Elon Musk pushes forward with XChat—what exactly is this "Bitcoin-style" crypto architecture?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Elon Musk pushes forward with XChat—what exactly is this "Bitcoin-style" crypto architecture?
X will not only be able to post and view tweets, but may gradually gain instant messaging features similar to Telegram or WeChat in the future.
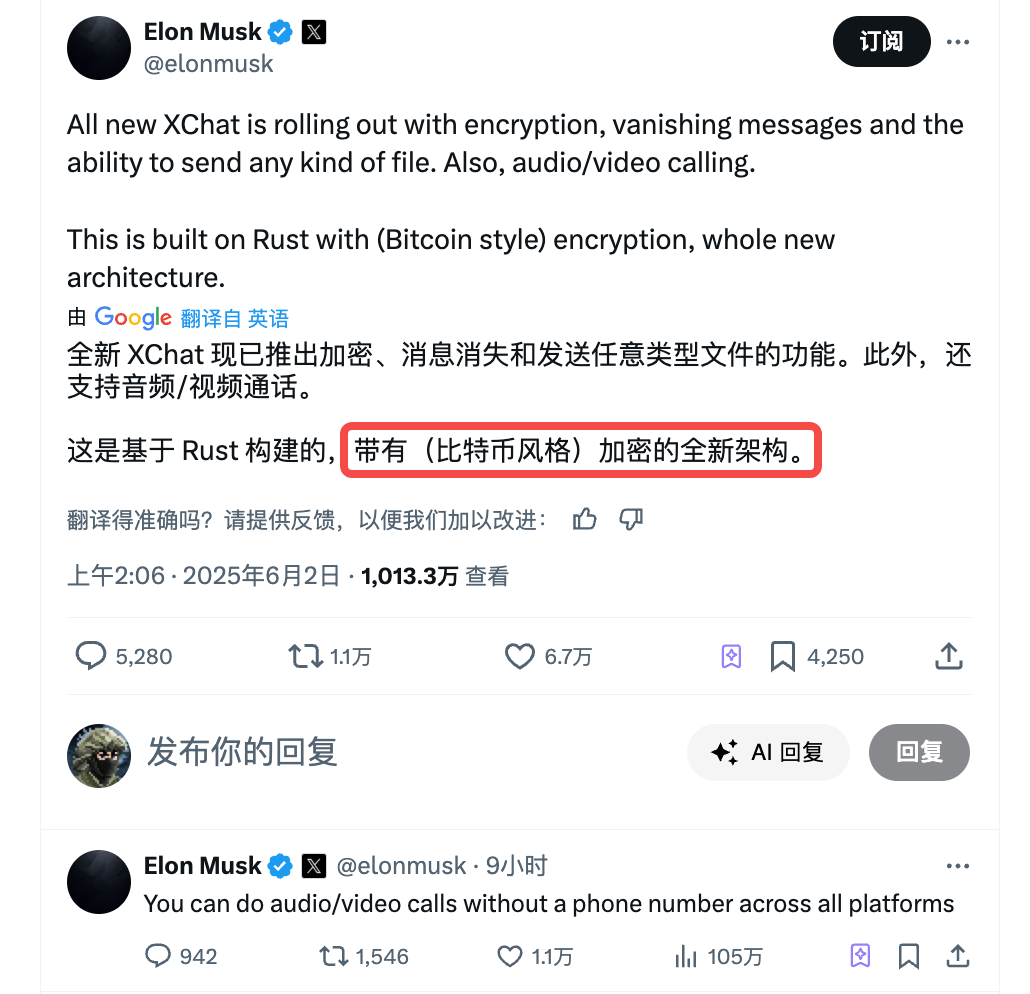
On June 1, Musk ramped up efforts by announcing that the X platform is launching a new messaging system called XChat, featuring end-to-end encryption, disappearing messages, any-file transfer, and cross-platform audio/video calling.
This means X is no longer just for posting and reading tweets—it may gradually evolve to include instant messaging capabilities similar to Telegram or WeChat.
Currently, this feature is still in testing and not all users can access it.
