A Guide to the Landscape of Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) Projects
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

A Guide to the Landscape of Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) Projects
FHE can prevent machines from learning any sensitive information while processing it, providing confidentiality for data, models, and outputs throughout the process.
Author: Poopman
Translation: TechFlow
FHE opens up the possibility of computing on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it.
When combined with blockchains, MPC, and ZKPs (for scalability), FHE provides essential confidentiality and enables various on-chain use cases.
Overview of the Current State of FHE
In this thread, I will cover:
-
Background of FHE
-
How does FHE work?
-
5 domains of the FHE ecosystem
-
Current challenges facing FHE and potential solutions
Enough talk—let’s dive in.
Background of FHE
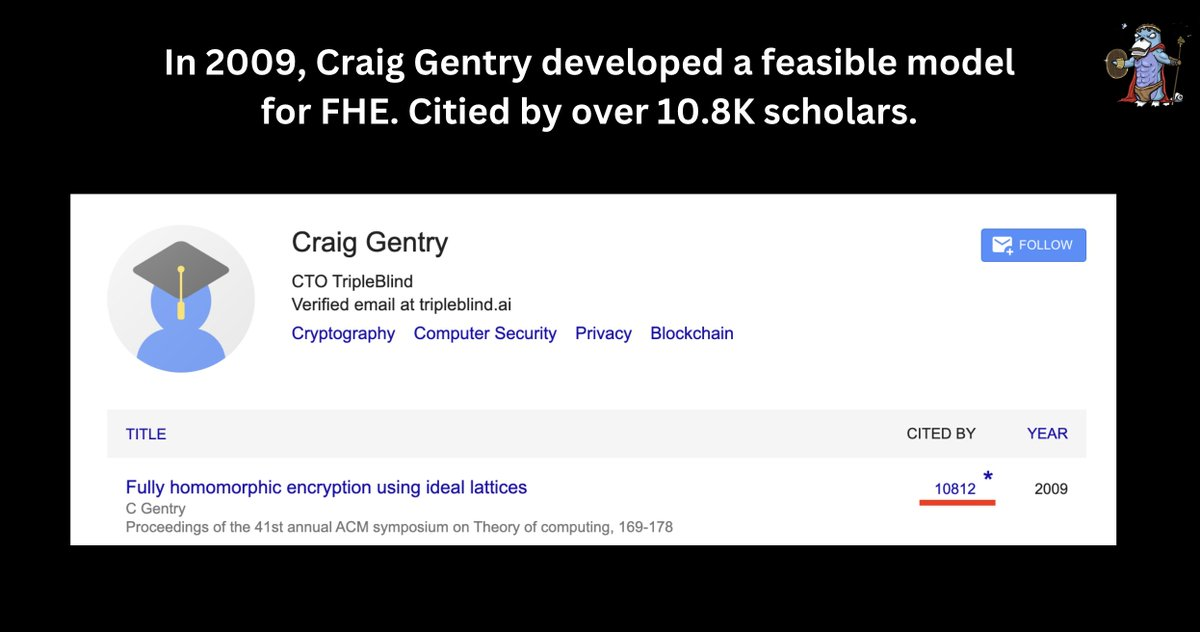
FHE was first proposed in 1978, but due to its computational complexity, it remained impractical and highly theoretical for a long time.
It wasn’t until 2009 that Craig developed a viable model for FHE, sparking renewed research interest in the field.
