EIP4337: The Future of Account Abstraction on Ethereum
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

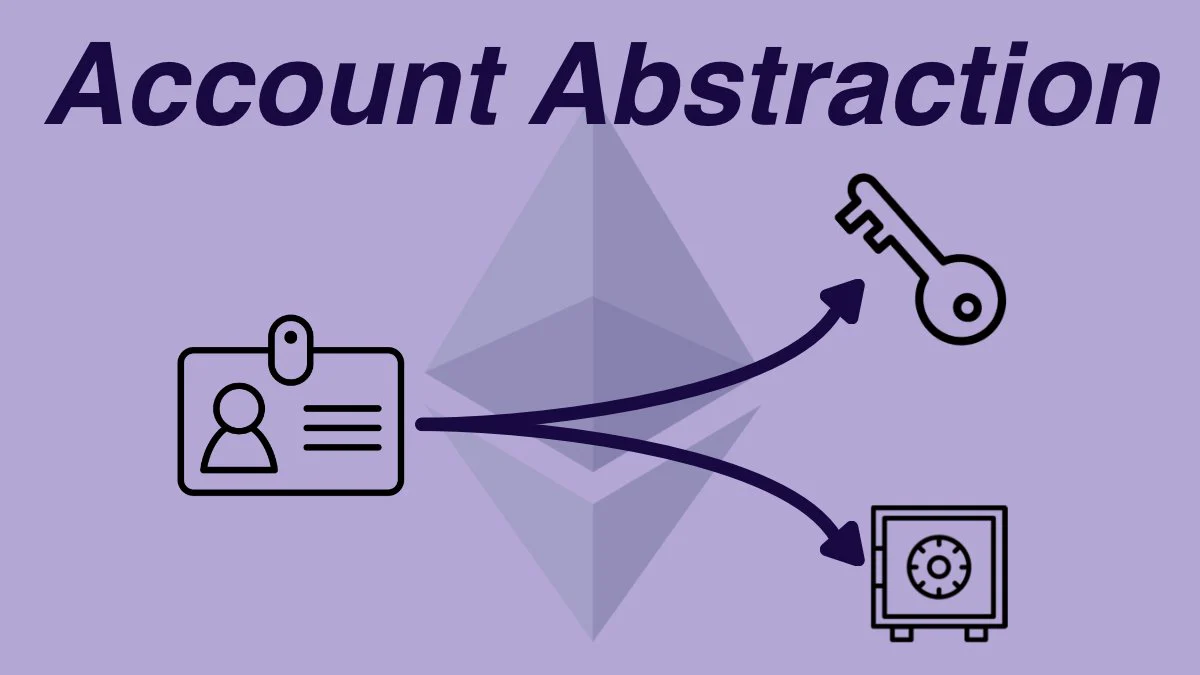
EIP4337: The Future of Account Abstraction on Ethereum
How Account Abstraction Creates a Success Paradigm for Wallet Tools in the Web3 Era.
When we first dive into decentralized finance (DeFi) trading, the first thing we need is a wallet. However, when operating on-chain wallet tools, most users quickly realize the experience differs significantly from what they're accustomed to—on-chain wallets enable full custody of digital assets, yet lack account security safeguards (such as Ethereum's Externally Owned Accounts, or EOA, and Contract Accounts, CA).
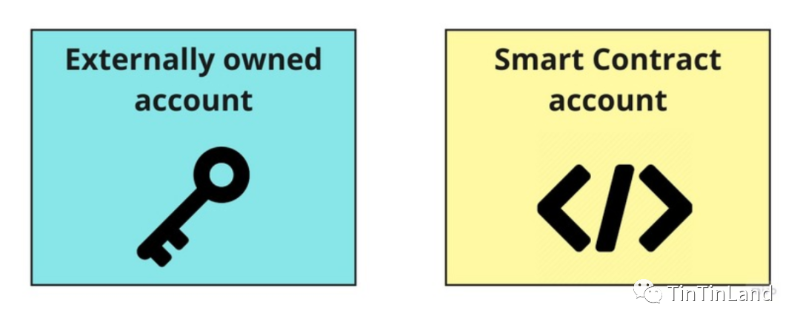
In executing transactions under the EOA and CA model, each on-chain transaction must be initiated and signed by an EOA. Users own an EOA wallet via a key pair, where the private key serves as the signer. Because the wallet address derives from the public key, the EOA wallet functions simultaneously as both account and signer—a setup that poses serious asset security risks. Essentially, the signer holds absolute control over the account. Imagine losing your account one day, and someone else happens to find your signer; that person would then gain complete access to your account and all associated digital assets.
