A Comprehensive Guide to the Principles and Current Market Landscape of Layer 3
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

A Comprehensive Guide to the Principles and Current Market Landscape of Layer 3
Layer 3 protocols can address various issues such as scalability, interoperability, and customization.
Author: Hwee Yan
Translation: TechFlow
What Are Layer 3 Protocols?
Layer 3 protocols are built on top of Layer 2 to provide enhanced scalability, enabling developers to create customized, application-specific blockchains tailored to their needs.
Key Takeaways
-
Layer 3 protocols operate on Layer 2 and are designed to host application-specific decentralized applications (dApps).
-
Layer 3 protocols address various challenges such as scalability, interoperability, and customization.
-
Examples of Layer 3 protocols include Orbs, Arbitrum Orbit, and zkSync Hyperchains.
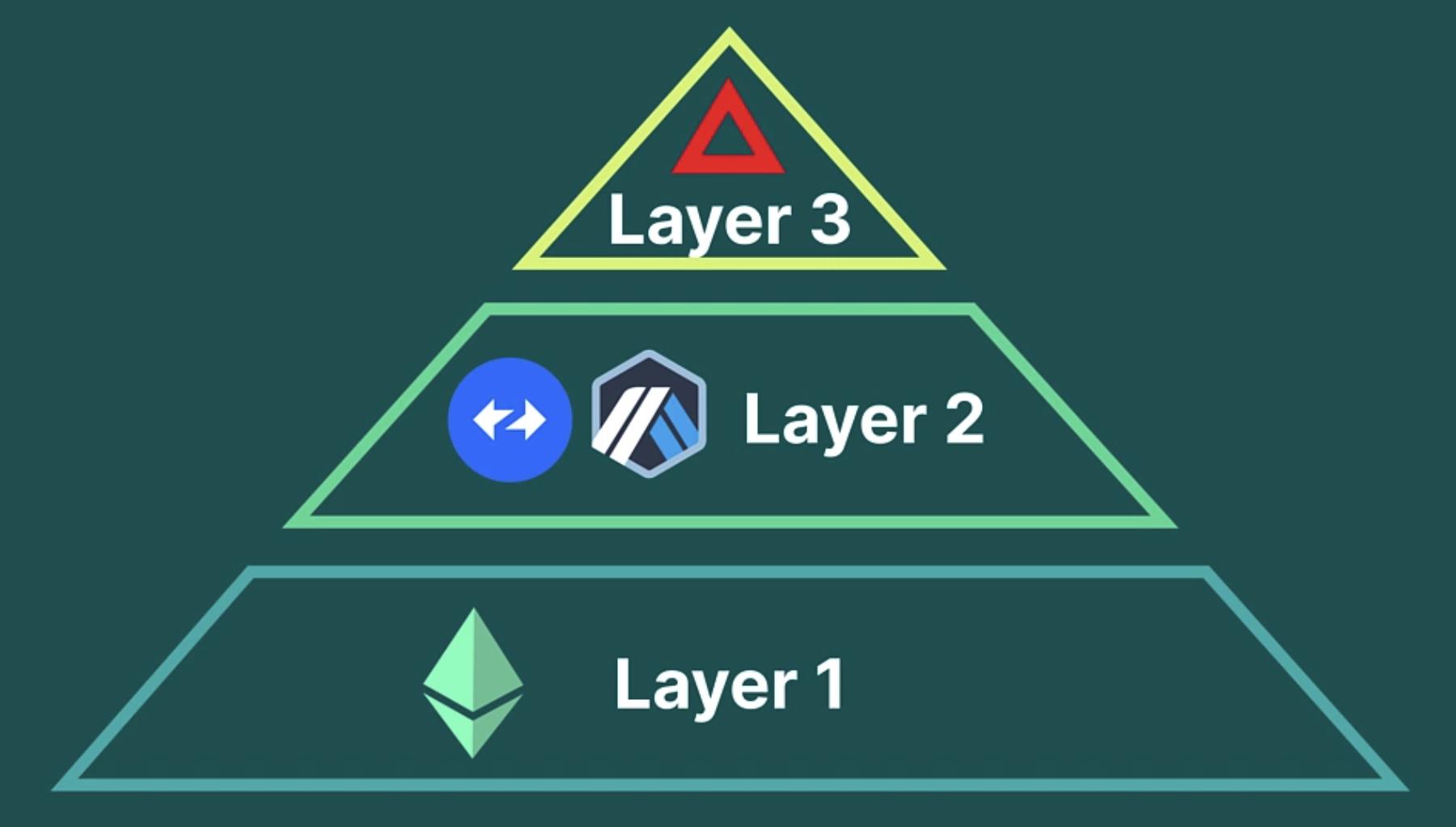
How Do L1, L2, and L3 Work Together?
