
Analyzing the Polygon zkEVM Ecosystem: Slow but Steady
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Analyzing the Polygon zkEVM Ecosystem: Slow but Steady
The main technical difference between Polygon zkEVM and other ZK rollup networks lies in its high EVM compatibility.
Written by: 100y
Translated by: TechFlow
Disclaimer: This article is sponsored by the Polygon Foundation. It is for general information purposes only and does not constitute legal, business, investment, or tax advice. It should not be relied upon as the basis for any investment decisions, nor should it be used for accounting, legal, or tax guidance. References to specific assets or securities are for illustrative purposes only and do not represent recommendations or endorsements. The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and do not reflect the opinions of any affiliated institutions, organizations, or individuals. Opinions herein are subject to change without notice.

1. Introduction
In 2022, many ZK rollup networks entered fierce competition. Today, numerous such networks have launched their mainnets and are actively developing their ecosystems. On March 23, 2023, Arbitrum's successful airdrop prompted users to migrate to ZK rollups in hopes of benefiting from future token distributions. This shift has been particularly evident on zkSync Era, StarkNet, and other ZK rollup networks that have yet to launch their own tokens.
Unlike other emerging ZK rollup networks without tokens, one network has received relatively less attention despite its technically stable infrastructure and developer-friendly environment—Polygon zkEVM. Developed by the Polygon Foundation and formerly known as Polygon Hermez, Polygon zkEVM stands out among other ZK rollups primarily due to its high EVM compatibility.
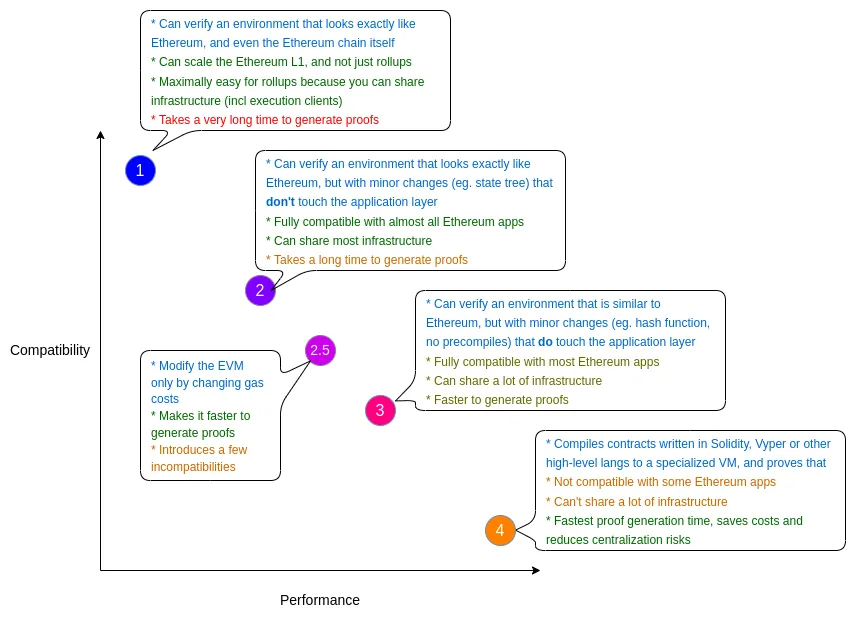
While other ZK rollup projects like StarkNet and zkSync Era build custom virtual machines, translating Solidity into zero-knowledge-friendly languages before compiling into bytecode, Polygon zkEVM supports Ethereum opcodes directly. As a result, Polygon zkEVM may not achieve the same level of scalability as other ZK rollups, but it offers developers a more accessible environment where existing Solidity code can be reused to build dApps seamlessly.

