Bitget Wallet Research Institute | The Interest Rate Cut Cycle Begins: Can Web3 Stablecoin Finance Become a New Frontier for Trillion-Dollar Capital?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Bitget Wallet Research Institute | The Interest Rate Cut Cycle Begins: Can Web3 Stablecoin Finance Become a New Frontier for Trillion-Dollar Capital?
A rational approach to embracing DeFi innovation in the new era of lower interest rates.
Author: Lacie Zhang, Researcher at Bitget Wallet
Introduction: Asset Anxiety in the Era of Low Interest Rates
On September 17, Federal Reserve Chair Powell announced a 25-basis-point cut to the federal funds rate target range, bringing it down to 4.00%–4.25%. This decision not only confirms the rate-cutting expectations that have built up since late last year but also strengthens market consensus that the easing cycle will continue: most anticipate two additional cuts totaling 50 basis points by year-end.
Every interest rate decision by the Fed is based on a comprehensive assessment of the U.S. labor market and economic outlook, with ripple effects spreading across global capital markets. The start of this rate-cutting cycle officially ushers global investing into a "low-interest-rate era"—whether bank savings, government bonds, or money market funds, the yield ceiling for traditional safe-haven investments continues to fall, intensifying investors' anxiety over an "asset shortage."
Just as traditional finance sees persistently low yield curves, Web3 stablecoin yield products have captured public attention with their seemingly "abnormal" high returns. These dollar-pegged financial products—whether on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols or centralized digital asset platforms—routinely offer annualized returns of 5%, sometimes reaching as high as 20%. This raises critical questions: as assets strictly pegged to the U.S. dollar, where does this interest come from? Are these astonishing yields fleeting market bubbles or signs of a disruptive new investment model emerging? In this article, Bitget Wallet Research unpacks the mechanics behind these high yields and objectively evaluates the opportunities and potential risks of this "new game."
I. "Demand Deposits" in the Digital World: Three Mainstream Models of Stablecoin Yield
