Cosmos Ecosystem Annual Overview: Prominent Projects Emerge, Core Developers Continue to Grow
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Cosmos Ecosystem Annual Overview: Prominent Projects Emerge, Core Developers Continue to Grow
This article will explore the significant changes, major technical updates, and standout new projects within the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023.
Author: Xangle
Translation: Felix, PANews
The Cosmos ecosystem experienced rapid growth in 2023, attracting numerous developers and projects with its unique interoperability and modular architecture, opening new frontiers for blockchain technology.
This article explores major developments, key technical upgrades, and standout new projects within the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023. It also examines technological advancements and market dynamics, and how Cosmos is redefining existing blockchain paradigms.
1. Infrastructure
1.1 Major Updates to the Cosmos SDK
Modules managed by the Cosmos SDK are primarily used for building blockchains within the Cosmos ecosystem. Below are the main SDK updates released in 2023.
Version 0.47 Update
Upgrade to CometBFT: The newly named CometBFT, a fork of the previously used consensus engine Tendermint, is now officially integrated into the Cosmos SDK. The 0.47 release contains no major changes; this update aims to help chains previously using Tendermint migrate smoothly to CometBFT.
Version 0.50 Update
ABCI 2.0: ABCI is the interface responsible for data exchange between the consensus engine and the application layer that handles various on-chain functions. The consensus engine CometBFT (formerly Tendermint) manages block production and transaction broadcasting—processes that determine transaction ordering. Due to limitations in the original ABCI design, transaction ordering within the mempool was constrained. To address this, ABCI 2.0 introduces a new process called "PrepareProposal" to define transaction order in the mempool before passing it to CometBFT.
Optimistic Execution: In earlier versions of the Cosmos SDK, all validators needed to reach consensus before executing and committing transactions to the chain. This slowed down transaction processing. To overcome this bottleneck, a feature called "Optimistic Execution" has been introduced. It allows transactions to be executed and committed without requiring agreement from all validators, thereby increasing transaction throughput.
SDK Modules: The Cosmos SDK includes various modules for application development. Previously, each module followed the SDK’s versioning system, making it difficult to track individual module update histories. With version 0.50, module versioning becomes independent, simplifying update tracking. Additionally, the data storage model Store and IAVL have been decoupled, enabling separate updates.
1.2 Cosmos on Metamask
Due to the presence of multiple chains in the Cosmos ecosystem, even with identical mnemonics, each chain has a separate address. While Keplr wallet currently integrates and manages these addresses, users must adopt a new wallet application, resulting in suboptimal user experience and higher entry barriers.
Cosmos is actively working on solutions to this issue. In this context, Metamask has implemented full support for Snap, allowing custom functionalities to be added within Metamask. It is now possible to create transactions on Cosmos-based chains, including through Leap Wallet. In other words, the technical foundation is now in place, making it easier for users familiar with EVM-based chains to transition into the Cosmos ecosystem.
Leap Wallet
1.3 MultiVM
Unfortunately, the Cosmos SDK does not natively support virtual machines for smart contracts. As a result, several projects have emerged aiming to integrate virtual machines either proven on other blockchains or specifically designed for the Cosmos ecosystem. Efforts are underway to integrate various VMs—such as EVM, WasmVM, SolanaVM, MoveVM—into the Cosmos SDK, with some receiving strong community interest. Supporting more widely adopted virtual machines will lower the barrier for dApp developers entering the Cosmos ecosystem.
2. Projects
Below are some notable and compelling projects that emerged in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023.
2.1 Celestia
Undoubtedly, the hottest project in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023 was Celestia. Celestia is a representative modular blockchain project that divides blockchain functionality into four main components:
-
Execution: The ability to process transactions and change the state of the chain.
-
Settlement: Verifying transactions processed by the computation layer.
-
Data Availability: Storing information from transactions and blocks and ensuring it remains accessible at all times.
-
Consensus: The ability to determine transaction validity and the order in which transactions are included in blocks.
Among these, Celestia focuses specifically on data availability. Its integration with the concept of "Layer 2" sparked a Rollup boom within the Cosmos ecosystem. To support this, a framework called "Rollkit" was developed, enabling ABCI communication between Celestia and the Cosmos SDK.