In Polygon zkEVM, ETH is used as gas, while MATIC serves as the incentive token for Sequencers and Aggregators—the roles responsible for ordering transactions into batches and generating ZKPs (zero-knowledge proofs) for those batches, respectively. Since both tokens are already issued, many users believe Polygon zkEVM won't conduct an airdrop, which initially contributed to its lower activity compared to other networks. However, recent trends show rapid growth in user numbers and TVL (Total Value Locked), driven by several key factors.
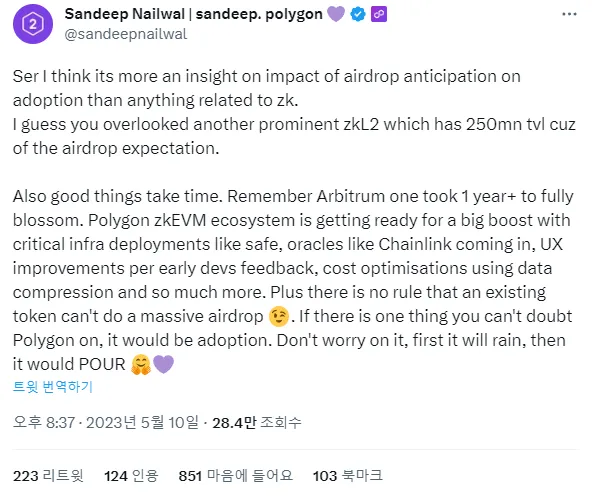
The first and most compelling reason is a tweet from Polygon co-founder Sandeep Nailwal. In response to criticism mocking Polygon zkEVM’s low TVL, Sandeep posted the image above, including the phrase “there is no rule stating existing tokens cannot receive large airdrops.” Following this statement, many users began actively using Polygon zkEVM in anticipation of a potential token drop.
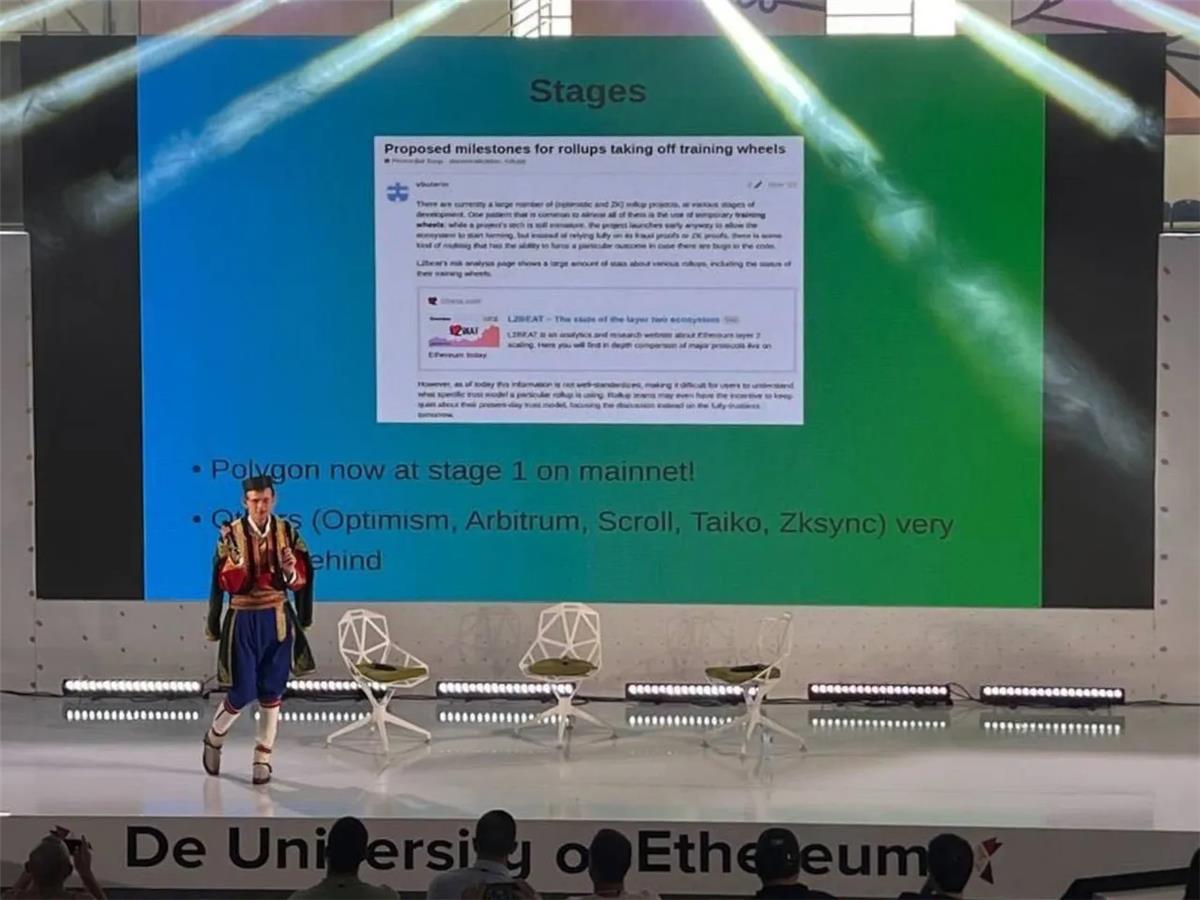
