Deep Dive into Autonolas: Off-chain Services Powered by AI Agents, Product and Economic Model Explained
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Deep Dive into Autonolas: Off-chain Services Powered by AI Agents, Product and Economic Model Explained
Do AI agents really need blockchain?
Author: Thomas
Translation: TechFlow
People seem extremely bullish on Autonolas—why is that? Is it simply because it's an "AI" project?
Or is it because AI services will transform our lives, and Autonolas ensures that “we” retain control over AI services built both on-chain and off-chain? After days of research, I’ve developed a clearer understanding of this project.

To understand Autonolas, we need to grasp the vision of its CEO, David: he recognizes the immense potential of AI services, but also the threats they pose. AI services will liberate people from routine cognitive labor, forcing them to seek new, meaningful forms of work.
However, the value created by these new fleets of AI will be enormous, and any single entity would struggle to manage it without introducing systemic risks to societal balance. If one entity controls what gets deployed and for what purpose, Orwellian scenarios could quickly emerge.

David’s solution: collectively owned AI.
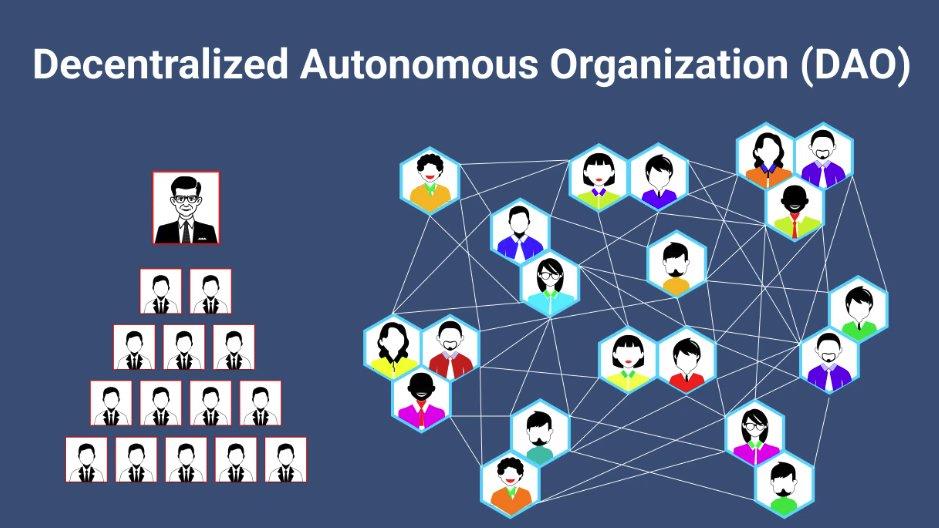
So, you mean something like a DAO?
Sort of. They’re similar. Both operate collectively, develop in a decentralized way, and feature democratized governance.
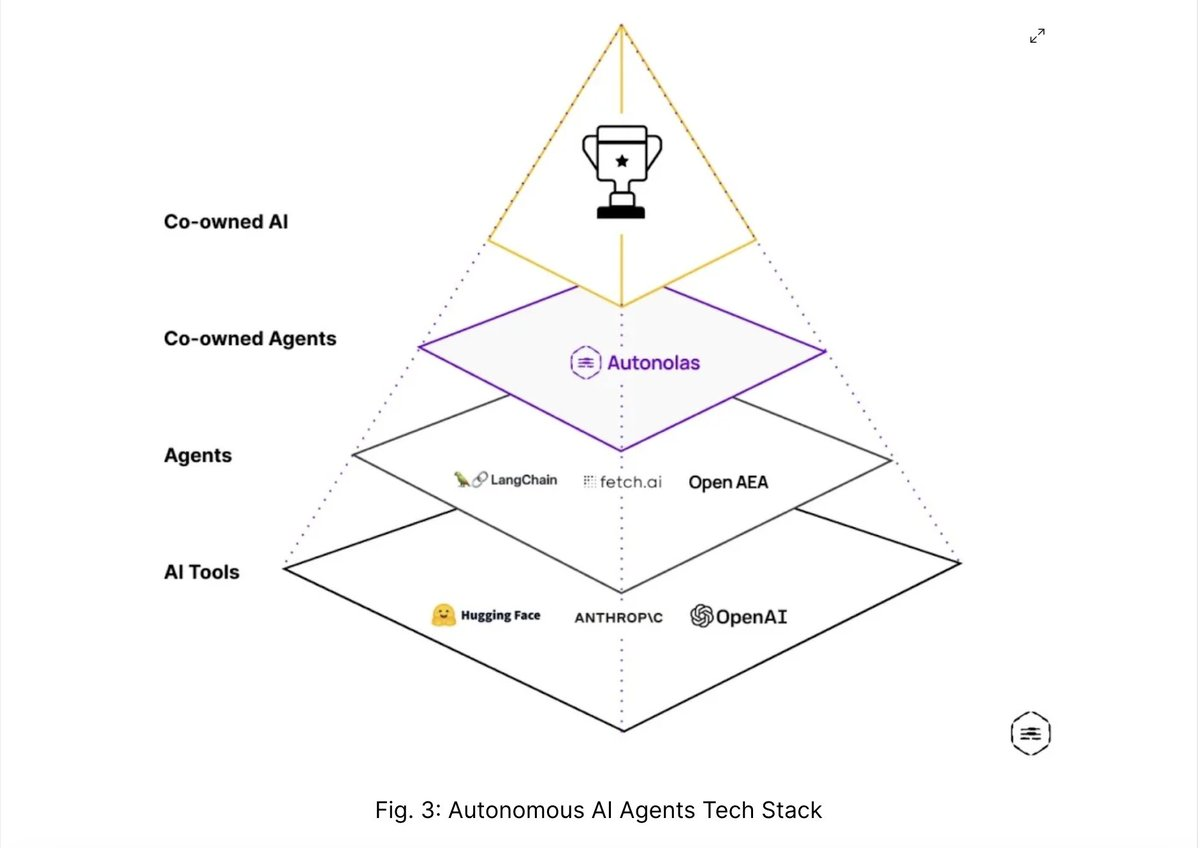
Yet, in their current form, DAOs are neither autonomous nor truly decentralized.
Why?
Because DAOs rely on smart contracts, and smart contracts depend on transactions to function.
Even if a smart contract represents an AI agent, you still need real-world entities (i.e., people) to sign transactions on the blockchain.
Smart contracts are excellent for simple transactional tasks. However, they cannot: perform computationally expensive processing; run continuously; or interact with the off-chain world.
Moreover, crypto protocols primarily do two things:
-
Launch their own chain to solve problems faced by other chains
-
Add functionality to existing chains (e.g., DEXs).