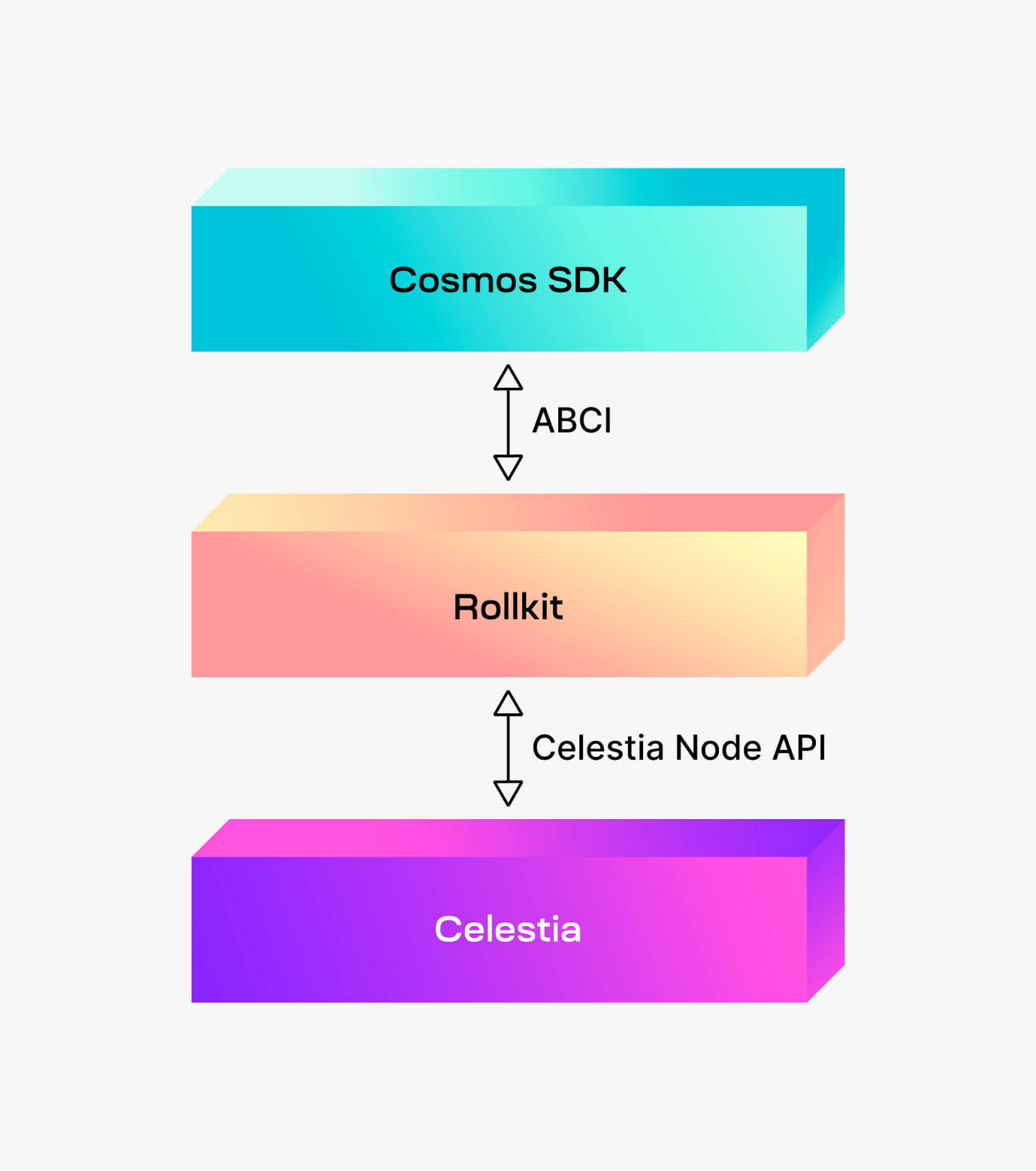
Celestia Rollkit
Rollkit replaces Cosmos’ consensus engine Tendermint (more precisely, CometBFT), enabling direct communication between Celestia and the Cosmos SDK. Rollkit facilitates Sovereign Rollups by aggregating transactions into a single block and leveraging Celestia’s consensus and data availability layers.
