Understanding Sei's Parallelization: The Key Puzzle Piece in Revolutionizing DeFi Product Experience
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Sei's Parallelization: The Key Puzzle Piece in Revolutionizing DeFi Product Experience
Sei is firmly committed to addressing scalability challenges through parallel execution, optimized data storage, and future upgrades.
Author: DAIC
Translation: TechFlow
The decentralized finance (DeFi) revolution has ignited a global wave of financial empowerment and disintermediation. Yet, the promise of instant peer-to-peer transactions is often hampered by slow blockchains. Imagine waiting minutes for transaction confirmation or enduring painful delays that expose you to extreme price volatility. These are precisely the friction points Sei aims to eliminate.
Key Takeaways
-
Sei is an L1 blockchain with an architecture optimized for multiple transaction applications, ensuring optimal performance.
-
A built-in native order matching engine is directly integrated at L1, enabling seamless order execution and exceptional scalability for trading applications.
-
Sei’s Twin Turbo consensus mechanism achieves sub-second finality, providing near-instant transaction confirmation.
-
Sei employs a market-based parallelization approach, particularly suitable for high-frequency trading demands.
-
Through batched order processing, Sei prevents front-running exploits by malicious bots.
-
Sei V2 upgrade — Parallel EVM, Optimistic Parallelization, and SeiDB.
Overview of Sei
Current mainstream blockchains serving as the foundation for many crypto projects face significant barriers. The Sei Labs team believes existing infrastructure cannot keep up with the demands of decentralized exchanges (DEXs). They often face limitations in throughput (number of transactions processed per second) and finality time (the time it takes for a transaction to be considered complete and irreversible). This results in sluggish performance, becoming a major obstacle for high-frequency trading strategies and large-scale trading activities.
Sei aims to break this barrier by meticulously optimizing every layer of the blockchain stack specifically for trading needs. The team offers a clear value proposition: any trading application—whether DeFi, NFT marketplace, or gaming—will run smoother and faster on Sei than on any other L1 network.
With this innovative solution, Sei positions itself as the ultimate game-changer in the DeFi space, aiming to become the go-to infrastructure provider for exchanges seeking a platform purpose-built for the fast-paced world of digital asset trading.
Leveraging the interoperable Cosmos SDK framework, Sei operates as a dedicated L1 blockchain equipped with a suite of synergistic features designed to enhance the trading experience.
Its native order matching engine simplifies trading operations by eliminating external dependencies, while the innovative Twin Turbo consensus mechanism delivers sub-second finality for near-instant transaction confirmation. Security and developer experience remain paramount, featuring frontrunning prevention and native price Oracles, ensuring a robust and user-friendly environment.
Let’s dive into the key features positioning it as the “turbo engine” for DeFi trading.
Twin-Turbo Approach
Sei relies on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocol based on a modified version of the Tendermint consensus mechanism, dubbed the Twin-Turbo Consensus.
Validators play a crucial role in processing transactions and confirming changes in network state. These validators are selected based on their total staked amount (including self-bonded and delegated SEI tokens). Currently, only the top 39 validators ranked by total stake participate in the consensus process, earning transaction fees and staking rewards.
SEI token holders can choose to delegate their SEI tokens to existing validators, thereby contributing to network security. Delegators also receive a portion of the validator’s SEI rewards after deducting the commission rate set by the validator.
Regarding consensus, Tendermint provides a solid foundation, ensuring transactions are finalized and irreversible once added to the blockchain (single-slot finality). However, its base 6-second block time isn’t suited for Sei’s vision of high-speed trading.
Thanks to improvements introduced via Twin Turbo consensus, Sei Labs has reduced Tendermint’s 6-second block time to less than 400 milliseconds, achieving single-slot finality.
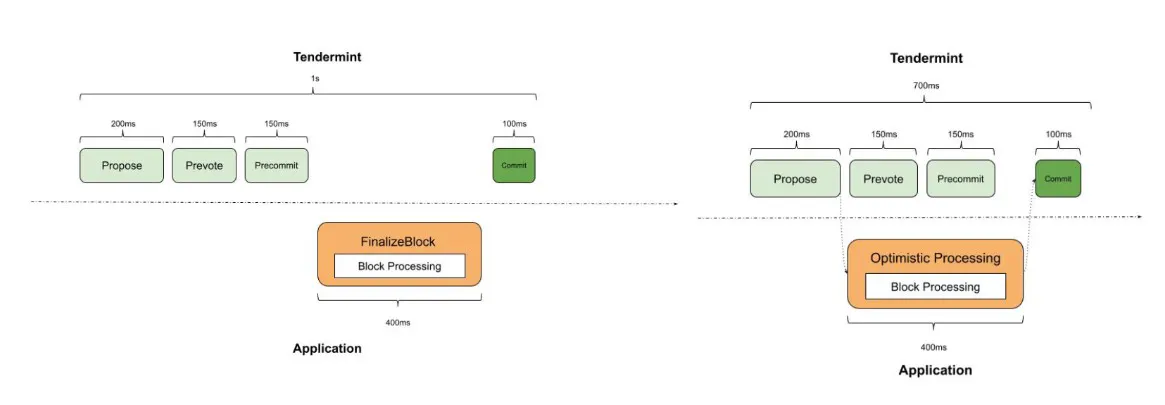
This result is achieved through two key optimizations to Tendermint, known as “Intelligent Block Propagation” and “Optimistic Block Processing.” Together, they create the final outcome seen in Sei today—transaction processing during consensus takes only milliseconds.
The Intelligent Block Propagation mechanism differs from traditional methods that transmit full transaction details within blocks. Instead, the block proposer initiates the process by sending a proposal containing unique identifiers and hashes for each transaction.
Given that validators typically have recent transactions in their local mempool, they can reconstruct the full block, avoiding unnecessary bandwidth consumption and reducing wait times for retrieving redundant data. This optimization promotes overall network efficiency, ultimately translating to faster transaction processing speeds for users.