Before examining mainstream models, it's important to clarify what is meant by "stablecoin yield." Simply put, it’s the digital equivalent of "bank deposits," where investors deposit dollar-pegged stablecoins (e.g., USDC, USDT) into specific platforms or protocols to earn interest. The core objective is to generate relatively attractive and predictable annualized returns through on-chain or platform-based strategies while maintaining principal stability, typically preserving liquidity similar to demand deposits.
Current stablecoin yield products in the market can be categorized into three main types based on their underlying mechanisms and custody models: native DeFi model, CeFi custodial model, and hybrid Ce-DeFi model.
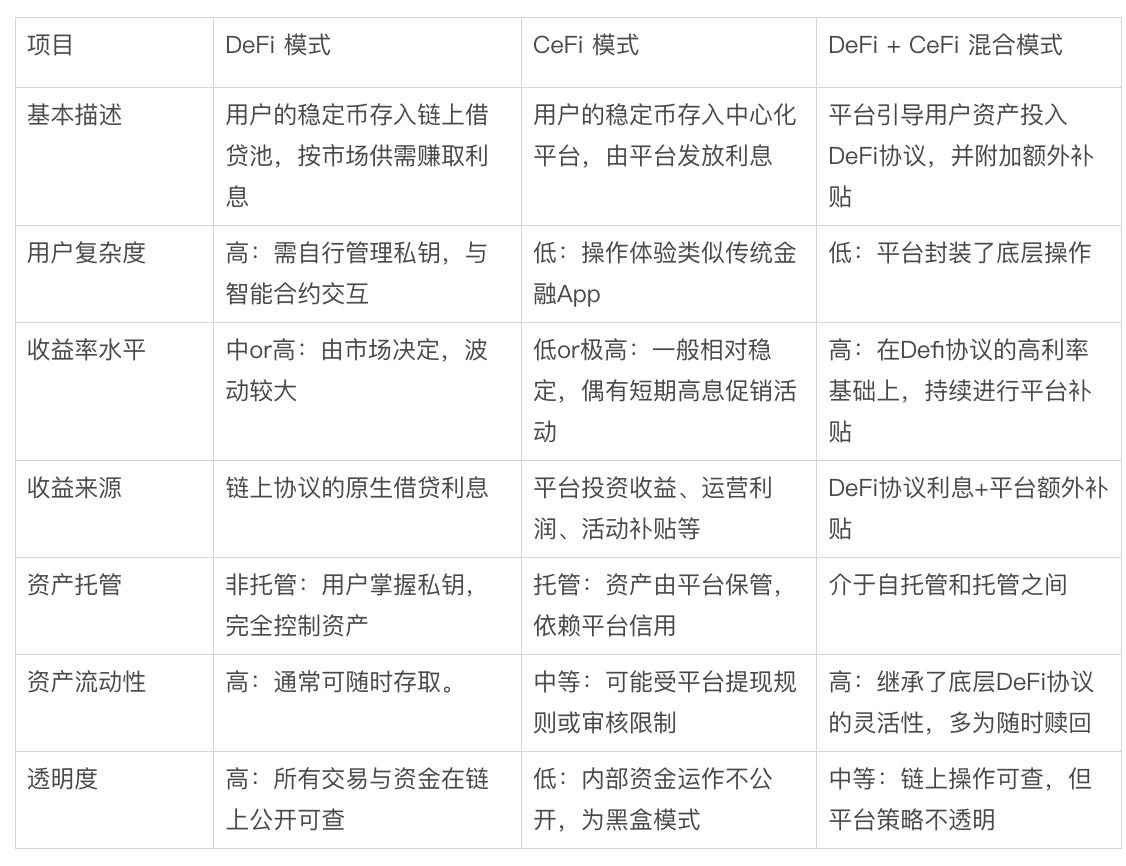
Comparison table of mainstream stablecoin yield models
-
Native DeFi Model: Building a fully transparent "on-chain bank." Users manage their own wallet private keys and interact directly with decentralized lending protocols such as Aave and Compound, depositing stablecoins into on-chain liquidity pools to earn variable interest based on real-time borrowing demand. The advantage is full user control over assets and complete transparency of all fund flows, though it requires higher technical proficiency and blockchain knowledge.
-
CeFi Custodial Model: Resembles traditional financial products. Users deposit stablecoins into centralized platforms (e.g., Coinbase, Binance), which then manage the assets and distribute interest. The user experience mirrors that of a mobile banking app—simple and intuitive. While convenient, users relinquish direct control over their assets, and fund operations remain a "black box" dependent on platform credibility.
-
Ce-DeFi Hybrid Model: Aims to combine the strengths of both models. Platforms use technical abstraction to route user funds into vetted underlying DeFi protocols for yield generation, sometimes adding extra yield subsidies. Users enjoy CeFi-like ease of use while retaining ownership of assets in their personal wallets (non-custodial), balancing high returns with self-custody. However, risks are compounded, encompassing both underlying DeFi protocol risks and platform-specific risks.
II. Tracing the Source of Returns: How Do DeFi Lending Protocols Support the High Yields in Stablecoin Yield?
After reviewing the three mainstream models, one clear conclusion emerges: setting aside temporary promotional campaigns by centralized platforms, the sustainable and high-yield foundation of stablecoin yield products rests entirely on on-chain DeFi protocols.
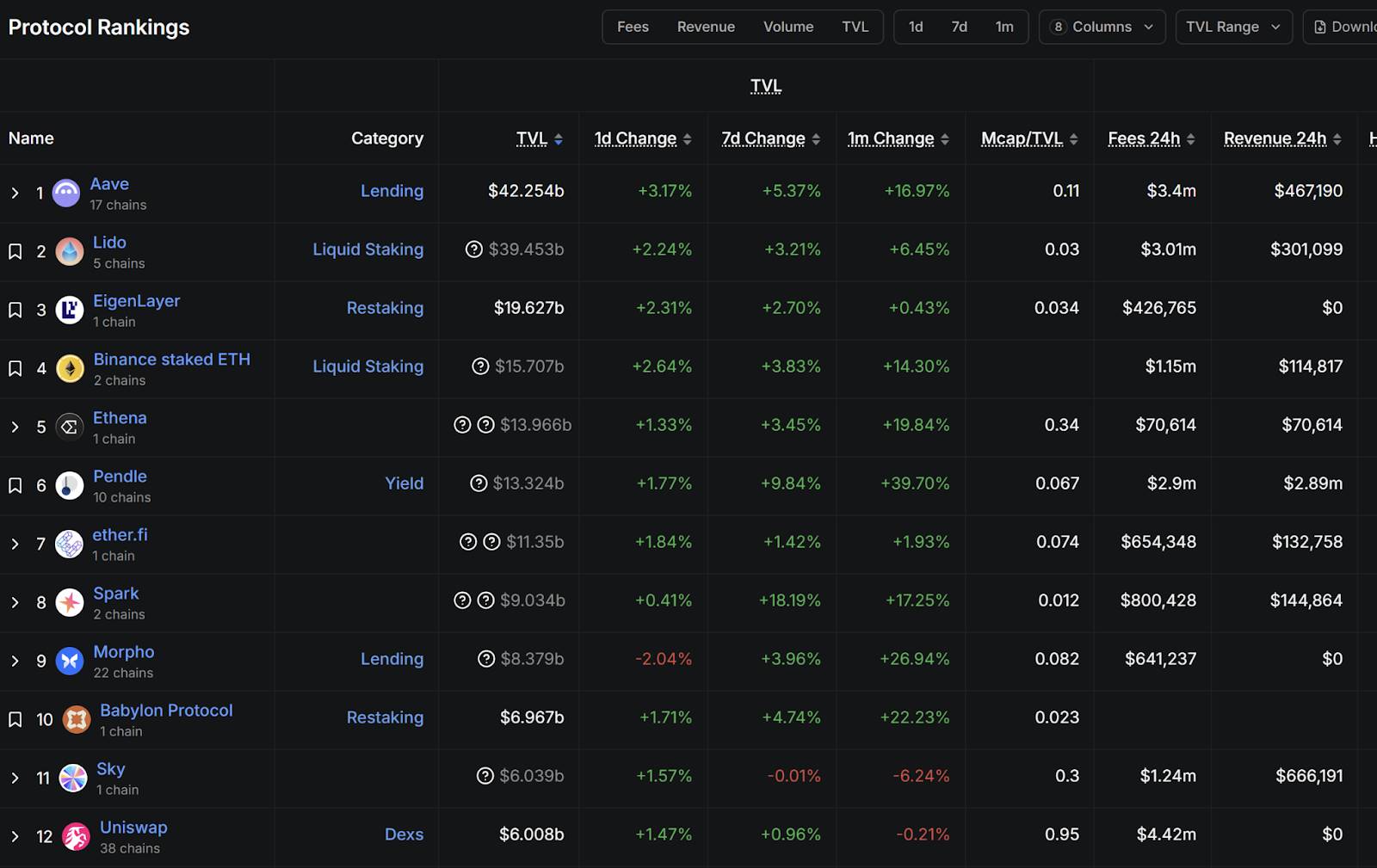
Source: DefiLlama, as of September 17, 2025