More eye-catching, however, is Musk’s claim that XChat uses “Bitcoin-style encryption” and is developed in Rust, touting a “completely new architecture.”
Bitcoin is so iconic that many people know its name by heart and treat it as a leading asset, even if they don’t fully understand the underlying technology.
So what exactly is this “Bitcoin-style encryption architecture” Musk refers to? I revisited the Bitcoin whitepaper and will interpret it from the perspective of an old crypto veteran.
First Look at XChat Beta Features
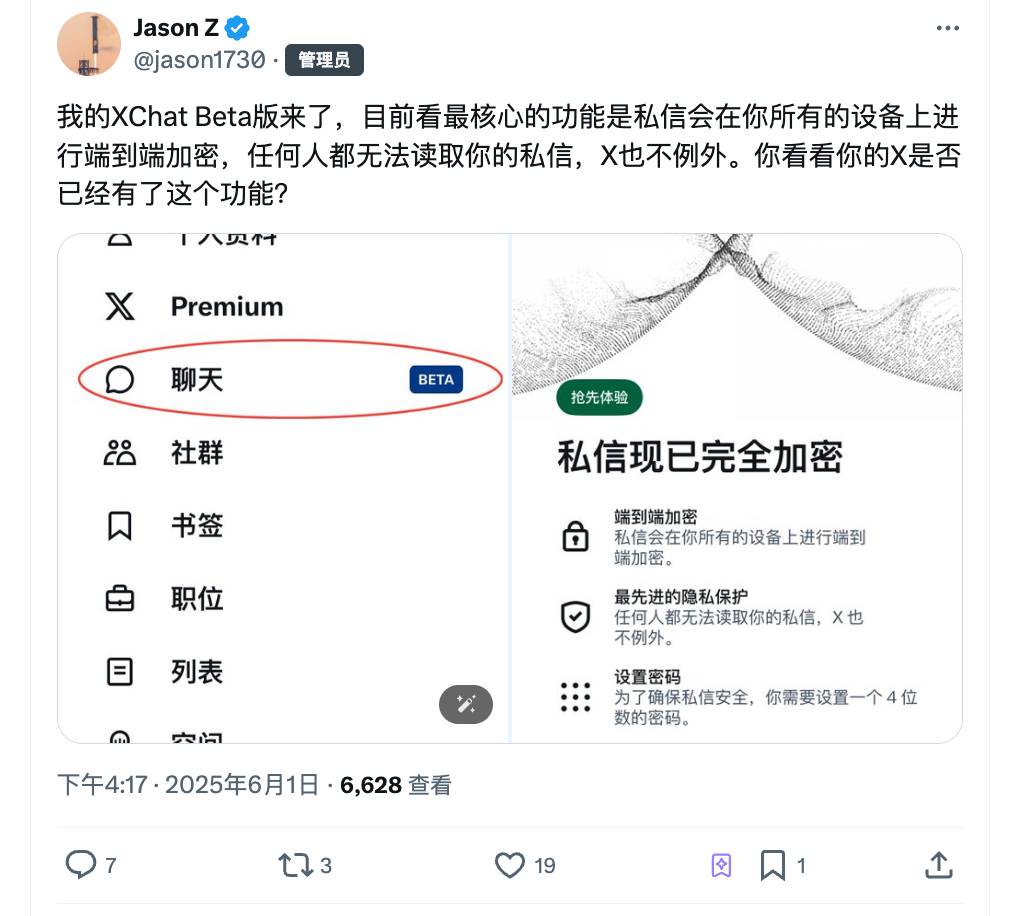
According to some user reports, their X accounts have already been pushed XChat, marked as "Beta." The core feature is that private messages are end-to-end encrypted across all your devices, meaning no one—not even X—can read your private messages.
Based on Musk's original post and user feedback, let's break down these features:
-
End-to-end encryption: Only the two parties involved can see messages and call content; third parties—including the X platform—cannot access them.
-
Disappearing messages: Messages can be set to automatically delete after a certain time (e.g., 10 minutes), offering stronger privacy protection.
-
Any-file transfer: Supports sending any file type, including photos, videos, and documents, without format or size restrictions.