A second factor was Vitalik Buterin mentioning Polygon zkEVM during a workshop at EDCON 2023. Previously, Vitalik had published an article on Ethereum Magicians outlining milestones Rollup networks must achieve, categorizing them into Stages 0, 1, and 2. During the workshop, he stated that Polygon zkEVM has reached Stage 1, whereas competing networks have not. This achievement brought significant attention to Polygon zkEVM. Notably, reaching Stage 1 requires not only a working proof system (such as fraud proofs or validity proofs) but also safeguards for upgrading Rollup smart contracts—unlike Stage 0.
Recently, Polygon zkEVM has attracted increasing interest, with TVL surging from around $2 million to $25 million within less than a month—an impressive tenfold increase. Although the ecosystem is still in its infancy, it shows strong momentum. This article provides an overview of the dApps currently active within the Polygon zkEVM ecosystem—a nascent yet rapidly evolving landscape.
2. Polygon zkEVM Ecosystem
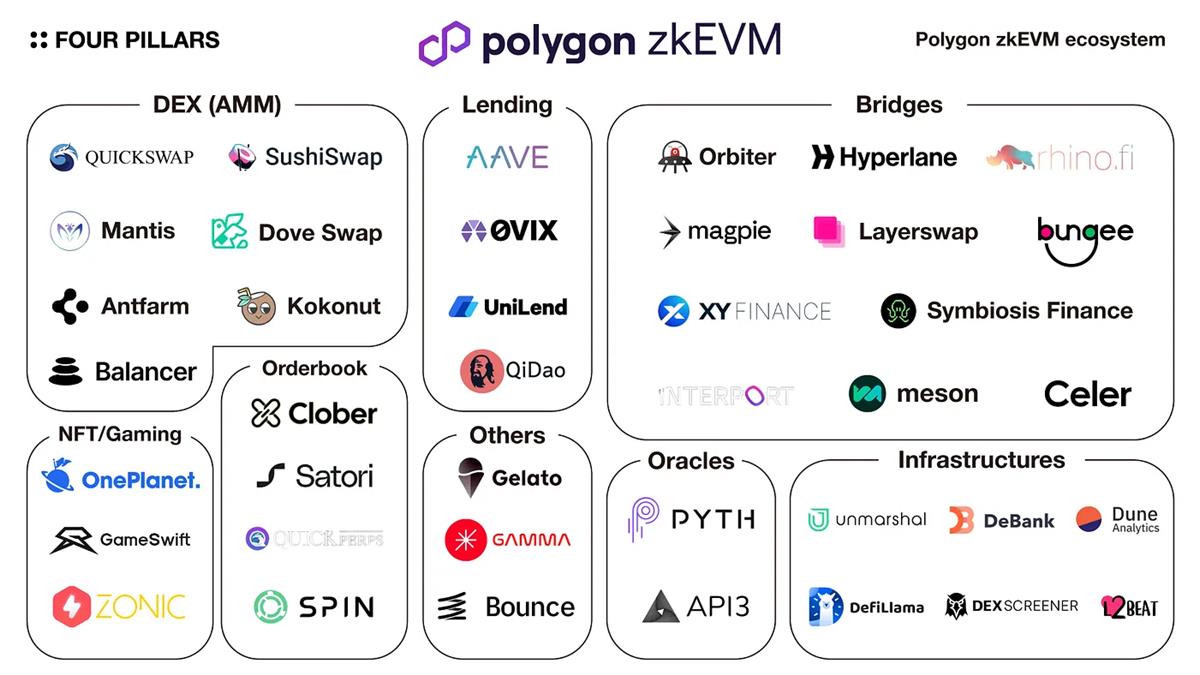
2.1 DeFi (AMM DEX)
2.1.1 Quickswap