Data from DefiLlama (as of September 17, 2025) shows the on-chain protocol ecosystem has become highly diversified, including staking, lending, restaking, and decentralized exchanges. Despite differing mechanisms, most mainstream stablecoin yield products rely on the most fundamental financial principle—"earning interest rate spreads"—a concept strikingly similar to traditional commercial banking. This section uses Aave, the leading protocol in DeFi lending, as a case study to analyze this typical yield-generating model.
Aave was founded in 2017 by Finnish entrepreneur Stani Kulechov, originally launched as ETHLend before rebranding. According to DefiLlama, Aave currently boasts a total value locked (TVL) exceeding $40 billion, ranking first among all DeFi protocols. Its official website states that Aave operates across 14 major networks, with net deposits surpassing $70 billion and a 30-day trading volume reaching $270 billion, making it a true giant in the "on-chain banking" space.

Source: Aave official website
Aave’s core business model is an efficient and transparent peer-to-pool lending market. Its ability to operate stably and deliver high yields relies on three key mechanisms:
-
Over-Collateralization: The foundation and safety net of all on-chain lending. Borrowers must first deposit crypto assets worth significantly more than their loan amount as collateral (e.g., depositing $150 worth of Ethereum to borrow $100 in stablecoins). This barrier greatly protects depositors’ funds, preventing bad debt due to borrower defaults.
-
Pool-to-Peer Model: Unlike traditional systems that match individual borrowers and lenders, Aave aggregates all depositors’ stablecoins into a large liquidity pool. Borrowers draw directly from this pool, and interest payments go back to the entire pool. This design dramatically improves capital efficiency and liquidity, enabling instant deposits and withdrawals without waiting for counterparties.
-
Dynamic Interest Rates: The direct source of high yields. Interest rates are not fixed but algorithmically adjusted in real time based on the "utilization rate" (the proportion of funds borrowed from the pool). When demand for crypto asset loans (e.g., BTC, ETH) surges—such as during bull markets when traders seek leverage—the utilization rate rises, prompting the algorithm to increase deposit rates to attract more stablecoin deposits and simultaneously raise borrowing rates. Thus, the high yields earned by stablecoin depositors fundamentally stem from strong demand by crypto borrowers. For example, on the active Base chain, Aave’s stablecoin deposit rates have consistently hovered around 5%, reflecting genuine market supply and demand.