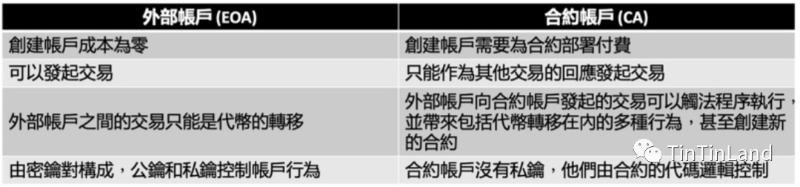
Comparison between common Ethereum on-chain self-custody wallets: EOA & CA
To address these issues, developers have explored various technical improvements based on EOA and CA accounts, adding components such as asset transfer controls, private contract management, and enhanced user control mechanisms. Despite their best efforts to prevent asset loss, vulnerabilities remain, drawing criticism from multiple fronts. For example, the well-known NFT project Bored Ape Yacht Club suffered an incident where hundreds of NFTs were stolen, further worsening the already subpar wallet experience for Ethereum users. Therefore, we seek an account abstraction solution that combines the strengths of both account types while overcoming their respective weaknesses—ultimately establishing a successful paradigm for Web3 wallet tools.
Account Abstraction: Fully Automated Integrated Payments
The current account system requires users to securely store and protect their private keys or seed phrases; otherwise, they risk losing their digital assets entirely. This security burden deters many potential users from entering cryptocurrency transactions and even hinders the usability of on-chain applications. So, what is the solution to wallet security? It's Account Abstraction—a framework enabling automated, programmable payments through smart contracts that support self-custodial wallets with automatic fund withdrawals.

Account abstraction simplifies account usage for users. Just like creating a web-based email account, users only need to learn how to operate it without understanding its underlying mechanics. With account abstraction, we can move beyond reliance on seed phrases and private keys, enable diverse signature options, and allow Gas fees to be sponsored by DApps or paid in Tokens.
The primary goal of account abstraction is to decouple the binding relationship between the signer and the account, eliminating the signer’s absolute control over wallet assets. In short, account abstraction integrates transaction validation and execution into a unified process, transforming it into modular components customizable to user needs, effectively merging EOA and CA into one.
Unlocking Account Abstraction with EIP-4337
After clarifying this development goal, Vitalik and core Ethereum developers continuously drafted solutions for "account abstraction." From the initial EIP-86 to today’s EIP-4337, transactional control has progressively shifted toward users, security risks have been significantly reduced, and the next generation of wallet tools is emerging.
Development Timeline

EIP-86 introduced a smart contract as a "forwarding contract," allowing anyone to send transactions from an entry address.
EIP-1014 enabled predicted deployment of contract addresses, enhancing the functionality of smart contract wallets and ensuring consistent contract addresses across all EVM chains.
EIP-2938 proposed creating new opcodes for "account abstraction" transactions but was later abandoned due to excessive protocol changes.
EIP-3074 introduced two new opcodes that, when used together, allow smart contracts to represent EOAs in sending transactions—but posed security risks and was not implemented.
Following the completion of Ethereum's merge roadmap, more developers joined efforts to refine account abstraction proposals. In September 2021, researchers from Nethermind and Opengsn, with help from Vitalik, proposed EIP-4337. Its key innovation: achieving "account abstraction" on Ethereum without modifying any consensus-layer protocols.
How It Works
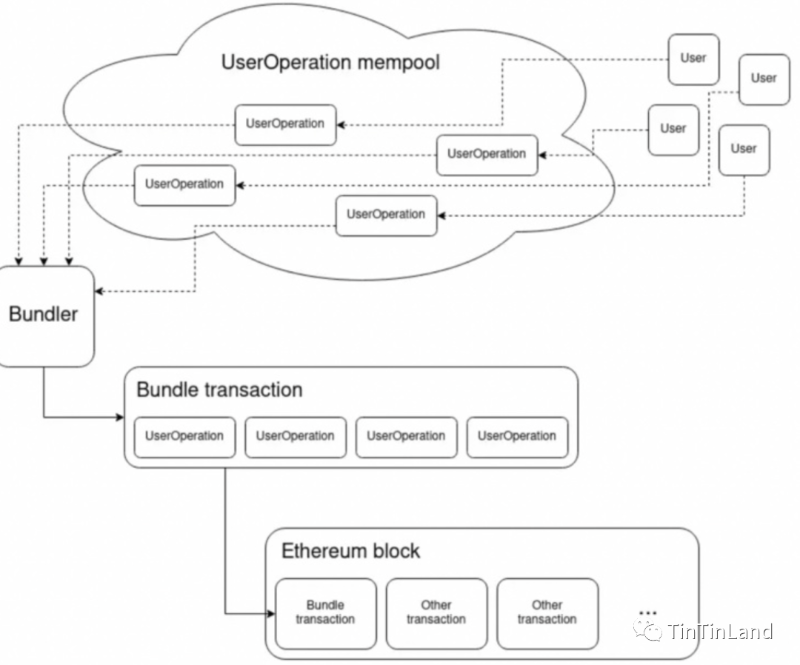
EIP-4337 does not alter the logic of the consensus layer itself. Instead, it replicates the functionality of the existing transaction mempool at a higher level, introducing the novel concept of "User Operations"—enabling custom functions to be encoded into smart contract wallets. User operations bundle intent, signatures, and other data for verification. The EIP-4337 workflow consists of three main steps:
-
User Operations: Initiate a "user operation" sent through a custom mempool.
