LD Capital: Exploring dappOS and the Flourishing Development of Intent-Centric Infrastructure
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

LD Capital: Exploring dappOS and the Flourishing Development of Intent-Centric Infrastructure
As blockchain infrastructure technology advances and various projects mature, future development will shift from infrastructure-focused efforts toward applications and user-friendliness, with intent-centric projects becoming the key focus of the industry's growth.
Authors: Alfred, Duoduo
1. What is Intent?
Since Paradigm's June 1, 2023 publication of "Intent-Based Architectures and Their Risks" explained the concept of intent, "intent-centric" has become a key concept and development direction in Web3.
1. Definition of Intent
According to Paradigm, "an intent is a set of signed declarative constraints that allows users to outsource transaction creation to third parties without giving up full control over outcomes." Simply put, intent focuses on desired results while abstracting away implementation details. For example, if I want asset D and am willing to pay asset A as cost, I don't need to manually execute a sequence A→B→C→D—the intermediate steps are outsourced to third parties. Conceptually, intent-centric systems follow a declarative paradigm, whereas most prior Web3 transactions followed an imperative paradigm.
2. Significance of Intent-Centric Systems: Web3's "1995 Moment"
In the early days of computing, users interacted through command-line interfaces—an imperative approach requiring high technical expertise, which limited widespread adoption and technological progress. The release of Windows 95 introduced graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and web browsers, drastically lowering the barrier to entry and expanding computer users from fewer than 50,000 to hundreds of millions. This pivotal shift became known as the internet's "1995 moment," marking a fundamental transformation in user interface design that enabled ordinary people to easily access and use the internet.

Similarly, with the maturity of Web2, many intent-centric products have become second nature—such as ride-hailing apps where the user's intent is simply "get from point A to point B," while driver matching, route optimization, fare calculation, and information sharing are all handled by the platform. In contrast, current Web3 interactions remain complex—for instance, purchasing an NFT often involves multiple intricate steps. With intent-centric solutions, these processes could be dramatically simplified.
By introducing more intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and workflows, Web3 may soon experience its own "1995 moment"—a breakthrough enabling hundreds of millions of new users to seamlessly join and use Web3. This transformation would greatly accelerate mass adoption and industry growth, making blockchain technology accessible for everyday use and driving broad acceptance and application.
3. Key Elements for Implementing Intent
(1) Focus on Outcomes, Not Processes
Intent-based projects should allow users to declare their goals rather than specifying execution steps.
(2) Execution Delegation
Intent systems must provide mechanisms to delegate execution to automated systems, smart contracts, or third-party providers. Whether executed automatically or manually, the process must align with the user’s original intent while allowing flexibility and optimization where appropriate.
(3) Verifiable Results
In blockchain environments, intent systems must ensure transaction outcomes are verifiable and traceable, so users and stakeholders can clearly understand and confirm that executions match expectations.
2. dappOS Fundamentals Overview
1. Introduction to dappOS
dappOS is an intent execution network that creates a two-sided market to convert user intents into on-chain outcomes. On the supply side, service providers stake collateral to run one or more execution services. On the demand side, it enables developers to find solutions that fulfill user intents.
2. dappOS Core Mechanism: Optimistic Minimum Staking (OMS)
At the network level, dappOS introduces Optimistic Minimum Staking (OMS), which links each task to predefined value and potential compensation upon failure, allowing execution before validation. If a task fails, the network uses a consensus process to penalize the responsible service provider, ensuring either successful execution or pre-specified compensation for users—significantly improving efficiency and generalizability.