Both approaches leave a significant gap in technologies that bridge the on-chain and off-chain worlds—and this is where $OLAS comes in.

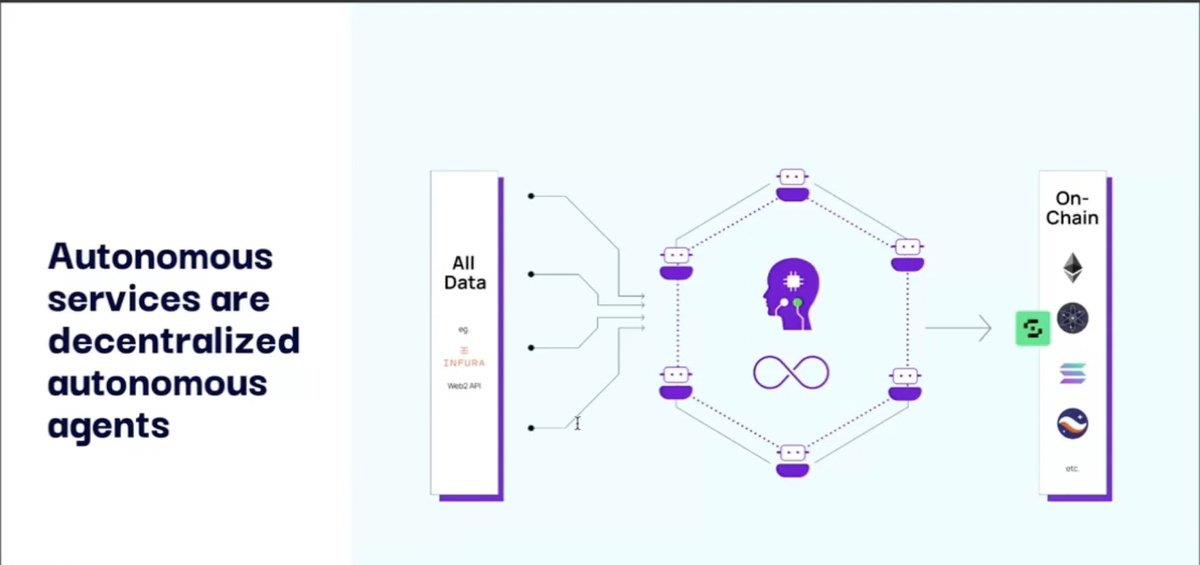
The goal of the $OLAS protocol is to unlock the potential of off-chain services—autonomous services that run off-chain but interact both on-chain and off-chain, without restrictions. These autonomous services are groups of AI agents forming networks to create (autonomous) services. They: run continuously, act autonomously, interact with the world beyond blockchains, and execute complex logic.
Crucially, they don’t require us to operate. Before Autonolas, this was impossible.