2.2 Skip Protocol
Skip Protocol is a project with the vision of becoming the "sovereign transaction infrastructure for sovereign blockchains." The protocol aims to enhance user experience on sovereign blockchains by making transaction ordering transparent, preventing malicious MEV, and improving network quality.
In terms of UX improvements, the project targets issues with the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. IBC enables asset transfers between different chains within Cosmos. To transfer assets via IBC, a communication "channel" must be established, with each connected chain requiring a unique ID. The image below illustrates an example of ETH being sent from Axelar to Terra2.

Additionally, Skip proposes an optimal routing algorithm for asset delivery across the Cosmos ecosystem and improves user experience by standardizing asset denomination handling.
Skip Protocol also provides various APIs useful for developing blockchains based on the Cosmos SDK, such as multi-chain transaction tracking. Skip has further proposed integrating its features directly into the Cosmos SDK, contributing to the broader ecosystem's development.
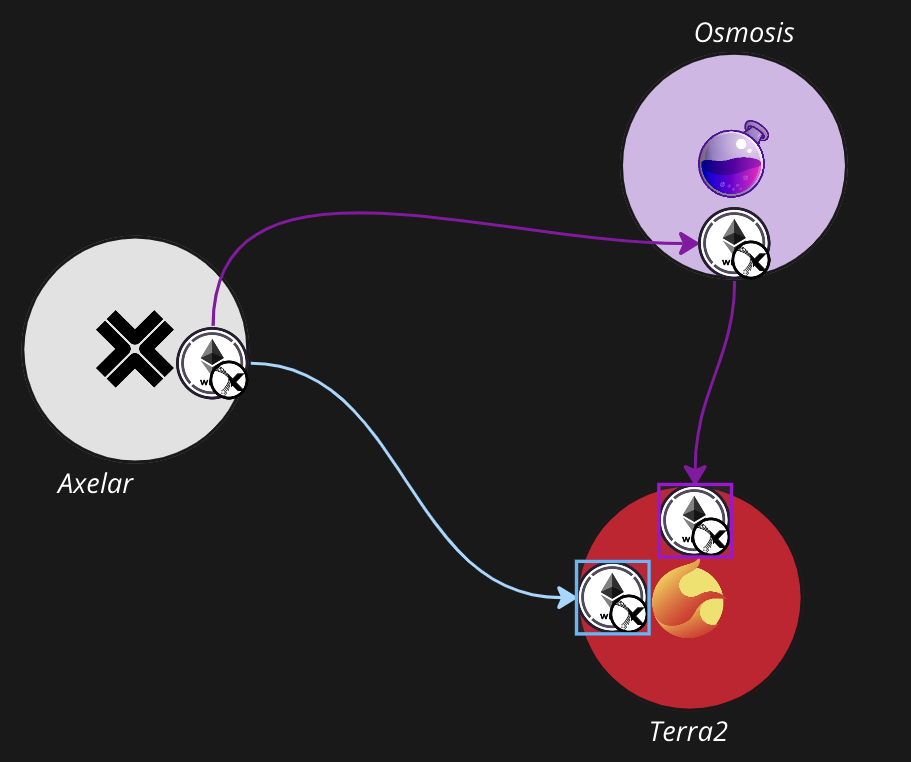
2.3 Other Projects
Sei
Sei is positioned as a chain specialized in trading, aiming to become a high-speed Layer 1 rather than a Rollup—a significant trend in blockchain development in 2023. Sei focuses on enhancing chain performance through various technological optimizations.
Injective
Injective is dedicated to building a blockchain ecosystem tailored for financial applications. Injective has formed partnerships with Figment and Binance and supports various dApps such as Helix and Hydro joining the Injective ecosystem.
dYdX
dYdX is considered one of the most successful DEXs and has successfully migrated to its own Layer 1 using the Cosmos SDK.
dYdX strengthens governance through its native token.
Stride
Stride is a liquid staking protocol similar to Lido on Ethereum. Liquid staking has traditionally been challenging in the Cosmos ecosystem due to assets being spread across multiple chains. Stride aims to enable cross-chain liquid staking in Cosmos by leveraging ICA (Interchain Accounts), ICQ (Interchain Queries), and ICS (Interchain Security).