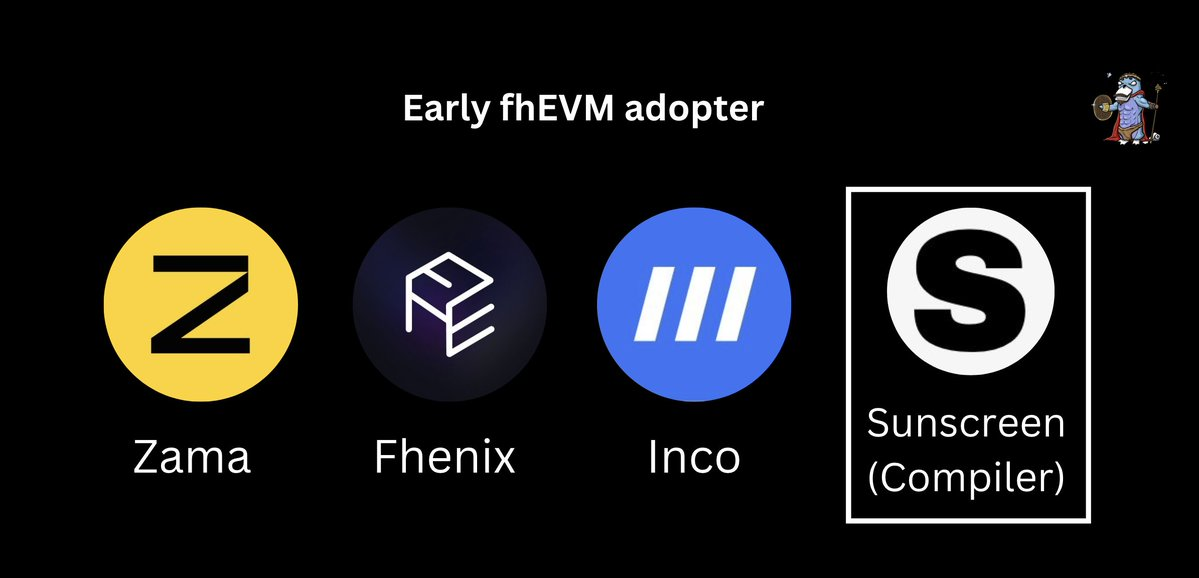
In 2020, the launch of TFHE and fhEVM by @zama_fhe brought FHE into the spotlight within the crypto space. Since then, we’ve seen the emergence of general-purpose EVM-compatible FHE L1/L2 blockchains such as @FhenixIO and @inconetwork, along with FHE compilers like @SunscreenTech.
How Does FHE Work?
Imagine a blind box containing a puzzle. The box cannot learn anything about the puzzle you put in, yet it can still perform mathematical computations and return results.
