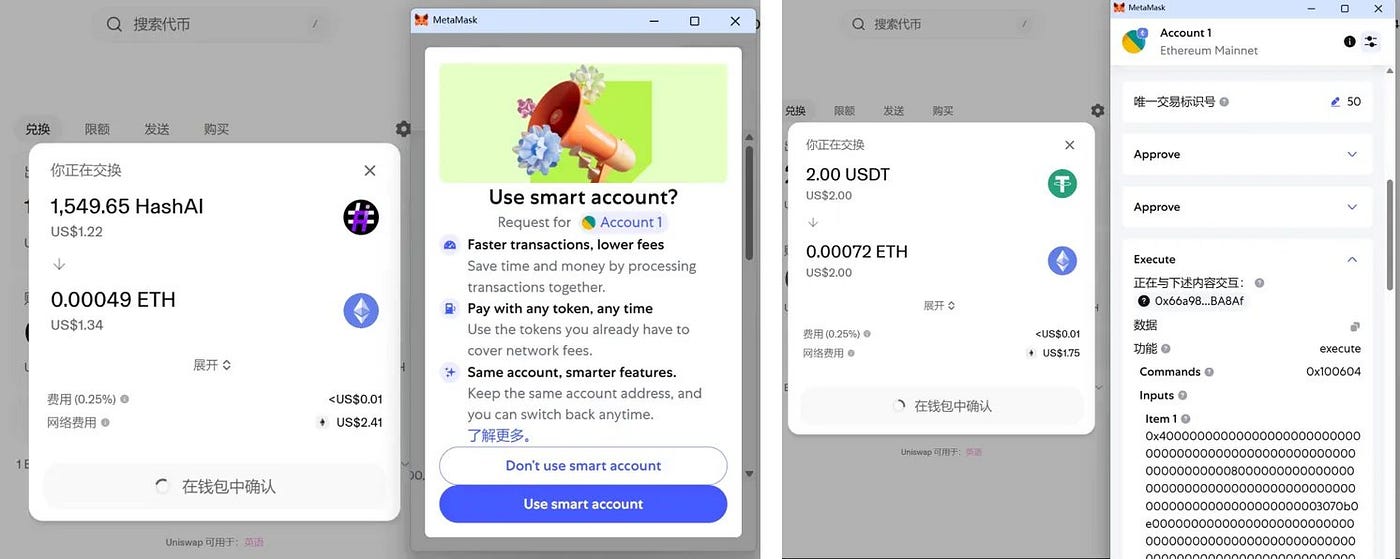
2.3 Switching Back to Regular EOA
Regardless of whether the account was upgraded proactively or passively, the bound Delegator Contract address is permanently stored on-chain as the account’s current execution logic.
If a user wishes to revert the account back to a regular EOA, they must manually initiate a "switch back to EOA" operation. This operation involves submitting address(0) as the new Delegator contract address via an EIP-7702 authorization. Once this transaction is confirmed on-chain, the account's code field will be cleared, reverting execution logic to the default empty state, effectively returning the account to a standard EOA.
Enter the account details page in the wallet and click the switch button to revert your Ethereum Mainnet account back to a regular EOA.
