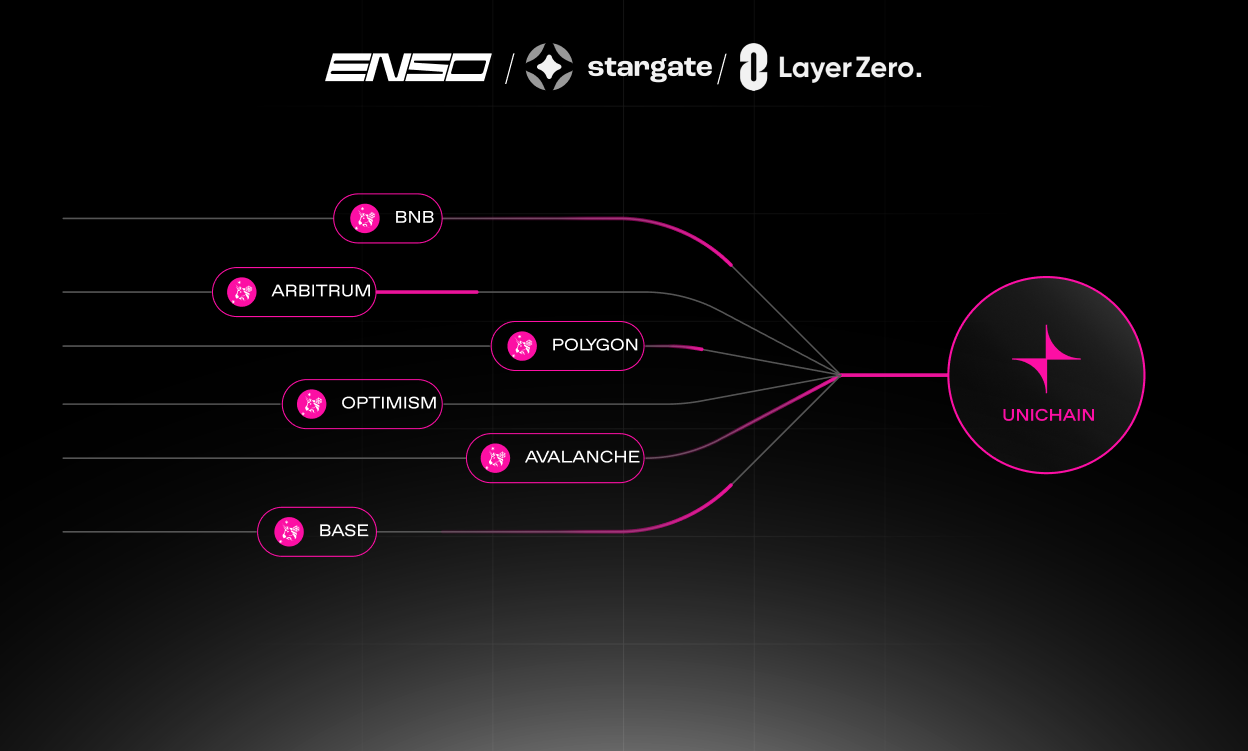
Becoming a universal gateway for on-chain interoperability: Enso builds blockchain development "shortcuts" through Shortcuts
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Becoming a universal gateway for on-chain interoperability: Enso builds blockchain development "shortcuts" through Shortcuts
With the imminent launch of the mainnet and the gradual implementation of various roadmap milestones, Enso could become one of the key driving forces on the path to mass adoption of blockchain technology.
Author: TechFlow
Blockchain is an extremely efficiency-driven market:
Public chains compete fiercely over TPS, aiming for faster transaction speeds; LST/LRT layers stack endlessly, dedicated to achieving higher capital efficiency; during meme supercycles, novel ideas emerge daily, with many projects rising and falling within just one day.
Yet this efficiency does not seem to extend to blockchain product development:
If you want to build a product on a specific blockchain, you must first undergo intensive learning of that chain—understanding its consensus mechanism, account model, gas design, programming language, testing tools, and other critical components;
If you aim to enhance your product features—for example, adding location and payment functionality to a hotel booking app—this is commonplace in Web2, where you can simply integrate mature solutions like Google Maps and Alipay. But in the blockchain world, most of the time you have to build everything from scratch;
If you wish to reach users across more ecosystems, you need to support multiple chains. However, each chain has its own rules, and the continuously lowering barrier to launching new chains floods the industry with even more options. You're forced to act like a general expanding territory, conquering each blockchain ecosystem one by one to achieve broader integration…
Each step significantly slows down development efficiency and directly impacts product functionality and user experience, as developers constantly spend 90% of their effort implementing basic functions instead of focusing on innovation.
