The Stablecoin Infrastructure Battle: 6 Major Projects Competing, Who Will Emerge Victorious?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

The Stablecoin Infrastructure Battle: 6 Major Projects Competing, Who Will Emerge Victorious?
Six major projects compete for the market, the future financial landscape remains to be seen!
Author: stablewatch & Castle_Labs
Translation: TechFlow
Summary
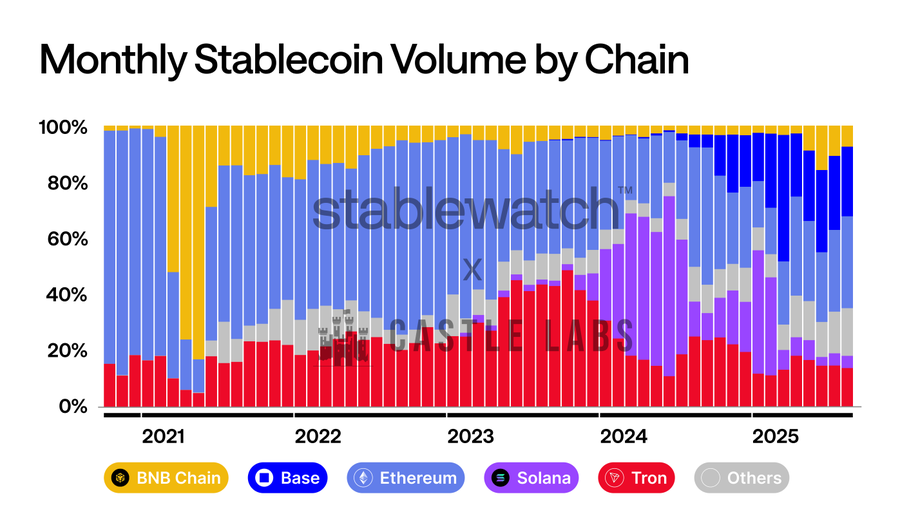
Stablecoins are dominating headlines in 2025. This raises the question: which blockchain network will carry and facilitate this asset class? As tokenized dollars gain broader acceptance and regulatory scrutiny, six upcoming Layer 1 blockchains are entering the race to compete with established stablecoin networks like Ethereum, Tron, Solana, and Base.
These blockchains include Plasma, Codex, 1Money, Arc, Stable, and Monad—following its recent acquisition of Portal Labs—each with distinct designs and visions to penetrate this booming industry.
This comparative analysis cuts through marketing noise, examining these networks across architecture innovation, consensus mechanisms, performance metrics, specialized features, and momentum. We'll use these findings to assess their positioning within the stablecoin economy.
With Citigroup projecting a $3.7 trillion market by the end of this decade, over $277 billion in current stablecoin market cap is up for grabs—stakes couldn't be higher. The winner won't just become another alternative Layer 1; given the momentum behind stablecoin adoption, it may become the infrastructure redefining how money flows in the digital age.
Disclosure:
Information in this article is primarily sourced from project documentation and official press releases. All discussed chains have not yet launched on mainnet, so statements do not guarantee actual performance or future outcomes.
The Infrastructure War Begins
Stablecoins emerged as an on-chain alternative asset class due to the need for a fiat-pegged token allowing crypto traders to avoid volatility. However, their unique properties as programmable and borderless fiat equivalents make them strong competitors to traditional financial channels in applications such as cross-border remittances, payroll, and treasury management.
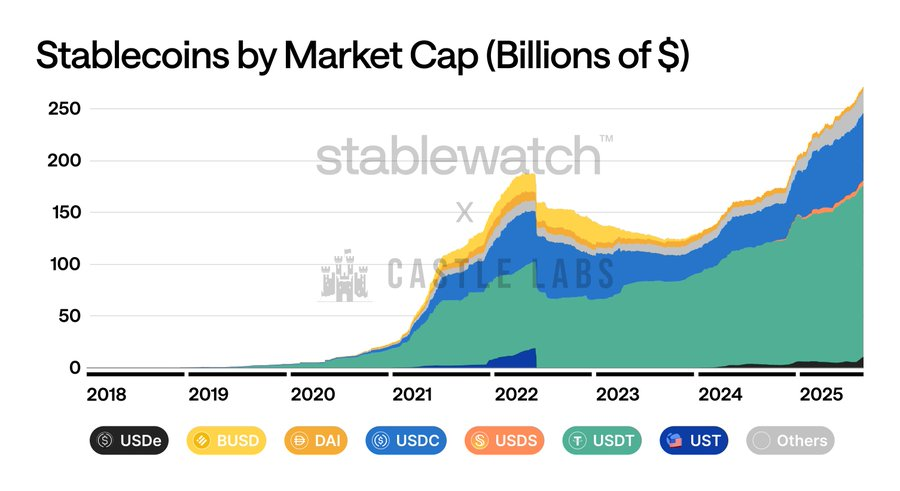
While stablecoins have achieved strong adoption, especially in countries suffering from local currency inflation, at the technical level they still rely on general-purpose blockchains not specifically designed for these use cases.
There are countless examples of general-purpose blockchains failing to meet the requirements of a globally scalable stablecoin network. They were not designed with predictable fees or execution guarantees in mind.
Examples of these shortcomings include:
-
The minting of Yuga Labs' "Otherside" NFT burned over $200 million in gas fees on Ethereum.
-
MEV and arbitrage opportunities on low-fee networks like Solana and Base have incentivized massive transaction spam.