Quickswap is the leading AMM DEX in the Polygon ecosystem, supporting Polygon, Dogechain, and Polygon zkEVM networks. It offers CPMM-based (x*y=k) AMM services along with a concentrated liquidity model similar to Uniswap V3. Additionally, Quickswap has launched a new service on Polygon zkEVM: perpetual futures trading. Leveraging the high scalability of Polygon zkEVM, the team appears to have prioritized deployment on Polygon zkEVM over Polygon PoS. The core mechanism resembles GMX, but with the advantage of Oracle-driven pricing, enabling trades without price impact. Liquidity in the market comes from QLP tokens; liquidity providers deposit QLP to earn trading fees and incentives.
2.1.2 Mantis Swap

Mantis Swap is a stablecoin exchange within the Polygon ecosystem designed for trading pegged assets like stablecoins. What sets Mantis Swap apart is its ability to aggregate multiple assets into a single liquidity pool while allowing single-asset liquidity provision. For example, the current Mantis Swap liquidity pool on Polygon zkEVM includes USDT, USDC, and DAI, offering the benefit that liquidity providers need only supply one token instead of two or more.
2.1.3 Antfarm Finance
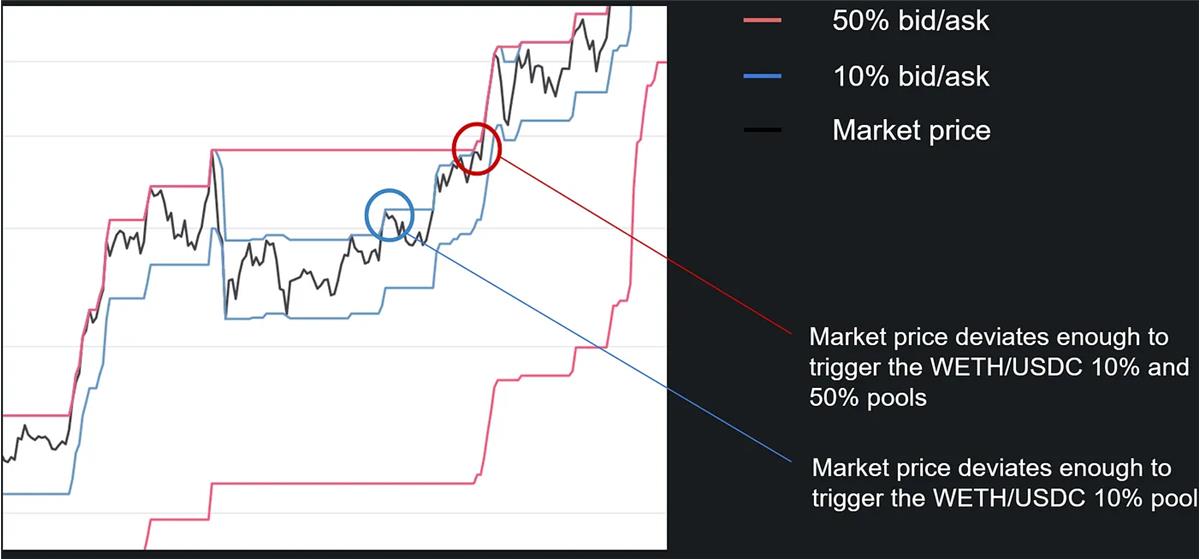
Antfarm Finance is a DEX operating on Ethereum, Arbitrum, and Polygon zkEVM, utilizing a novel strategy called Band Rebalancing AMM. Taking the ETH/USDC liquidity pool as an example, liquidity providers can choose fee bands of 1%, 10%, 25%, or 50%. But who would trade in a 10% fee pool? Such scenarios arise during extreme volatility—for instance, when 1 ETH trades at 1,000 USDC on one market but exceeds 1,100 USDC elsewhere, creating arbitrage opportunities. Thus, providing liquidity to Antfarm Finance’s high-fee pools allows users to effectively bet on volatility.
2.1.4 Balancer