By the way, you might be wondering: what exactly is an AI agent? Here’s the definition:
“An artificial intelligence that acts intelligently by perceiving its environment and taking autonomous actions to achieve goals.”

Back to Autonolas. The Autonolas tech stack includes:
-
Autonomous services (as described above).
-
Composable autonomous applications.
-
On-chain protocols that protect agent services and incentivize development.
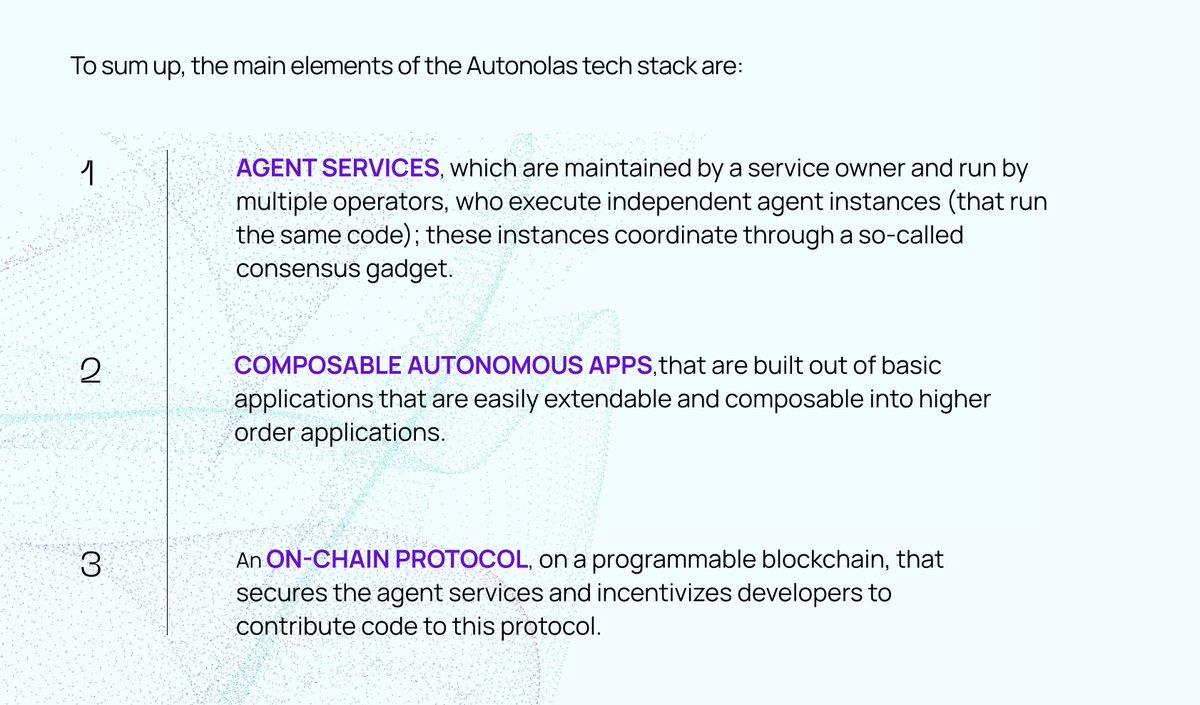
Let’s go through each one.
Agent Services
The AI agents composing these services can pull data from any AI model in the world. Every GPT, LMM, or subnet is included (yes, including $TAO). Through service coordination, specific models are assigned to certain agents.
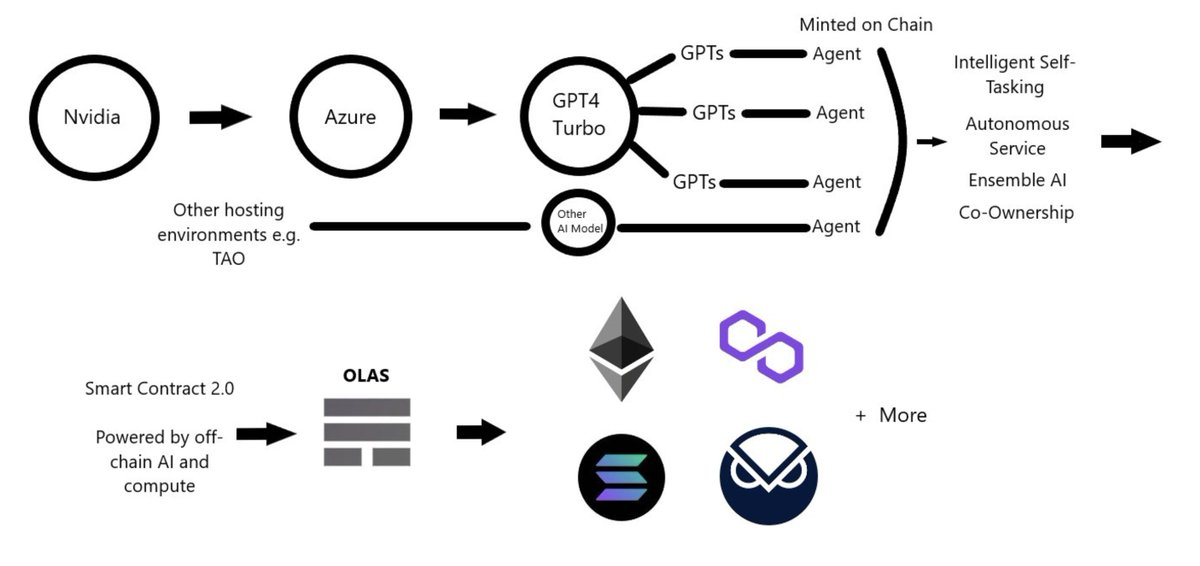
Selection depends on several factors such as economic feasibility, availability, and performance. Each agent can use different data sources (making it even more decentralized). In some cases, knowledge graphs are distributed via Origin Trail or through The Graph using GraphQL.
Agents can be used to perform many Web3 tasks:
1) Oracles – Agents can supply accurate data to smart contracts.
2) Autonomous Keeper Services (AKS) – Adding off-chain computation and reasoning to DeFi.
3) Through ACN, AI agents can handle team communication tasks.
Composable Autonomous Applications
The tech stack is designed to encourage composability.
Developers can build basic apps that serve as building blocks for more complex AI agents. Everything is open-source.
On-Chain Protocols
Autonolas has built an on-chain protocol (a set of smart contracts) that functions like an app store: it allows developers to register and monetize their services. It enables these services to interact economically and lets members vote on rules.

Importantly, although DAOs are a primary focus, these services can also be deployed in the “real” world. Imagine a farming station using IoT sensors, or AI agents using data to trigger irrigation tasks.

Back to DAOs. DAOs have internal operations (e.g., payroll, governance) and service delivery (e.g., yield aggregators).
AI agents can perform all these tasks better, faster, and more autonomously.

What other types of services can AI agents improve?
-
Managing liquidity pools
-
Prediction markets
-
Asset acquisition
-
Oracles and cross-chain bridges.
By leveraging AI, Autonolas enables the creation of services that fundamentally enhance performance.