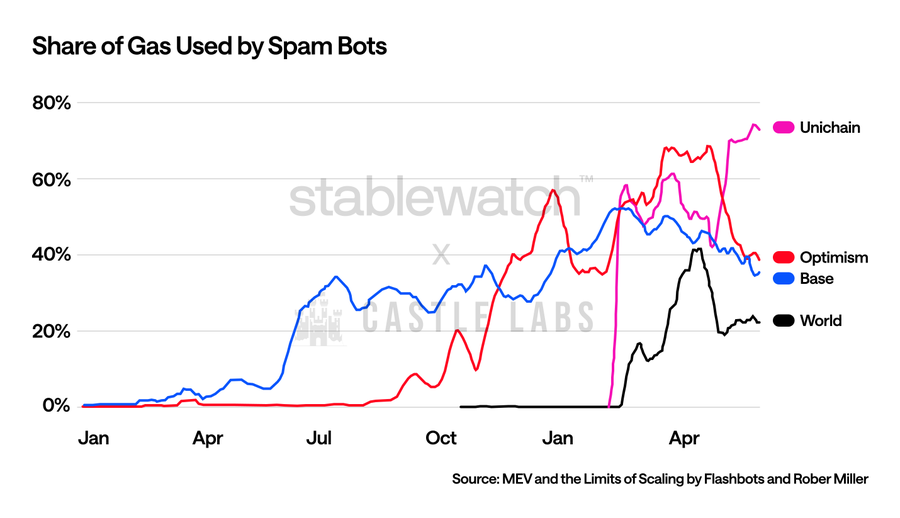
Source: MEV and the Limits of Scaling by Flashbots and Robert Miller
This infrastructure gap has spawned a new category of blockchains: stablecoin-dedicated Layer 1s. Five projects have emerged as leading contenders: Plasma was first to announce a public chain focused on stablecoin usage, backed by leading stablecoin issuer USDT0 and its partner exchange Bitfinex. Stable followed closely, also supported by USDT0 and Bitfinex, building a dedicated public chain for USDT. Meanwhile, Monad joined the race with its high-profile acquisition of stablecoin infrastructure provider Portal Labs. Codex, while independent like Plasma, is primarily funded by Circle and Coinbase and aims to become a custom layer for USDC payments. However, Circle recently announced creating its own payment blockchain, Arc. Founded by former Binance.US CEO Brian Shroder, 1Money positions itself as a stablecoin-dedicated payment network.
Requirements for Stablecoin Chains: What Truly Matters for Global Adoption
Real-world demand drives the stablecoin movement forward. This is particularly true in inflation-hit countries. Stablecoin users include Turkish freelancers seeking protection from 35% lira inflation, Nigerian manufacturers wanting to pay unbanked suppliers, and Filipino families who should be able to receive remittances in seconds without paying high Western Union fees.

Beyond individuals, more enterprises see stablecoins as tools to improve back-end efficiency and bypass the high costs of existing payment networks like Mastercard and Visa.
These users care less about ideology and decentralization—they care about solving practical problems. Therefore, successful stablecoin infrastructure must excel in specific criteria that directly impact user experience and economic viability.

Transaction Fees and Gas Tokens
To offer meaningful improvements over traditional payment gateways, stablecoins must address some frictions inherent in conventional systems.
Among these, stablecoin payments aim to eliminate friction taxes associated with traditional remittances. According to the World Bank, remittance users lose an average of 6.35%, with banks charging an average of 12.66% on $200 transfers.
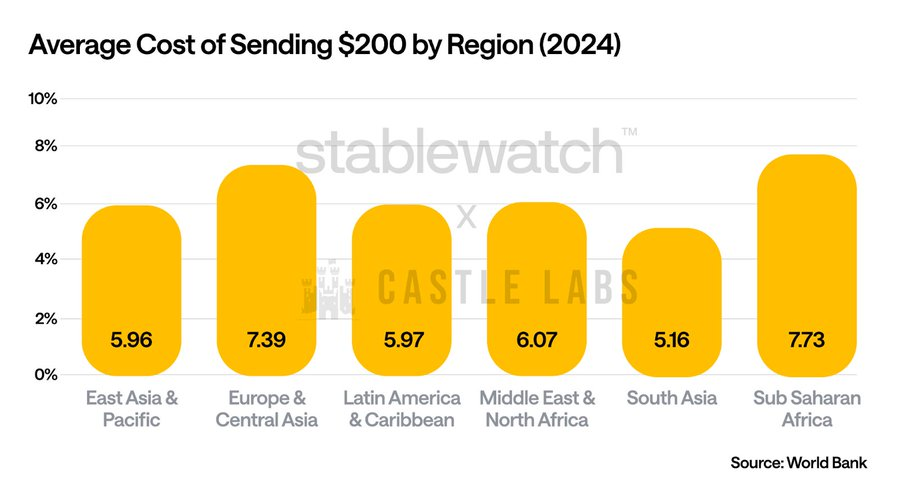
Source:World Bank
Truly zero-cost transactions enable microtransactions and remove adoption barriers for the world's poorest users—precisely those most in need of this technology.
This is not just about cost reduction but also enhancing user experience competitiveness:
-
Users don’t have to deal with hidden provider fees embedded in transactions
-
They don’t need to understand dual-token systems or gas economics when using stablecoins for payments
-
Transfers become as simple as sending a text message
Instant Transaction Finality
Traditional banking’s 3–5 day settlement times create working capital traps, forcing the global economy to operate on implicit credit, increasing costs and inefficiencies tied to every transaction. As commerce goes global, payments should keep pace. When a manufacturer in Lagos pays a supplier in Vietnam, the payment should settle in seconds—not minutes or hours—eliminating any implied trust assumptions and working capital needs from credit-based systems. Instant finality enables new business models like real-time payroll for global remote workers, just-in-time inventory financing, and instant settlement for e-commerce.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
While this feature might surprise crypto-native users who prioritize transparency at all costs, commercial payments require full privacy:
-
Companies paying employee salaries cannot have their payroll data publicly visible
-
Supply chain payments need confidentiality to prevent competitors from analyzing proprietary information about business relationships
-
Imagine a world where having a public wallet means everyone can track you through your daily payments
Blockchains enabling future payments need to provide inherent privacy safeguards for users. However, this cannot be Monero-style complete anonymity but rather selective privacy that allows transparency to comply with global KYC and AML regulations.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
For stablecoins to achieve broad adoption, they must be interoperable across different blockchain networks. Currently, the launch of new networks continues fragmenting this landscape. Successful stablecoin infrastructure must seamlessly integrate with other blockchains, allowing users to transfer value and access active DeFi ecosystems on Ethereum, Solana, Hyperliquid, Base, and Arbitrum.
Native cross-chain functionality prevents ecosystem lock-in (a common issue in traditional fintech) and liquidity fragmentation, letting users access the best apps regardless of underlying blockchain.
Traditional Finance Integration
For stablecoins to become a primary means of value transfer and surpass traditional finance, they must seamlessly integrate with existing systems to facilitate this transition. This means direct bank account connections, integration with credit/debit cards, and support for traditional banking functions like ACH, wire transfers, and merchant services. During the transition, users need to switch seamlessly between both worlds, and blockchain networks must enable this, offering users a seamless application experience.
Developer Experience and Ecosystem
Network effects are one of the main drivers pushing application adoption. This requires attracting developers into your ecosystem, placing developer UX at the core of blockchain success. To achieve this, successful platforms must provide:
-
Excellent developer tools
-
Comprehensive documentation
-
Strong ecosystem support
-
Sufficient liquidity to build stablecoin-centric applications
A robust developer ecosystem not only attracts existing flagship DeFi and payment products onto the chain but also has the potential to inspire creation of chain-specific new products.