Balancer is a representative AMM DEX protocol in the Ethereum ecosystem, offering various liquidity pools—including dual-asset pools with different weightings and stablecoin pools—beyond basic CPMM (x*y=k). Through BIP-224, Balancer proposed deployment on zkEVM and has recently confirmed it officially.
2.1.5 Others
Beyond the aforementioned DEXs, several other protocols include:
-
DoveSwap is a native zkEVM DEX supporting concentrated liquidity features akin to Uniswap V3, where liquidity can only be provided within specific price ranges.
-
Kokonut Swap is a Klaytn-based AMM DEX that now supports Polygon zkEVM. It uses Curve’s stablecoin AMM for equally valued assets and dynamic PEG mechanisms for differently valued assets, delivering more focused liquidity than standard CPMM models.
-
Sushiswap, a leading AMM DEX in the Ethereum ecosystem, now supports Polygon zkEVM following community forum proposals.
2.2 DeFi (Lending)
2.2.1 0vix

0vix is a lending protocol in the Polygon ecosystem supporting both Polygon PoS and Polygon zkEVM. Users can deposit collateral to earn interest or borrow through over-collateralization. 0vix supports major tokens such as WBTC and WETH, liquid staking tokens like wstETH and stMATIC, and various others including vGHST, jEUR, and gDAI.
2.2.2 Aave

Aave is a leading lending protocol in the Ethereum ecosystem, supporting various EVM-compatible networks. Like other lending protocols, it enables over-collateralized borrowing. Since 2022, Aave V3 has been deployed and tested on the Polygon zkEVM testnet and is expected to go live on the mainnet soon, having received overwhelming support in a March snapshot governance vote for mainnet deployment.
2.2.3 Qi Dao

Qi Dao is a stablecoin issuance protocol. Users can deposit collateral via over-collateralization to mint the MAI stablecoin. A key feature of Qi Dao is that users pay no interest on borrowed stablecoins, and there is no maturity date for repayment. Of course, if collateral value drops too low, liquidation occurs with associated penalties.
2.2.4 Others
UniLend Finance is a multi-chain decentralized money market protocol supporting over-collateralized loans.
2.3 DeFi (Order Book DEX)
2.3.1 Clober
Clober is an on-chain order book for EVM networks, currently supporting Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, and Polygon zkEVM. Implementing on-chain order books is challenging due to high transaction volumes, which Clober addresses using proprietary technologies called Segment Tree and Octopus Heap. By leveraging Clober, users enjoy an order book experience similar to centralized exchanges while executing trades fully on-chain.
2.3.2 Satori

