Understanding Crypto Market Makers: How to "Manipulate" the Crypto Market?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Crypto Market Makers: How to "Manipulate" the Crypto Market?
How do market makers manipulate the cryptocurrency market? Why are they always behind the sharp price surges and crashes?
Author: Rekt Fencer
Compiled by: TechFlow
Have you ever wondered how market makers manipulate the cryptocurrency market? Why are they always behind the scenes during massive price surges and crashes? In this article, crypto analyst Rekt Fencer reveals everything you need to know about cryptocurrency market makers.

Market makers facilitate trading by buying and selling assets, profiting from the bid-ask spread. There are now two types of market makers:
1. Traditional market makers;
2. Project advisory market makers;
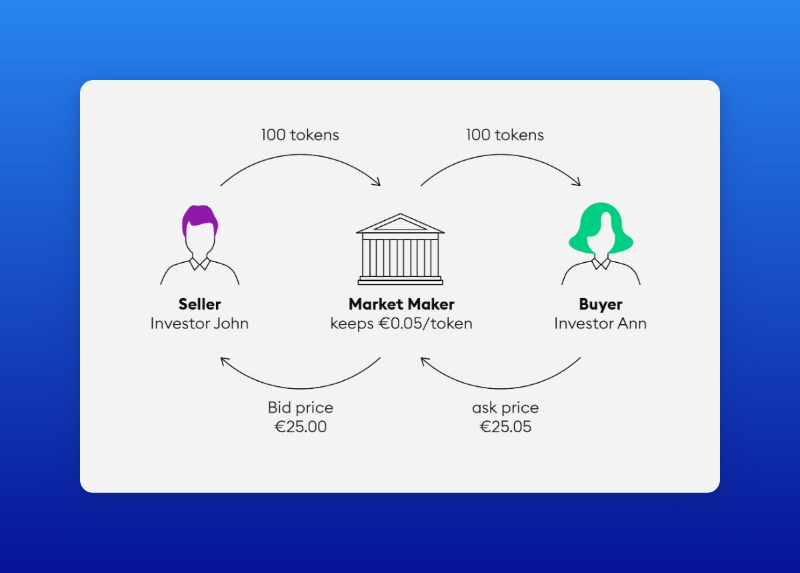
Traditional market makers focus on large-market-cap projects, aiming primarily to maintain stable prices, ensure market liquidity, and establish trading strategies for token unlocks.
Project advisory market makers mainly:
• Assist projects in fundraising;
• Provide DEX liquidity;
• Develop token pricing strategies for TGEs;
• Help teams cash out;
Thus, these market makers fulfill all necessary conditions for a project at an early stage.
Cashing out essentially means selling team tokens during TGE. Reasons include:
-
Raising funds for project development;
-
Raising capital to buy back seed or private sale tokens;
-
Purchasing "Lambos, houses, and yachts" for the project team;

Market makers' strategies depend on the phase of the cryptocurrency market—simply put, they revolve around bull and bear markets.
During bull markets, their main tasks are:
-
Providing opportunities for buyers of any size to purchase tokens;
-
Creating FOMO among investors;

Conversely, key tasks during bear markets are:
-
Buying tokens as cheaply as possible in preparation for the next bull run;
-
Generating daily trading volume on CEXs to avoid delisting;

The listing price of a token on a CEX depends on:
-
The popularity of the CEX;
-
The popularity of the project;
-
The current market phase;
-
Other factors;
Therefore, it can range from free to millions of dollars. Based on trading volume, there are three tiers of CEXs:
Tier 1: Binance, Kucoin, and OKX (real users, high purchasing power, high listing prices).
Tier 2: Gate, MEXC, and Huobi (lower purchasing power, lower listing prices).
Tier 3: Lbank, Bitrue, etc.
How to identify cooperation between market makers and tokens:
-
Token surges before major news announcements.
-
Steadily increasing trading volume without significant price movements.
-
Repetitive patterns on charts (e.g., recurring spikes and drops every two months).
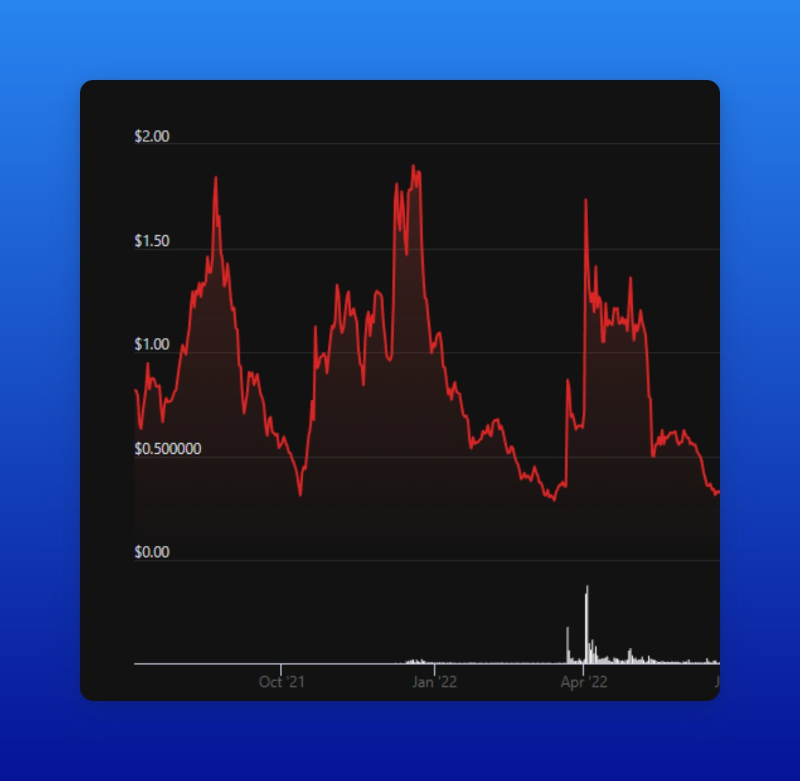
Trading volume can be real or fake. Some volume comes from genuine human trades, while some is artificial—generated by bots executing orders between accounts controlled by market makers.
How to identify fake volume? Place a $5–10 buy order:
-
If the seller's order changes rapidly and you cannot execute a small trade, the trading pair likely has fake volume.
-
If you successfully complete your order, the volume is most likely real.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