Optimistic Block Processing further accelerates transaction handling by bypassing the “pre-vote” and “pre-commit” rounds. Its goal is to streamline the process by allowing consensus steps to occur simultaneously, significantly saving time. This approach leads to faster block validation and voting, contrasting sharply with the sequential processing common on other blockchains.
Through the synergy between Optimistic Block Processing and Intelligent Block Propagation, the consensus mechanism advances with remarkable efficiency.
After receiving the initial block proposal for a given height, the system runs rationality checks and processes it simultaneously during “pre-vote” and “pre-commit.” Optimistic Block Processing writes the candidate state to cache.
This innovative approach allows validators to optimistically process transactions upon receiving a valid block proposal, bypassing the delay of waiting for the “pre-commit” phase to conclude. The logic behind this strategy lies in observing that, in most cases, the first proposed block at a specific height wins after voting. Thus, initiating transaction processing from the start maximizes this trend.
If the block is accepted, the cached candidate state from optimistic processing seamlessly integrates into the blockchain. Conversely, if the block is rejected, the cached data is discarded, and subsequent rounds at the same block height will avoid Optimistic Block Processing. Validators reset their position and prepare to process the next block proposal. This concept cleverly leverages the predictability of block acceptance to significantly boost transaction processing speed, while reducing the risk of block rejection—meaning substantially increased throughput compared to traditional solutions.
This provides traders with a smoother user experience, minimizing confirmation times and reducing market makers’ risks—two major pain points in the current DeFi ecosystem.
Parallelization
On a chain like Sei running on the Cosmos SDK, validators follow a structured three-step process upon receiving a block: “BeginBlock,” “DeliverTx,” and “EndBlock.” Sei customizes the latter two steps to introduce parallel processing.
Traditionally, transactions in the DeliverTx phase are processed sequentially. However, Sei modifies this approach to allow simultaneous processing, adopting the concept of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to manage transaction ordering and prevent conflicts.
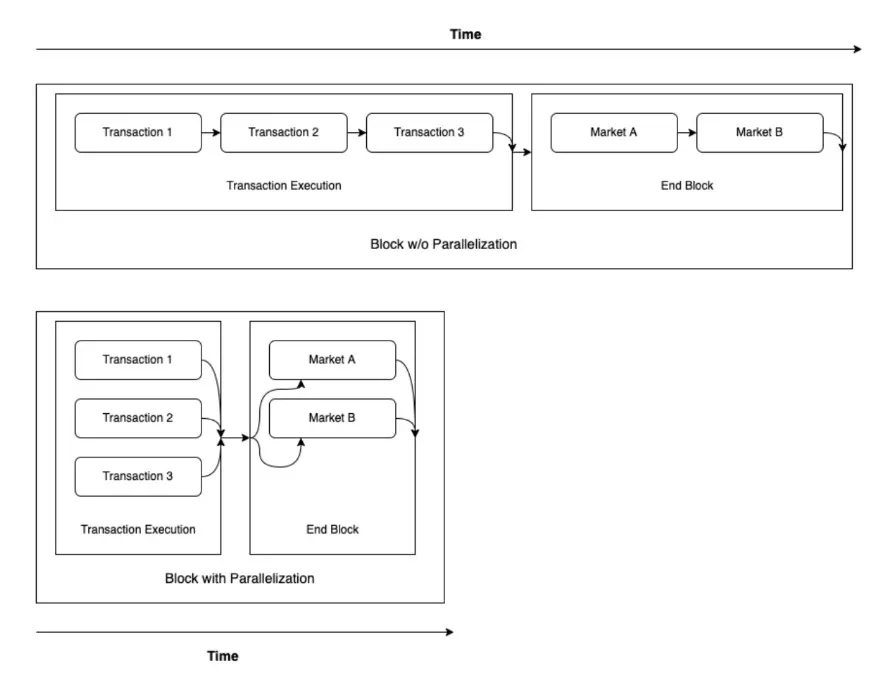
Additionally, Sei performs parallel processing of order execution at the end of a block, particularly for independent orders related to its native order matching engine. These orders are treated as independent if they involve different markets within the same block; developers can define market dependencies.
Sei’s native order matching engine allows decentralized exchanges to create their own order books. We’ll explore this in more detail below.
The Hidden Cost of Tendermint
While Sei leverages the modified Tendermint consensus, renowned for its rapid block finality, it comes with a hidden cost: quadratic communication complexity. This principle states that the number of messages required for communication among validators grows quadratically as the number of validators in the network increases.
Imagine a conference call—the conversation flows smoothly with a small group. But as the number of participants increases, managing the dialogue becomes much more complex. Similarly, in a blockchain using Tendermint, growth in the validator set leads to a surge in message traffic, potentially straining network bandwidth and validator processing capacity. This can hinder scalability, making it difficult to add many validators without impacting performance.
As the current validator set steadily expands, Sei is committed to proactively addressing this challenge through enhanced decentralization initiatives. The goal is to maintain network performance by fostering a globally distributed network of validators, supplemented by light clients for trustless verification.
Order Matching Engine
Sei integrates an order matching engine at the chain level, enabling developers to create order-book-based exchanges on the Sei blockchain.
This feature supports the development of Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) systems, commonly used in traditional centralized trading platforms. Sei also supports Automated Market Maker (AMM) systems frequently used in decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
How It Works
All transactions involving the matching engine are atomically executed within a single block. These transactions are routed to the DEX module, where each transaction may contain multiple orders. Upon submission, the transaction handler adds the orders from each transaction to the internal MemState of the DEX module. During block processing, the DEX module’s EndBlocker hook batches and merges the orders recorded in MemState. This merging aggregates orders by market (e.g., all BTC perpetual contract orders), forming a single smart contract call.