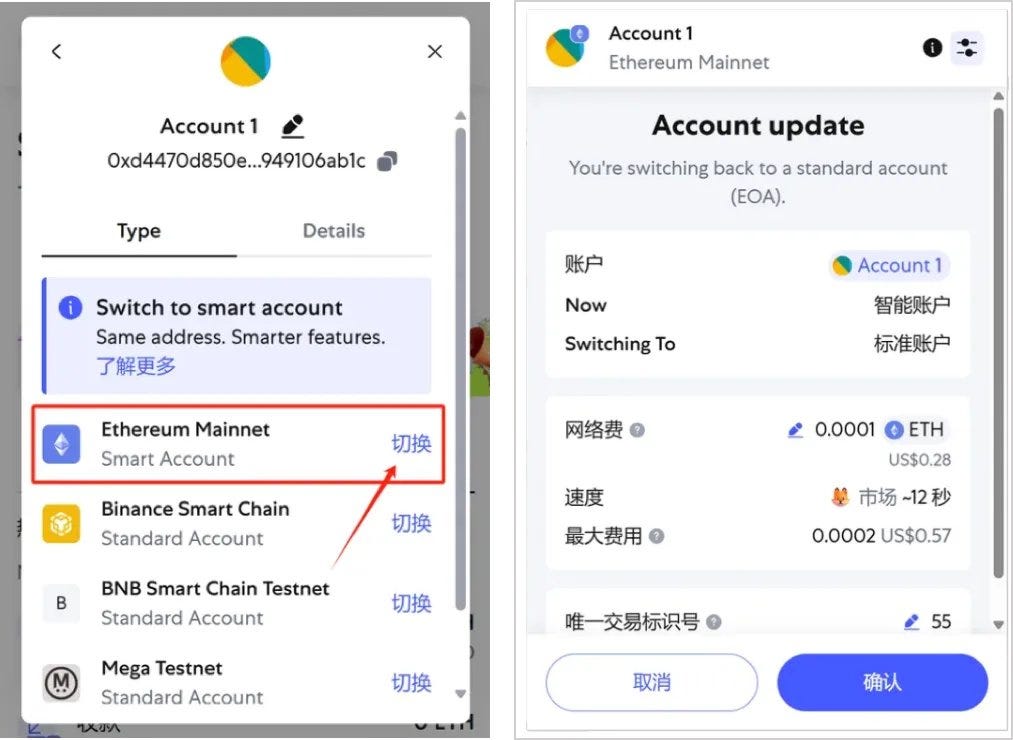
After confirming, wait for the transaction to be confirmed on-chain. Success means the user has switched back from a smart account to a regular EOA. Transaction details can also be found on the Etherscan page for the current wallet address.

2. EIP-7702 Phishing Attack Case Study
On May 24, phishing group #InfernoDrainer exploited the batch execution feature of MetaMask's 7702 Delegator contract to obtain multiple token approvals from a user (0xc6D2…06DC), executing a phishing attack resulting in losses exceeding $146,000 in $HashAI, $HUMANS, $ParallelAI, $NeuralAI, $DSync, $Zero1, $NodeAI, $Sensay, and $Virtual.
-
Fraudulent addresses
0x0000db5c8B030ae20308ac975898E09741e70000 0x00008C22F9F6f3101533f520e229BbB54Be90000 0xa85d90B8Febc092E11E75Bf8F93a7090E2ed04DE 0xC83De81A2aa92640D8d68ddf3Fc6b4B853D77359 0x33dAD2bbb03Dca73a3d92FC2413A1F8D09c34181
-
Example phishing transaction
https://etherscan.io/tx/0x09c264618e93983510aaeb7aa2c91c8254a8b2ec66167438f3f6c28b866b6eba
-
Reason for being phished
The user (0xc6D2…06DC) executed a malicious batch authorization transaction:
Ethereum Transaction Hash: 0x1ddc8cecbc... | Etherscan
Call 0xe9ae5c53 Method By 0xc6D289d5...0d2E606DC on 0xc6D289d5...0d2E606DC | Success | May-23-2025 02:31:35 PM (UTC)

-
#InfernoDrainer and #PinkDrainer are experimenting with more covert and impactful EIP-7702-based phishing operations.
According to our research, both phishing groups #InfernoDrainer and #PinkDrainer are currently researching and testing more stealthy and large-scale EIP-7702 exploitation models. Related addresses include:
Inferno Drainer:
0x0000db5c8B030ae20308ac975898E09741e70000
Pink Drainer:
0xe49e04F40C272F405eCB9a668a73EEAD4b3B5624
3. Security Recommendations
Wallet providers:
-
Follow MetaMask’s implementation and security management for 7702 Delegators—prohibit users from authorizing arbitrary Delegators and restrict such actions to in-app operations only. Warn users that any signature request initiated through a webpage is likely a phishing attempt.
-
Verify that the chain matches the current network and alert users about replay risks when signing with chainID 0.
-
Display the target contract during authorization signing, and show detailed function call contents when users perform batch executions via a Delegator, reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
Users:
-
Private key protection remains paramount. Not your keys, not your coins.
-
Never perform Delegator authorization based on standalone webpages. Secure authorizations should only occur within trusted apps like MetaMask.
-
Always carefully review the content of any signature request before approving—avoid blind signing or accidental approvals.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News