Coreum
Coreum is an enterprise-focused Layer 1 blockchain supporting Wasm-based smart contracts, RWA tokenization, NeoBanking applications, and more.
3. On-Chain Performance
3.1 Development Activity
While overall development activity across the Cosmos network remains healthy, Q2 2023 saw the highest number of smart contract deployments (2,226) and the highest growth rate (21.4%). The number of core developers shows a steady upward trend, indicating active infrastructure development within the ecosystem.
Meanwhile, the number of smart contracts deployed in Q2 and Q3 last year was 2,226 and 1,777 respectively, compared to 1,701 in Q4. Although development activity did slow compared to the first two quarters, the level of activity remained strong, especially considering typical year-end declines.
3.2 Network Activity
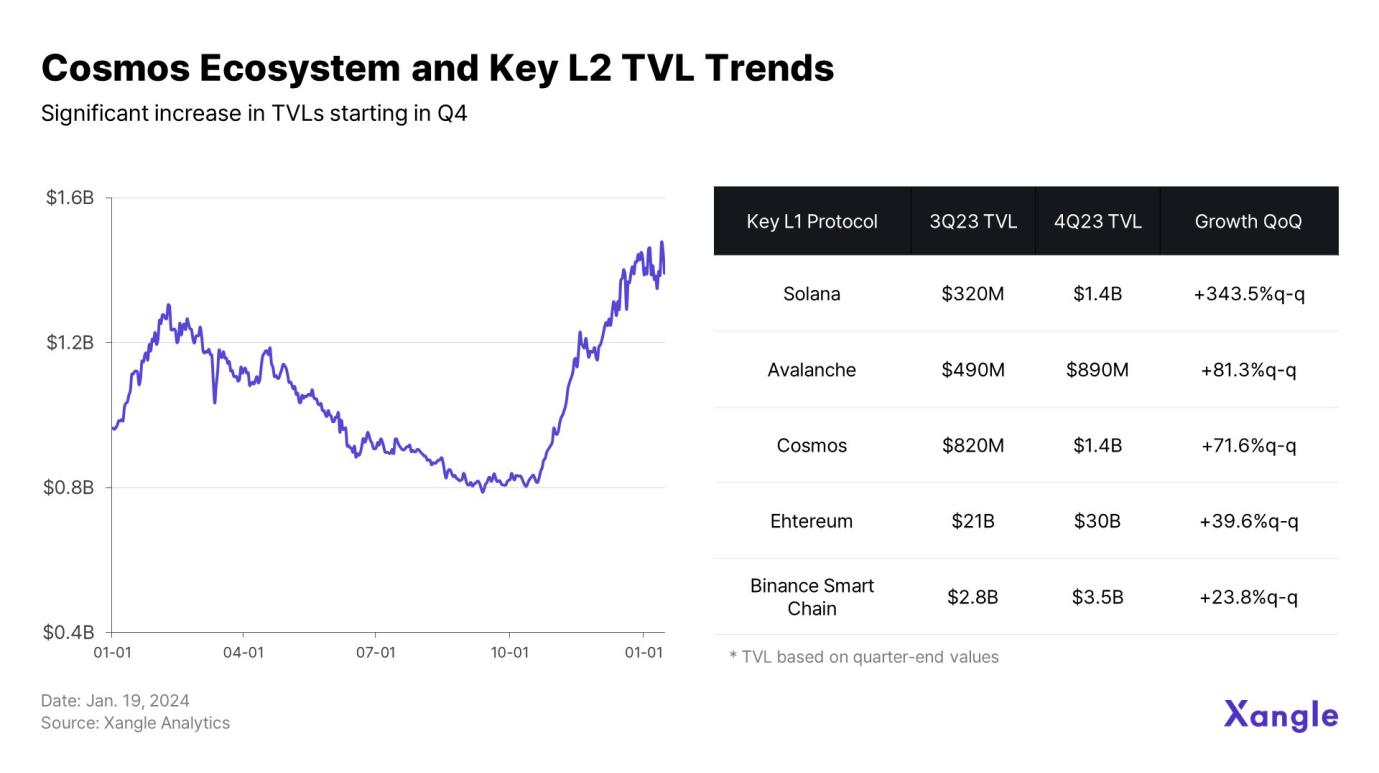
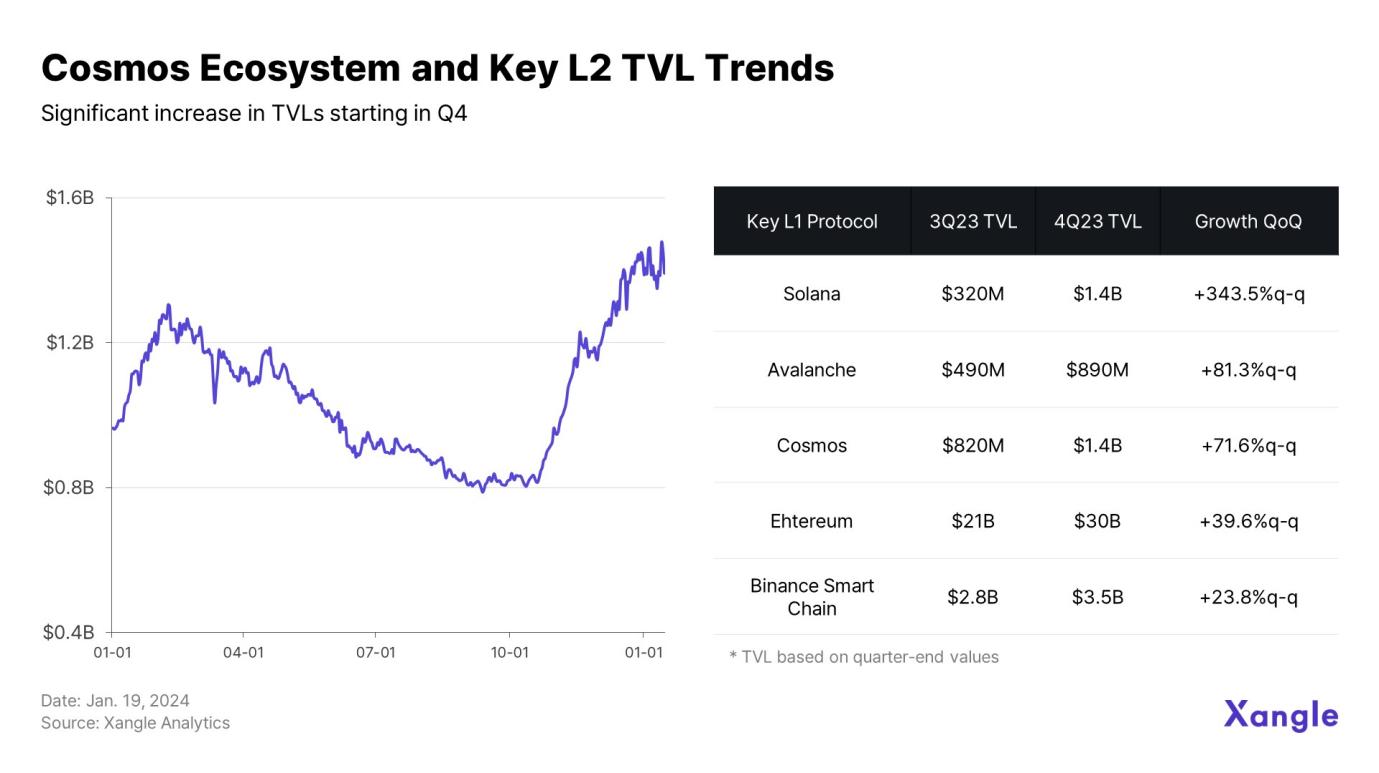
The most notable aspect of Cosmos network activity is how development momentum in Q2 and Q3 translated into ecosystem-wide growth in Q4. As shown in the chart, TVL within the Cosmos ecosystem continued to decline in Q3 but then surged significantly in Q4.
Two main factors contributed to the explosive growth in Cosmos TVL during Q4. First, mid-October saw a liquidity influx driven by the Layer 1 narrative. In the second half of the year, substantial capital flowed into Layer 1 ecosystems, with Solana, Cosmos, and Avalanche driving overall TVL growth with explosive performance.
