From Visa to Coinbase: Mapping Big Tech's 2025 Moves in AI-Payment Infrastructure
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

From Visa to Coinbase: Mapping Big Tech's 2025 Moves in AI-Payment Infrastructure
This article will guide you through a series of topics, starting with an understanding of the existing financial system. This lays the foundation for understanding how to integrate "agents" into the system to enable autonomous commerce (i.e., agents paying on your behalf). Finally, we will provide a comprehensive overview of companies building autonomous capital infrastructure to enable autonomous commerce.
Author: cookies
Translation: TechFlow
Hey, welcome back! This is part two of the series. If you're wondering where part one is, just click here. I highly recommend reading part one first to understand the necessity of blockchain in agentic capital before diving into companies building infrastructure for it.
The Age of Agentic Capital | Part One So... did you read part one? If not, go ahead and do so—just kidding. But if you haven't read part one, here’s one thing you must know before continuing:
Agentic Capital: Refers to AI systems capable of independently holding, managing, and deploying financial resources to achieve specific goals without human intervention. In this context, an "agent" is an autonomous economic entity with its own capacity for economic action.
Introduction
This article will guide you through a range of topics, starting with an understanding of the existing financial system. This sets the foundation for integrating “agents” into the system to enable agentic commerce (i.e., agents paying on your behalf). Finally, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of companies building infrastructure for agentic capital to realize agentic commerce.
Traditional Financial System
Commonly known as the “four-party model,” this is the standard way payment processing works:
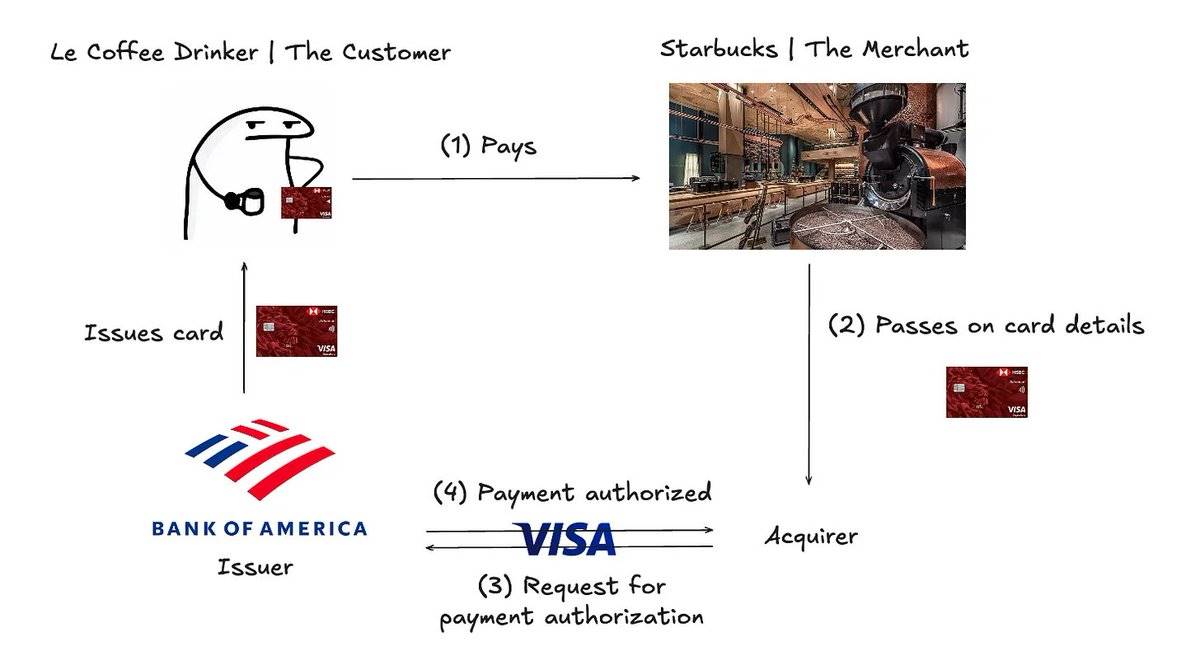
Four-party model of payment processing
-
The user makes a payment using a credit card.
