Understanding Mango Network: The Technical Principles of a Transaction-Oriented Omnichain Infrastructure Network
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Mango Network: The Technical Principles of a Transaction-Oriented Omnichain Infrastructure Network
Mango Network is leading a new wave of innovation in the DeFi industry with its unique advantages of high performance and modularity, as well as the concept of cross-chain liquidity pools.
Born for Omnichain—Mango Network, the Transaction-Oriented Omnichain Infrastructure
In 2024, the blockchain industry is undergoing a new paradigm shift, with the omnichain narrative emerging as the central theme. Mango Network ($MGO), positioned as the industry's first Layer 1 public chain dedicated to becoming a transaction-oriented omnichain infrastructure network, is leading a new wave of innovation in DeFi through its unique advantages of high performance and modularity, along with the concept of omnichain liquidity pools.
—Mango Chain is about to launch, enabling seamless transfer of tokens, NFTs, data, and information across heterogeneous L1/L2 blockchains.
—Fragmented crypto assets and liquidity mining pools across different blockchains are efficiently interconnected via Mango.
—Mango’s omnichain applications give rise to omnichain liquidity pools, unlocking new possibilities for Web3, especially DeFi innovation.

In the past year of 2023, the global blockchain sector experienced a bull-bear transition, with key narratives including Layer 2 networks, new Meta-affiliated public chains launching mainnets, LayerZero leading cross-chain competition, and BRC20 inscriptions breaking into the meme space. As more users join and ecosystem use cases expand, demand for seamless multi-chain interoperability has grown stronger than ever. On the other hand, the industry increasingly recognizes that building omnichain infrastructure is the most direct and effective way to overcome the blockchain trilemma. The omnichain narrative is now at the forefront, driving a new wave of paradigm shifts in 2024.
Addressing these industry pain points, Mango Network ($MGO) has taken an early lead by positioning itself as the first Layer 1 public chain focused on becoming a transaction-oriented omnichain infrastructure network. By building an all-in-one omnichain liquidity service network, Mango delivers a safer, more trustworthy, diverse, convenient, and user-autonomous omnichain trading experience.
Built on Move, Inherently Secure
Move is a programming language originally developed for Facebook's Libra (now Diem), a supranational cryptocurrency project. Designed specifically for digital assets, Move addresses the shortcomings of Solidity and the EVM, offering a high-performance, secure, and reliable environment for smart contract development on blockchains.
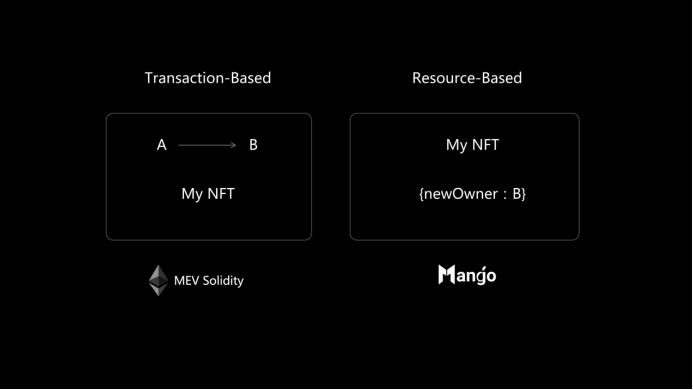
Mango Move is a statically typed programming language with multi-threading capabilities that effectively reduces concurrency issues. The combination of static typing and smart contracts provides a secure environment for application development, ensuring project source code cannot be tampered with during attacks. Moreover, Move treats digital assets as first-class citizens, defining tokens as a distinct resource type (Resource) separate from other data. Asset transfers in Mango Move are object transfers, guaranteeing asset uniqueness and security, adding an extra layer of protection for on-chain DeFi projects.
Modular & High-Performance: Breaking the Impossibility Triangle
Built on the Mango Move language, Mango’s modular blockchain architecture decomposes blockchain functions into distinct layers, achieving high security, high performance, and low cost—effectively overcoming the "impossible triangle" of decentralized networks.
Traditional blockchain systems typically integrate consensus, settlement, data availability, and execution within a single monolithic architecture. As application complexity and demands grow, such architectures struggle to meet diverse requirements.