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
As stablecoin usage expands beyond retail, enterprises will need customized features—from guaranteed transaction throughput to dedicated development SDKs. Institutions demand reliable performance; this doesn’t change even as they move on-chain. Consumer-focused blockchains unable to meet these requirements will miss out on mass adoption. We’ve already seen companies like Robinhood choose to build their own blockchains to have a controllable environment. Successful stablecoin chains will have these features built in from day one.
Competitors

Plasma|@PlasmaFDN
Plasma is building the foundational stack to scale global stablecoin adoption. Their approach focuses on USDT payments—the leading stablecoin with over 60% market share—to meet user needs. However, Plasma is also onboarding a broad range of stablecoin issuers and protocol ecosystems, making diversity a strength. Additionally, Plasma has proactively built a native Bitcoin bridge, aiming to become the central hub for BTC finance backed by stablecoins. This strategy positions Plasma as a nexus for the two most widely adopted on-chain asset classes.
Plasma has raised $74 million across multiple funding rounds, including a $24 million seed and Series A led by Framework Ventures and Bitfinex/USD₮0. Key investors include Bybit and Japan’s leading investment bank Nomura, along with trading and venture firms: IMC, Cumberland, Flow Traders, Founders Fund, Katarage, and 6th Man Ventures. Notable angel investors in Plasma include Peter Thiel, Paolo Arduino, Cobie, and Zaheer Ebtikar. Recently, Plasma conducted a public sale of its native token XPL, oversubscribed by over 700%, with total committed funds reaching $323.5 million.
Chain Architecture
Plasma’s architecture combines its consensus mechanism PlasmaBFT (derived from Fast HotStuff) for ordering and finalization, with a Reth-based execution layer ensuring state transitions, transaction execution, and EVM logic. These two components communicate via the Engine API, creating a system optimized for both performance and compatibility, allowing Plasma to inherit full EVM equivalence without modifications.
Plasma BFT supports pipelining, allowing new blocks to begin proposing while the previous block is still being finalized. This overlaps block proposal and finalization steps, improving performance and throughput.
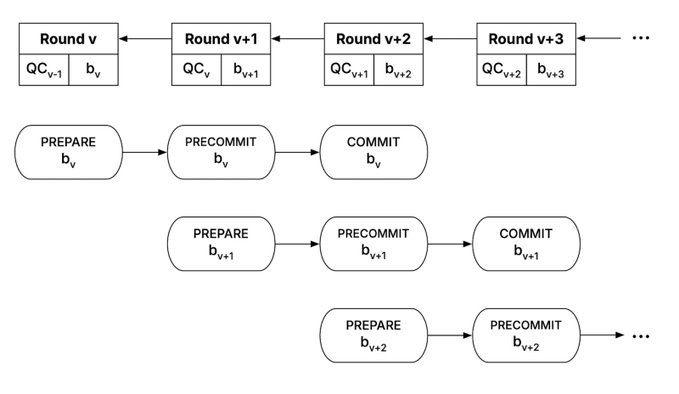
Plasma’s proof-of-stake model innovates on traditional approaches by slashing rewards instead of stake for misbehaving validators. Additionally, validators are not penalized for liveness faults, and the team is exploring optional non-locked staking allowing instant unstaking.
Plasma’s consensus follows a phased decentralization approach:
Phase 1
-
Trusted Validator Launch: At mainnet launch, a small set of known validators secures the network, allowing stability and protocol iteration without operational risk.
Phase 2
-
Validator Expansion: Expand the validator set to test horizontal performance at larger committee sizes and verify throughput under additional trusted entity load.
Phase 3
-
Permissionless Participation: Open validator access to the public, achieving full decentralization through built-in safeguards while maintaining protocol-level security guarantees.
Another core component of Plasma’s chain architecture is the native Bitcoin bridge, enabling BTC usage in smart contracts without relying on custodians, synthetic assets, or isolated wrapped tokens. This is achieved through pBTC, a synthetic version of the underlying asset inheriting cross-chain interoperability from the LayerZero OFT standard. According to Plasma, the bridge is secured by a network of validators that will decentralize over time, composed of independent institutions each running their own infrastructure. The signing process involves multi-party computation (MPC) or threshold Schnorr signatures, ensuring no single validator holds the complete private key.
Plasma is currently in testnet phase, with 338.47k confirmed transactions from 137,927 addresses.
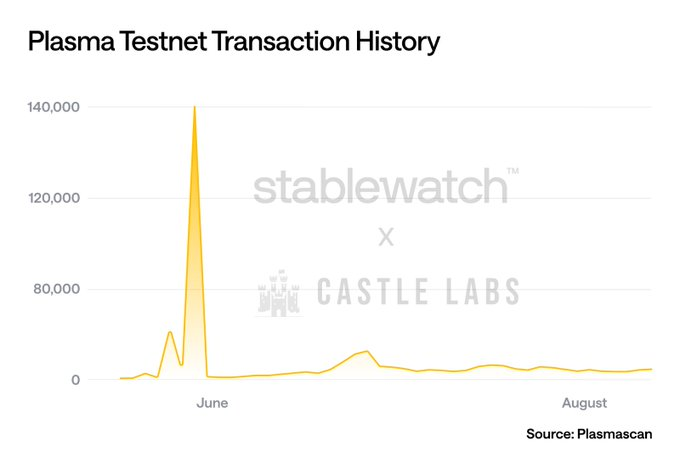
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
Plasma offers fully sponsored gas for USDT through its protocol-level payment system. This mechanism provides gas sponsorship for eligible USDT transfers via lightweight authentication and rate limiting, funded from a protocol-managed XPL quota. Additionally, users can pay gas using whitelisted assets like USDT and BTC, automatically swapped, completely eliminating the need to hold native XPL tokens when making payments.
Instant Transaction Finality
Plasma is secured by PlasmaBFT, a high-performance Rust implementation of Fast HotStuff. It combines the security of Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus with low-latency finality, achieving “near-instant settlement” with sub-second block times. This ensures the high throughput and deterministic guarantees needed for stablecoin-scale applications.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
Plasma is exploring a confidential payment framework featuring stealth address transfers based on recipient public keys, protecting recipient information from public view and allowing only the recipient to see and claim funds. Users will be able to natively move payments into and out of confidential flows without needing new tokens, wrappers, or bridges. Embedded Memos allow optional encrypted metadata to be attached to each transfer. Authorized access via selective disclosure and verifiable proofs ensures full privacy while maintaining auditability and compliance.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Plasma is a USDT-focused blockchain planning to adopt USDT0 rather than issuing native USDT. Beyond integration with LayerZero, Plasma will launch features including Hyperlane (cross-chain messaging and asset transfer), Relay (cross-chain payment system), and Stargate (cross-chain asset transfer). Plasma is also building a native Bitcoin bridge enabling BTC usage in smart contracts without relying on custodians, synthetic assets, or isolated wrapped tokens.