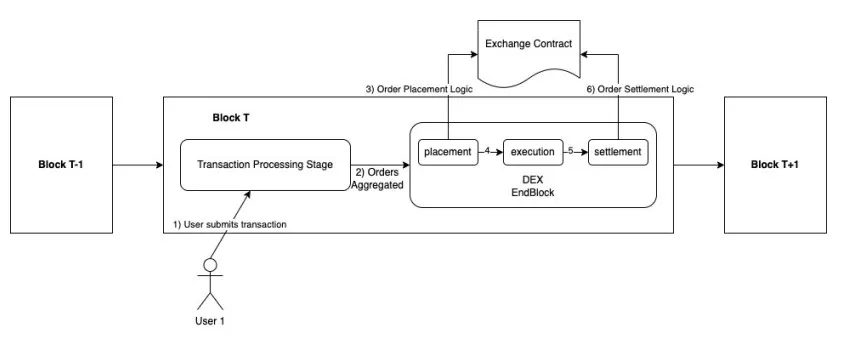
Order Batching
Sei introduces multi-layer order batching to enhance user experience and optimize performance:
-
Client-side order batching: Sei allows transactions containing multiple market orders across different trading pairs, including cross-contract orders (e.g., orders for both BTC/USDC spot pair and BTC perpetual contracts). During block processing, Sei accurately routes these orders to their respective smart contracts, helping market makers minimize gas fees associated with position updates.
-
Chain-level order batching: Instead of instantiating a virtual machine (VM) separately for each transaction related to the matching engine, Sei consolidates all orders (by market) from transactions and instantiates the VM only once. This significantly reduces order latency by approximately 1 millisecond, especially during periods of high throughput.
Hook Integration
Sei allows contracts to set “hooks” within the network. These registered hooks trigger once per block, facilitating operations such as flash loan repayments, settled within the same block as transaction settlement. Contracts can define two types of hooks: one executed at the beginning of a block to prepare for potential transactions, and another executed at the end of a block, after order matching and settlement, allowing contracts to execute any necessary post-transaction logic.
Asset Agnosticism
The matching engine does not require direct token transfers; instead, it provides a versatile interface allowing DEXs to decide how to represent assets. For example, a DEX can opt to track positions within its smart contract state rather than tokenizing them.
Frequent Batch Auctions
Sei introduces a method called “Frequent Batch Auctions” to address a phenomenon known as “MEV” (Maximal Extractable Value), ensuring fair market conditions. MEV occurs when validators prioritize their own transactions to maximize profit, potentially at the expense of other participants.
To mitigate this issue, Sei combines all market orders and executes them at a consistent settlement price. For instance, if there are two sell orders (ask prices) at P1 and P2, and two buy orders (bid prices), Sei calculates a unified settlement price—simply taking the average of P1 and P2. Subsequently, both buy orders are executed at this unified settlement price.
By avoiding individual transaction ordering, Sei eliminates validators' incentives to manipulate transaction sequences for personal gain, thus fostering a fairer trading environment.
Price Oracle
To facilitate asset pricing, Sei implements a native price Oracle. Validators act as Oracles, ensuring reliability and accuracy in asset pricing. To maintain freshness of Oracle pricing, the voting window can be as short as one block, enabling rapid updates to current asset prices.
During the voting step within the voting window, validators propose exchange rates. At the end of the voting period, all exchange rate votes are aggregated, calculating a weighted median based on validator voting power to determine accurate exchange rates for each asset. Validators who fail to participate or provide inaccurate data are penalized.
Validators have a misbehavior counter tracking instances where they fail to provide data or submit data significantly deviating from the weighted median. If a validator’s misbehavior count exceeds a certain threshold within a specified voting period, they face slashing penalties for prolonged misconduct.
Sei V2 Upgrade
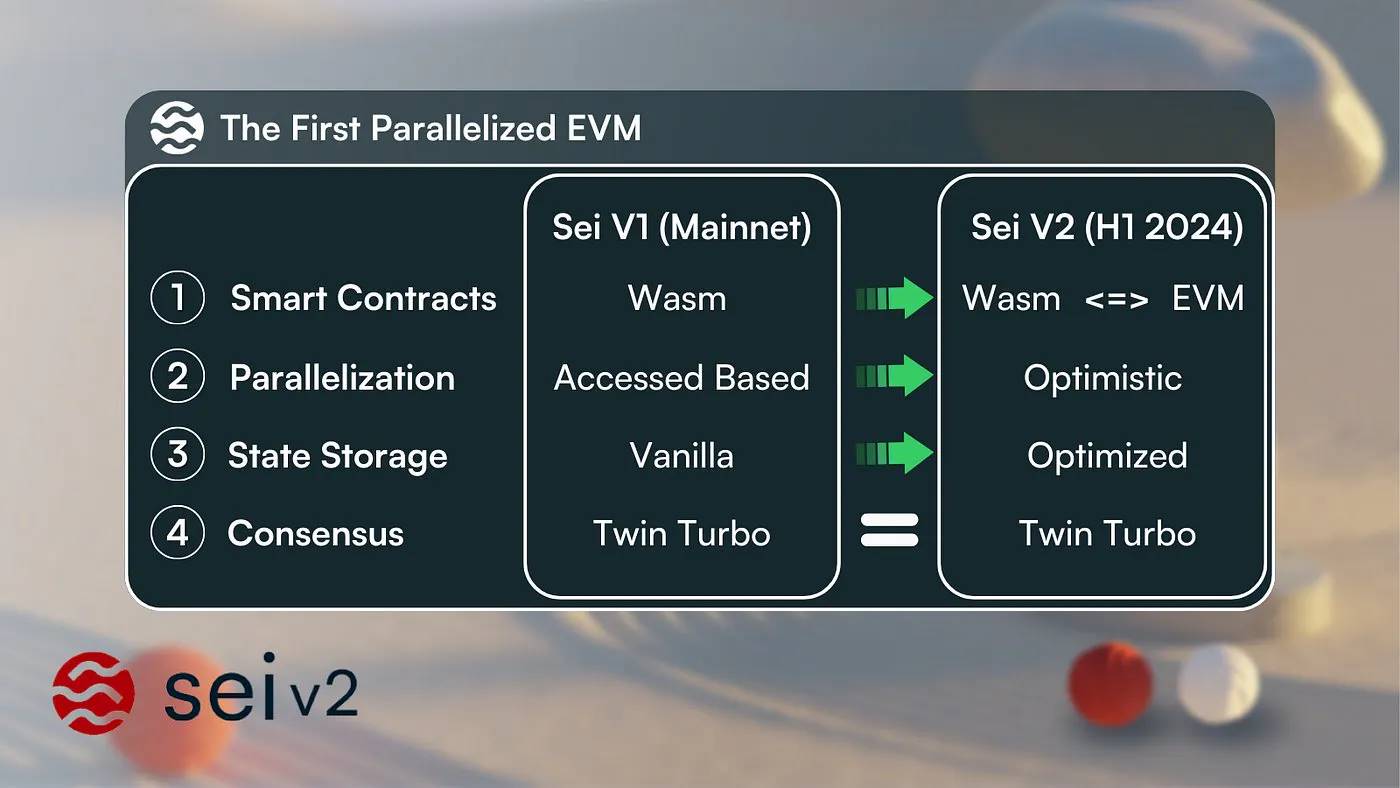
In November 2023, Sei unveiled the blueprint for Sei V2, marking three transformative enhancements to the network: Parallel EVM, Optimistic Parallelization, and SeiDB.