Mango’s modular blockchain separates these core functions, allowing each module to operate independently while maintaining inter-module collaboration. This architecture enhances flexibility and scalability, enabling customization and optimization based on specific needs.
Through horizontal scaling, composability, and on-chain storage, Mango Chain achieves over 100,000 TPS in parallel transaction processing with sub-second finality. It supports rich on-chain assets and solves common L1 pain points with unparalleled speed and low costs, delivering an outstanding user and developer experience.
Born Omnichain: Pioneering a New Application Paradigm
As an L1 public chain designed for omnichain applications, Mango’s greatest strength lies in serving as a highly efficient execution and settlement layer. This allows developers to design applications with full omnichain interoperability in mind, while users can access dApps seamlessly from any L1 or L2 chain—significantly reducing operational complexity.
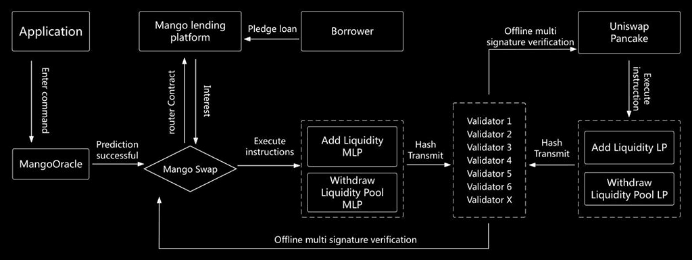
The technical architecture of Mango’s omnichain applications consists of a mainchain contract and modular contracts. The core application logic resides on the Mango mainchain, acting as the “central controller,” while remote access modules are deployed on other chains to interact with end users, receive inputs, and deliver results.
For example, a DEX developer can deploy their dApp on the Mango mainchain. Users can then interact with it either directly on the Mango chain or remotely from any other chain—just as conveniently as using a native app. This means users only need one token as gas, without needing to know which chain hosts the dApp, to perform any cross-chain operation.
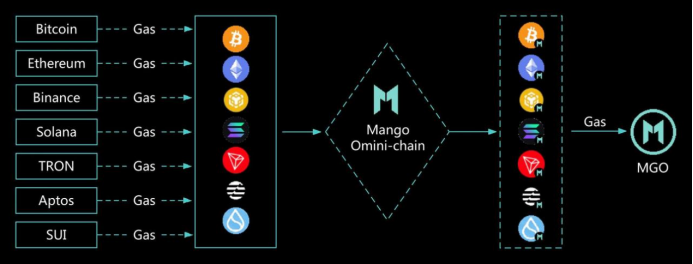
The biggest advantage of this architecture is drastically reduced complexity in cross-chain integration. With core logic centralized on the Mango mainchain, applications maintain a unified state. When deploying on a new chain, users inherit all prior state records and liquidity from the mainchain. Additionally, other applications integrating with it only need to connect once on the mainchain to access its full functionality and liquidity.
Compared to cross-chain protocols like LayerZero, Mango’s omnichain applications eliminate the need for frequent asset bridging between chains—resulting in lower costs, faster confirmations, and higher efficiency. Furthermore, since assets and data aren’t stored with third parties, security is significantly enhanced.
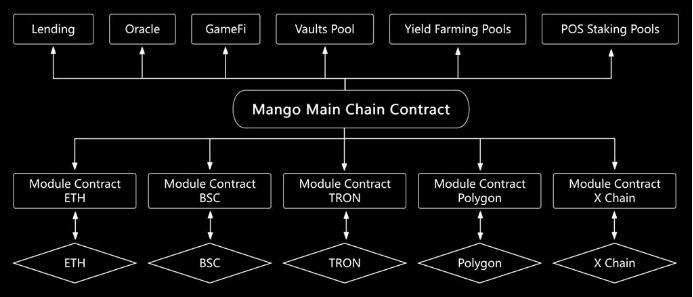
Omnichain applications enable seamless connectivity across heterogeneous blockchains, solving multiple pain points in Web3 and DeFi—including fragmented user experiences and isolated liquidity. By combining mainchain and modular contracts, Mango builds an all-in-one liquidity service network, delivering a unique and seamless trading experience.