Traditional Finance Integration
Plasma will support a wide range of payment partners, including card issuers, global on/off-ramps, stablecoin orchestration, liquidity partners, and risk & compliance tools. Announced partners include:
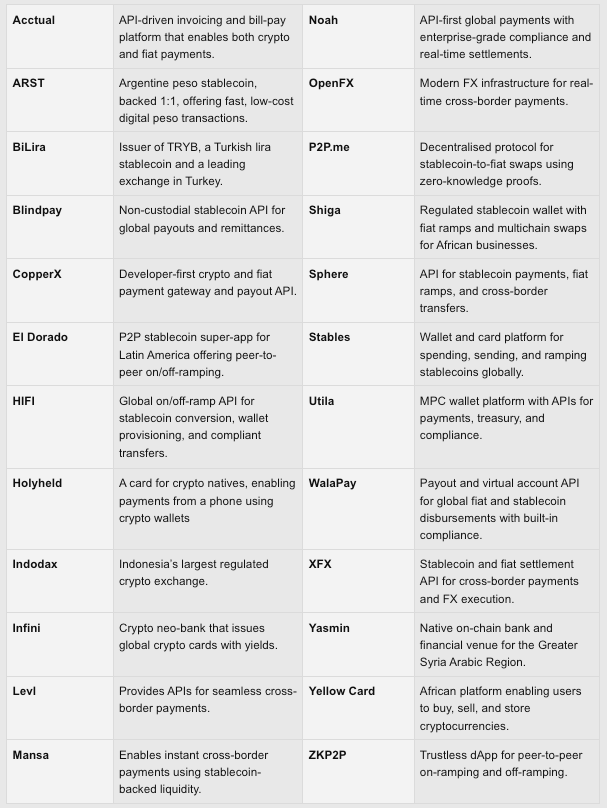
Developer Experience and Appeal
Plasma gained significant attention before testnet launch, integrating multiple key partners and tools. It currently collaborates with 24 payment service providers, plus 5 account abstraction infrastructure/wallet providers (Gelato Relay, Protofire Safe, Thirdweb, Privy, and Turnkey), analytics platform Dune, four blockchain indexers (Arkham, Goldsky, Quicknode, and Zerion), and oracles like Chainlink and Blocksense. This means Plasma will launch with a vast application ecosystem and, crucially, infrastructure providers incentivizing user adoption. Additionally, Plasma conducted a public sale of its native token XPL. To qualify, potential buyers had to lock stablecoins, resulting in $1 billion worth of stablecoin liquidity locked. These stablecoins will be converted to USDT0 and issued on Plasma after mainnet launch. This strategy released massive liquidity pre-launch, effectively addressing the cold-start problem for new blockchains. Plasma recently announced several heavyweight crypto projects launching on it, including Aave, Fluid, Pendle, and Binance Earn, which has already received over $1 billion in USDT deposits.
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
Plasma offers comprehensive payment infrastructure designed for seamless business integration, providing developers and merchants with a full toolkit including APIs, SDKs, point-of-sale modules, and webhook systems. This robust architecture enables businesses to easily build payment workflows, implement USDT checkout, automate payment systems, and embed stablecoin functionality. This allows digital and physical merchants to natively accept stablecoin payments, offering instant settlement, significantly lower fees compared to traditional processors, and unrestricted global access.

Codex|@codex_pbc
Codex is a Layer 2 blockchain designed specifically for institutional stablecoin payments and programmable financial automation. With a founding team from Meta, Coinbase, and Jane Street, backed by Dragonfly Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Circle Ventures, and other institutional leaders, Codex has raised $15.8 million to provide a secure, compliant environment for high-frequency, mission-critical digital currency flows.
While most Layer 2s focus on reducing cost and increasing speed for decentralized applications, Codex specializes in regulated financial environments, supporting FX settlement, enterprise APIs, and stablecoin-native fee mechanisms.
Chain Architecture
Codex is built on OP Stack, a rollup framework fully compatible with EVM. This enables native compatibility with Ethereum smart contracts, wallets, and development tools. Transactions are instantly confirmed on the Codex Layer 2 network, then submitted to Ethereum Layer 1 for fraud-proof validation and final settlement, typically completed within 5 to 10 minutes.
Unlike standalone Layer 1 chains, Codex anchors its security and data integrity to Ethereum’s decentralized validator network. OP Stack relies on a centralized sequencer to quickly order and process transactions on Codex, delivering high throughput and low latency for end users. After batching, transactions are submitted to Ethereum and subject to fraud proofs, allowing challenges and preventing invalid state transitions.
This architecture allows Codex to balance institutional clients’ needs for fast, cost-effective settlement with Ethereum’s proven security. The modular nature of OP Stack further enables Codex to adapt its execution, governance, or data availability layers in response to market and compliance changes, ensuring long-term flexibility and cross-chain interoperability within the broader Ethereum ecosystem.
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
Codex supports paying transaction fees in USDC, providing deterministic pricing and eliminating the need for volatile gas tokens. This simplifies accounting and enhances institutional usability. Stablecoin-denominated gas tokens also support institutional-grade reporting and legal audits—unlike many other blockchains where fluctuating gas token prices create uncertainty, requiring compliance teams to hedge.
Instant Transaction Finality
As a Layer 2 blockchain, Codex delivers rapid settlement, with most transactions achieving finality on Codex within seconds. However, irreversible finality is only achieved once transactions are published and confirmed on Ethereum Layer 1, typically taking 5–10 minutes. Due to this structure, institutions can choose their own risk management strategies: for speed, they can settle on Layer 2; for absolute certainty, they can wait for Layer 1 finality. This Layer 2/Layer 1 model is central to Codex’s ability to offer users fast payment settlement and high transaction throughput while still inheriting Ethereum’s strong security guarantees.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
Codex is currently public by default and plans to introduce a compliance-focused privacy layer using zero-knowledge proofs. Access is managed through KYC onboarding and infrastructure-layer controls. If Codex achieves its zero-knowledge proof compliance roadmap, it could pioneer a regulatory-grade privacy solution without compromising enterprise audits or operational oversight. This remains a key challenge—most enterprises still struggle to balance confidentiality with regulation.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Codex is EVM-compatible and supports native USDC issuance without bridging. Its architecture reduces systemic risks for stablecoin transfers, though bridge risks may persist for non-USDC assets.