A Layer 1 blockchain is the foundational layer where blocks are added and transactions finalized. However, Layer 1 blockchains face the blockchain trilemma—they cannot simultaneously achieve optimal levels of scalability, decentralization, and security. Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum prioritize decentralization and security over scalability, resulting in slower transaction speeds as network usage increases.
This is where Layer 2 solutions come into play to address scalability. Layer 2s are off-chain vertical scaling solutions that run on top of Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum, offering improved scalability with faster transaction speeds and lower gas fees. They often use rollups or validation mechanisms, as seen with Polygon 2.0. Many Layer 2 solutions, including Polygon, zkSync, and Arbitrum, have launched tools enabling developers to build application-specific chains atop Layer 2—ushering in the era of Layer 3.
Layer 3 refers to advanced protocols built on existing Layer 2 solutions, providing interoperability and specialized application functionality. This means Layer 3 networks are highly customizable, capable of meeting specific developer needs—such as enhancing privacy, supporting high-volume transactions—while still inheriting the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain. Currently, most Layer 3s are built on Ethereum, and at the time of writing, some blockchains (like Bitcoin) are not suitable for hosting Layer 3 applications.
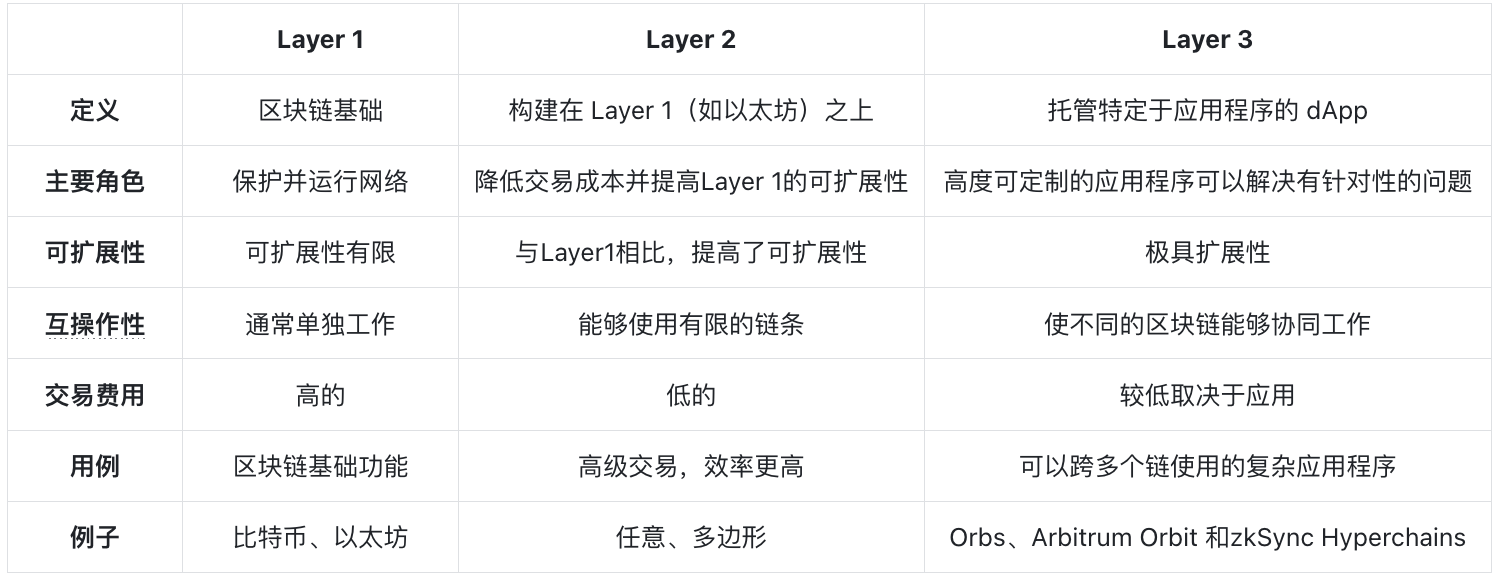
What Problems Can Layer 3 Solve?
Now that we understand how Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 work together, let’s examine Layer 3 more closely and how it further extends blockchain capabilities.