Additionally, the developer-friendly infrastructure—including the Cosmos SDK—and the extensive interconnected blockchain network built on IBC provided tangible utility for users. Observing TVL trends reveals this is not just a temporary spike but a sustained upward trajectory. Market confidence in protocol maturity may continue to drive liquidity toward Layer 1, fueling Cosmos' growth and reducing user attrition.
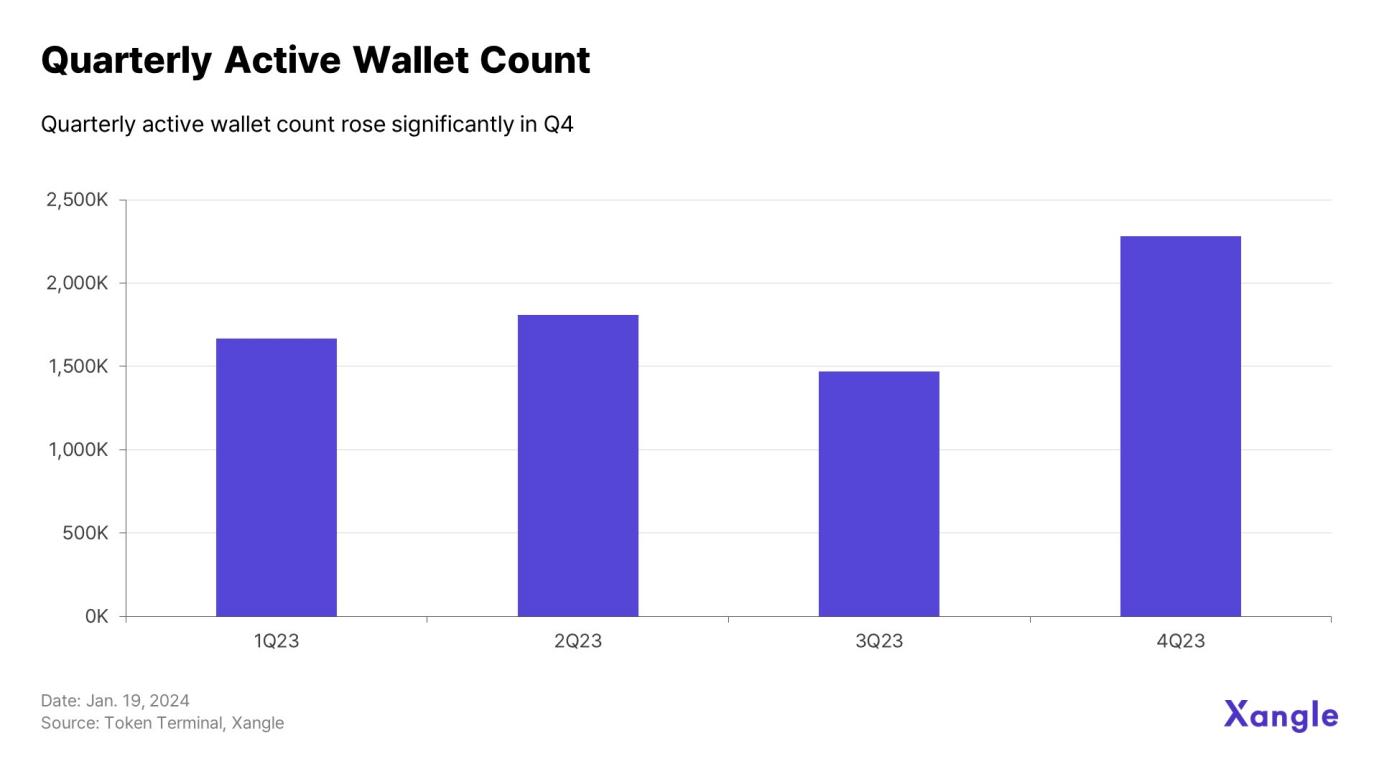
Compared to the lowest point in Q3 (1,470,050), the number of active wallets in Q4 increased by nearly 55% to 2,280,335, reflecting a vibrant ecosystem. The interoperability enabled by the Cosmos IBC ecosystem has driven increased on-chain activity.