Traditional Finance Integration
Codex is deeply embedded in the institutional stablecoin ecosystem. It supports fiat on/off ramps, FX conversion, and T+0 settlement, backed by partners like Circle and Coinbase. These integrations enable Codex to support high-throughput cross-border fund flows, B2B financial operations, and direct fiat connectivity, making it attractive to banks, payment networks, and fintech platforms. The combination of on/off ramps, FX channels, and KYC-certified pathways narrows the gap between on-chain programmable finance and the realities of global B2B cash flows, making Codex an ideal settlement network for institutions seeking more open DeFi channels.
Developer Experience and Ecosystem
Codex stands out not only through EVM compatibility but by offering specialized enterprise SDKs, wallet-as-a-service integration, and compliant APIs for automating large-scale stablecoin flows. Codex’s technical and compliance composability gives enterprise developers a one-stop path to integrate programmable money with traditional infrastructure without sacrificing the audit trails required by real-world finance.
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
Codex currently does not offer enterprise-specific service-level agreements or dedicated blockspace allocation, but it provides a secure, audited rollup infrastructure with compliance solutions tailored for institutional use cases.

1Money|@1MoneyNetwork
1Money is the next-generation Layer 1 payment network built exclusively for stablecoin transactions. Founded by Brian Shroder (former Binance.US CEO) and backed by leading fintech and crypto investors including F-Prime Capital, Galaxy Ventures, and Hack VC, 1Money raised $20 million in seed funding to launch the first stablecoin-native payment chain. 1Money’s mission is to deliver the fastest, safest, and most compliant global digital payment platform. By focusing on stablecoin payments rather than general-purpose blockchain applications, 1Money aims to eliminate the technical and regulatory barriers hindering stablecoin adoption in cross-border trade, remittances, and financial inclusion.
To support this mission, 1Money’s architecture differs significantly from traditional Layer 1 designs.
Chain Architecture
At the core of 1Money is its patent-pending Byzantine Consistent Broadcast (BCB) protocol, replacing traditional block-based processing. The BCB protocol reaches consensus through transaction-level broadcasting and validation, eliminating batch-processing delays inherent in traditional blockchains. This enables parallel transaction processing, delivering ultra-fast and irreversible settlements while completely eliminating chain reorganization risks. This parallel, blockless structure can process over 250,000 transactions per second, ensuring sub-second settlement with horizontal scalability—capacity growing linearly with node count.
Security is maintained through a permissioned validator set, with each participant undergoing strict KYC and AML procedures. This model significantly reduces risks related to double-spending, MEV, and smart contract vulnerabilities. The network does not support smart contracts, eliminating a common source of exploits, and processes each transaction independently without block production delays.
Fees are charged directly in supported stablecoins based on a fixed pricing model designed for operational predictability. Protocol-level compliance features include automatic sanctions enforcement and reporting, while support for multiple stablecoin assets makes 1Money a strong contender for core global payment system infrastructure.
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
1Money charges fixed, low fees in stablecoins without using a native token. It avoids volatility-based pricing and aims to subsidize fees through third-party partnerships. This non-speculative model aligns with corporate accounting expectations, rejects financialization of blockspace, and appeals to operators who prefer clarity over complexity. This model is uncommon among other Layer 1 platforms, where native tokens often serve dual roles as incentives and speculative assets. By completely eliminating token-induced friction, 1Money directly appeals to CFOs and financial managers seeking operational clarity rather than crypto-native complexity.
Instant Transaction Finality
Sub-second, transaction-level finality is achieved through the BCB protocol. Each transaction is independently validated and broadcast, avoiding batch-processing delays. The blockless model enables deterministic, irreversible settlement and horizontal scaling with validator participation. This makes 1Money one of the few blockchains offering deterministic sub-second settlement without relying on probabilistic finality—a technological leap with striking similarities to high-frequency payment rails. The ongoing patent application for BCB further validates this, signaling credible innovation beyond marketing.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
1Money prioritizes compliance over anonymity. All accounts must undergo full KYC/AML onboarding, and every transaction is visible to authorized network validators. Rather than pursuing cryptographic privacy tools, 1Money offers pseudonymity under regulatory oversight, making it well-suited for regulated entities but less ideal for privacy-focused users. This deliberate prioritization transforms privacy from a technical feature into a regulated service: transaction metadata is kept confidential from the public but fully auditable by designated authorities, setting a new compliance benchmark for enterprise chains and potentially outlining a blueprint for global payment regulators.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
1Money is designed for financial interoperability, seamlessly integrating with traditional financial institutions and other Layer 1 chains. Through atomic message passing and API-based architecture, it supports stablecoin transfers across networks without relying on smart contracts or liquidity bridges. Its infrastructure is designed to act as a payment backbone, not a composable layer. By avoiding general composability, 1Money reduces risks of security and liquidity fragmentation—issues that have plagued bridge-centric DeFi protocols—focusing on reliability over coverage.
Traditional Finance Integration
1Money offers APIs for digital accounts, on/off ramps, debit card programs, and merchant payments. Its focus includes remittances, financial inclusion, and B2B settlement, aiming to align with enterprise partners’ compliance and operational standards. By abstracting away cryptocurrency complexity, 1Money allows emerging-market businesses to join using familiar processes, making the network accessible to compliance teams and non-technical operators—something unachievable with Layer 1 networks optimized primarily for DeFi architecture.
Developer Experience and Ecosystem
Unlike programmable chains, 1Money does not support smart contracts. Instead, it offers a powerful suite of APIs tailored for financial service providers, banks, and fintech developers. The network trades composability for predictability, attracting developers building regulated financial infrastructure rather than consumer-facing dApps. 1Money’s ecosystem strategy resembles traditional enterprise software platforms, prioritizing onboarding, auditability, and API reliability.
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
1Money’s infrastructure is optimized for compliance, with validator participation limited to entities that pass formal onboarding and governance review. This ensures reliability and auditability of transactions are maintained at the protocol level, placing operational trust above underlying decentralization. This stance represents a conscious trade-off: by strengthening validator gatekeeping and service assurances, 1Money implicitly bets that the next era of stablecoin settlement will depend on trust, compliance, and uptime—not maximizing permissionlessness.