By cleverly combining parallel execution with EVM compatibility, Sei V2 addresses performance and usability issues in one move, offering users and developers an escape from Ethereum's constraints while preserving the familiar environment of the EVM ecosystem. This breakthrough approach improves transaction processing efficiency, significantly alleviating Ethereum’s bottlenecks during periods of high demand, while providing a seamless experience for EVM veterans.
This upgrade is expected to be deployed on mainnet in the first half of 2024. Meanwhile, Sei opened its public devnet in February 2024 as a testing ground for Sei V2 innovations.

(Image source: Source)
Sei is making a significant leap forward with Sei V2, its first major upgrade. This upgrade unleashes the power of a parallelized Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), providing developers with a super-optimized execution layer and enhanced state storage efficiency.
Additionally, a new component will be introduced to accommodate EVM smart contracts. These contracts will leverage advancements in consensus and parallelization while seamlessly interacting with existing Cosmwasm smart contracts.
(Image source: Source)
This upgrade will equip Sei with the following capabilities:
-
Backward compatibility for EVM smart contracts
-
Optimistic Parallelization
-
SeiDB — improvements to the storage layer
-
Interoperability — composability between EVM and other execution environments
Backward Compatibility
With this update, all existing and audited smart contracts from EVM-compatible chains can be seamlessly deployed on Sei without code changes, leveraging familiar tools like Foundry, Remix, and Hardhat.
Sei nodes will integrate Geth, the Go implementation of the Ethereum Virtual Machine, responsible for handling Ethereum transactions. Any subsequent updates (such as state modifications or non-EVM contract calls) will be handled through special interfaces created by Sei specifically for EVM.

(Image reference: Source)
Optimistic Parallelization
Optimistic Parallelization will apply to all transactions running on Sei, including Sei-native transactions, Cosmwasm transactions, and EVM transactions.

(Image reference: Source)
In Sei V2, developers will no longer need to manually define state access. Instead, the chain will adopt an optimistic approach to parallelize transaction execution.
When conflicts arise—for example, transactions affecting the same state—the chain will monitor which storage regions each transaction interacts with. Transactions involving different storage regions will be re-executed in parallel, while those affecting the same state will be re-executed sequentially.
This process will continue iteratively until all conflicts are resolved. Since transactions within a block are ordered, this method ensures determinism while simplifying the developer workflow and retaining parallelization at the chain level. For additional technical details, please refer here.
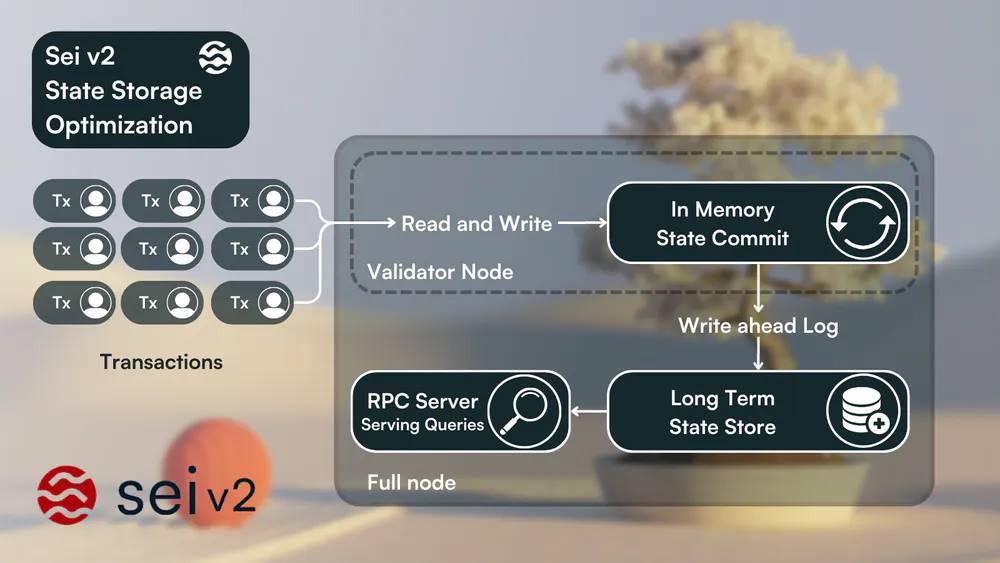