Who will help blockchain developers trapped in the cycle of reinventing the wheel?
Dedicated to abstracting on-chain smart contract interactions and building shortcuts for blockchain development, Enso has been gaining increasing attention due to its outstanding performance in lowering developer barriers and enabling intent-based interactions. According to official data, Enso currently supports over 75 projects and has facilitated more than $16 billion in on-chain settlements.
In addition, Enso has raised a total of $9.2 million in funding, backed by prominent institutions including Polychain Capital, Multicoin Capital, Cyber Fund, Spartan, TheLAO, IDEO Ventures, Hypersphere, and Selini Capital, while also attracting over 60 industry leaders as angel investors.

Behind the dual endorsement from developers and institutions, how does Enso address the core issues of complexity, redundancy, inefficiency, and high cost in blockchain development?
From its initial API offering, to the Enso Shortcut Engine, and now the upcoming decentralized network Enso Network built on Cosmos—designed for universal participation and shared benefits—let’s explore Enso’s concrete approach to achieving chain abstraction through Shortcuts (shortcuts) and driving mass blockchain adoption.

1.5 Days vs. 7 Months: A Direct Look at Enso’s Efficiency
Leveraging Enso’s powerful advantage in eliminating complexity across multi-protocol access and execution, this astonishing comparison in development efficiency comes from a real-world partner experience:
Plug is an intent-driven automation platform for on-chain activities, aiming to build a Web3 version of Zapier, allowing users to manage, create, schedule, and execute all their on-chain actions on its platform.
Prior to partnering with Enso, OnPlug spent seven months integrating protocols—an arduous and repetitive process that consumed enormous resources. After collaborating with Enso, OnPlug rebuilt its entire integration layer and completed the equivalent of seven months of work in just 1.5 days. This leap in development efficiency allowed OnPlug to focus more deeply on automating Web3 activities, delivering significant convenience to users.
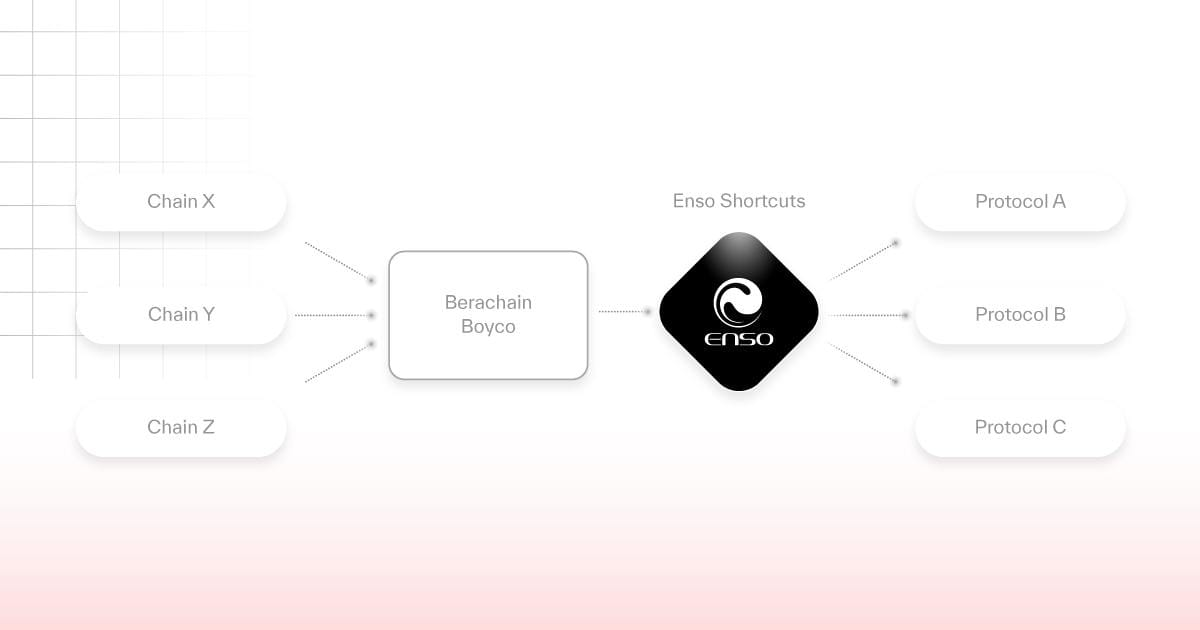
Beyond boosting development speed, Enso excels at handling complex DeFi executions on-chain. Boyco, Berachain’s pre-deposit market, sparked widespread community engagement—and Enso, as a key enabler behind Boyco, earned wide acclaim:
We know that depositing single tokens into multi-token strategies creates highly complex demands in the Boyco market. Manually integrating protocols, writing custom code for each market requirement, and conducting extensive testing and audits would be inefficient and costly.