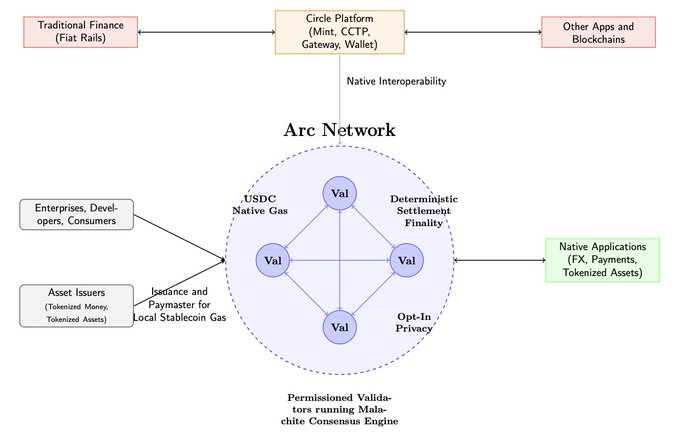
Arc|@Arc
Arc is Circle’s Layer 1 blockchain built specifically for stablecoin finance and programmable money. Unlike competitors building from scratch, Arc leverages Circle’s existing advantages as the issuer of USDC, which has over $68 billion in circulation. This gives Arc immediate access to stablecoin liquidity and institutional partnerships that others must work hard to establish. Circle’s regulatory standing and compliance infrastructure make Arc the most institutionally integrated solution in the stablecoin infrastructure space.
Circle has raised over $1 billion from institutional investors including Goldman Sachs, BlackRock, Fidelity, and Digital Currency Group through multiple funding rounds. Circle recently went public on the New York Stock Exchange under ticker CRCL, enabling access to public market financing as well.
Chain Architecture
Arc is built on the Malachite consensus engine, a high-performance implementation of the Tendermint BFT protocol. The network uses a permissioned Proof-of-Authority (PoA) validator set composed of mature, geographically distributed institutions meeting strict operational and regulatory standards. This design prioritizes institutional requirements and regulatory compliance over maximum decentralization.
The architecture delivers deterministic finality and full EVM compatibility, allowing developers to use familiar Ethereum tools while benefiting from sub-second settlement guarantees. Arc achieves around 3,000 TPS throughput with 20 geographically distributed validators, finalizing in under 350 milliseconds. In an optimized configuration with four validators, the network can exceed 10,000 TPS with finality under 100 milliseconds.
The roadmap includes multi-proposer support to increase throughput by approximately 10x, and optional low-fault-tolerance configurations to reduce latency by about 30%. The modular architecture supports future integration of advanced privacy technologies without fundamental protocol changes.
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
Arc uses USDC as its native gas token, eliminating fee volatility and simplifying corporate accounting. The network implements an enhanced EIP-1559 mechanism using exponential weighted moving averages to smooth fee fluctuations and provide predictable transaction costs. Through dedicated payment rail integrations, users can pay fees using other local stablecoins and tokenized currencies, eliminating the need to hold volatile native tokens.
Transaction fees will go directly into an on-chain treasury (Arc Treasury) upon network launch to support long-term development. This provides enterprises with dollar-denominated transaction costs, enabling predictable financial planning and operational budgeting.
Instant Transaction Finality
Arc delivers deterministic finality in under 350 milliseconds via its Malachite consensus engine. Transactions on Arc are either unconfirmed or 100% final and irreversible—no probabilistic settlement phase required. Once a block receives commitment from over two-thirds of validators through multiple voting rounds, it immediately becomes final, providing the settlement certainty required for institutional financial workflows.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
Arc’s privacy roadmap begins with confidential transfers aimed at hiding transaction amounts while keeping addresses visible to ensure compliance. The solution uses EVM precompiles connected to an encrypted backend, leveraging Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) for high-performance, auditable privacy.
This privacy model supports institutional compliance through “view keys,” granting authorized parties read-only access to specific transaction data. This enables selective disclosure to auditors and regulators while preserving business confidentiality. The modular architecture allows future integration of advanced privacy technologies including multi-party computation (MPC), fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), and zero-knowledge proofs.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Arc provides comprehensive traditional finance integration through Circle’s mature platform products. Native integrations include Circle’s Mint service, which issues USDC directly from fiat bank deposits, seamlessly bridging traditional finance without credit requirements. The network supports direct bank account connections, enterprise-grade compliance tools, and traditional banking functions.
Circle’s regulatory relationships and compliance infrastructure give Arc institutional-grade connections to traditional finance. This includes support for regulated financial services, institutional custody solutions, and direct integration with existing corporate treasury workflows through Circle’s mature partner ecosystem.
Traditional Finance Integration
Arc offers enterprise-grade developer tools, including dedicated SDKs, comprehensive APIs, and native payment modules for invoice-linked payments, refund protocols, and smart financial agents. While maintaining EVM compatibility, the platform offers financial-specific primitives, lowering the barrier to building compliant financial applications.
Circle’s mature ecosystem enables Arc to immediately access institutional relationships, regulatory frameworks, and proven infrastructure. The network natively supports Circle’s product suite at launch—including USDC, EURC, USYC (tokenized money market funds)—and a full payment infrastructure, giving developers access to battle-tested financial primitives from day one.
Developer Experience and Appeal
Arc launches with battle-tested financial primitives. It natively supports USDC, EURC, and USYC (Circle’s tokenized money market fund), providing developers with verified and regulated building blocks for financial applications. Dedicated SDKs support complex workflows including invoice-linked payments, automated refund protocols, and programmable treasury management.
EVM compatibility ensures developers can leverage existing Ethereum tools while accessing Arc’s financial-specific features. This familiar development environment combined with specialized financial primitives significantly lowers the technical barrier to building enterprise-grade financial applications.
Circle’s ecosystem provides immediate access to institutional customers, regulatory frameworks, and mature use cases. Rather than building a developer community from scratch, Arc inherits Circle’s established customer relationships and proven market demand.
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
Arc is designed as institutional-grade infrastructure, featuring permissioned validators, guaranteed performance metrics, and comprehensive compliance features. The validator model ensures operational resilience and regulatory compliance, while the modular architecture supports customization for specific enterprise needs.
The network natively supports complex financial workflows including programmable FX engines, tokenized asset issuance, and automated treasury management. Arc’s roadmap includes transitioning to a permissioned Proof-of-Stake model to achieve broader validator decentralization while maintaining institutional-grade security and compliance standards.