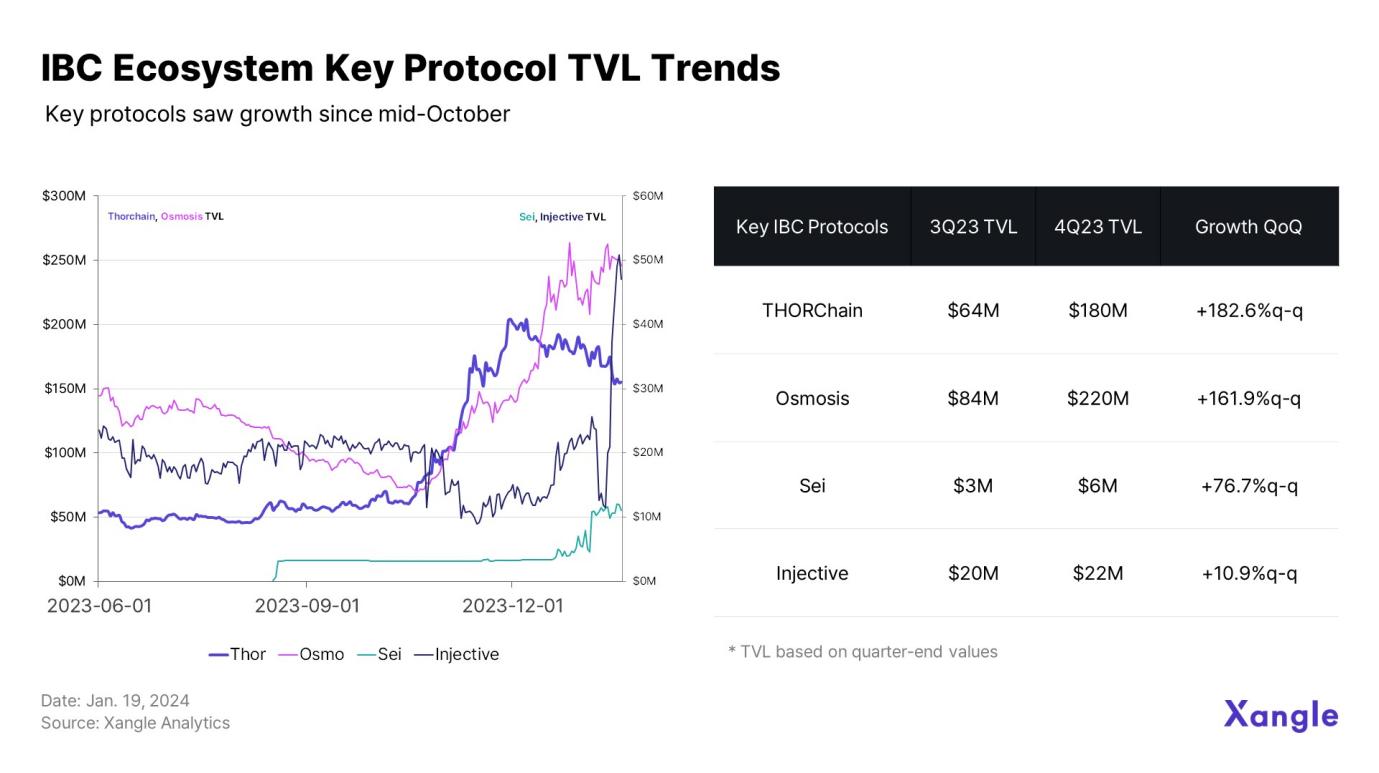
Furthermore, TVL trends among key protocols in the IBC ecosystem indicate that ongoing hype around Cosmos SDK-based protocols in the second half of the year also played a role in revitalizing the ecosystem.