Satori is a perpetual futures order book trading protocol that has raised over $10 million in funding from prominent institutions such as Polychain Capital, Jump Crypto, and Coinbase Ventures. Satori enables users to trade perpetual futures on-chain with a user interface and experience closely resembling centralized exchanges.
2.3.3 Others
Spin Fi is an all-in-one DeFi platform originally built on Near Protocol, offering spot and futures order book trading, decentralized options vaults (DOV), and more.
2.4 DeFi (Others)
2.4.1 Gamma

Gamma is not an AMM DEX but a protocol offering automated liquidity provisioning services for DEXs like Uniswap V3, enabling concentrated liquidity within specified price ranges. A drawback of concentrated liquidity is that if prices move outside the set range, liquidity becomes inactive, earns no fees, and exposes LPs to larger impermanent losses. Gamma mitigates this by automatically rebalancing price ranges based on market movements. Currently, Gamma collaborates with Quickswap to offer this service on Polygon zkEVM.
2.4.2 Gelato

Gelato is a protocol that automates smart contract execution, widely adopted by many DeFi protocols. Developers use Gelato to implement limit orders on AMM DEXs, manage liquidation risks in lending protocols, or enable automatic price range rebalancing in concentrated liquidity protocols like Uniswap V3. Gelato plans to deploy its relay network on Polygon zkEVM to help automate smart contracts across the ecosystem.
2.4.3 Others
Bounce Finance is an auction-as-a-service protocol enabling easy implementation of various auction types on-chain, including fixed-price auctions, Dutch auctions, and sealed-bid auctions.
2.5 NFTs and Gaming
2.5.1 OnePlanet

OnePlanet is a leading NFT marketplace in the Polygon ecosystem that recently announced deployment on Polygon zkEVM. Unlike other NFT marketplaces, OnePlanet curates its NFT collections—not every project can list here; only those verified by the team are allowed, ensuring users can safely and reliably purchase high-quality NFTs. Various projects within the Polygon ecosystem have partnered with OnePlanet to host events.
2.5.2 Others
-
Gameswift (formerly StarTerra on Terra blockchain) is an integrated gaming platform offering IGO, INO, and game services.
-
Zonic is an NFT marketplace specializing in Layer 2 networks such as Optimism, Arbitrum, Nova, zkSync Era, and Polygon zkEVM.
2.6 Cross-chain Bridges
2.6.1 Orbiter Finance

Orbiter Finance is a cross-Rollup bridging protocol specifically designed for Rollups and supporting various L2 networks beyond Ethereum. In Orbiter Finance, entities called "Makers" hold liquidity on each network. The bridge process involves users sending funds to a Maker on the source chain and receiving funds from a Maker on the destination chain. While there is a cap on the amount of ETH that can be transferred per transaction, the bridging process itself is extremely fast.
2.6.2 Hyperlane
 Hyperlane is a modular cross-chain communication protocol enabling anyone—whether L1, L2, or application-specific chains—to adopt it. Currently limited to EVM chains, non-EVM support is planned for the future. Verification relies on external validators. Integrating Hyperlane will enhance composability between Polygon zkEVM and other networks adopting Hyperlane.
Hyperlane is a modular cross-chain communication protocol enabling anyone—whether L1, L2, or application-specific chains—to adopt it. Currently limited to EVM chains, non-EVM support is planned for the future. Verification relies on external validators. Integrating Hyperlane will enhance composability between Polygon zkEVM and other networks adopting Hyperlane.
2.6.3 Rhino Fi

Rhino Fi is an all-in-one DeFi platform focused on the Ethereum ecosystem, supporting multiple Rollup networks including Optimism, Arbitrum One, Polygon zkEVM, and zkSync Era. Beyond swaps, liquidity pools, and yield vaults, users can bridge to Polygon zkEVM.
2.6.4 Magpie Protocol