Let’s take prediction markets as an example.
With Autonolas, you can create AI agents that scan entities using GPT-4 to improve your win rate. There are already AI agents achieving 88% win rates, and they keep improving...
Future use case:
-
Using Autonolas, an insurance service is created for farmers
-
A group begins running AI agents executing this logic
-
Farmers register for the service and pay an annual fee
-
Due to seasonal losses, a farmer files a claim
-
Each agent on the network pulls climate data from different AI models trained by professionals
-
Agents share data, validate, and vote to reach consensus using ACN and MAS
-
If the claim matches the data, payment is made
This use case illustrates what makes Autonolas unique.
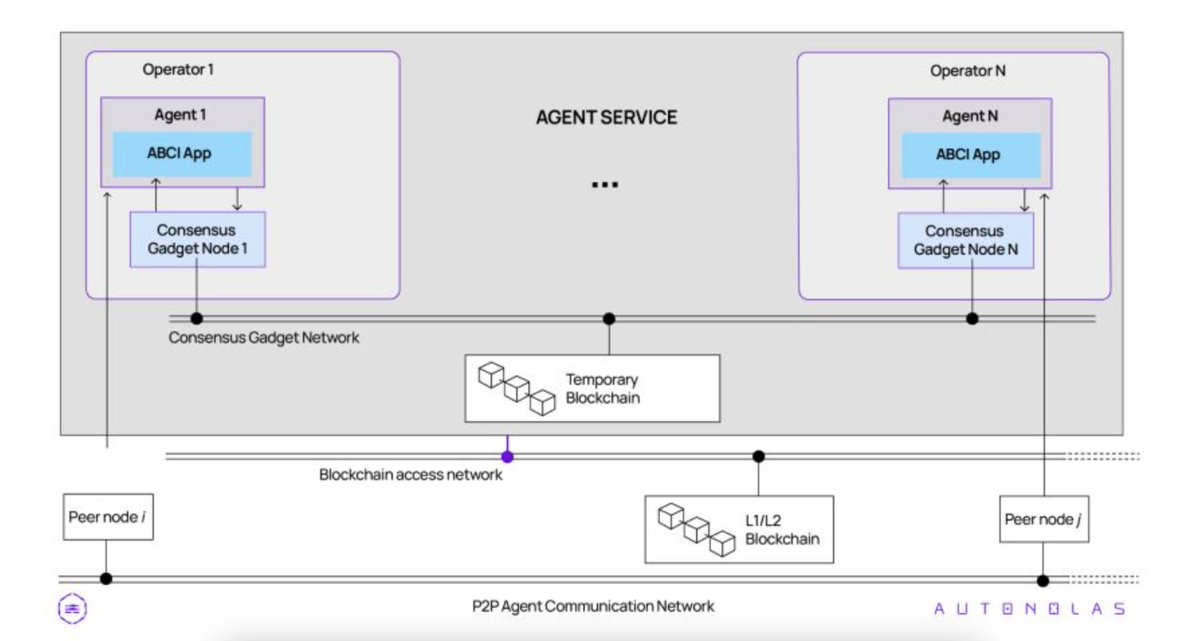
Open Autonomy is a new standardized framework for creating autonomous services. It enables blockchains and decentralized agent services to work together as multi-agent systems (MAS).
Fun fact: CEO David created the first open-source, crypto-friendly MAS network called the open-aea framework. This framework enables AI agents to communicate, interact, and implement business logic with blockchains and smart contracts.
Agent communication happens through a message-based Agent Communication Network (ACN), with transactions always targeting a wallet address. This process is enabled via a temporary blockchain powered by a Consensus Gadget (CG). Currently, Tendermint nodes serve as CGs.
