Four Pillars: As the U.S. ushers in a "Crypto Golden Age," how will South Korea respond?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Four Pillars: As the U.S. ushers in a "Crypto Golden Age," how will South Korea respond?
The momentum for change is becoming increasingly evident, and as the pieces of the puzzle come together, now is the critical moment to gain a deep understanding of the blockchain industry.
Author: Heechang Four Pillars
Translation: TechFlow
Key Takeaways
The Executive Order 14178 Working Group today released a 166-page report outlining how the United States can lead the blockchain industry and usher in the “Crypto Golden Age.”
The core of the report can be summarized into four main points: (i) Establishing a unified classification framework for digital asset markets; (ii) Interconnecting banking and blockchain industries; (iii) Accelerating stablecoin adoption; (iv) Developing guidelines for combating illicit financial activities and taxation.
In the real world, momentum for transformation is growing. Collaborations between traditional financial institutions (such as JPMorgan Chase) and blockchain-based platforms (such as Coinbase, Robinhood) are demonstrating an important trend toward practical financial innovation.
While countries like the U.S. are leading in this field, South Korea should also take more proactive steps and remain open—essentially saying, “Let’s seriously examine and try to understand all of this.” Only by starting to understand now can we avoid being left behind amid rapid change.
1. Those Who Recognize the Power of Blockchain Will Lead
In the United States, the government is actively recognizing the potential of blockchain and digital assets and is pushing forward aggressively. On January 23, 2025, President Donald Trump issued Executive Order 14178, “Strengthening U.S. Leadership in Digital Financial Technology,” which established clear regulatory guidelines and encouraged innovation in the sector. In accordance with this order, the Executive Order 14178 Working Group today released a 166-page report outlining how the U.S. can lead the blockchain industry and welcome the “Crypto Golden Age.”
The report reviews America's long tradition of technological innovation and assesses that blockchain and digital assets (cryptocurrencies) have the potential to fundamentally transform financial systems and structures of asset ownership. It also notes that overly restrictive measures under previous administrations, such as so-called “Operation Choke Point 2.0,” excluded compliant crypto companies from the banking system. The report recommends that future governments actively support business activities related to these innovative technologies rather than suppress them.
Guided by the spirit of Executive Order 14178, the report emphasizes that U.S. regulators should promote innovation through clear and consistent rules and attract crypto firms to operate domestically. It urges agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) to cooperate in establishing clear standards and a unified classification framework to eliminate regulatory gaps. At the same time, it suggests adopting technology-neutral and flexible regulatory approaches in emerging areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), ensuring innovation isn't hindered by outdated rules.

Source: Strengthening U.S. Leadership in Digital Financial Technology – White House
Meanwhile, Hong Kong has responded swiftly, following suit. In June 2023, the Hong Kong government formally introduced a licensing regime for virtual asset exchanges, aiming to regulate cryptocurrency trading while allowing limited retail investor participation. In May 2025, it passed Asia’s most advanced “Stablecoin Act,” setting licensing requirements for institutions issuing fiat-backed stablecoins, effective August 1, 2025. Thanks to this “regulation-friendly and innovation-supportive” approach, Hong Kong is poised to advance blockchain development and become one of Asia’s leading digital asset hubs.
2. Key Messages from the Report “Strengthening U.S. Leadership in Digital Financial Technology”
Since the Trump administration took office, sentiment toward cryptocurrency in the U.S. has shifted. A survey conducted as of June 2025 found that 72% of cryptocurrency investors support the president's related policies, and over one-fifth of Americans now hold some form of cryptocurrency. Among these investors, 64% said the administration’s pro-crypto stance made them more inclined to invest in crypto than before. This optimism is spreading to institutional investors as well: a poll shows 83% of institutional investors plan to increase their allocation to digital assets in 2025.
These figures indicate that a friendlier regulatory environment is injecting new vitality into the crypto industry. Under the government’s rallying cry of “supporting responsible innovation and growth,” the report repeatedly stresses that by implementing pro-crypto policies and establishing a clear regulatory environment, the U.S. is well-positioned to take the lead in the coming blockchain revolution.
The core content of the report can be summarized into four key points. Let us explore each in depth.

2.1 Establish a Unified Classification Framework for Digital Asset Markets
This section explores the legal and regulatory classification of digital assets and ways to improve market structure. Currently, the U.S. lacks a clear standard for determining whether a given cryptocurrency is a security or a commodity. This ambiguity leads to jurisdictional conflicts between regulators (e.g., SEC vs. CFTC) and creates regulatory overlaps and loopholes. The report states, “The absence of a comprehensive classification framework results in chaotic interpretations, making well-intentioned market participants feel like they’re walking through a minefield,” highlighting the urgent need for a clear and unified classification system for digital assets.