-
Card information is sent to the acquirer.
-
The acquirer forwards the card data to the payment network.
-
The payment network requests authorization from the issuer—the issuer verifies card details and checks for sufficient funds.
To learn more about how payment settlement works, refer to this article.
Breaking it down further:
-
Issuer: The financial institution that issues credit cards to customers. Issuers can be banks, credit unions, or other institutions offering credit lines. When a customer disputes a transaction, the issuer decides whether to support a chargeback. Major issuers include Chase and Bank of America.
-
Acquirer: The bank or financial institution representing merchants by collecting payments from the issuer. The acquirer ensures smooth transactions by passing information through the payment network. In case of a chargeback, the acquirer is responsible for refunding the customer (ultimately deducted from the merchant).
-
Payment Network: Processes card transactions by connecting customers, merchants, acquirers, and issuers. Common networks include Visa and Mastercard.
For deeper insight into each party's role in payments, see this article.
The Rise of Agentic Commerce
Now, we’re handing over the shopping cart to “agents”—they’re becoming the new spenders.
Agentic Commerce: Streamlines shopping experiences via agent-driven payment flows, including search and recommendation features.

Agentic commerce isn’t the only form of agentic capital, but in this article, we use it as an example to illustrate why agents need autonomous access to funds.
The rise of agentic commerce is evident:


Source The purpose of this article is not to dive deep into why these tech giants are establishing footholds in agentic commerce. At a macro level, here are some advantages enterprises gain by becoming the consumer interface layer for agentic commerce:
-
Economic gains: Platforms earn fees every time users complete a payment within their ecosystem.
-
Data flywheel effect: Platforms gain valuable insights from agents’ purchasing patterns and use analytics to recommend complementary products—imagine YouTube’s algorithm always showing you videos you want to watch.
-
Network effects: When a platform becomes a source for product discovery, it attracts more merchants to list goods on it.
Read this excellent article by my team member Evan, which details how business and advertising models will evolve as commercial paradigms shift. Personally, I believe monetization of agents and advertising is an underexplored area, and this article captures the nuances of this digital new era well.
Traditional Companies' Agentic Capital Infrastructure
You've seen how big tech companies are positioning themselves in agentic commerce. But how exactly are they achieving this?
This section details agentic capital infrastructure built by major traditional financial institutions—including Visa, Stripe, PayPal, Coinbase, and Mastercard. (Note from TechFlow: More colloquially, this refers to AI payment infrastructure at present.)
Visa | @Visa
On April 30, 2025, Visa announced the launch of “Visa Intelligent Commerce,” a framework enabling AI to shop and pay autonomously. The design treats agents as end consumers.
Architecture & Key Features:
-
Payment Passkeys: Used for authentication when agents check out. This boosts merchant confidence in accepting payments, accelerating adoption of agentic commerce.
-
Access Controls: Payment passkeys allow users (agent owners) to define parameters such as spending limits and approved merchant categories. These are implemented via APIs and SDKs designed by Visa.
-
Dispute Resolution: Specifically designed to handle potential issues during agent-initiated payments.
Workflow:
-
User inputs a product request into the Visa Agentic Wallet.
-
Agent begins searching for the item.
-
Upon receiving results, the user authorizes the agent to complete payment via a payment passkey.