-
Bundler Packing: Bundlers select UserOperation objects based on fee priority and use a bundler to call the EntryPoint contract for validation.
-
Transaction Execution: If no errors occur during the above processes, the transaction is included in the next block.
In the design of EIP-4337, the EntryPoint contract verifies accounts to ensure compliance with predefined rules and proper execution; Bundlers, operating as EOA addresses, submit all transactions on-chain. Additionally, Paymaster—a supplementary smart contract—can be integrated to provide auxiliary support. Compared to earlier proposals, EIP-4337 reduces security risks while maintaining orderly and stable transaction execution, all without altering consensus-layer protocols—offering greater convenience and efficiency for both developers and users.
Analyzing the Superior Performance of EIP-4337
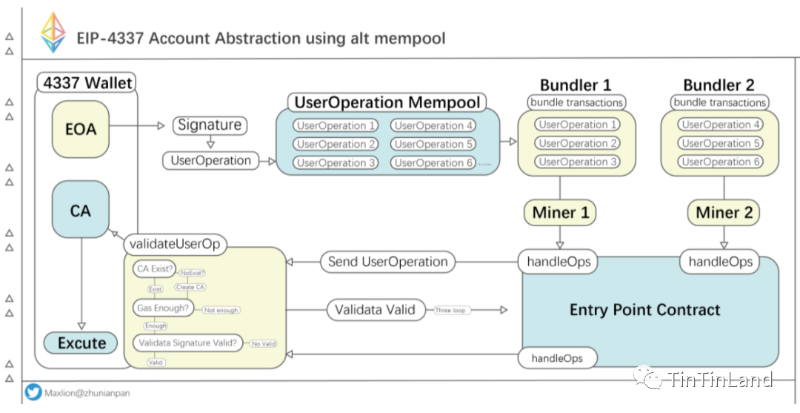
Security Enhancements
The foremost advantage of EIP-4337 is its robust security. By supporting customizable signing schemes, it natively enables multi-signer setups on Ethereum—transactions require approval from two or more users, significantly enhancing security. If a user loses their private key or account, they can simply contact friends or family to recover access. This represents a qualitative leap in security compared to previous drafts.
Operational Flexibility
Although EIP-4337 separates validation and execution into two smart contracts, once a wallet contract successfully validates a transaction, the EntryPoint contract automatically proceeds to execute and submit it to the appropriate block. Developers and users can freely encode desired features into wallet contracts—including multisig, social recovery, quantum-resistant signature schemes—overcoming EOA's limitation to ECDSA cryptography.
Architectural Compatibility
While enabling custom functionalities, multi-threaded architectural compatibility is essential to meet additional runtime demands. EIP-4337 introduces dedicated User Operations for abstracted accounts. Both the mempool for User Operations and the Bundler relaying them to the EntryPoint contract operate efficiently in parallel, avoiding high energy consumption or unnecessary costs. Even if consensus-level changes or network hard forks occur, adding a new mempool only requires updating Ethereum node clients.
Fee Subsidization
Bundlers are not only crucial nodes in the EIP-4337 workflow but also serve as cost-saving enablers. By bundling multiple transactions and operations, approvals and token spending can be executed as a single operation, eliminating redundant costs from parallel transactions. Moreover, the Paymaster feature allows third parties to cover Gas fees for certain User Operations, subsidizing protocol usage for users. Both user and payer account balances update dynamically throughout execution, making "pay once, operate multiple times" a reality.
Overcoming Challenges: Paving the Way for EIP-4337 to Build the Next-Gen Wallet
Capitalizing on the momentum from Ethereum's merge upgrade, EIP-4337 has emerged as a promising avenue for unlocking account abstraction. We see EIP-4337 reshaping the clunky on-chain account experience, becoming the preferred method for Web3 applications to enable user-controlled asset custody, and opening doors for widespread adoption by projects. This isn't just a focal point within the smart contract wallet trend—it represents a major technological advancement for blockchain in the internet era.
However, despite its many advantages, EIP-4337 must continually overcome its limitations to sustain long-term viability. For instance, the added complexity increases susceptibility to DoS attacks compared to simple ECDSA verification; accounts cannot queue multiple transactions in the mempool and must process one at a time; although Gas subsidies are available, the operational Gas costs themselves remain non-trivial. These critical areas demand deeper exploration and innovative solutions from developers. Only through continuous refinement of the proposal and technical enhancements can EIP-4337 become the definitive path to account abstraction.
We look forward to the Ethereum developer community bringing more innovations to EIP-4337 in 2023, building the next generation of wallets and delivering more convenient, secure payment tools to users.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News