Therefore, Berachain partnered with Enso to achieve rapid integration with all major DeFi protocols, ensuring ecosystem-wide compatibility. Users can now complete asset interactions across multiple protocols in a single transaction within the Boyco app—no more switching between platforms or searching for optimal asset paths—delivering a seamless user experience and laying a solid foundation for Berachain’s mainnet launch.
At the time of writing, Boyco’s TVL has surpassed $3.1 billion, powered by Enso Shortcuts.
In addition, the automated crypto trading market Glider uses Enso to deliver powerful portfolio automation features to users; Enso launched on ZKsync to help developers build faster and more efficiently; multichain liquidity restaking protocol Bedrock partnered with Enso to offer users one-click swapping and depositing assets into uniBTC Berachain vaults, among other features.
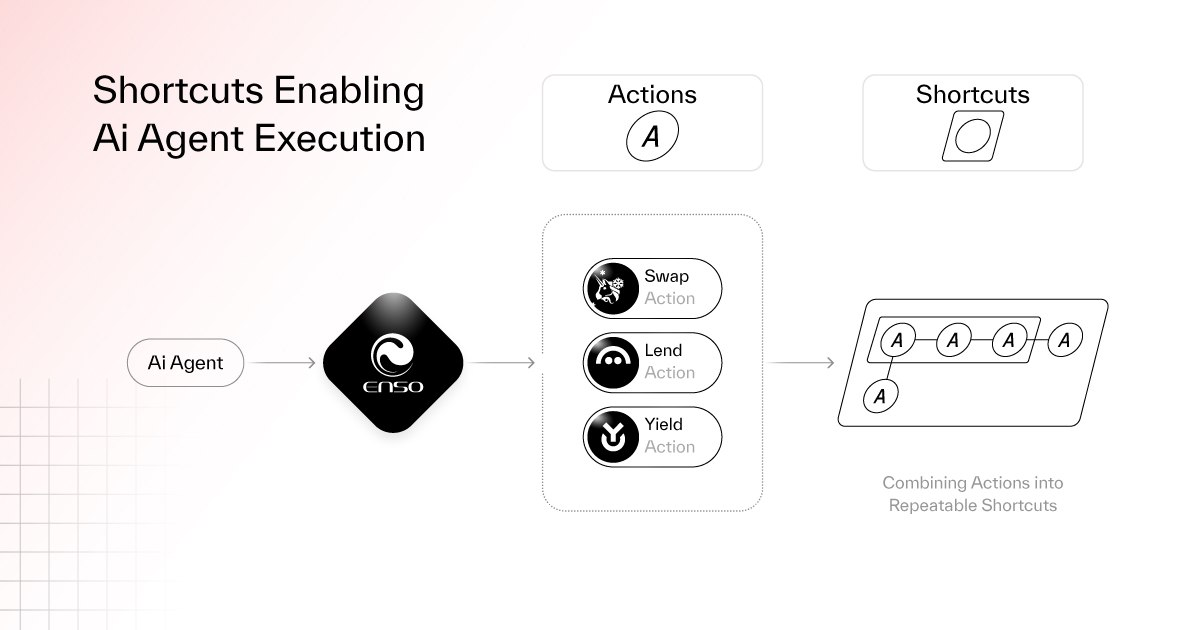
Beyond DeFi, Enso’s integration with AI is equally impressive:
As AI agent trends continue and the DeFAI narrative gains momentum, DeFi—the backbone of the crypto world—is widely seen as having great potential when combined with AI to simplify complex DeFi operations.
While AI agents evolve toward greater intelligence, Enso aims to help them overcome the complexities of interacting with multiple protocols, bundling transactions, and managing operations—empowering them with stronger execution capabilities:
BrianknowsAI integrated with Enso, allowing it to focus on refining its intent recognition engine without worrying about integrating with numerous blockchain protocols;
Velvet Unicorn, an autonomous hedge fund manager, leveraged its collaboration with Enso to rapidly build advanced features such as neural routing and multi-step yield strategies;
Hey anon, a DeFi-focused AI agent, uses Enso to interact with over 180+ on-chain protocols…
The list goes on.