Scalability
Layer 3 aims to enhance scalability beyond the current capabilities of Layer 1 and Layer 2, achieving extremely high scalability. As a result, Layer 3 networks can handle significantly higher transaction volumes while supporting more complex applications.
Support for Complex dApps
Layer 3 provides the necessary infrastructure to develop more sophisticated decentralized applications requiring advanced features. This could lead to better web design, inclusion of advanced functionalities within apps, and improved usability for non-technical users. Depending on developer requirements, Layer 3 also enables more complex smart contract designs that would be unfeasible under the limited scalability of Layer 1 and Layer 2.
Blockchain Interoperability
Layer 3 also addresses interoperability. It can act as a bridge between different blockchains, allowing transactions and data to flow across platforms. This means Layer 3 dApps can connect to multiple blockchains such as Ethereum and Solana.
Customization
Layer 3 can be customized according to developers’ unique needs. For example, developers can implement application-specific mechanisms that allow only private transactions and contracts, disclosing only partial data. Thanks to its high degree of customizability, developers can tailor governance models, rules, and functions of their dApps.
Arbitrum Orbit allows developers to customize various aspects of their chain. For instance, developers can choose which tokens are accepted as transaction fees on their chain. This flexibility enables them to select—and potentially include—a platform’s native token, allowing developers to tailor the functionality of their decentralized applications (dApps) to their specific needs.
Additionally, developers can optimize their dApp to ensure users experience more consistent and predictable gas prices. They can also launch their own blockchain networks with specific features—for example, Nitro-powered blockchain networks from Arbitrum and Stylus for EVM+ compatibility. Other customizable features offered by Arbitrum Orbit include privacy settings, permission controls, fee tokens, governance, and more.
Cost Efficiency
Since Layer 3 networks process certain transactions and operations off-chain, this helps reduce network congestion and significantly lowers transaction fees. This cost efficiency reduces entry barriers, making it easier for both developers and users to adopt.
For example, the Xai Network is a gaming-focused network built on Arbitrum’s Layer 3. Xai introduces parallel processing to boost efficiency and scalability while further reducing costs.
Accessibility
Layer 3 can also become more accessible and easier to deploy. For example, Arbitrum Orbit allows anyone to build and deploy their own Layer 3 network on Arbitrum Nitro without requiring approval. In contrast, launching a Layer 2 requires proposals around trust models and full decentralization plans.
Use Cases of Layer 3
Now that we’ve explored the problems Layer 3 solves, here are some potential use cases:
Gaming Applications
One use case for Layer 3 is blockchain gaming. Running on Layer 3 allows applications to operate on dedicated blockchains, enabling faster processing of large transaction volumes. This is particularly important for gaming applications, helping developers maintain smooth in-game experiences for users.
Gaming applications often involve numerous microtransactions, which can be costly. Running these on Layer 3 allows developers to ensure cost efficiency for users due to lower transaction fees.
Decentralized Finance Applications
Another potential use case is decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Running DeFi apps on Layer 3 is ideal because it allows customization based on application needs. Developers can tailor privacy settings and other functionalities. Additionally, Layer 3's high scalability ensures rapid processing of large transaction volumes, crucial for real-time trading. Layer 3 also enables interoperability across various blockchain networks, allowing users to transfer assets across different ecosystems.
Examples of Layer 3
While Layer 3 is still considered a relatively new development in crypto, here are some notable projects:
Orbs
Orbs is a Layer 3 blockchain that works alongside existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, focusing on solving Ethereum’s scalability challenges. According to its website, Orbs positions its Layer 3 as “enhanced execution,” allowing developers to build smart contracts that run as a decentralized serverless cloud.