3.3 Network Security
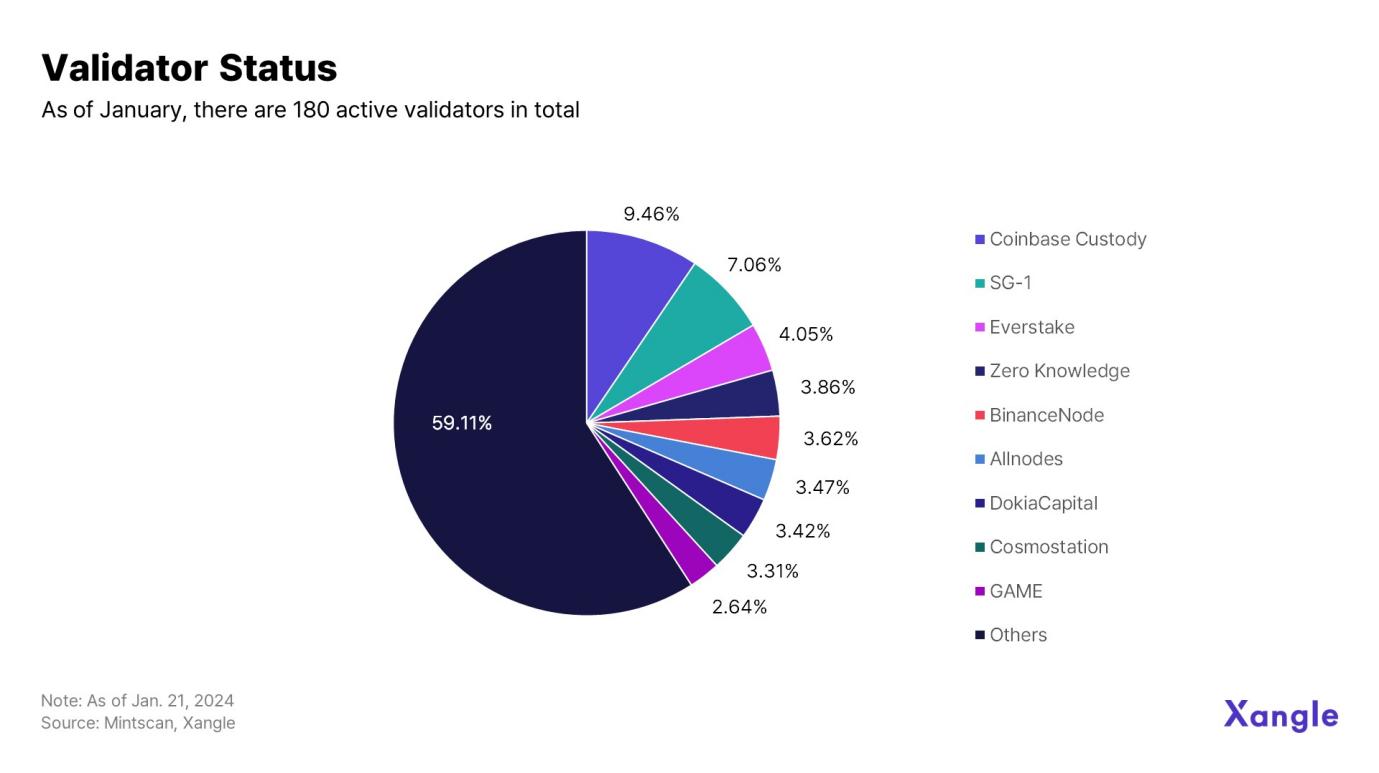
Cosmos currently has 180 active validators. The top nine validators control 40.89% of the ATOM supply. Approximately 2.44 billion ATOM are staked on Cosmos, representing about 65% of the total supply.
4. Conclusion
2023 was a landmark year for the Cosmos ecosystem, witnessing significant developments and transformations. These changes demonstrate that Cosmos is not merely a niche within blockchain technology but a driving force behind innovation across the entire blockchain landscape.
Projects like Celestia, Skip Protocol, and others highlight the diversity, flexibility, and continuous evolution of the Cosmos ecosystem. They are pioneering new use cases for blockchain technology and helping build more efficient, user-friendly environments.
The growth and maturation of the Cosmos ecosystem have heightened excitement about the future of blockchain technology, opening doors to new opportunities for developers, users, and investors alike, and paving the way for sustained innovation in the years ahead. The Cosmos ecosystem is expected to maintain this positive momentum, with new technical challenges and opportunities emerging along the way.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