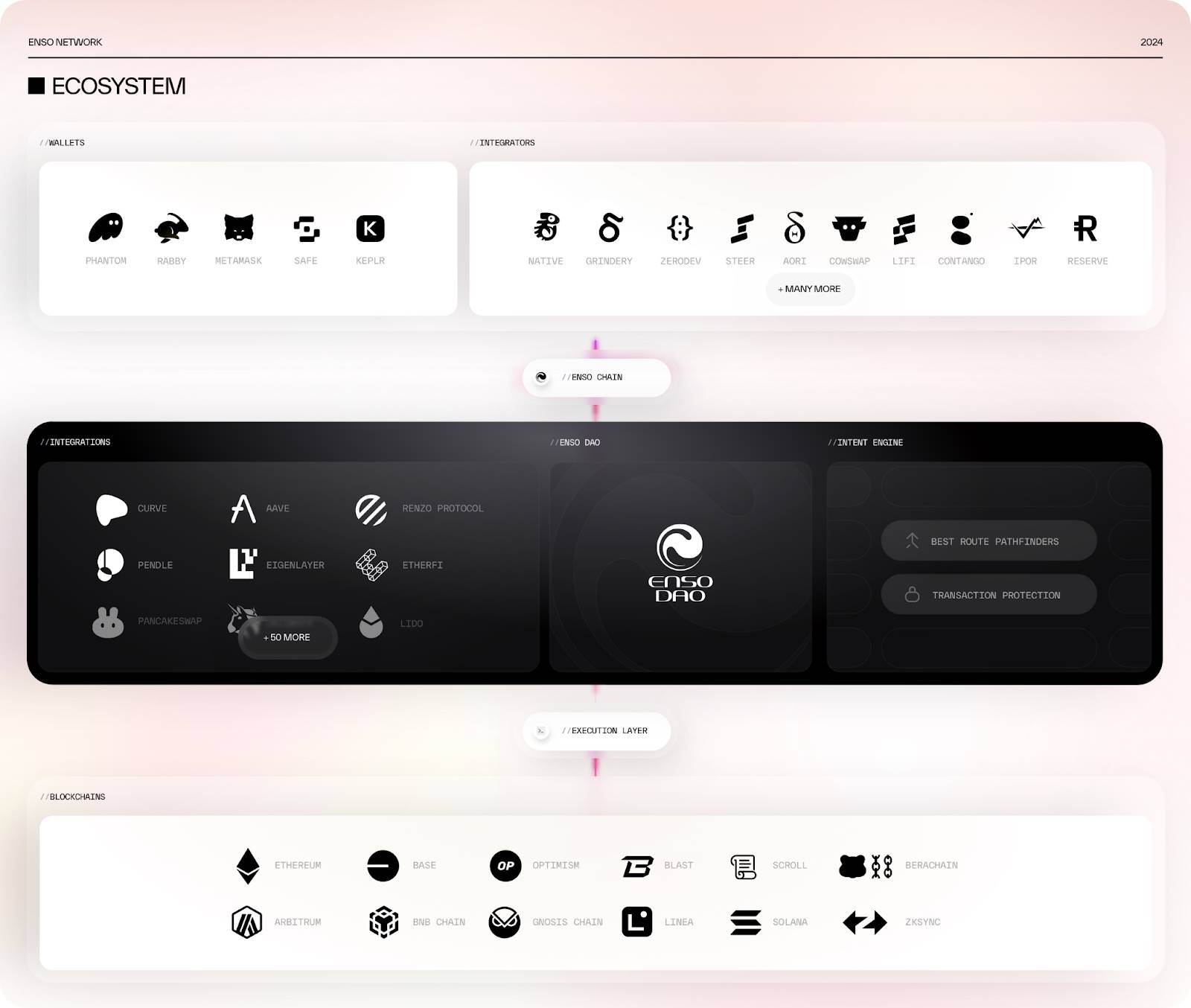
Currently, Enso has integrated over 180 protocols, with more than 60 apps actively using Enso to leverage these integrations—and the Enso ecosystem continues to expand rapidly.
Behind these success stories, many wonder:
How does Enso—the secret weapon behind numerous projects’ streamlined development, enhanced efficiency, and seamless user experiences—make it all possible?
From API to Intent Engine to Shortcuts: Tracing Enso’s Product Evolution
As the saying goes, practice reveals truth.
Enso did not start out with a clear strategy centered on Shortcuts. Through early product iterations and long-term observation of crypto market needs, Enso gradually clarified its approach to improving blockchain development efficiency.