For example, a digital token used for fundraising may be considered a security (investment contract) at issuance, but once sufficiently decentralized, some argue it should no longer qualify as a security. Currently, there is no standard accounting for such dynamic changes across a project’s lifecycle, leaving projects facing significant uncertainty about which laws will apply over time.
In this context, the report endorses the proposed Digital Asset Market Structure Clarity Act (CLARITY Act), which passed the U.S. House of Representatives in 2025 with bipartisan support. The CLARITY Act divides digital assets into securities tokens and non-securities (commodity) tokens, clearly assigning the SEC jurisdiction over the former and the CFTC over the latter and the spot crypto market. The act also includes provisions protecting Americans’ rights to self-custody assets and engage in peer-to-peer transactions, and recognizes the value of decentralized governance and decentralized finance (DeFi).
The report notes the CLARITY Act would “lay a solid foundation for the structure of U.S. digital asset markets,” but recommends several improvements during the legislative process. First, it emphasizes the need to clarify the legal status of fully decentralized protocols. It offers lawmakers several factors to consider, such as:
-
Whether a given software protocol exercises actual “control” over user assets;
-
Whether the protocol can technically be modified or upgraded;
-
Whether there is a centralized operator or governance structure;
-
And whether current regulatory obligations can be technically enforced.
Given these criteria, the report argues truly decentralized projects cannot be regulated like traditional intermediaries and therefore require a new approach. Regulators should develop a flexible framework that achieves policy goals without stifling innovation.
The report hopes the CLARITY Act can provide this foundation and urges Congress to pass it swiftly. It also recommends that, even before the law takes effect, regulators use existing authorities to immediately provide greater regulatory clarity for market participants.
2.2 Banking and Blockchain Industries Should Be Interconnected
This section discusses the integration of banking and the cryptocurrency industry and offers policy recommendations on how U.S. banks can expand their participation in digital assets under prudent regulation. The report criticizes the prior administration’s move to cut off banking services for crypto firms—known as “Operation Choke Point 2.0”—as a mistaken attempt to stifle a legitimate industry by pushing it out of the banking system.
It notes that top-down pressure led many U.S. crypto firms to face bank account closures, resulting in unintended consequences such as consumer harm and the growth of unregulated “shadow” markets.
The report emphasizes that banks leveraging blockchain technology can significantly boost efficiency and reduce costs. For instance, integrating distributed ledgers into payment and settlement systems could enable 24/7 real-time payments and atomic settlement of transactions, eliminating business hour constraints and reducing reliance on central clearing entities. Some major banks have already moved in this direction, testing their own digital dollar tokens or blockchain platforms for bond settlements.
Recommendations in this section include:
-
Clarifying permissible crypto-related activities for banks and reinstating initiatives like the Office of Innovation to guide banks in this space.
-
Increasing transparency in bank charter approvals and Federal Reserve account applications, to encourage new entrants and prevent unfair denial of services to existing banks serving crypto clients;
-
Aligning bank capital requirements with actual risks, and developing regulatory guidance for new exposures like tokenized assets.
2.3 Stablecoins Should Be Treated as Innovative Digital Tools and Actively Promoted
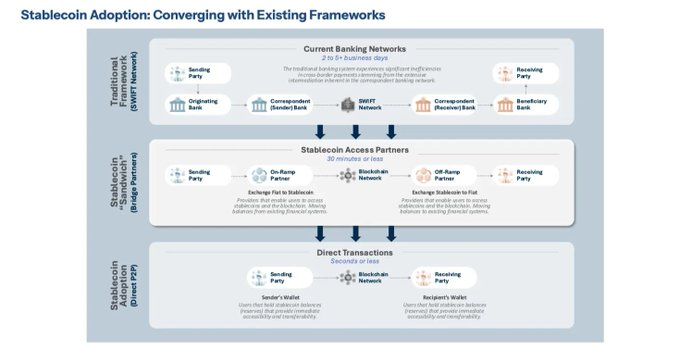
This section focuses on stablecoins within the context of digital payment innovation and how they can reinforce the dominance of the U.S. dollar. Stablecoins are price-stable crypto assets designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with fiat currencies like the U.S. dollar. Due to their low volatility, they effectively function as digital cash within the crypto ecosystem.