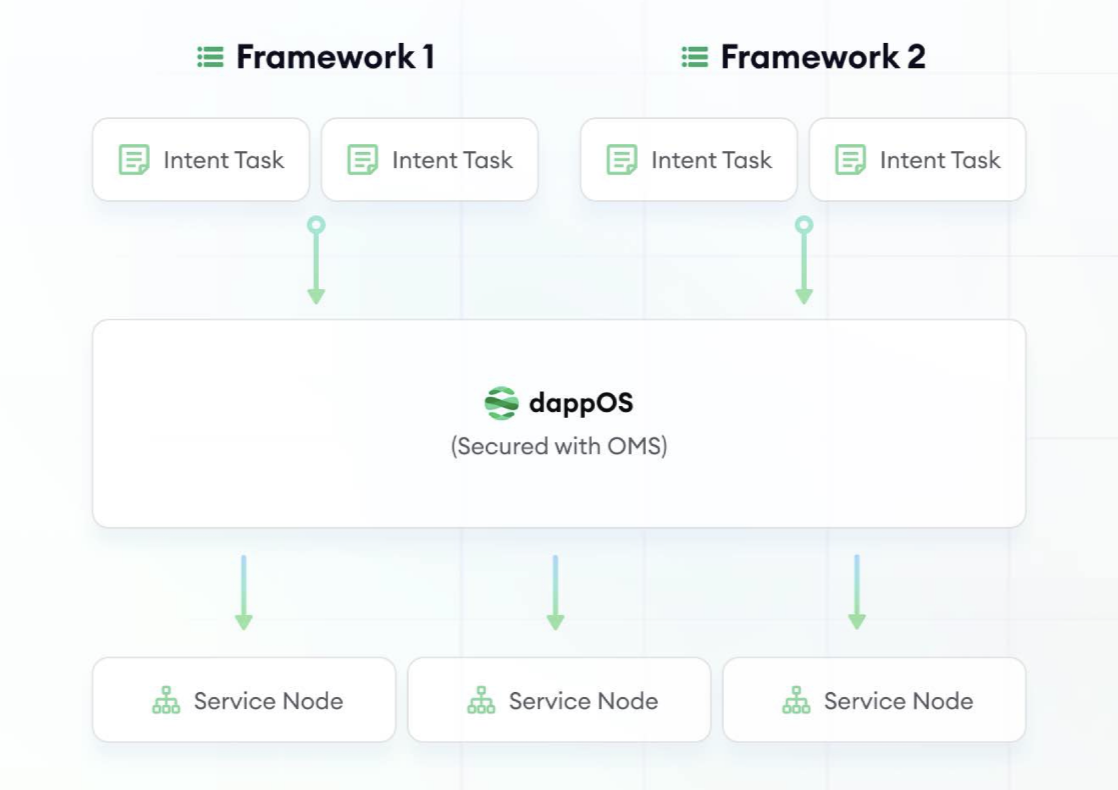
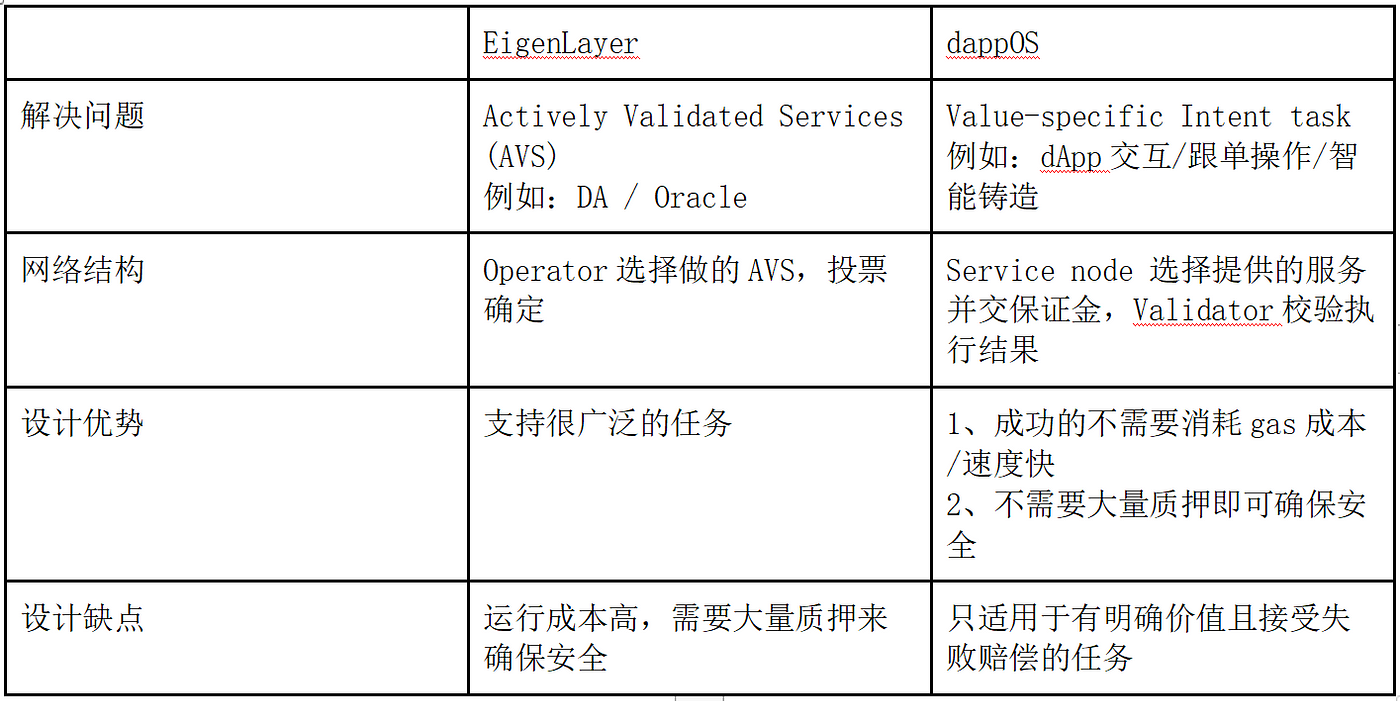
Technically, dappOS’s OMS shares similarities with EigenLayer’s AVS architecture, where dappOS service providers resemble EigenLayer operators. The main difference lies in focus: EigenLayer targets general-purpose use cases like data availability (DA), oracles, and ZK processors, while dappOS specializes in intent-centric tasks, assigning each intent a defined settlement value. As long as staked collateral exceeds this value, the system remains secure and efficient.
3. dappOS Use Cases
Currently, dappOS supports various applications:
(1) Unified Account
dappOS offers a unified account compatible with intent execution. Similar to centralized exchanges, assets within this account can be used across any dApp on integrated chains, and fees can be paid using most major tokens. Even when assets are scattered across multiple blockchains, users can control accounts on different chains via a single signature.
Additionally, the unified account supports flexible external interactions. Any application accessible via externally owned accounts (EOAs) can also interact through the unified account using scalable execution interfaces and custom service logic.
(2) Intent Assets
dappOS’s intent assets enable seamless usage of different asset forms across scenarios. For example, dappOS will issue intentUSD—an intent-based stablecoin that functions as USDT when needed, USDC when required, and automatically earns yield when idle. These assets solve the biggest usability issues for stablecoins and LSD assets, allowing new users to avoid understanding distinctions between fungible assets like USDC and USDT.
Simply put, dappOS’s intent assets could become Web3’s “Yu’ebao” (a popular money market fund in China). By handling backend complexities via the dappOS intent execution network, they enhance digital asset efficiency and lower barriers to entry.
(3) Real-Time dApp Contract Interaction
dappOS provides an excellent execution framework for real-time dApp interactions. Users can achieve seamless transitions from initial to final states with just a single signature. Traditional implementations of intents often involve cross-chain operations, asset swaps, and contract approvals—procedural means, not ends. dappOS’s real-time interaction framework abstracts these steps away; users achieve their goals directly with one signature, greatly enhancing user experience.
Moreover, through mechanisms like OMS, dappOS ensures all operations meet blockchain standards for decentralization and security, while maintaining high efficiency and low cost. This intent-first approach to simplifying complex blockchain operations not only improves convenience but also promotes broader blockchain adoption and development.
3. Advantages of dappOS
(1) Innovative Base-Layer Design
As infrastructure for the intent space, dappOS’s OMS mechanism is specifically tailored for intent use cases. It ensures user security while significantly boosting execution efficiency. In fact, dappOS’s OMS is to the intent赛道 what EigenLayer’s AVS is to restaking—it underpins the entire ecosystem, positioning dappOS at the core of intent infrastructure.