Monad|@monad
Monad represents a different category from the other chains discussed—a general-purpose blockchain strategically pivoting to capitalize on stablecoin adoption growth. Rather than building stablecoin infrastructure from scratch, Monad acquired Portal Labs to integrate comprehensive payment foundations while maintaining its performance edge. Portal Labs is a stablecoin finance developer platform enabling enterprises to create wallets, transfer stablecoins, and scale on-chain operations via SDKs and dedicated APIs. This acquisition, unprecedented among blockchain foundations, likely brings an exciting new competitor to the stablecoin arena.
Monad has raised $248 million across three funding rounds, with its latest Series A completed in May 2024 valuing the company at $3 billion. Key investors include Paradigm, lead investor in the Series A, and Dragonfly, lead investor in the seed round. Additional backers include Coinbase Ventures, GSR Ventures, Wintermute Ventures, and OKX Ventures. Notable angel investors include Naval Ravikant, Cobie, and Hasu.
Chain Architecture
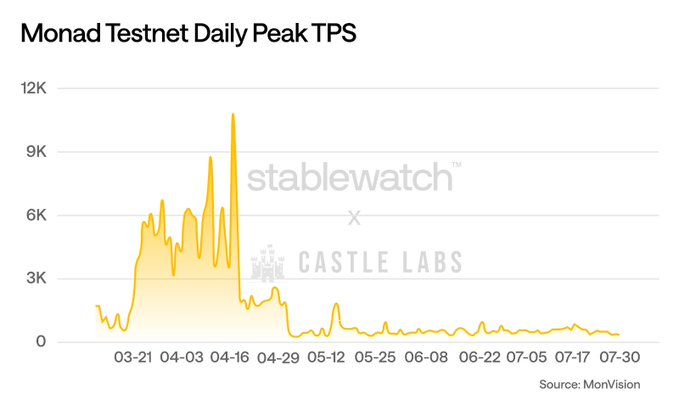
The Monad team rebuilt nearly every component of their client almost from scratch to push boundaries at the intersection of scalability and decentralization. Monad claims these innovations will enable 10,000 TPS performance, 500ms block frequency, and 1-second finality—positioning it as one of the highest-performing EVM-based Layer 1s. Monad achieved this feat on testnet, hitting a peak TPS of 10,832 on April 17.
Monad solves speed issues by running multiple processes simultaneously rather than executing all operations sequentially. It uses the MonadBFT consensus mechanism—based on the proven HotStuff algorithm—that handles malicious actors and pipelines transaction batches. This allows Monad to process different transactions simultaneously in parallel pipelines, significantly boosting throughput.
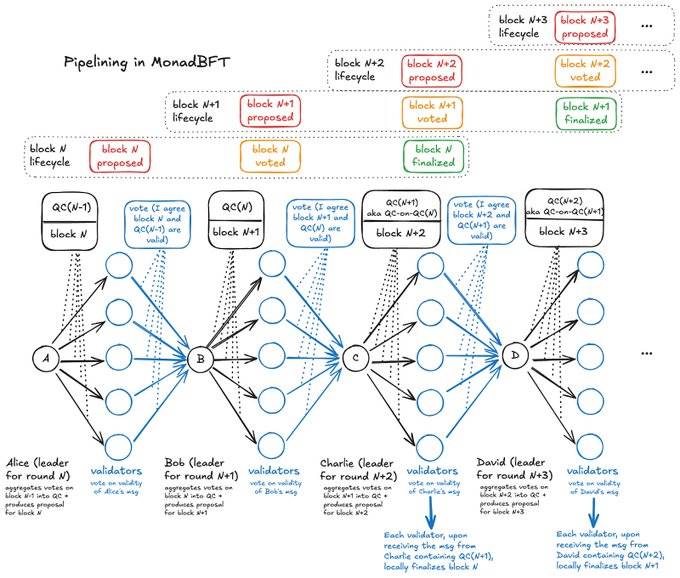
In MonadBFT, the path from proposal to finalization for block N ideally follows linear communication, typically following a “fan-out, fan-in” pattern. The leader sends messages directly to validators; validators send messages directly to the next leader.
Monad uses two additional technologies to maximize speed: MonadDB, a custom database optimized for blockchain data storage, and RaptorCast, a method using erasure coding and a two-tier broadcast system to propagate new blocks across the network. This efficiently utilizes each validator’s internet upload capacity, minimizing the time required for everyone to receive new blocks.
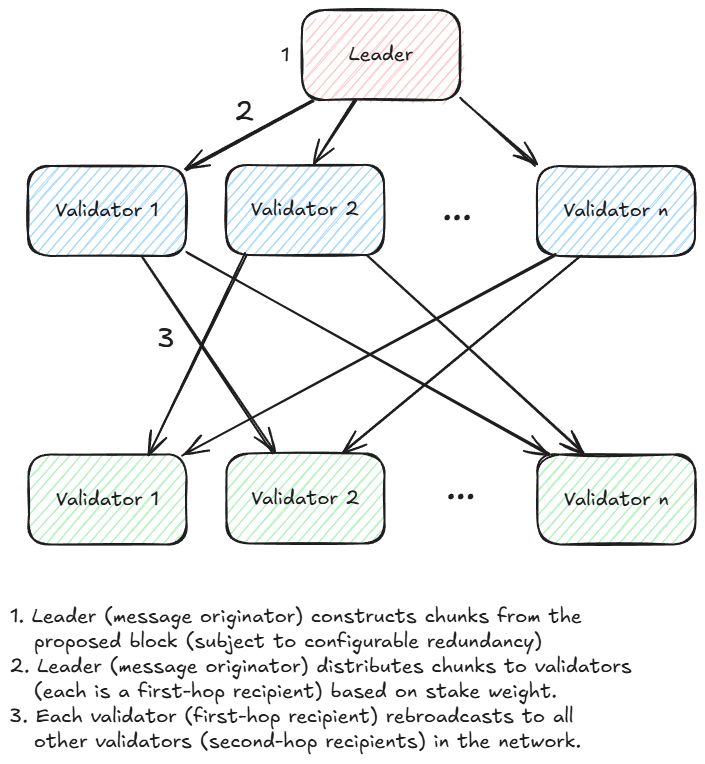
RaptorCast is used to send erasure-coded data chunks from the leader to each validator.
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
Monad aims for “near-zero gas fees” and is compatible with EIP-1559. While this represents an improvement over traditional blockchains, Monad retains traditional gas economics, requiring users to hold and manage a native token to pay gas fees. This approach is cost-competitive while avoiding friction from holding volatile native tokens.