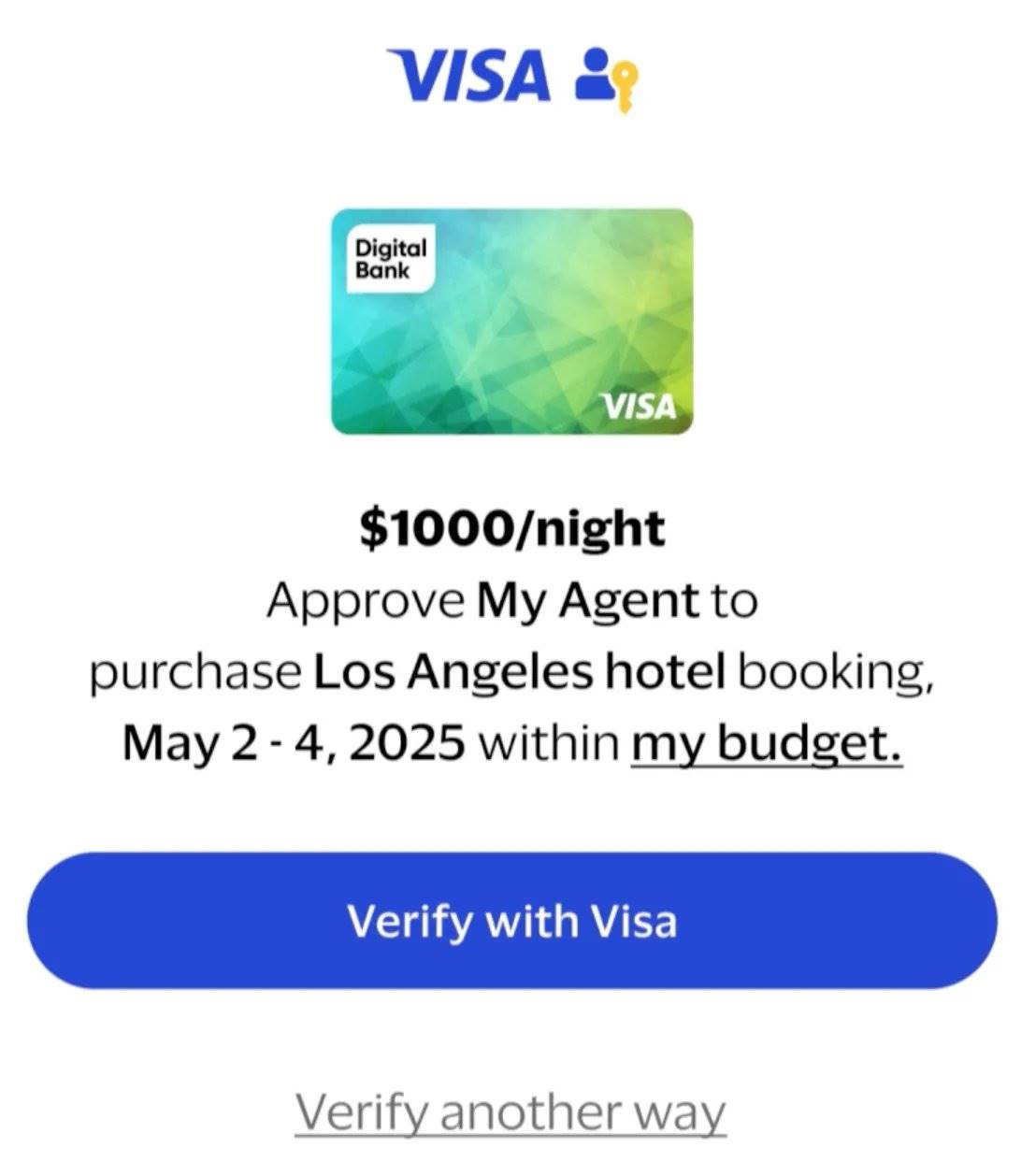
User authorization
You can view the demo video.
Advantages:
-
Trust: Authorized transactions ensure users that agents won’t go rogue or make inappropriate purchases.
-
Network Effects: 99.9% of merchants already accept Visa, meaning users can buy almost anything.
-
Personalization: By analyzing user transaction patterns, agents learn preferences and make better decisions over time—e.g., selecting budget-friendly hotels.