For more details, check out my overly simplified explanation of FHE.

Some FHE use cases include:
-
Private on-chain computation
-
On-chain data encryption
-
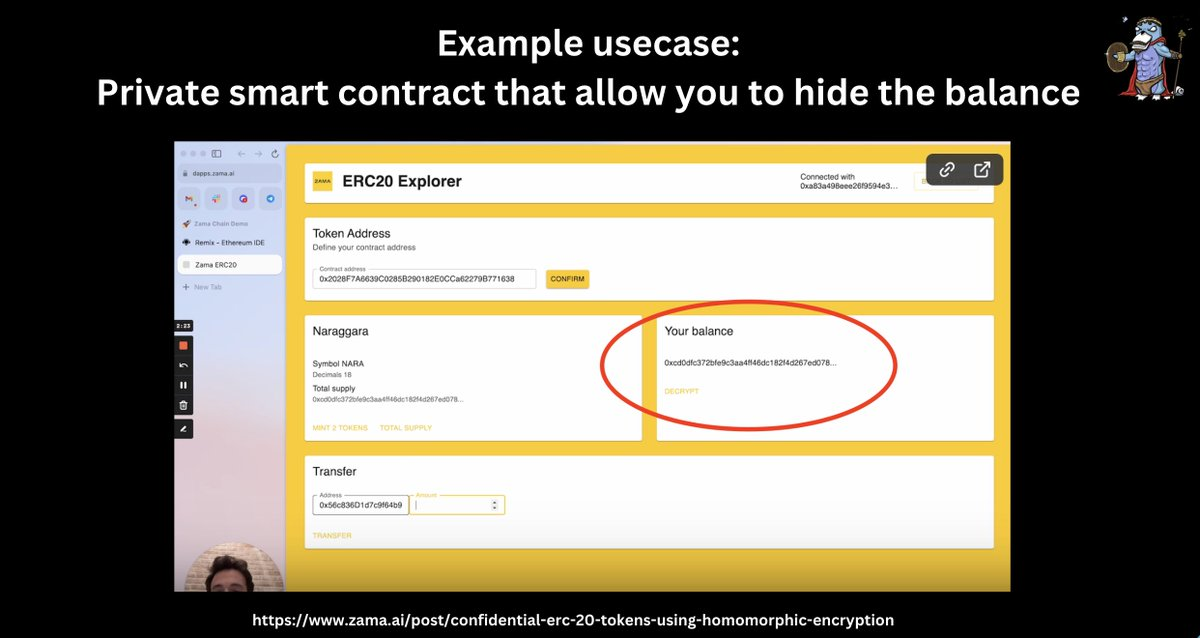
Private smart contracts on public networks
-
Encrypted ERC20 tokens
-
Private voting
-
NFT blind auctions
-
More secure MPC
-
Front-running protection
-
Trustless cross-chain bridges
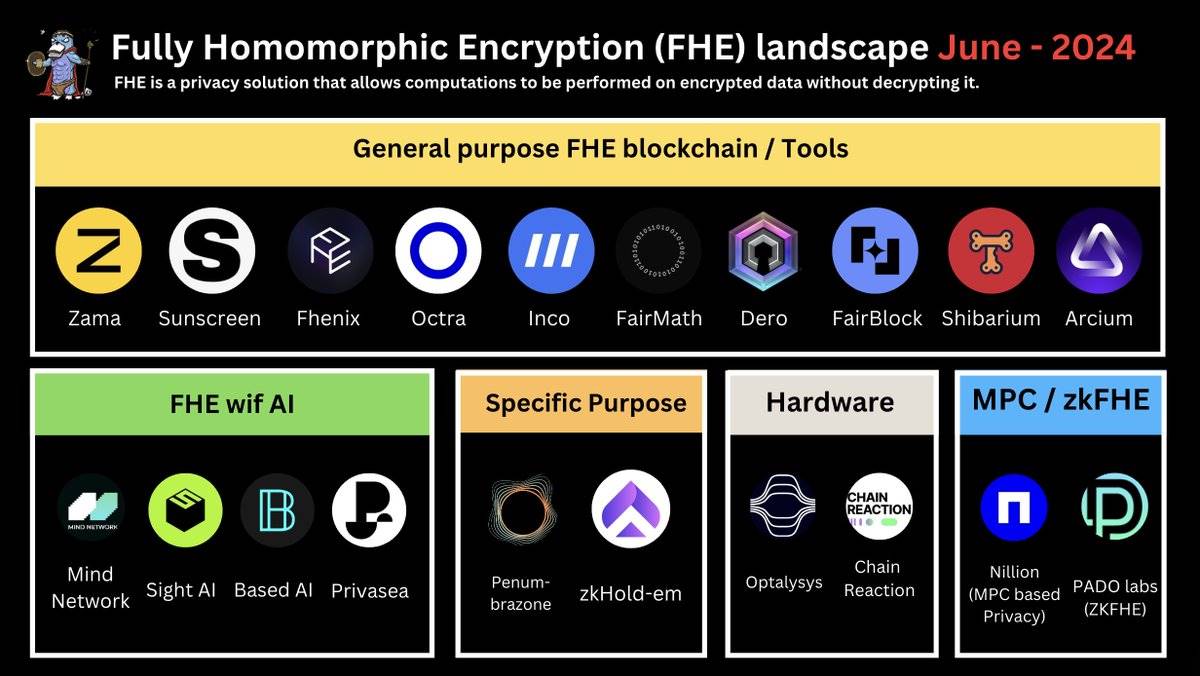
The FHE Ecosystem
Overall, the landscape of on-chain FHE can be summarized into five areas.