Starting in DeFi, Enso previously launched a social trading platform where anyone could create social investment strategies and monetize their DeFi and ERC20 token portfolios. However, integrating additional DeFi protocols took considerable time and cost over $500,000 in audit fees for just 15 protocols.
This experience led Enso to realize that rather than specific DeFi products, the market needed services that solve fundamental development challenges. The team rethought its product design, rebuilt its underlying logic, and launched a suite of APIs—including Route API, Bundle API, and Metadata API—to provide tools for executing and retrieving all relevant metadata from DeFi protocols. These covered key functionalities such as executing multiple transactions atomically, bundling DeFi operations into custom workflows, finding optimal routes based on desired paths, and accessing all DeFi-related metadata. Developers could now embed on-chain operations into their products with simple API calls, significantly accelerating next-generation DeFi development.
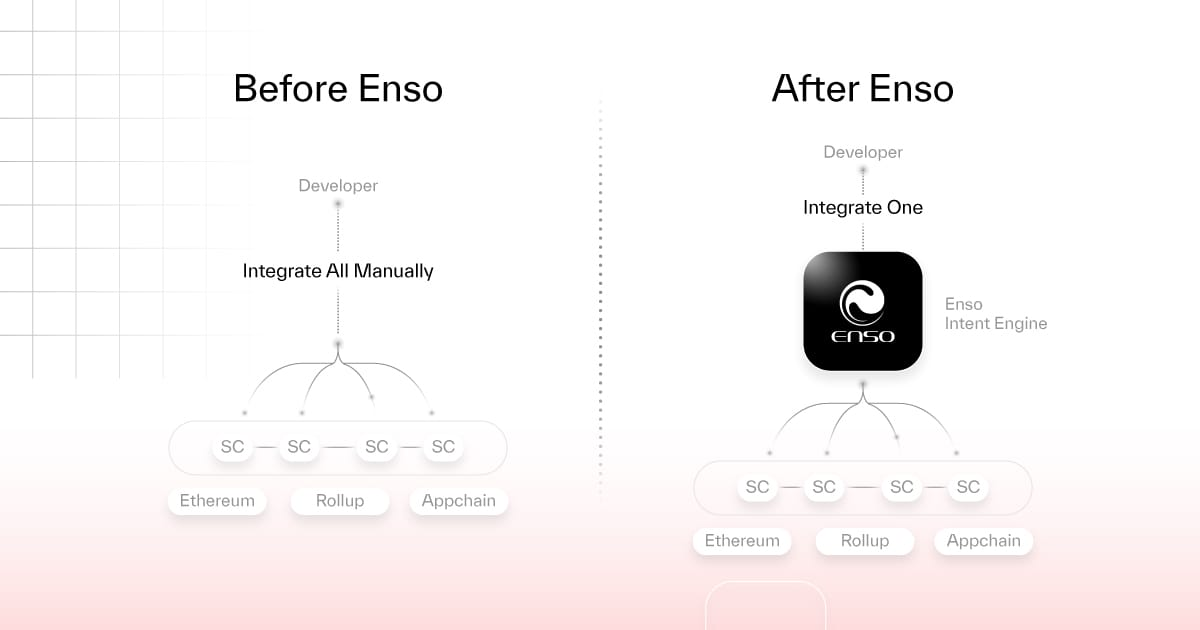
After the success of its APIs, Enso dug deeper into lowering development barriers: How could it further enable developers to easily build products that interact with any smart contract on any blockchain framework?
To address this, in June 2024, Enso launched the Intent Engine.
As a fully decentralized shared network state, the Enso Intent Engine simplifies smart contract interactions on blockchains and enables tradable data construction across various blockchain frameworks—achieved by mapping all smart contract interactions within blockchain frameworks.
Simplifying the analogy: if the blockchain industry were Earth, each blockchain would be a country, and each application within a blockchain would be a city. Cities contain facilities like schools, malls, and parks, just as applications contain operations like lending, borrowing, swapping, transferring, approving, and depositing.
Previously, countries had no interaction—blockchain data wasn’t shared. To integrate a chain or smart contract, you had to learn and adapt to that country’s and city’s rules.
Enso aims to draw a global map, documenting the rules of every country and city (i.e., every blockchain and smart contract), presenting them in standardized formats for data, transactions, and execution. This way, developers can easily integrate via Enso’s standardized layer.
Thus, at Enso, developers only need to express their intent—the complex blockchain interactions are handled automatically. And intent requests don’t have to target a single use case—they can include multiple types of smart contract interactions across different blockchain frameworks.