The report evaluates that widespread use of dollar-pegged stablecoins could modernize payment infrastructure and help the U.S. move beyond its aging traditional payment networks. For example, using stablecoins for international remittances or securities settlements could enable near-instant processing without intermediary banks, significantly lowering fees. This would also enhance the dollar’s global influence. Currently, dollar-based stablecoins represent a significant share of global crypto transaction volume, circulating in the tens of billions of dollars. The report stresses that to lead this trend, the U.S. must establish a clear federal regulatory framework for stablecoins.
In this context, the report highlights the recently passed congressional legislation: the “Guiding and Establishing National Innovation in U.S. Stablecoins Act,” or GENIUS Act. The GENIUS Act (i) establishes a system for private issuers of dollar-backed stablecoins approved and regulated by the Federal Reserve; (ii) prohibits the Fed from building a central bank digital currency (CBDC), thereby clearly favoring private-sector-led digital dollar innovation. The report praises the GENIUS Act for “embedding an innovation-friendly framework into federal law” and strongly urges the Treasury and other relevant agencies to implement it diligently and promptly.
The report also notes that alongside establishing stablecoin regulations, addressing tax issues is critical. Under current U.S. tax law, the definition of stablecoins remains unclear, and their tax treatment may vary depending on whether they are classified as currency or property. This ambiguity burdens market participants, so the report recommends updating tax laws to clarify stablecoin classification once the federal regulatory regime is in place, thus eliminating uncertainty.
The core message of this section can be summarized as: “Actively promote stablecoins as tools for digital dollar innovation and firmly reject CBDCs, which threaten American freedom and financial stability.” Regarding stablecoins, the report urges strict enforcement of the newly enacted GENIUS Act and recommends additional legislation when necessary to strengthen privacy protections and consumer safeguards.
The report also emphasizes that the U.S. should lead internationally in setting global standards for stablecoins and drive innovation in cross-border payments.
2.4 Clear Guidelines Must Be Established for Illicit Financial Activities and Taxation
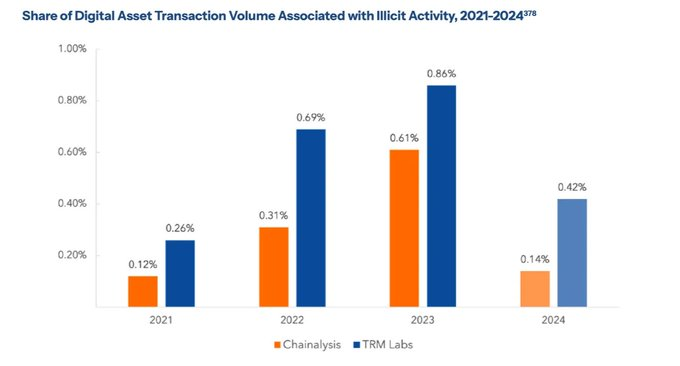
This section discusses risks of illicit financial activity involving cryptocurrencies (such as money laundering, terrorist financing, tax evasion) and countermeasures. The report opens by stating, “To ensure national security while embracing innovation, we must modernize anti-money laundering (AML) regulations,” and analyzes vulnerabilities in the current system.
Due to the anonymous, borderless, and real-time nature of crypto transactions, the report acknowledges challenges in enforcing laws like the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) or the “Travel Rule,” which were designed for traditional banking. For example, criminals may use decentralized exchanges or mixing services to repeatedly swap or split funds, making transactions difficult to trace. The report cites specific cases—such as North Korean hacker groups exploiting DeFi in 2022 and ransomware attackers demanding crypto payments—to illustrate the need to update current AML mechanisms to counter these new tactics.
At the same time, the report repeatedly emphasizes that AML and counter-terrorist financing (CFT) enforcement must not be abused or deviate from their legal intent. If AML regulations are weaponized for political purposes or to suppress specific industries, public trust in the financial system will erode. Therefore, regulators themselves must operate under democratic oversight and transparency, clearly articulating guidelines to avoid unfairly restricting legitimate businesses and users.
The final part of this section offers recommendations to resolve ambiguities and uncertainties around “taxation” of digital assets. Although the IRS generally classifies crypto as property, it has not issued specific tax guidance for newer activities such as staking, mining, airdrops, or token wrapping. This lack of clarity causes significant confusion among taxpayers. The report urges the IRS and Treasury to issue clearer, more practical tax guidance and suggests considering tax exemptions for small crypto transactions to avoid penalizing users who adopt crypto for everyday payments.