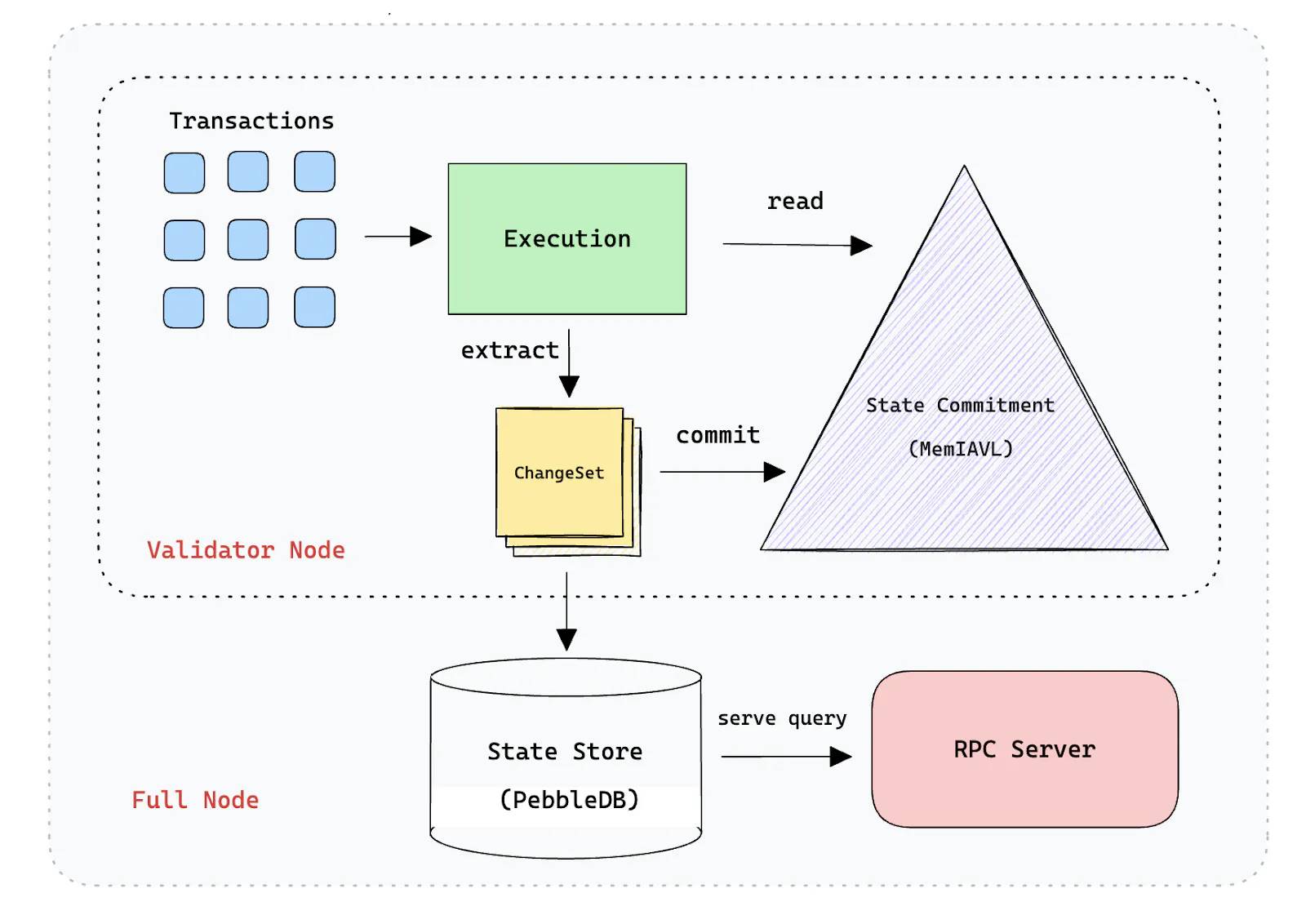
SeiDB
Increased transaction processing leads to more blockchain state creation, necessitating consideration not only of runtime parallelization but also state management. Sei v2 introduces SeiDB as a core component, fundamentally changing the mechanisms for state access, state commitment, and state storage.
(Image reference: Source)
The current Sei implementation uses a database layer composed of IAVL tree data structures. However, due to its schema and additional metadata, this structure is inefficient in terms of storage and latency, causing write amplification and slower disk access.
Based on the foundation proposed in ADR-065 (Architecture Decision Record), the Sei Labs engineering team developed SeiDB. Its primary strategy is to avoid storing all data in a single large database. Instead, data is separated into two distinct layers:
-
State Commitment uses a highly optimized in-memory IAVL tree to quickly commit data, minimizing disk access and enabling validators to reach consensus faster.
-
State Storage facilitates low-latency direct access to raw key-value pairs, enhancing RPC nodes’ ability to efficiently handle queries.
(Image: Diagram showing SeiDB separating state commitment and state storage)
Separating active state and historical data significantly enhances performance for all node operators in the Sei ecosystem. This architectural decision enables the Sei Lab engineering team to represent the current chain state as a memory-mapped IAVL tree using MemIAVL. As a result, validator nodes can track blockchain state via mmap, reducing state access time from hundreds of microseconds to just hundreds of nanoseconds. This significant advancement greatly improves state synchronization time and read/write amplification.
Storing raw key-value pairs with minimal metadata in the state storage layer improves locality within LSM trees, while asynchronous pruning prevents nodes from falling behind. These changes reduce state storage requirements by at least 60% and lower total data growth rate by 90%, saving substantial long-term disk usage as nodes continue operating.
Moreover, Sei conducted thorough benchmarking across various leading databases in the industry. Consequently, Sei V2 will transition from GoLevelDB to PebbleDB. This switch is expected to significantly improve read/write performance, especially for multi-threaded access.
Key benefits of SeiDB:
-
Reduces active state size by 60%;
-
Reduces historical data growth rate by ~90%;
-
Improves state sync time by 1200%, block sync time by 2x;
-
Reduces block commit time by 287x;
-
Provides faster state access and state commitment, doubling overall TPS;
-
Ensures Sei archival nodes achieve the same high performance as any full node.

(Image reference: Source)
These major upgrades to the network’s storage layer solve data overload issues, optimize performance, and simplify the onboarding process for new nodes. This ensures consistent network scalability and performance.