For example, just as you could collect all “parks” globally using the “park” tag on a world map, you could use the “Lend” operation type to aggregate data and analysis across all lending protocols.
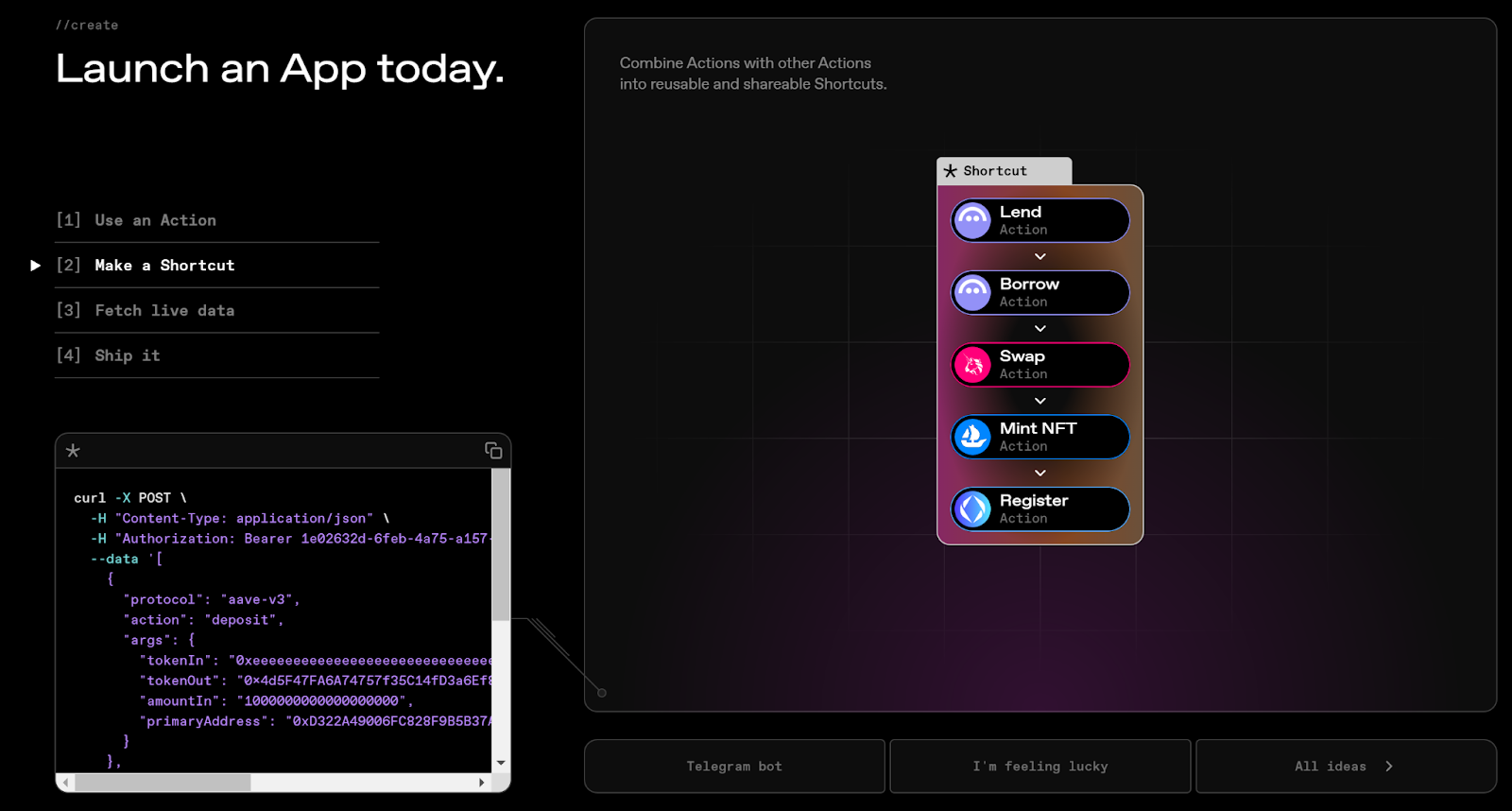
Building upon this shared map concept of the Enso Intent Engine, combining different operation types on demand gives rise to a series of Shortcuts that dramatically boost blockchain development efficiency—transforming complex on-chain operations into simple, verified, reusable building blocks.
In short, standardized operation types are like Lego bricks. Developers can assemble them into desired shapes—just as pre-built Lego components like doors, windows, and walls can be used to easily construct schools, hospitals, or malls.
Similarly, developers can combine different operation types into Shortcuts for DeFi routing, asset management, automated execution, etc., and integrate these Shortcuts into various product features.