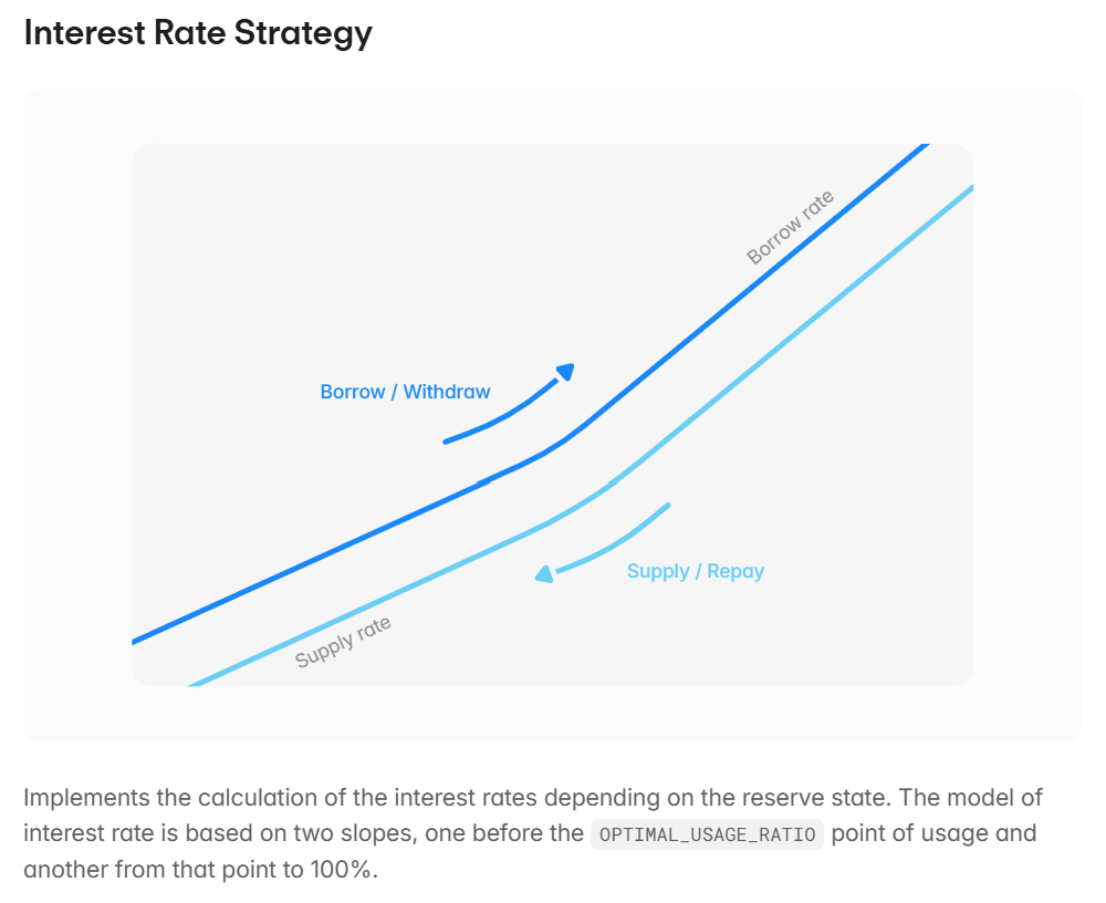
Source: Aave official documentation
Therefore, the high yields in stablecoin yield products are not illusory—they are rooted in the unique borrowing activities within the crypto market, driven by high volatility and intense trading demand. Protocols like Aave essentially function as decentralized financial intermediaries powered by code and algorithms.
III. Two Sides of the Coin: Opportunities and Realities of Stablecoin Yield
With its underlying mechanics clarified, the market positioning of stablecoin yield becomes increasingly evident. It directly addresses investors’ core pain point in today’s low-rate environment: by investing in dollar-pegged stablecoins, holders can avoid the extreme price volatility of major assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum while earning steady returns far exceeding those of traditional channels.