3. Help More People Better Understand Cryptocurrency
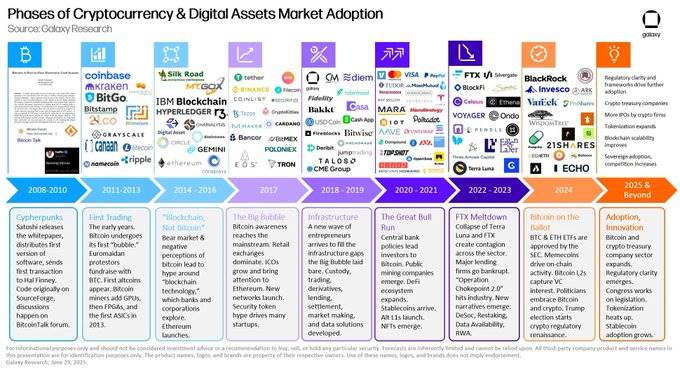
Source: X (@glxyresearch)
Many nations and companies—the U.S. being a prime example—are racing to announce and implement blockchain strategies not merely to follow trends, but because they have anticipated market trajectories and prepared accordingly. In the U.S., firms like Messari, Delphi, Galaxy Research, and rwa.xyz have consistently provided high-quality research, helping institutions formulate forward-looking blockchain and digital asset strategies. Protocols like Ondo Finance and Morpho have built secure on-chain financial services, while companies like BitGo and Coinbase offer reliable infrastructure enabling institutional investment in crypto assets.
In contrast, South Korea’s foundational understanding and preparedness for the blockchain industry—especially stablecoins—remain insufficient. Discussions around stablecoins still center on Terra’s collapse or debates about why stablecoins are unfeasible, focusing solely on issuance rather than practical applications. Yet stablecoins have already demonstrated diverse global use cases. Efforts should focus not only on issuance but also on developing products that integrate them into daily life. Achieving this requires policy support and a clear regulatory environment.
Because the blockchain industry—particularly stablecoins—is still in its early stages, it is difficult to cite concrete success stories proving their utility. Nevertheless, maintaining an open mindset—essentially saying “Let’s seriously examine and try to understand it”—is crucial. Only by beginning to understand now can we keep pace with rapid change.
4. The Puzzle Is Coming Together—The Future Is Emerging
The boundaries between finance and blockchain are blurring, and leading players from both sides are beginning to collaborate. A prime example is the announced partnership between JPMorgan Chase, the largest U.S. bank, and crypto exchange Coinbase. JPMorgan will allow its credit card customers to convert rewards points into USDC on Coinbase’s Base blockchain and directly link customer accounts to the Coinbase platform, enabling seamless, near-instant conversion between fiat and crypto. This landmark integration between a traditional bank and a crypto exchange signals that major financial institutions now view digital assets as legitimate components of their financial services.
This trend extends beyond banks and exchanges. Coinbase has also partnered with Morpho to expand into on-chain finance, specifically decentralized finance (DeFi). Through this collaboration, users can deposit their Bitcoin via the Coinbase app and use it as collateral to borrow USDC for daily expenses. This demonstrates an asset utilization strategy impossible in traditional finance. In practice, investors can continue holding Bitcoin while managing daily cash flow, indicating that blockchain-based financial innovation has reached a viable stage.
New developments are also emerging in fintech. Popular trading platform Robinhood is launching its own Layer-2 blockchain to provide infrastructure for on-chain issuance and trading of listed and private stocks. Robinhood Chain will eventually connect to the Ethereum ecosystem. This means fintech platforms can not only offer brokerage services but also leverage their own blockchains to handle broader on-chain financial assets. In short, a new trend is forming: traditional fintech platforms are adopting blockchain technology to achieve asset ownership and liquidity previously impossible.
Regrettably, compared to these global financial innovations, South Korea lags behind. There has been no substantial cooperation or integration between Korean banks, exchanges, fintech startups, and DeFi projects. Perhaps Korean institutions should at least experiment with private blockchain platforms (like JPMorgan’s private Kinexis network) to gain practical experience. Leading nations and financial institutions worldwide are already mapping out blockchain-driven financial blueprints and actively collaborating. If South Korea remains stagnant, domestic discussions will inevitably stay theoretical, never reaching implementation.
Of course, adopting blockchain is not easy, and cautiousness is understandable when market impacts are unclear. But avoiding the issue due to uncertainty or indefinitely delaying action is not the best path. The transformation of financial systems driven by blockchain has already begun, and pioneers are rapidly learning and advancing. All that remains is for others to decide when and how to join this wave.
The momentum for change is growing. As the pieces gradually come together, now is the critical moment to deeply understand the blockchain industry—and the ideal time to seriously consider and act on adopting blockchain technology.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News