Does this sound incredibly simple and efficient?
Currently, Enso offers Shortcuts including:
-
Token swaps and DeFi routing
-
Asset management
-
Financial tools and automation
-
DeFi protocol integration
-
Smart contract interaction
-
Complex transaction bundling
Meanwhile, more Shortcuts are in development. Projects including Berachain, ZKsync, and Bedrock have drastically reduced integration and maintenance time and costs through Enso, collectively achieving over $16 billion in on-chain settlements—bringing greater liquidity aggregation, innovative features, and high-quality user experiences to the blockchain ecosystem.
Behind this elegant product design is an elite team with a decade of blockchain experience steering the project.
Connor Howe, Enso’s CEO and co-founder, has worked full-time in blockchain since 2016 and authored one of the earliest Ethereum research papers in the UK. Before founding Enso, Connor served at Sygnum, Switzerland’s fully licensed digital asset bank, where he established the blockchain division and developed products including a fully collateralized stablecoin, tokenization suite, and multisig solutions, managing over $5 billion in assets using raw HSM technology.
Peter Phillips, the other co-founder and Enso’s CTO, has also worked full-time in blockchain since 2016. Prior to joining Enso, Peter worked at a blockchain development firm serving clients like DuckDuckGo and Mozilla, and previously developed Aragon through Autark—giving him deep expertise in blockchain development.
Milos Costantini, Enso’s core developer and co-founder, built validator infrastructure for Swisscom Blockchain—the largest telecom company in Switzerland—before joining Enso, and played a key role in developing Enso’s network architecture.
It's worth noting that many community members may already have observed that the Enso Intent Engine currently operates in a centralized manner. However, Enso’s core vision is decentralization—aiming to build an organic ecosystem where everyone can contribute and benefit.
With the upcoming launch of Enso Network, the final piece of decentralization falls into place, accelerating the realization of Enso’s decentralized network vision.
Next Stop: Enso Network – Moving Toward Full Decentralization
As an independent L1 Tendermint blockchain, Enso Network is driven collectively by participants, offering efficient execution and broad integration. We know that "achieving intent via Shortcuts" is Enso’s core concept, and intent fulfillment involves three key steps:
-
Intent expression: Users specify their desired outcome within an application.
-
Intent execution: Solvers compete in auctions to determine the optimal solution for fulfilling the user’s intent.
-
Intent settlement: Solvers are rewarded for providing optimal solutions.
Enso Network achieves a closed-loop decentralized logic by introducing four key roles.
Consumers are the demand initiators—they state their desired outcomes and pay fees to submit requests to the Enso Network.
Action providers are developers who publish abstracted smart contracts on-chain. The network rewards developers who become Action providers based on the proportion of solutions generated using their abstractions.
Graphers are those who generate solutions based on Consumer demands. Whenever a new request arises, Graphers traverse all contributed abstractions in the Enso Network and combine them in optimal sequences to produce executable bytecode. As proposers of optimal solutions, Graphers receive rewards.
Finally, Validators are responsible for maintaining network security. They monitor and broadcast valid consumer requests, verify the smart contract abstractions submitted by Action providers (only verified abstractions can be used by Graphers), and determine the best solution from Graphers before feeding it back for execution by Consumers.