-
Strong Partner Lineup: Includes leading LLM users like OpenAI, Perplexity, Microsoft, Anthropic, and Mistral AI.
For more on Visa’s agentic payment architecture, see this article.
Stripe | @stripe
As early as November 2024, Stripe launched the Stripe Agent Toolkit, allowing businesses to integrate payments into their agentic workflows.
Architecture & Key Features:
-
One-time Virtual Cards: Designed specifically for agent spending, created via simple LLM function calls.
-
Access Controls: Parameters such as budget and merchant selection can be defined via the Order Intent API.
-
Native Billing Support: Stripe monitors usage and bills businesses accordingly.
Workflow: Example of an agent helping book a flight:
-
Agent builder completes KYB (Know Your Business) with Stripe to obtain an API key, granting the agent autonomous fund management capability.
-
User prompts: “Find me a flight to Rome under $1,000.”
-
Agent finds a flight priced at $800.
-
Using Stripe Issuing, a one-time virtual card limited to $800 is generated.
-
Agent generates a payment link, requiring user authorization.
-
After payment, Stripe notifies the agent, updates status, and closes the card.
For a visual workflow, see this video. For detailed architecture, consult Stripe’s developer documentation.
Advantages:
-
Easy Access: Agents can pay using traditional methods—credit cards, bank transfers, Apple Pay, etc.
-
Broad Integration: Toolkit integrates with widely used platforms including OpenAI’s Agent SDK, CrewAI, LangChain, and Vercel’s AI SDK.
PayPal | @PayPal
On April 14, 2025, PayPal launched the PayPal Agent Toolkit, supporting the creation of autonomous workflows handling financial operations.
Architecture & Key Features:
-
End-to-end Support: Enabled via PayPal account linking, encrypted wallets, and emerging payment passkey checkout processes.
-
Core Business Functions: Agents can access payments, invoicing, dispute handling, shipment tracking, product catalogs, subscriptions, reporting, and more.
Workflow:
-
User searches for a product via Perplexity.
-
After finding the item, user checks out quickly via PayPal or Venmo (with identity verification).
For more on Google Cloud’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) protocol, visit this page.
Merchant Use Cases:
-
Order Management & Shipment Tracking: Agents intelligently manage order status and shipping info.
-
Smart Invoice Processing: Agents generate invoices from templates or dynamic parameters, send them to clients, track payment status, and send reminders for overdue payments.
-
Simplified Subscription Management: AI agents manage the entire subscription lifecycle—creating new products, plans, and processing recurring payments via PayPal-supported methods.
Drawbacks:
-
Network Effect: Only about 72.5% of retail websites accept PayPal, lower than the ~99.9% acceptance rate of other networks.
Coinbase | @coinbase
On May 7, 2025, Coinbase announced the x402 protocol—a payment protocol enabling direct stablecoin payments over HTTP.
Architecture & Key Features:
-
Leverages the original HTTP status code “402 Payment Required” to embed stablecoin payments into web interactions.
-
x402 allows developers and AI agents to directly pay for APIs, services, and software using stablecoins over HTTP.
Workflow:
-
Agent requests a resource (e.g., GET /api) from an x402-enabled HTTP server.
-
Server responds with “402 Payment Required” status, including payment details (price, accepted tokens).
-
Client sends signed payment packet via standard HTTP headers using supported tokens (e.g., USDC).
-
Client resends the request with encoded payment data in the X-PAYMENT header.
-
Payment service (e.g., Coinbase x402 Facilitator) validates and completes on-chain payment while fulfilling the request.
-
Server returns requested data with confirmation in the X-PAYMENT-RESPONSE header.
Advantage:
Usage-based billing: Users can make micropayments instead of paying high upfront fees.
Mastercard | @Mastercard
Mastercard launched Agent Pay—an initiative integrating payment capabilities seamlessly into conversational AI platforms.