Magpie Protocol is a cross-chain DEX allowing users to trade assets directly across multiple networks. Normally, trading assets across different chains requires bridging first, then swapping—but Magpie enables both steps in one seamless flow. No locking/burning mechanism is used; instead, token transfers rely on Wormhole’s universal message protocol. The swap process works as follows: 1) User submits trade on source chain. 2) Assets are converted into stablecoins. 3) Stablecoins are deposited via existing bridges (e.g., Wormhole, Stargate). 4) Trade and deposit data are sent via Wormhole to the target chain. 5) Upon verification, stablecoins are used to buy desired tokens and deliver them to the user.
2.6.5 Others
-
Layerswap is a cross-chain bridge protocol supporting 17 exchanges and 20 blockchains. Unlike most bridges, it also supports CEX integration.
-
XY Finance is a cross-chain swap protocol where liquidity providers fund Y Pools on each network, and traders use the X Swap function to access liquidity across networks to obtain desired assets.
-
Bungee is a cross-chain swap protocol built atop Socket, a cross-chain infrastructure supporting various EVM networks. Fund transfers occur via a liquidity layer.
-
Meson Fi is a cross-chain stablecoin swap protocol enabling users to exchange stablecoins across multiple networks by leveraging liquidity provided by LPs on each chain. It uses HTLC atomic swaps as the bridging method.
-
Interport Finance is another cross-chain DEX protocol enabling simultaneous cross-chain swaps using liquidity supplied by providers.
-
Symbiosis Finance is a multi-EVM-network cross-chain DEX protocol. For bridge security, it relies on validators maintained through an incentive mechanism called Symbiosis Relayer.
-
Celer is an optimized cross-chain bridge for EVM chains, where transactions are validated by the State Guardian Network—an economically incentivized entity. Bridging leverages liquidity provided by LPs on each network.
2.7 Oracles
2.7.1 Pyth

Pyth is an oracle delivering price data for cryptocurrencies, stocks, forex, commodities, and more, operating across over 13 blockchains. Pyth sources data directly from primary providers including Cboe, Jane Street, Binance, and many other major institutions. Pyth price feeds are currently available to the 0vix protocol on Polygon zkEVM and will expand to support additional protocols on Polygon zkEVM.
2.7.2 API3

API3 is an oracle similar to Pyth, sourcing data directly from first-party APIs. Its product Airnode benefits from direct third-party data access and is highly user-friendly, low-maintenance, and cost-effective. API3 is currently being used to provide price data for Dovish, a perpetuals protocol on Polygon zkEVM.
2.8 Infrastructure
2.8.1 Unmarshal

Unmarshal provides cross-chain data infrastructure and API services across multiple networks. Offerings include Xscan, a user-friendly block explorer UI, and Parser, a no-code smart contract indexer. Unmarshal will serve as the indexing and query layer for the Polygon zkEVM network.
2.8.2 Others
-
Defillama is one of the most well-known DeFi analytics platforms, aggregating on-chain DeFi data from multiple networks.
-
DeBank is an asset dashboard service tailored for EVM networks, displaying wallet holdings via an intuitive UI. It also offers messenger and other features.
-
Dexscreener analyzes and presents data from DEXs that are harder to track than CEXs, allowing users to view price charts of tokens listed exclusively on DEXs or explore various liquidity pools.
-
L2beat displays comprehensive information about various Ethereum Layer 2 networks, offering quantitative metrics like TVL and transaction count alongside qualitative risk analysis.
-
Dune is an on-chain data analytics platform enabling users to query and visualize data from diverse networks.
3. Conclusion
Recently, Polygon outlined its vision for building a network of ZK-based Layer 2 chains and introduced the Polygon 2.0 roadmap. While further details will emerge later, we can expect the Polygon ecosystem to expand around Polygon zkEVM and related technologies. In this context, the early-stage Polygon zkEVM ecosystem will play a crucial role. With recent proposals suggesting extending Rocket Pool’s rETH to Polygon zkEVM, more dApps and users are expected to join the network in the near future.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