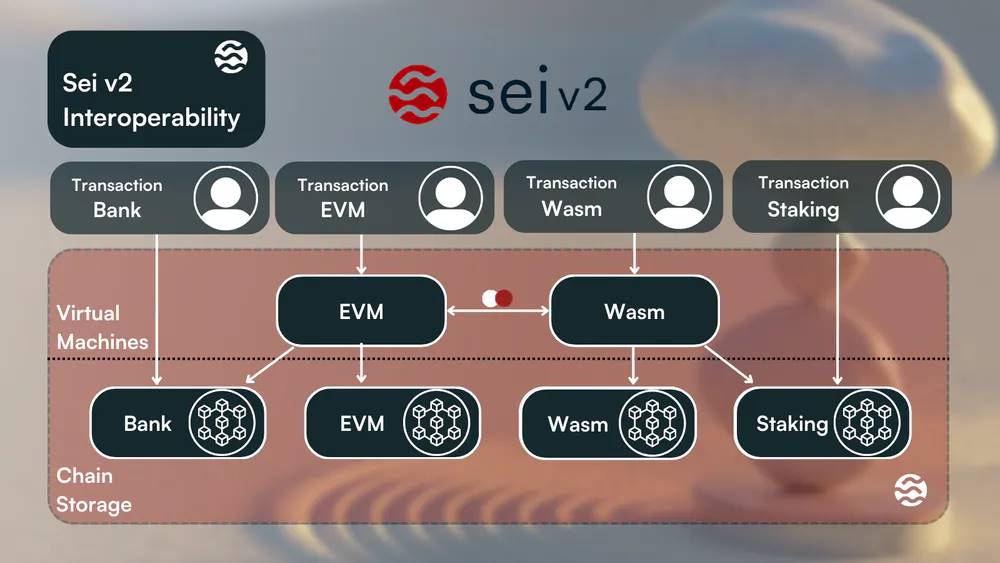
Interoperability
The upcoming Sei v2 upgrade brings revolutionary features, particularly the advanced high-performance parallel EVM. This advancement will enhance user experience and open doors to innovative development possibilities.
Sei is committed to enabling seamless composability between EVM and other supported execution environments, driving interoperability within existing chains.
(Image reference: Source)
As an integrated blockchain, Sei will allow transactions to interact seamlessly across various Sei components (banking, EVM, Wasm, staking). Despite differing purposes, these transactions share common characteristics such as gas, sender, and transaction body. Once received, the chain treats these transactions as Sei-native and routes them to the relevant storage section (e.g., routing CosmWasm transactions to the Wasm module for execution). This integration facilitates a smooth developer experience, enabling EVM developers to easily leverage native tokens and other chain functionalities like staking.
Furthermore, since Sei v2 will be enhanced to support two execution environments (CosmWasm and EVM), all token standards available on the Ethereum blockchain will also be available on Sei. Some users might worry this introduces excessive complexity into the ecosystem and harms user experience, but Sei has already accounted for this.
Each token on Sei, whether an NFT (CW-721) or standard token (CW-20), can be made compatible with EVM wallets and applications through pointer contracts. These contracts establish a link between tokens in EVM and CosmWasm, enabling seamless use without requiring assets to be “wrapped.” This ensures the same token balance can be controlled simultaneously on both EVM and CosmWasm.
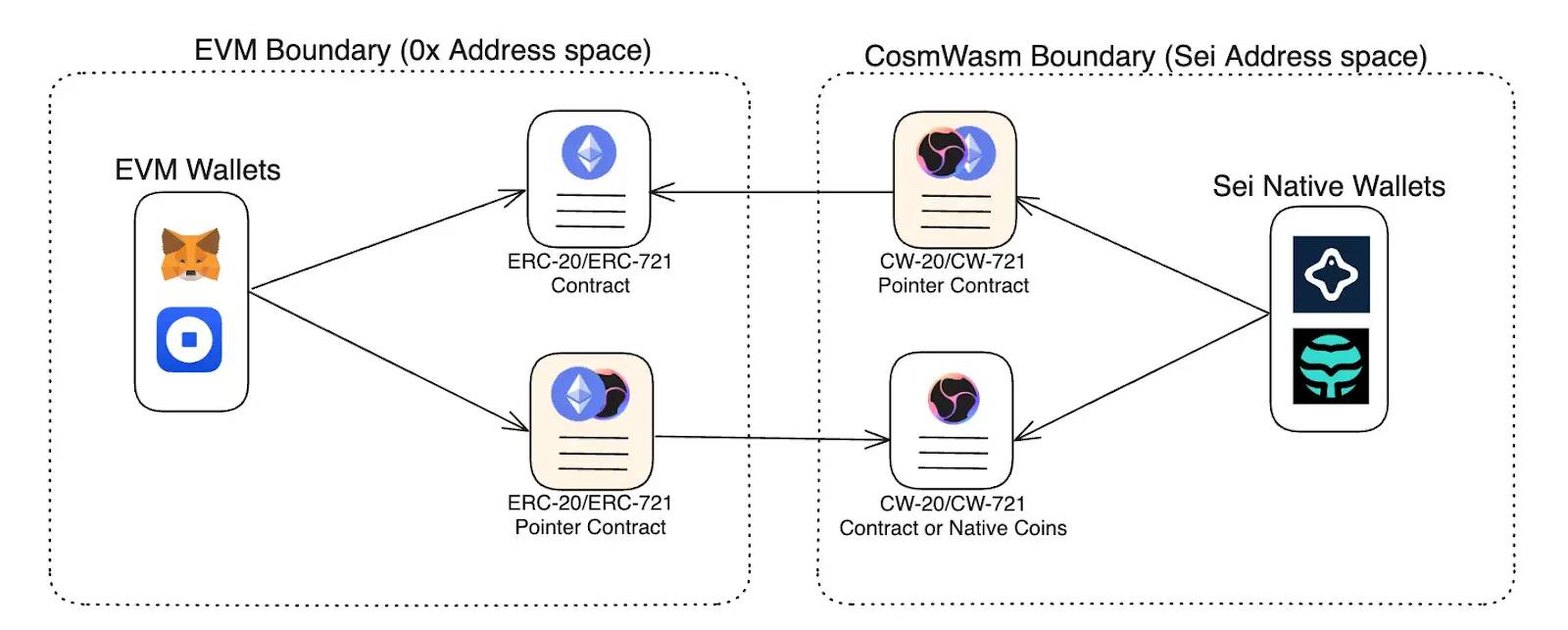
(Image: Pointer contracts enable wallets from either environment to access all tokens)
Pointer contracts also allow CW-20, CW-721, and native tokens to be used in EVM applications and vice versa. However, they do not conveniently enable EVM wallets to interact with existing Sei applications, which requires another feature called “precompiles.”