As shown in the table below, stablecoin yield stands out compared to mainstream conservative dollar-denominated products. It aligns with Treasury bonds and money market funds in risk profile—prioritizing capital preservation—yet offers return potential more than double. Additionally, it provides demand-deposit-level liquidity, extremely low entry barriers, and high transparency via on-chain operations. This combination of "high yield, high flexibility, high transparency" forms its core competitive advantage in the current market.
Comparison of Mainstream Conservative Dollar-Denominated Financial Products
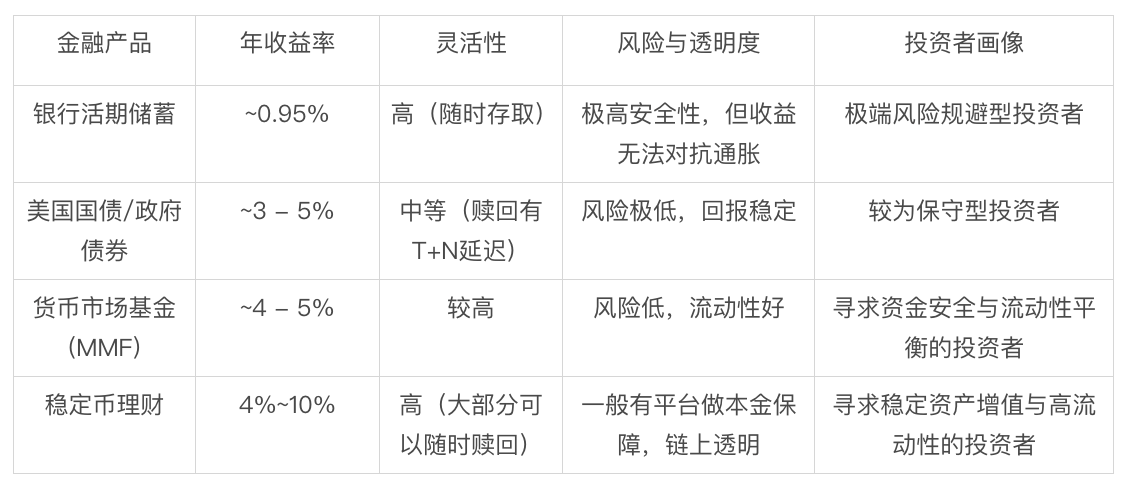
Source: Public information compiled
However, every opportunity carries inherent risks. As Aave’s official documentation notes, “decentralized access to liquidity is not without risk, but risks can be mitigated and managed.” While drawn to high yields, investors must remain aware of several potential risks:
First is protocol security risk. This is an inherent technological risk in the blockchain world. Vulnerabilities in smart contracts, oracle attacks, or cross-chain bridge compromises could serve as entry points for hackers. Although multiple code audits and community oversight help reduce risk, they cannot eliminate it entirely.
Second is extreme market condition risk. While stablecoin yield products themselves invest in stablecoins, their returns depend on lending demand for major crypto assets (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). If the crypto market suffers a systemic crash, it could trigger widespread liquidations, placing immense liquidity pressure on underlying protocol pools. Such "black swan" events would severely test the risk management capabilities of these protocols.
Finally, there is stablecoin de-pegging risk. History has shown that stablecoins are not absolutely stable—even major ones may temporarily deviate from their peg due to market panic or issuer credit crises. Should a systemic collapse akin to Lehman Brothers occur in traditional finance, the cascading impact on the entire ecosystem would be incalculable.
IV. Conclusion: Embracing DeFi Innovation Rationally in a New Era of Rate Cuts
Returning to the initial question posed in this article: as the Fed gradually opens its rate-cutting door and global investors scramble for new sources of yield, DeFi innovations like stablecoin yield undoubtedly present a compelling option. These are no longer niche experiments for tech enthusiasts but are evolving into a financially coherent, scalable, and efficiently operating ecosystem. They cleverly transform the intense capital demand within the Web3 world into products resembling "high-interest dollar savings"—something external investors can understand and participate in—building a bridge between traditional investors and decentralized finance.
Of course, one undeniable reality remains: this "new frontier" is still under construction, with opportunities and risks coexisting. For ordinary investors, the right approach is neither blind adoption nor outright rejection, but rather a rational evaluation—viewing stablecoin yield as a noteworthy addition to a diversified portfolio after fully understanding its yield sources and potential risks. Only by acknowledging and learning to manage these deeply embedded technological and market risks can this emerging investment avenue achieve long-term sustainability, allowing the innovative light of DeFi to truly reach the everyday investor.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News