-
Cross-platform audio/video calls: Calls can be made without a phone number, supported across mobile and desktop devices, with encrypted content.
You know, this actually feels a bit like Telegram.
What does this have to do with Bitcoin?
When hearing “Bitcoin-style encryption,” many people might wonder: Isn’t Bitcoin used for payments? What does it have to do with encrypted chat?
Hold on. Let’s first revisit Bitcoin’s encryption technology, then explore how XChat might borrow from it.

The title of the Bitcoin whitepaper over a decade ago was already very clear: “A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” Here, peer-to-peer (P2P) is the key.
BTC — enables P2P (me-to-you) transfers without intermediaries;
XChat — aims for P2P (me-to-you) chatting without intermediaries.
These are different applications of the same foundational concept.
How does Bitcoin achieve peer-to-peer communication?
Setting blockchain ledger technology aside, Bitcoin uses cryptographic techniques to enable P2P transfers—simply put, they’re based on “locks” and “signatures.”
-
“Lock”: Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): Bitcoin uses ECC—a highly secure digital lock. Each person has two keys: a public key (publicly shared, like a lock) and a private key (known only to you, like a key). For example, when you send Bitcoin to a friend, your wallet encrypts the transaction using their public key. Only your friend can decrypt it using their private key. No one else—including the Bitcoin network—can view or alter the transaction details.
-
“Signature”: Digital Signatures (ECDSA): In addition to “locking,” Bitcoin uses digital signatures to prove identity. When you initiate a transfer, your wallet generates a signature using your private key, proving the transaction originated from you. Others can verify this signature using your public key, but cannot forge it.
-
“Tamper-proofing”: Hash Algorithm (SHA-256): Bitcoin also uses SHA-256 hashing to turn transaction data into a fixed-length “fingerprint.” If the data changes—even by one character—the fingerprint becomes completely different, allowing the network to instantly detect tampering.
Note: These encryption and signature algorithms weren't invented by Bitcoin—they were combined in a novel way.
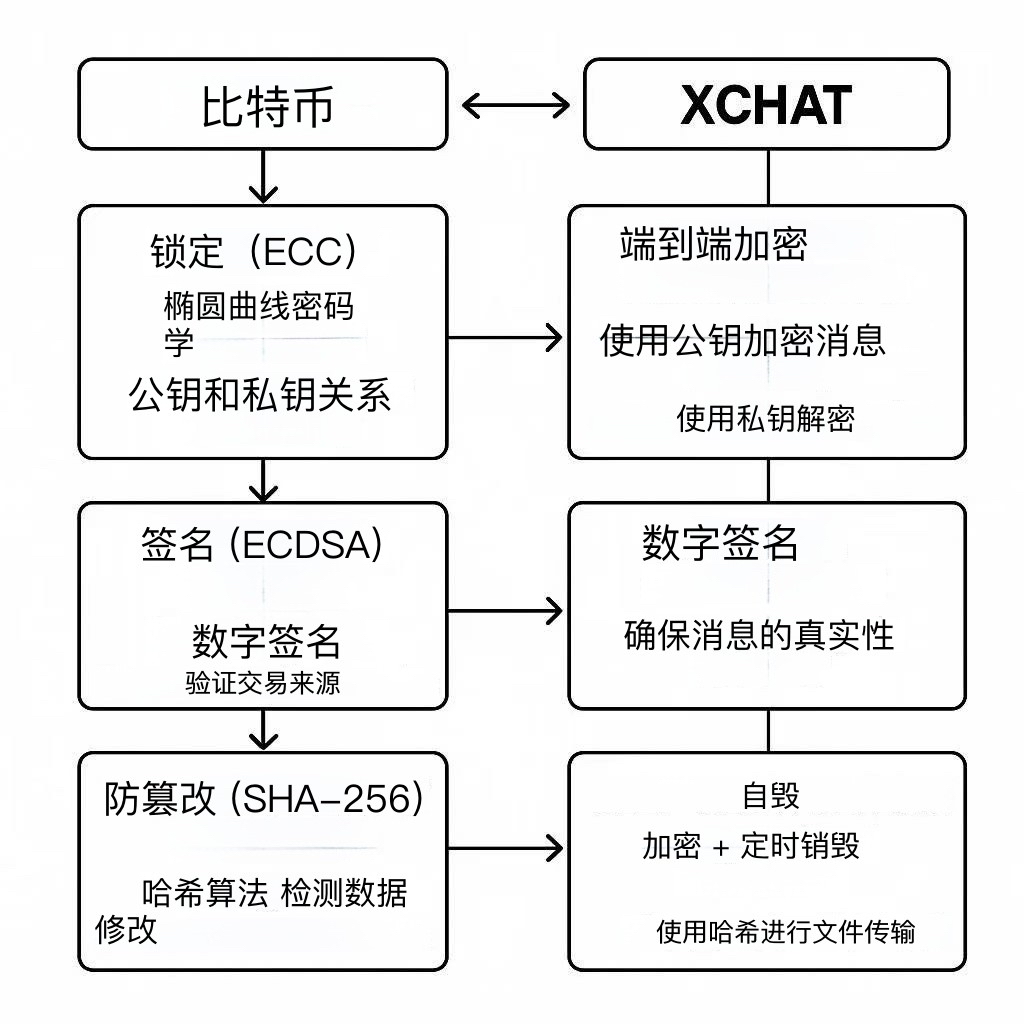
Therefore, combining XChat’s features, we can speculate how it might apply Bitcoin-like technologies—what Musk calls “Bitcoin-style encryption”:
-
End-to-end encryption: The message “safe box”: XChat may use variants of ECC (e.g., ECDH protocol). When you send a message, your device encrypts it with the recipient’s public key. Only their private key can decrypt it. Example: Sending “I’ll arrive at 7 PM” turns into unreadable ciphertext, only decipherable by the recipient’s device. Audio/video calls likely use similar methods to prevent eavesdropping.