To address this, Sei Labs has implemented “precompile” smart contracts directly within the Sei blockchain. These contracts serve as gateways for users and developers to access native Sei functionalities via the EVM RPC interface, ensuring interaction with smart contracts using their preferred wallets.
Precompiled contracts available on Sei include:
Developers seeking guidance on using these precompiles can find illustrations in the “Example Usage” section.
Once funds are deposited into your EVM address, you can seamlessly use them with your Sei address, and vice versa. This integration merges them into a single account, ensuring smooth interaction between the EVM and Sei ecosystems.
User Account Setup on Sei
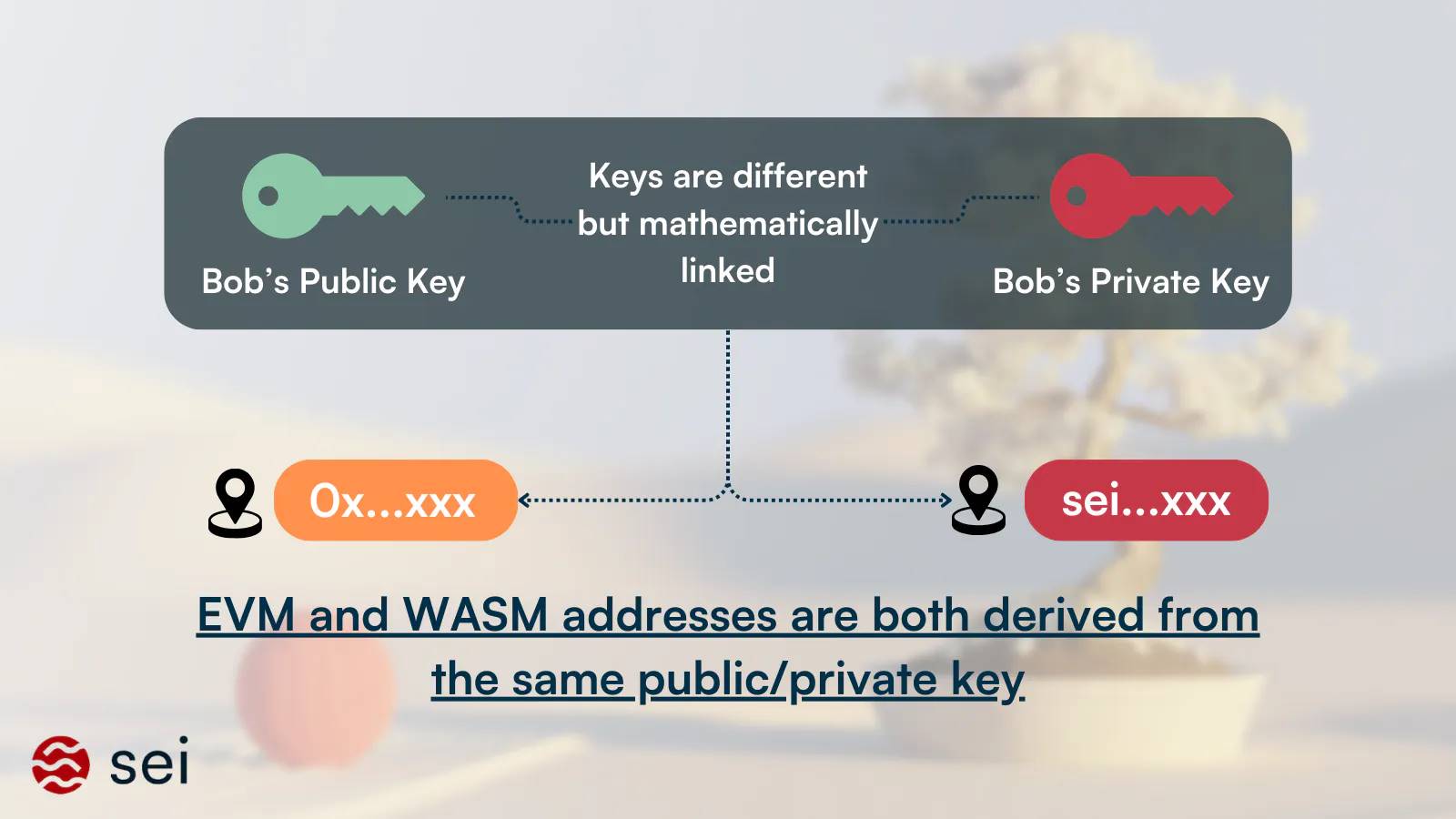
In Sei, each user “account” is associated with a unique public key. However, after upgrading to Sei V2, this public key will correspond to two types of addresses:
-
EVM address: starting with 0x, used for Ethereum-related operations.
-
SEI address: starting with sei, used for Sei-native operations.
(Image reference: Source)
Although these addresses appear different on the surface, they are essentially linked to the same underlying account. This means any operation performed with one token address will inevitably affect the other.