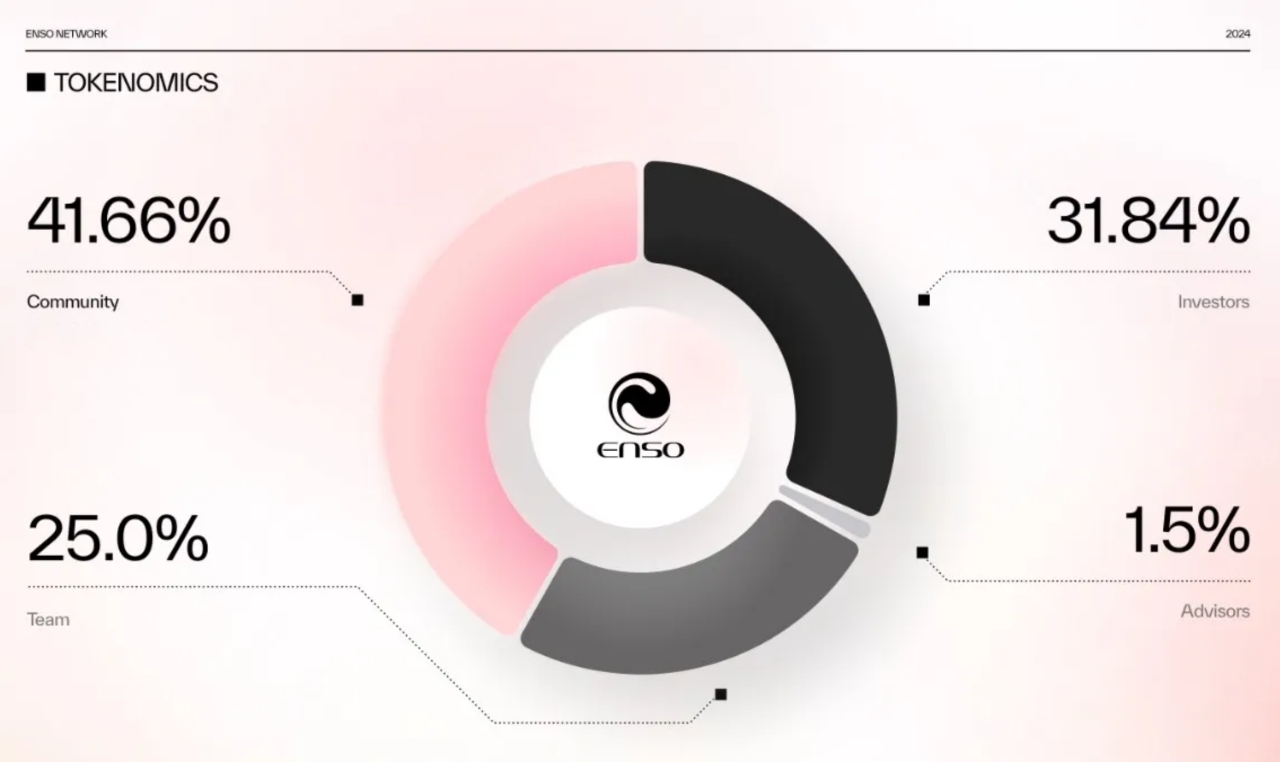
We know that economic model design is crucial for stable and healthy ecosystem operation. Enso Network uses its native token $ENSO to incentivize participation and deter malicious behavior.
As a key component of the Enso ecosystem, $ENSO has a total supply of 100 million and serves the following core functions:
-
Gas: Pays for fees required to initiate requests and modify states on the Enso Network;
-
Governance: Enables voting on protocol upgrades;
-
Staking: Action providers, Graphers, and Validators must stake a certain amount of tokens to participate in network contributions. Malicious actors will have their staked $ENSO slashed. Token holders can also delegate stakes to network participants to further secure the network.
With this structure, Enso’s positive feedback loop—where everyone can participate, contribute, and benefit—becomes clearly visible.
Conclusion
Certainly, while Enso APIs are already mature and widely integrated into dozens of well-known projects, Enso Network remains in relatively early stages.
According to its whitepaper, the Enso Network rollout will occur in two phases:
In Phase One, the centralized Enso service will coexist with the decentralized network. Developers interested in becoming Action providers can contribute to Enso’s centralized hosted service, while independent Validators will simulate bytecode solutions.
In Phase Two, Enso Network will gradually evolve into a fully sustainable ecosystem, offering completely permissionless participation for key contributors like Action providers and Graphers. Additionally, Enso Network will expand beyond supporting only the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to include the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) and Move Virtual Machine (MVM), further enhancing the developer experience across multichain ecosystems.
According to the official roadmap, Enso Network is currently in testnet phase and is expected to officially launch in 2025.
Notably, although Enso has achieved remarkable results in areas like DeFi and AI, fundamentally, any application seeking optimal solutions for interacting with smart contracts across blockchains can leverage Enso Network.
In other words, Enso Network can support any type of project—not merely improving development efficiency and service quality for DeFi and similar applications, but potentially becoming a universal gateway for all smart contract interactions across all blockchains. As the trend toward a multichain future becomes increasingly clear, Enso may serve as a vital pathway for developers to build truly scalable, mass-market killer applications.
At a time when public chains are multiplying, DeFi interactions are growing more complex, and cross-chain demands are surging, Enso’s focus on boosting development efficiency and becoming a universal gateway for all on-chain smart contract interactions is undoubtedly compelling. Its evolution—from API to Intent Engine to Enso Network—also reflects a consistent commitment to refinement and deep exploration.
With mainnet launch approaching and milestones steadily progressing, Enso may well become one of the key drivers on the path to mass blockchain adoption.
Enso Website: https://www.enso.build/
Enso X/Twitter: https://x.com/EnsoBuild
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News