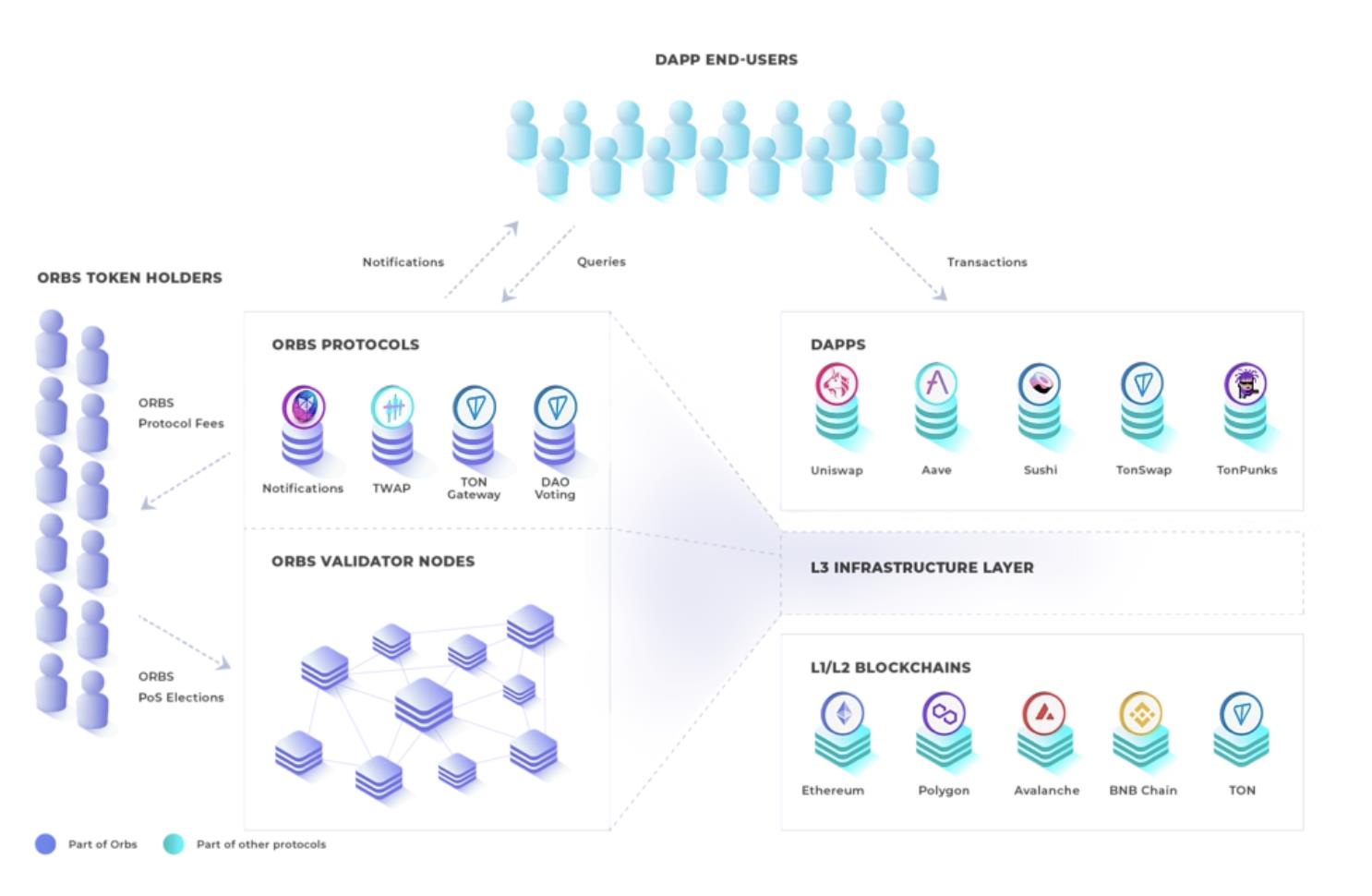
Source: Orbs
This means developers can write and deploy smart contracts on Orbs’ own decentralized network without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It also offers the convenience of not having to maintain physical servers. Currently, Orbs is compatible with several Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Polygon.
Arbitrum Orbit
In 2023, the Arbitrum Foundation launched a new feature—Arbitrum Orbit—envisioned as a Layer 3 blockchain built on the Arbitrum Nitro platform. Beyond lower transaction costs and improved scalability, developers can now create their own self-governed, dedicated blockchains on the Arbitrum Nitro platform, enabling customized blockchains tailored to specific needs.
zkSync Hyperchains
Launched by the zkSync team, zkSync Hyperchains represent a Layer 3 solution that uses Layer 2 for settlement. Powered by the same zkEVM engine available on ZK Stack, all ZKP circuits remain consistent, and security from Layer 1 is inherited regardless of deployment. A key benefit is faster message passing between Layer 3 chains settled on the same Layer 2, enabling greater interoperability across the broader ecosystem.

Source: zkSync Era
Final Thoughts
The development of Layer 3 is an exciting innovation in the crypto space. By combining the best aspects of Layer 1 and Layer 2, it improves upon previous capabilities—making networks more scalable and secure. Still, it’s important to remember that each layer plays a vital role in the blockchain ecosystem without competing against one another. While Layer 3 is still in development, it’s clear that it will play a key role in shaping how we leverage blockchain technology in the future, making blockchains better equipped to handle high transaction volumes.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