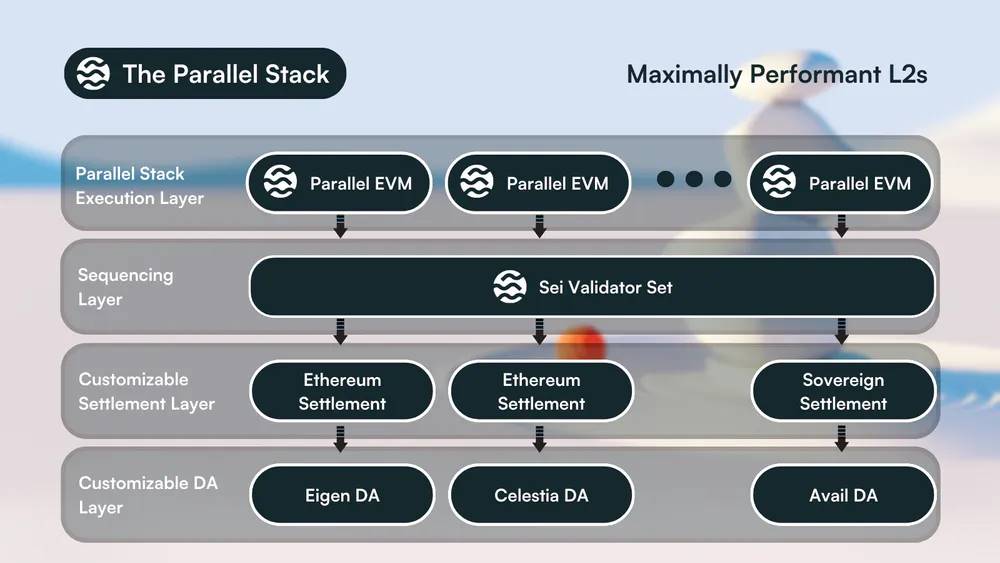
Sei’s Parallel Stack
With the rollout of Sei V2, the team is focused on introducing Sei’s Parallel Stack, which will serve as the gateway for Layer 2 networks entering the Sei ecosystem.
(Image reference: Source)
Born from the build experience of Sei V2, this open-source powerhouse tool empowers developers to create high-performance Layer 2 solutions and rollups, harnessing the magic of parallel processing. The Parallel Stack solves the performance bottlenecks currently faced by Layer 2 blockchains in the Ethereum ecosystem.
The framework provides developers with a powerful and secure foundation upon which to build innovative Layer 2 solutions. Notably, the Parallel Stack offers unparalleled customization capabilities, allowing developers to tailor their creations to specific project needs. Moreover, projects inherently benefit from the robust security provided by the Ethereum blockchain or any data availability layer they integrate with. As part of the default configuration options, projects can choose to leverage Sei’s proven validator set. This integration further enhances security while maximizing the project’s benefit from the innovative architecture of the Parallel Stack.
Democratizing the Parallel EVM
Building a rollup from scratch can be a daunting task. Sei’s collaboration with Altlayer further unlocks developers’ potential in the high-performance DeFi domain.
Altlayer’s “Rollup-as-a-Service” (RaaS) product removes the complexity of managing node infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on building innovative dApps using the Parallel Stack’s capabilities. This saves developers significant time and resources.
Beyond simplification, Altlayer’s “restaked rollups”—a set of three vertically integrated Actively Validated Services—seamlessly integrate with the Parallel Stack, adding a strong layer of security to these high-performance rollups. This translates to faster transaction finality, a more decentralized sequencing environment, and continuous validation of rollup states—critical factors in fostering trust and security in DeFi applications.
Developers gain access to a powerful toolkit enabling them to create ultra-fast and highly secure DeFi applications on the Ethereum ecosystem. This collaboration not only empowers developers but also paves the way for a more scalable and accessible DeFi landscape, ultimately benefiting the entire user base.
Future Developments
Unified NFTs: The New xERC-721 NFT Standard
The thriving Ethereum ecosystem faces a challenge—fragmentation. With the emergence of various scaling solutions (Layer 2 rollups, high-performance EVMs), NFTs are isolated within specific platforms. This isolates communities and hinders innovation.
Sei Labs and Omni Foundation propose a solution: the xERC-721 standard. xERC-721 NFTs are introduced as a streamlined upgrade to ERC-721. They offer greater freedom to NFT creators and holders, no longer confined to a single domain, opening doors to innovation and experimentation across the Ethereum ecosystem.
Advantages of xERC-721:
-
xERC-721 tokens can securely move across multiple domains without introducing unnecessary risks or reliance on any privileged third party (like a specific interoperability network), as described by the vault interface functionality here. This ensures sovereignty remains in the hands of the NFT community.
-
xERC-721 token contracts extend the interface with mintBatch and burnBatch functions. This was a pain point for developers, leading to the introduction of new standards like ERC-1155. This issue is further exacerbated when programming across multiple blockchains, as it introduces asynchronicity and requires compensating for the costs of validation and transaction relay by interoperability networks.
-
Existing NFT collections can be simply upgraded to xERC-721 by deploying a new portal contract, making them accessible throughout the rollup ecosystem.
This initiative, along with EIP-7281, lays the groundwork for a standardized approach to NFTs in the fragmented Ethereum environment. By leveraging these open standards, developers gain access to powerful tools, paving the way for further innovation in the digital asset space.
Sei Creator Fund: $10 Million Grant Program
The Sei Foundation is committed to fostering the growth of the Sei ecosystem, launching the Sei Creator Fund—a $10 million grant program. This program aims to spark innovation by supporting the development of new projects and expansion of existing ones in the NFT and social experience domains.
Whether you’re brimming with ideas for new infrastructure or tools and want to bring your creative vision to life, or wish to propel an existing NFT project forward, the Sei Creator Fund has you covered.
Conclusion
Sei is firmly committed to tackling scalability challenges through parallel execution, optimized data storage, and future upgrades, paving the way for groundbreaking progress, enabling projects to leverage diverse platforms to address complex financial challenges.
This pioneering approach heralds an era of unprecedented transaction processing throughput, promoting fast and low-cost interactions for traders. The resulting enhancement in user experience signals the potential for broader DeFi adoption.
As Sei’s technology evolves, its impact on the DeFi landscape could be transformative, ushering in an era of unprecedented scalability, efficiency, and accessibility. By fostering a more inclusive DeFi future, Sei empowers creators and users alike to redefine decentralized finance.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