-
General-Purpose FHE
-
FHE/HE for Specific Use Cases (Applications)
-
FHE Acceleration Hardware
-
FHE and AI
-
"Alternative Solutions"
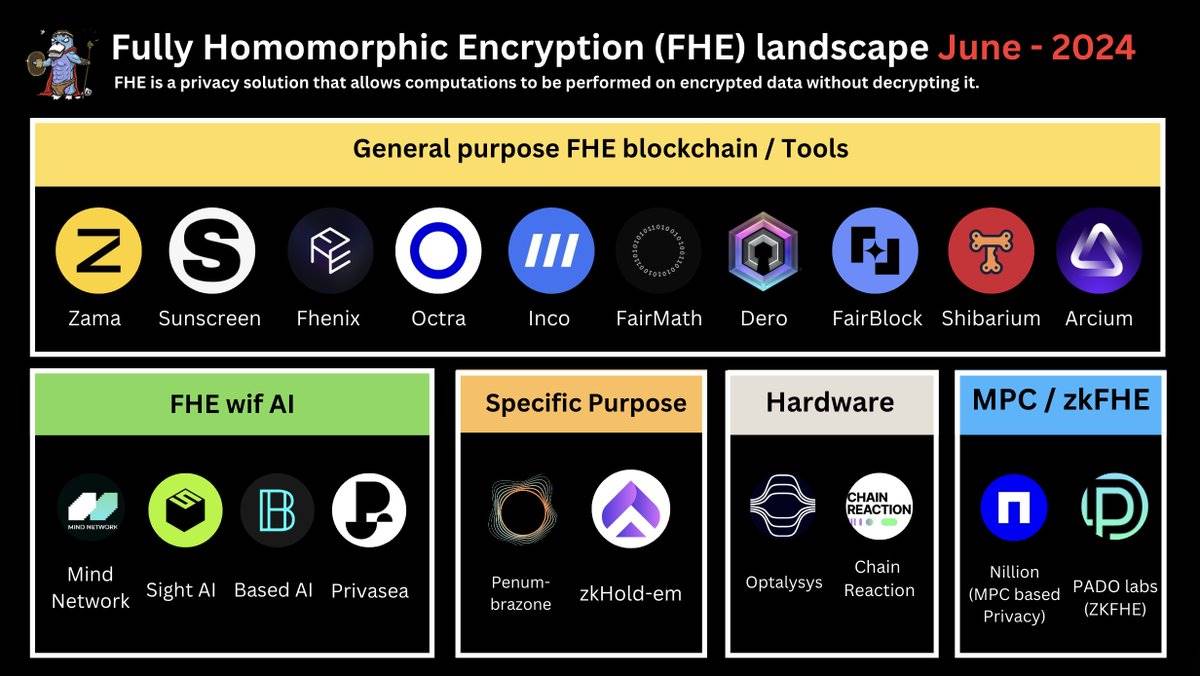
General-Purpose FHE Blockchains and Tools
These are the pillars for achieving confidentiality in blockchains. This includes SDKs, coprocessors, compilers, new execution environments, blockchains, and FHE modules.
The most challenging part is bringing FHE into the EVM—this is known as fhEVM.

Key projects in general-purpose FHE/fhEVM:
FHE Tools / Infrastructure:

FHE/HE for Specific Use Cases (Applications)
@penumbrazone — A cross-chain Cosmos DEX (appchain) using tFHE for shielded swaps/pools. @zkHoldem — A poker game where @MantaNetwork uses HE and ZKPs to prove fairness in gameplay.

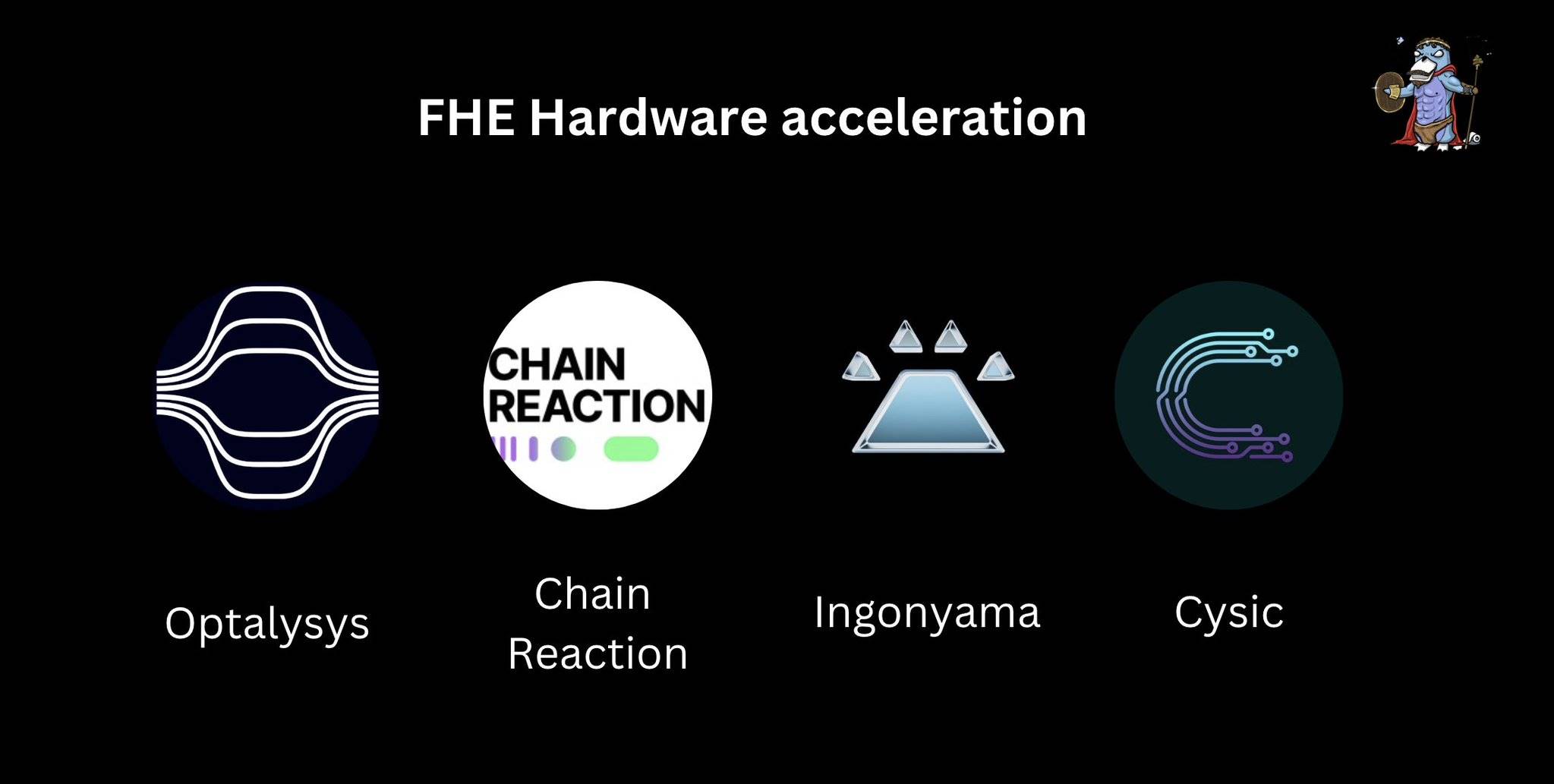
FHE Acceleration Hardware
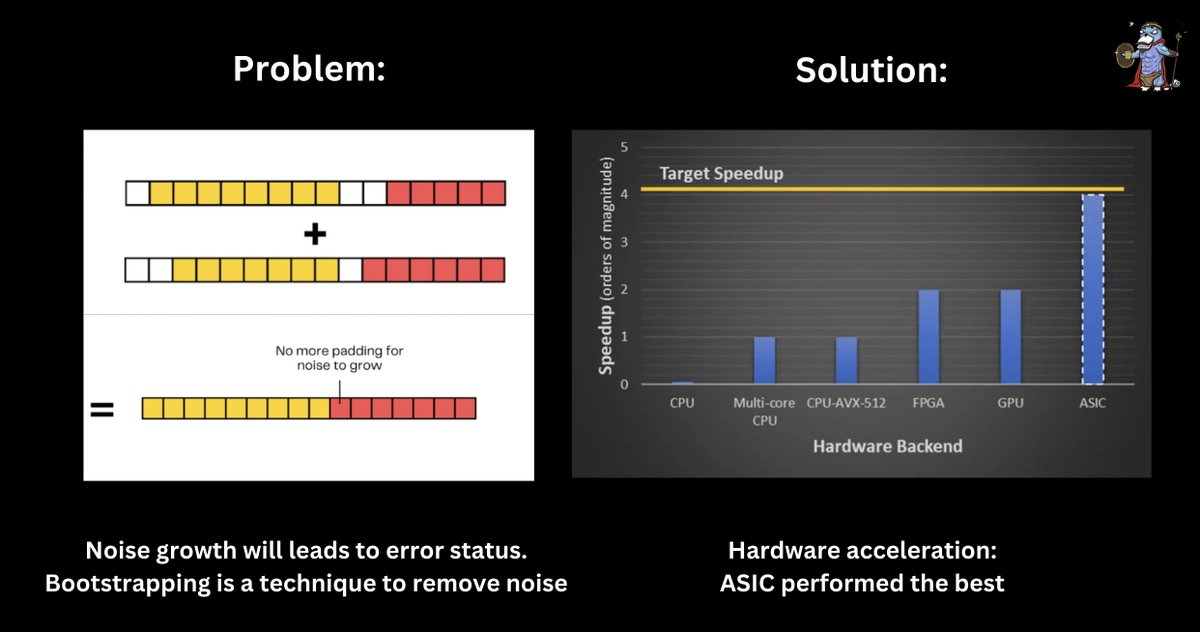
Whenever FHE is used for intensive computations such as FHE-ML, bootstrapping to reduce noise growth becomes critical.