-
Digital signatures: Proving the message is from you: XChat may use ECDSA-like digital signatures to ensure message authenticity. For instance, when you send a contract, XChat signs it with your private key. The recipient verifies it using your public key, confirming it came from you and wasn’t altered.
-
Disappearing messages: Encryption + timed deletion: This feature likely combines encryption with automatic deletion. After being read, messages are deleted from servers after a set period (e.g., 10 minutes). Even if a device is hacked, historical messages won’t be recoverable.
-
File transfer: Tamper-proof “fingerprints”: During file transfer, XChat may generate a SHA-256 hash (fingerprint) of the file. Upon receipt, the system rechecks the hash to ensure the file hasn’t been modified in transit.
As for the programming language—Rust or otherwise—I’m not technically trained, so I won’t speculate further.
More Than Just Chat
The launch of XChat isn’t just about adding a chat tool.
Musk has long wanted to turn X into an “everything app”—a super app akin to China’s WeChat.

His intentions are evident in actions such as acquiring Twitter, borrowing features from WeChat, and integrating Grok AI.
With the U.S. stablecoin bill progressing and a more crypto-friendly regulatory environment emerging, we can reasonably expect payment features like XPay to follow.
WeChat succeeded in China by leveraging social relationships and strong user stickiness, integrating chat, payments, ride-hailing, shopping, and more. If XChat integrates payments (XPay), AI assistants (Grok 3), social features (X Communities), and robust privacy protections, it could become the Western world’s “super WeChat.”
Finally, is “Bitcoin-style encryption” really that unique? Not necessarily.
Technologies like Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), digital signatures (ECDSA), and hash functions (SHA-256) are no longer exclusive to Bitcoin.
Many secure apps use similar methods: WhatsApp and Signal rely on ECC and hashing for end-to-end encryption; Apple’s iMessage adopted ECC back in the 2010s. While Bitcoin’s encryption is reliable, it’s more of an “industry standard” than something truly innovative.
Musk’s choice of the term “Bitcoin-style” is likely more about marketing. As the de facto symbol of cryptocurrency, Bitcoin brings built-in attention and trust.
Still, the more pro-crypto messaging we see, the better.
In today’s attention-economy era, future features and innovations from X and Musk are definitely worth watching.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News