Omnichain Liquidity Pools Fueling DeFi Innovation
Mango’s omnichain applications make omnichain liquidity pools a reality. Previously, DeFi projects had to deploy separate liquidity pools on each chain, reducing capital efficiency and increasing user complexity. Now, thanks to Mango, building a “one-stop” liquidity pool that supports cross-chain assets and operations is possible.
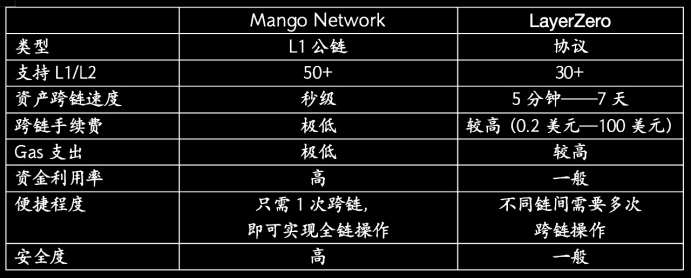
Mango’s liquidity service network offers the following advantages:
- Unified user experience: Users can access DeFi apps on other chains through a single gateway on Mango Chain.
- Low cost: Cross-chain asset transfers via Mango Network incur minimal fees and lower gas costs.
- High asset liquidity: Users can freely move assets across chains using just one token as gas.
- Efficient and secure: Built on Move, offering inherent security benefits.
Users can deposit on-chain assets into liquidity pools deployed on the Mango mainchain, then use modular contracts on target chains to participate in DeFi activities across any chain. This approach simplifies cross-chain operations, enhances security, reduces gas consumption, and eliminates slippage.
For instance, a user can bridge ETH assets to a liquidity pool on the Mango mainchain and, via Mango’s module contract on the target chain, interact with PancakeSwap on the BNB Chain. This enables users holding only BTC or ETH to participate in DeFi across any chain, greatly expanding the potential size of liquidity pools—and paving the way for innovative DeFi applications such as omnichain lending, omnichain staking, novel flash loans, and new algorithmic stablecoins.
For example, omnichain liquidity lending centers around single-token pools across various blockchains, with Mango Network serving as the bridge and settlement layer. These single-token pools allow users from any chain to provide liquidity. Compared to Aave, which relies on single-chain liquidity and third-party bridges for cross-chain functionality, Mango-based omnichain lending allows all operations to occur seamlessly across chains—significantly improving capital utilization.
BeingDex: An Innovative Omnichain Order-Matching Trading Platform
BeingDex is a decentralized exchange built on Mango Move, supporting omnichain on-chain order matching. Its standout innovations include peer-to-peer wallet-based order matching, an order book model, support for K-line charts, and no reliance on liquidity pools.
This differs significantly from Uniswap V3. Order book trading offers greater market depth and higher price transparency—users can view all open orders, making it easier to find optimal prices. Additionally, Mango Move uses static calls with immutable execution ordering, effectively resisting MEV attacks and further reducing trading slippage.
BeingDex supports omnichain on-chain assets including tokens, NFTs, and inscriptions, serving as a liquidity gateway that brings omnichain liquidity into various Web3 applications. The BeingDex team continues to expand its offerings, providing users with one-stop asset management through key Web3 infrastructure such as Crypto Wallet, DeFi, yield aggregators, POS staking pools, IDO platforms, NFT marketplaces, decentralized social apps, and DAOs.
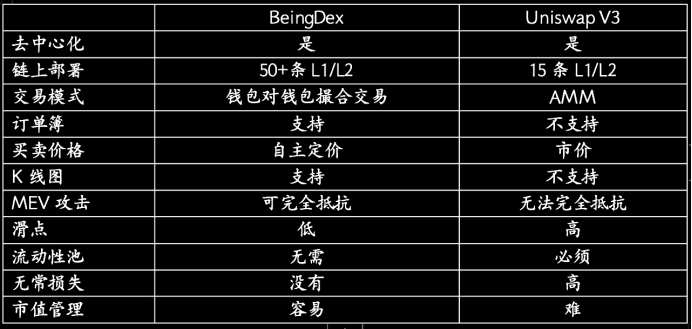
Overall, omnichain trading is the inevitable trend in Web3 application development. It enhances asset liquidity, improves capital efficiency, lowers transaction costs, expands use cases, and delivers more convenient, efficient, and enriched services to users.