Solutions such as hardware acceleration play an important role in facilitating bootstrapping, with ASICs offering the best performance.
Key players in the hardware space include: @Optalysys, @chainreactioni0, @Ingo_zk, @cysic_xyz. Each specializes in developing chips, ASICs, and semiconductors designed to accelerate FHE bootstrapping and computation.

FHE and AI
Recently, there has been growing interest in integrating FHE into AI/ML systems.
FHE can prevent machine learning models from learning any sensitive information during processing, thereby ensuring confidentiality of data, models, and outputs.
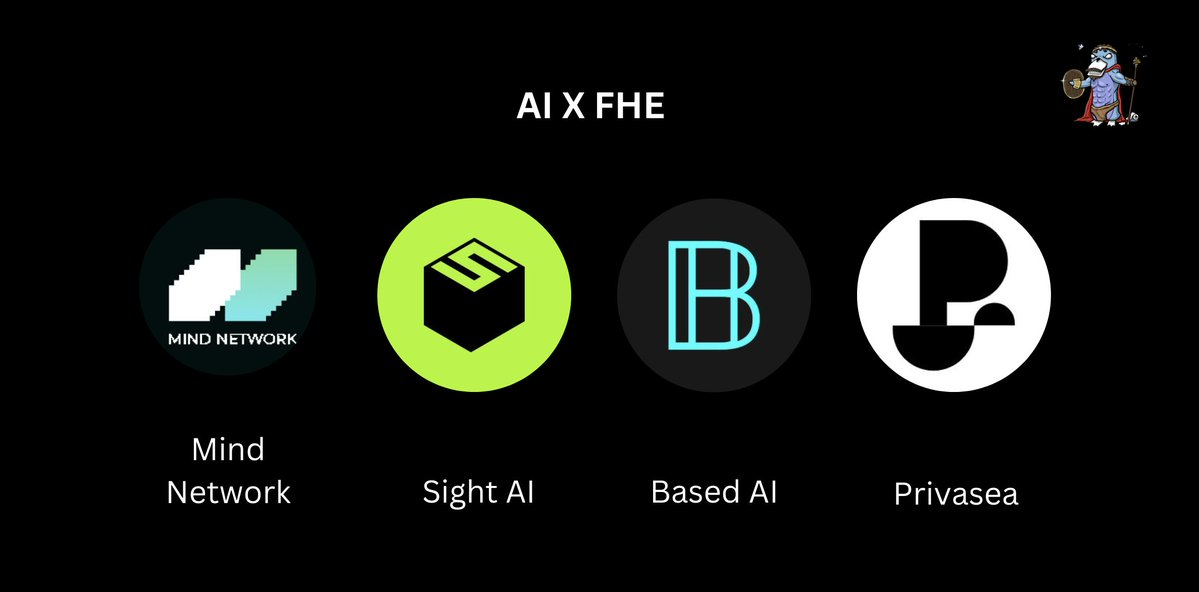
-
Projects at the intersection of AI and FHE include: @mindnetwork_xyz

"Alternative Solutions"
Some teams use MPC instead of FHE to protect high-value data and perform "blind computation," while others use ZK-SNARKs to verify the correctness of FHE computations on encrypted data. Examples include: @nillionnetwork, @padolabs.