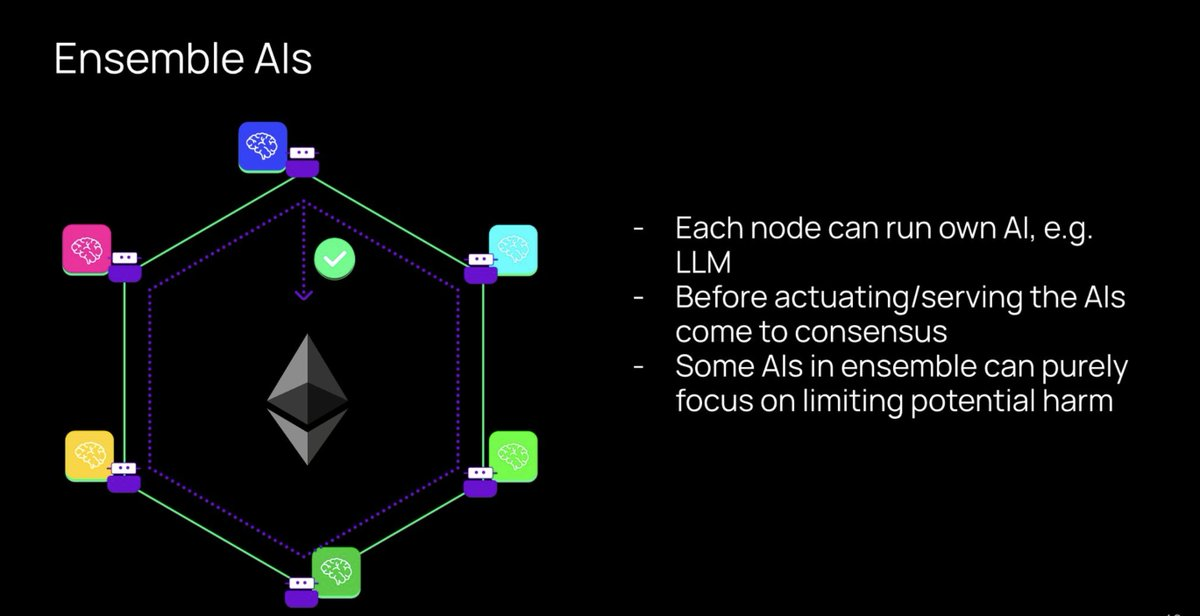
Finally, Autonolas enables Ensemble AI and Networked AI.
Ensemble AI: Within a single service, each node can run its own AI (LLMs, etc.). Each service can consist of multiple AI models. They communicate and reach consensus through combined intelligence.
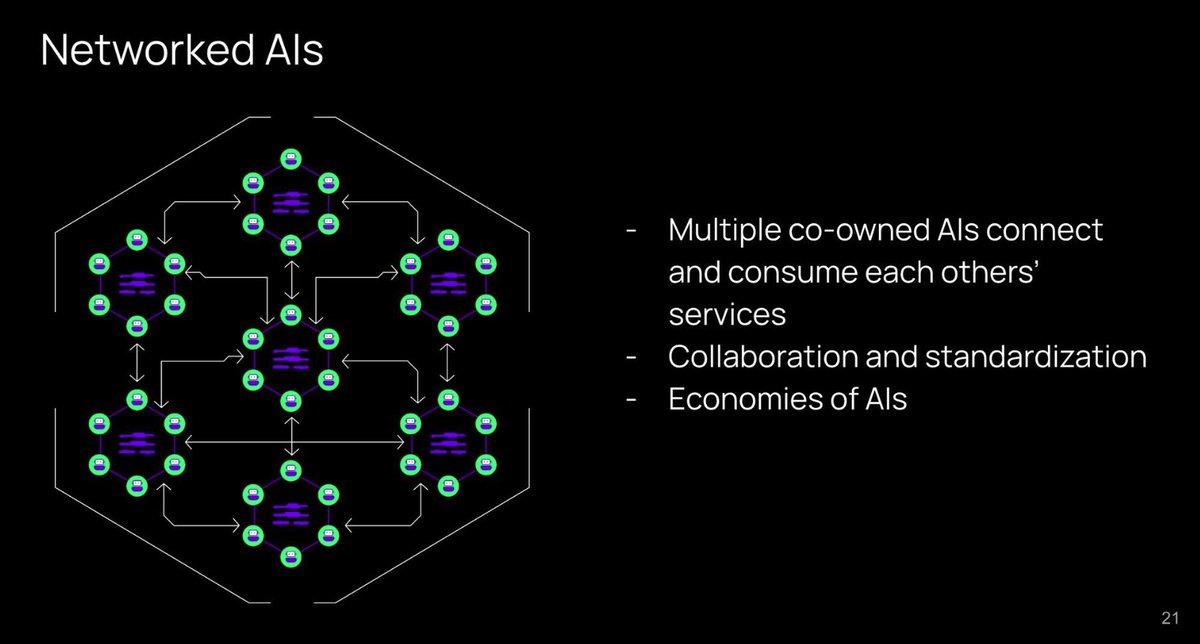
Networked AI: Services themselves can utilize each other’s services (i.e., leverage each other’s intelligence). This opens the door to collaboration and standardization.
But you might ask: do AI agents really need blockchain?
Well, yes.
Why?
Because it enables agent services to scale. Centralized AI agents relying on bank-stored allowances cannot scale effectively. Not to mention monetary censorship that arises from centralized control.
Therefore, smart contracts are necessary to abstract business logic and eliminate the need for human oversight. Thanks to the Open Autonomy framework—and because AI agents have their own vaults and public addresses—scaling becomes possible. Also: no monetary censorship!
Adoption
The number of transactions generated by AI agents has already exceeded 200,000.
Secondly, use cases include:
▶️ Prediction market agents (Omen Prediction Markets)
▶️ Smart funds (Balancer)
▶️ Wallet management (Safe)