(2) Rich Use Cases and First-Mover Advantage
dappOS already supports diverse applications—including unified accounts, intent assets, and real-time dApp interactions—a rarity in the still-emerging intent space. Compared to other intent infrastructure projects still in conceptual or development phases, these live use cases enable dappOS to collaborate with numerous Web3 projects early, expand its ecosystem, iterate rapidly, and establish a first-mover advantage, positioning itself as a leading player in intent infrastructure.
3. dappOS Ecosystem Growth
Since late 2023, the dappOS ecosystem has accelerated. Because intent-centric interactions are easier for users, integrating dappOS infrastructure often drives significant growth for partner projects. Consequently, many leading and emerging projects—including Manta, GMX, BENQI, and KiloEx—have partnered with dappOS.
For example, after KiloEx integrated dappOS on April 16, 2024, its trading volume surged 217% week-over-week, and DAU increased by 3,000%.

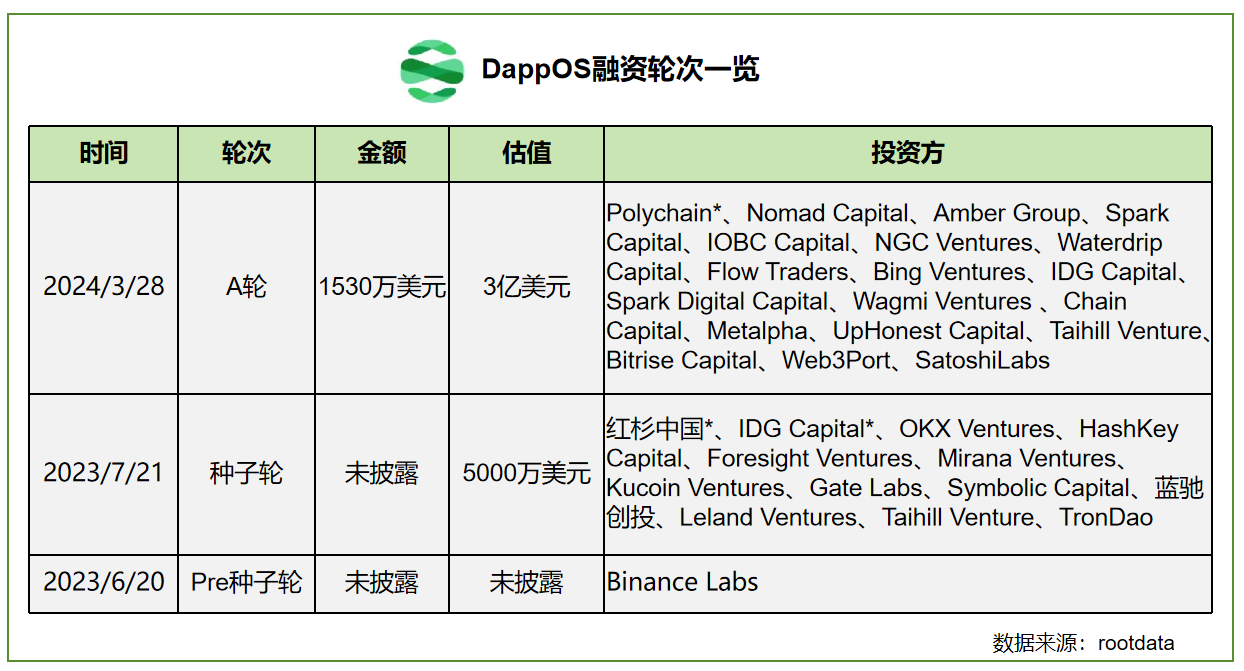
4. Funding Information
dappOS has attracted strong backing from top-tier investors including Polychain, Binance Labs, Sequoia, IDG, and Hashkey. Polychain, lead investor in its Series A round, has demonstrated strong performance in this cycle, investing in leaders such as EigenLayer (restaking) and Celestia (modular blockchains). dappOS represents Polychain’s strategic bet in the intent sector.
5. Conclusion
As blockchain infrastructure matures, the industry is shifting from foundational development toward user-friendly applications. Intent-centric projects are poised to lead this next phase. With solid underlying technology, support from premier investors like Polychain and Binance Labs, and growing adoption by leading projects such as GMX, dappOS is well-positioned to become the dominant player in the intent space—ushering in a new era of mass adoption and large-scale user traffic.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News