Current Challenges Facing FHE and Potential Solutions
-
Not developer-friendly yet.
The current state still lacks standardized algorithms and comprehensive FHE development tools.
-
High computational overhead (cost)
Due to noise management and bootstrapping for complex computations, this could lead to node centralization.
-
Risks of insecure on-chain FHE
To ensure the security of any threshold decryption system, decryption keys must be distributed among nodes. However, due to the high overhead of FHE, the number of validators may be small, increasing the risk of collusion.
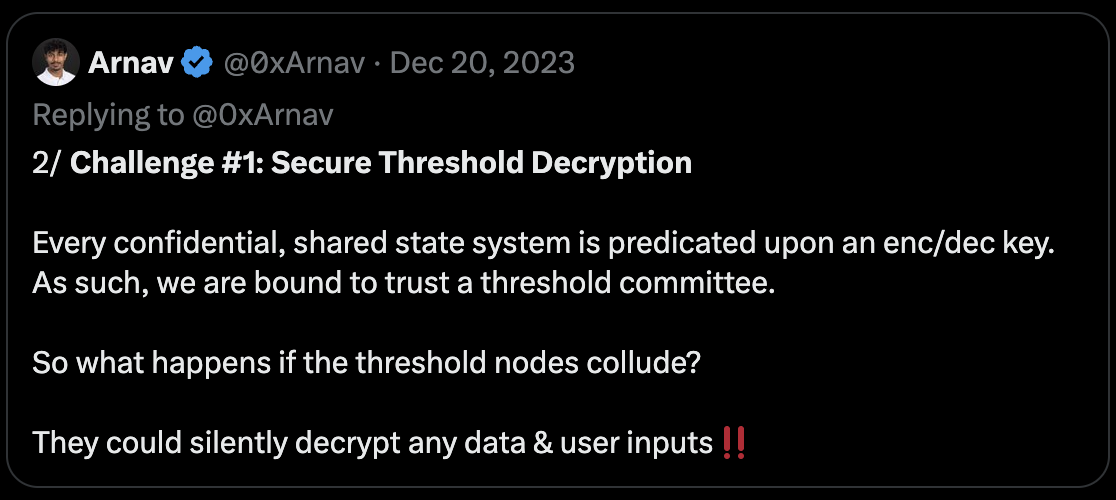
Solutions?
-
Programmable Bootstrapping:
This allows computations to be applied during the bootstrapping process, improving efficiency while remaining application-specific.