Team
CEO David Minarsch is a Cambridge graduate with a PhD, who established the AI agent division at Fetch.ai. At Valory, the company behind $OLAS, there are currently 16 employees.

Tokenomics
The tokenomics are complex and innovative. The CEO has a background in game theory, which shows in the design.
The technology is open-source and needs developers. But developers are scarce.
Thus, Autonolas has created a flywheel to attract them.
First, let’s explain this flywheel, designed to incentivize developers to create useful code.
Developers write code and register it as an NFT (DAO decides whether it passes). Then, this code can be used as a Lego-like component within autonomous services.
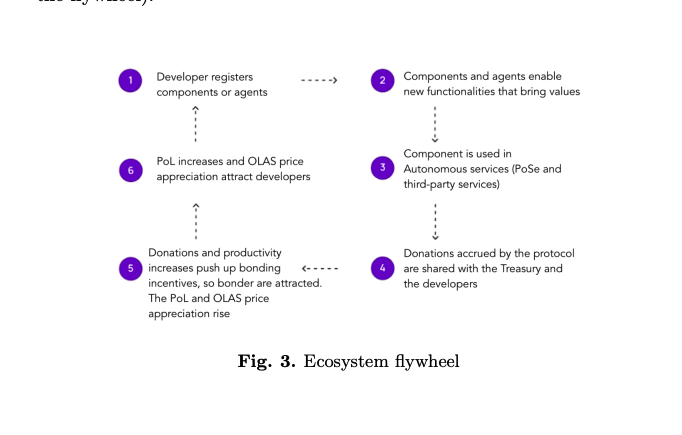
Services receive donations when used. Thanks to the NFT, contributions can be traced back to the original developer, who then receives rewards through (code, capital) distribution.
These rewards account for 10% of all inflation Autonolas will release.
Another goal of Autonolas is to pair code with capital.
They achieve this by using a bonding mechanism to grow capital in the form of Protocol-Owned Liquidity.
$OLAS holders can provide liquidity on a DEX and stake those LP tokens at a discount for $OLAS.
The discount is determined by the difference between the permanent staking market value and the LP’s current market value. If asset prices crash, the bond rate turns negative, artificially curbing inflation.
The entire flow of funds works as follows:
Autonomous services are minted → Users add funds to services → veOLAS holders donate to services → Useful code contributors are rewarded → Developers continue building new code.
Autonolas has three main revenue targets:
-
Protocol-owned services: profits from donations
-
Protocol-owned liquidity: all profits go into the DAO treasury
-
Voluntary donations from third-party services.
$OLAS Token Utility
-
DAO governance. Typically, this utility isn’t very strong. But in Autonolas, it’s crucial—it determines which AIs get built.
-
Can be staked to gain whitelist access and additional incentive rewards
-
Used to purchase LP tokens via bonds.
All three support long-term growth of $OLAS.
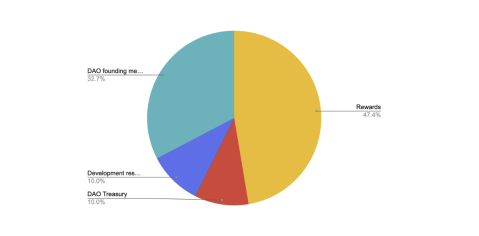
In the token distribution, the team allocation percentage is high. However, the team’s tokens are locked until 2026. Moreover, the team is not VC-backed and won’t rush to dump tokens upon unlocking.
Roadmap
Autonolas is currently focused on:
-
Build-A-PoSe: enabling the creation of protocol-owned services
-
Triple Lock: a protocol upgrade improving bonding, developer rewards, and staking
-
Expanding the network via AIP-1
-
Ecosystem partner network.

Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News