The emergence of Mango Network brings new opportunities to the blockchain industry. It is poised to become a leader in omnichain interoperability and is well-positioned to serve as the foundational transaction-oriented omnichain infrastructure for the next wave of industry transformation.
Mango Network Whitepaper Key Insights
A. Positioning: Transaction-Oriented Omnichain Infrastructure
Keywords: L1 public chain, DPoS, omnichain applications, Move language, modular architecture
B. Technical Highlights
- Supports omnichain applications—users only need one token as gas to interact and operate across heterogeneous blockchains;
- High performance—over 297.45K+ TPS, sub-second settlement, low gas fees, excellent user experience;
- High security—built on Move language; static typing combined with smart contracts ensures code integrity and resistance to attacks;
- Modular architecture—decomposes blockchain functions into independent modules (e.g., consensus, execution, data availability), allowing customization for different use cases. Modular blockchains offer strong scalability—modules can be added or removed as needed—and improved security through functional isolation.
C. How Mango Omnichain Applications Work
Mango’s omnichain applications adopt a dual-contract architecture: mainchain contracts and modular contracts. Core business logic is deployed on the Mango mainchain for centralized coordination. Remote access modules are deployed on other blockchains to interact with end users—receiving inputs and delivering outputs.
Operation flow: Users input data via a remote module on a new chain. The module relays this data cross-chain to the Mango mainchain. After processing, the result is sent back to the corresponding remote module on the target chain, presenting users with a localized interaction experience. For scalability, certain mainchain modules can also be deployed externally, forming a virtual mainchain system.
Overall, this architecture achieves cross-chain omnichain connectivity through abstraction and decoupling between mainchain and modular contracts. Users enjoy lightweight, unified access to services distributed across multiple chains.
D. Technical Advantages of Omnichain Applications
Provides a settlement and execution layer across heterogeneous blockchains. Previously, transferring assets between heterogeneous chains required bridges like LayerZero and preparing native gas tokens on each chain. Now, users only need to bridge assets to the Mango mainchain once, then use modular contracts to interact on any target chain. Compared to traditional bridges, omnichain applications offer clear advantages:
- Easier scalability—core logic runs on the Mango mainchain with a unified state. When deploying on a new chain, users inherit all state records and liquidity from the mainchain, avoiding redundant work.
- Better user experience—users don’t need to know where the app is deployed; they can access it from anywhere on the omnichain mainchain, just like a local app. No need for repeated bridging; one token as gas suffices for all interactions.
- Simpler cross-chain integration—other apps only need to integrate once on the mainchain to access all functionalities and liquidity.
E. Components of Mango’s Infrastructure Protocol
- ZK Proofs—enable private transactions, privacy protection, and cross-chain authentication
- Distributed Storage—uses IPFS for data storage, ensuring redundancy, reliability, and scalability
- MgoDNS Domain Service—a decentralized, cross-chain domain solution providing non-custodial domain naming and analytics. MgoDNS sits at the intersection of blockchain and traditional internet, connecting various public and consortium chains into a super hub.
- Mango Client—maintains a consistent copy of the system’s valid state, used for auditing and building transactions or operating services.
F. Roadmap and Timeline
Mango Network will launch its testnet in Q2.
Its ecosystem applications, including Being Wallet and BeingDex (an order-book-style omnichain trading platform), have already been deployed on the devnet.
About Mango Network
Mango Network is a Move-based Layer 1 public chain aiming to become a transaction-oriented omnichain infrastructure network. Through modularity, it enables omnichain applications and builds an all-in-one liquidity service network, delivering a more secure, trustworthy, asset-rich, convenient, and autonomous trading experience. $MGO is its native token.
Developed by MangoNet Labs, a technology company focused on Web3 infrastructure, Mango Network’s vision is to empower one billion users to seamlessly adopt Web3.
- Mango Network official
- Web
- X
- Mango Network Dev
- Blockchain Browser
- GitHub open source
- Developer Documentation
- Swap interactive application
- Github
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News