-
Hardware Acceleration
Developing ASICs, GPUs, and FPGAs, along with OpenFHE libraries, to accelerate FHE performance.
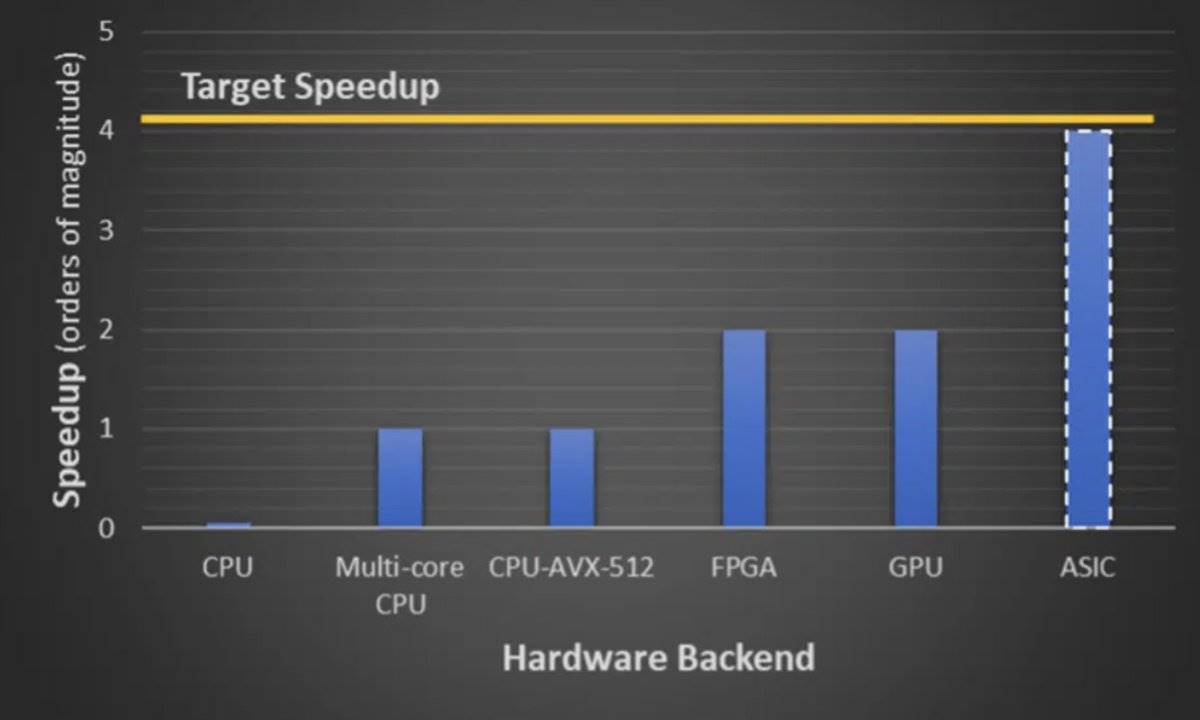
Better Threshold Decryption Systems
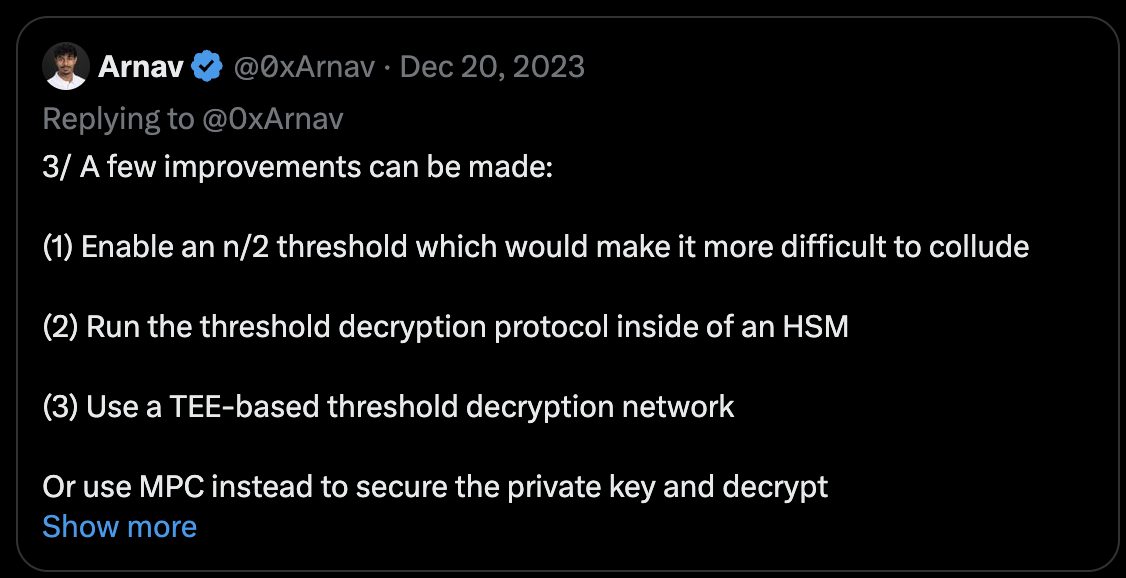
In short, to improve the security of on-chain FHE, we need a system (which could be based on MPC) that ensures:
-
Low latency
-
Lower barrier to entry for decentralized nodes
-
Fault tolerance
Here's a technical breakdown by @0xArnav.
That's all for now. Honestly, this thread is just scratching the surface. There’s much more to explore in the FHE landscape.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