Instant Transaction Finality
Monad commits to superior finality performance, achieving 1-second single-slot finality and 1-second block time. This means transactions become irreversible within one second—ideal for real-time payment applications.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
As a general-purpose chain, Monad does not include privacy features natively but relies on its general EVM capabilities to serve as a foundation for potential application-layer solutions.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
The Portal acquisition provides important built-in functionality for Monad’s stablecoin users, including cross-chain interoperability. Portal enables clients to easily perform cross-chain swaps across over 100 supported blockchains. It also supports multiple interoperability partners, including Chainlink CCIP (a standard allowing developers to build secure cross-chain applications that transfer tokens, send messages, and initiate actions across blockchains), Garden (cross-chain Bitcoin swaps), Hyperlane (cross-chain messaging and asset transfer), LayerZero (cross-chain messaging), Polymer (cross-chain operation proofs via Merkle proofs), and Wormhole (cross-chain messaging protocol).
Traditional Finance Integration
Monad’s payment ecosystem includes three projects integrating the chain with TradFi:
-
Agora, a stablecoin issuer facilitating on/off ramps.
-
DAU Cards, issuing crypto-backed debit cards.
-
Fizen, offering on/off ramps and a crypto payment gateway enabling businesses to accept crypto payments.
Additionally, the Portal Labs acquisition gives Monad a dedicated stablecoin payment infrastructure provider, including embedded wallets with TSS MPC security and easily integrable APIs/SDKs. Other key features of Portal’s products include gas sponsorship, batch transactions, and enterprise-grade security.
Developer Experience and Appeal
Monad demonstrates strong commitment to developer ecosystem development through founder residency programs, Madness competitions, hackathons, and the Mach Accelerator program. These initiatives provide not only funding but mentorship and ecosystem connections. Additionally, the foundation actively pursues business development, with over 273 projects committed to launching on Monad mainnet. These projects span categories including AI, gambling, DeFi, DePIN, gaming, governance, NFTs, payments, prediction markets, RWA, and social. Full list available at the Monad ecosystem directory: https://www.monad.xyz/ecosystem
Enterprise-Grade Infrastructure
Monad’s reported high performance (10,000 TPS, 1-second finality) delivers the predictable service levels enterprises require. However, aside from the Portal acquisition, its dedicated stablecoin enterprise features have not been detailed extensively.

Stable|@Stable
Stable addresses a core problem in stablecoin infrastructure: USDT has $160 billion in circulation and over 500 million users, generating billions in daily transfers, yet operates without a blockchain specifically optimized for it. Unlike general-purpose blockchains treating stablecoins as just another asset, every component of the Stable protocol is meticulously designed to minimize friction in USDT transfers, delivering a streamlined, high-performance, and tailor-made environment.
Stable recently announced completion of a $28 million seed round led by Bitfinex, USDT0, and Hack VC. Other participants include Franklin Templeton, Castle Island Ventures, E-girl Capital, ByBit Mirana, Susquehanna International Group, Nascent, Blue Pool Capital, BTSE, and KuCoin Ventures. Notable advisors include Paolo Arduino, Nathan McCauley, Brian Johnson, and Gabriel Abed.
Chain Architecture
The network is a Layer 1 using StableBFT, a variant of CometBFT (a mature fork of Tendermint), providing deterministic finality and fault tolerance against up to one-third of faulty validators. The platform achieves sub-second block times and finality, ensuring rapid transaction completion and supporting real-time settlement. Through the Stable SDK, StableBFT communicates with Stable EVM—an Ethereum-compatible execution layer—via a set of precompiled contracts. These precompiled contracts expose native StableSDK module functions to EVM smart contracts, enabling them to securely and atomically interact with core chain logic.
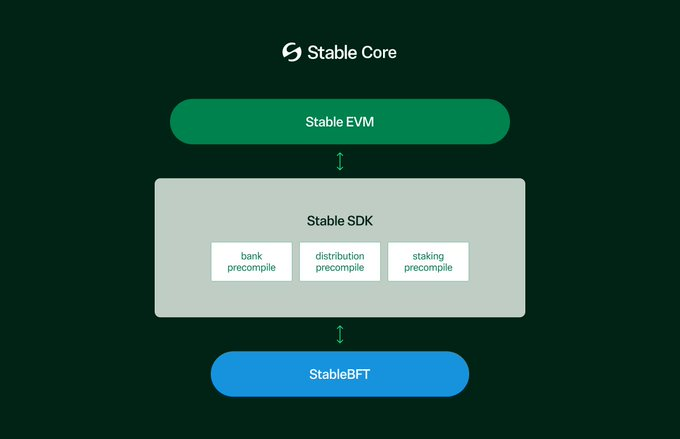
The technical roadmap reveals ambitious performance targets through a 3-phase optimization strategy, with Phase 1 being the current Stable implementation:
Phase 2
-
Introduce optimistic parallel execution (2x throughput improvement)
-
Optimize state database via MemDB and VersionDB with memory-mapped storage
-
USDT transfer aggregator for large-scale transaction processing
Phase 3
-
Advanced consensus via StableBFT built on Autobahn (demonstrated 200,000+ TPS in controlled environments)
-
StableVM++ implemented in C++ as a replacement for Go-based EVM (expected 6x execution performance improvement)
-
High-performance RPC architecture supporting over 10,000 TPS with sub-100ms latency
Transaction Fees and Gas Token
Stable uses USDT0 as its primary token and enables gasless USDT0 transfers via EIP-7702 and account abstraction. For non-USDT0 transactions, users pay gas fees using USDT0 tokens, with bundlers and paymasters automatically converting these into gasUSDT. Users only need to hold USDT0 tokens—the protocol handles all gas conversions automatically, eliminating the complexity of traditional dual-token systems.
However, peer-to-peer USDT transactions on Stable are completely free, leveraging the EIP-7702 permit mechanism and account abstraction.
Instant Transaction Finality
Stable will deliver sub-second block times and single-slot finality on EVM, uniquely optimized for scalable issuance, settlement, and management of USDT.
Compliant Confidential Transactions
Stable’s roadmap includes confidential transfers using zero-knowledge (ZK) cryptography to hide transaction amounts while keeping sender/receiver addresses visible for compliance. This will provide enterprise-grade privacy for business payments while maintaining KYC and AML auditability.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
The USDT0 token used on Stable follows the LayerZero OFT standard, enabling seamless cross-chain USDT transfers without relying on traditional bridge complexities. This allows direct interoperability with other LayerZero-connected blockchains, consolidating USDT liquidity across networks. This positions Stable as a central hub for cross-chain USDT activity, not an isolated network.
Traditional Finance Integration
Stable has implemented native TradFi integration. The Stable App offers social login, providing a familiar user experience for non
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News