Architecture & Features
-
Agentic Tokens:
-
A system to register and verify agents—essentially KYC (Know Your Customer) for authenticating agent identity.
-
Tokenization: Replaces card numbers with “surrogate numbers” to protect data.
-
A one-time code (encrypted) is generated during transactions for authentication.
-
Learn more about tokenization here.
-
-
Payment Passkeys:
-
Identity confirmed via device (e.g., biometrics).
-
-
Access Controls:
-
Consumers can define what agents are allowed to purchase.
-
Advantages
-
Transparency: Agentic tokens make it possible to identify and track transactions performed by agents.
-
Partnerships: Collaborates with acquirers and checkout providers like Braintree and checkout.com.
For more on Mastercard’s partners, see this article.
Blockchain-Based Agentic Capital Infrastructure
The next section dives into companies focused on building autonomous payments using stablecoins. Before that, let’s clarify two key roles in agentic payments:
Agent Builder: Developer who creates agents providing specific services, which then receive payments.
Agent User: Individual who deposits funds into an agent for its use; the agent subsequently makes payments.
Skyfire | @trySkyfire
Skyfire aims to become a Visa-like payment network—specifically built for AI agents to create a global, instant, and secure payment network enabling agents to autonomously pay and receive payments. This allows agents to access resources such as MCP servers, APIs, LLMs, and datasets.
Architecture Highlights:
-
Stablecoins: Enable programmable payments.
-
Unique Identifiers: Verified identities for agents, allowing them to open accounts and begin sending/receiving payments.
-
Trust Badges: Multiple vendors offer “blue-check” verification for agents, enabling businesses on Skyfire to trust and interact with agents (both buying and selling).
Key Features:
-
Agent-to-Agent Payments: Instant payments between agents.
-
Autonomous Payments: Agents complete payments without human involvement and can receive payments without needing a bank account.
-
Agent Funding: Agents can be funded via debit cards, credit cards, wire transfers, and stablecoins.
-
Access Control: Spending limits can be set per agent.
-
Agent History: Provides verifiable records of agent activity. For builders, this enables tracking demand for their agent services.
Skyfire's agent tracking interface
Workflow: Example of an agent purchasing data access:
-
Agent initiates service request by calling a data provider’s API.
-
Service verifies the agent’s identity.
-
Upon successful authentication, the agent receives the requested data.
-
Payment is released to the data provider upon completion.
Advantages
-
Market Expansion: Businesses can sell services not only to humans but also to agents (an untapped market).
This is particularly compelling in long-tail markets.
-
Traditionally, selling long-tail services to enterprises is difficult due to low customer volume, making it hard to justify costs like business development (BD) and user acquisition.
-
With a universal marketplace, you can simply upload long-tail datasets, etc., and agents discover them via metadata—eliminating BD and advertising expenses.
Industry Applications & Impact
-
Pricing Culture: Proprietary real-time contextual data intelligence is being purchased and used by agents.
-
Denso: Enables agents to locate required materials across the global automotive parts manufacturing industry.
Funding Update
-
Skyfire raised $9.5 million backed by Coinbase Ventures, a16z CSX, Circle, and others.
Payman | @PaymanAI
Payman is a platform where AI agents pay humans for professional tasks (think of AI outsourcing work to freelancers).
Architecture
-
Human Marketplace:
-
Payman is developing a vetted database of skilled workers to ensure high-quality task completion. This market provides human labor resources for AI agents.
-
-
Verification Agents:
-
Dedicated agents that verify whether human-completed work meets requirements.
-
-
KYC Verification:
-
Individuals wishing to join Payman’s worker database must pass KYC, ensuring agents pay for legitimate services.
-
-
Wallet System:
-
USD Wallets: Hosted via Stripe.
-
USDC Wallets: Custodied by Bridge.
-
-
Payment Network:
-
Payman uses Skyfire to facilitate agent-to-human payments.
-
Feature Highlights
-
Payment Methods: Agents can pay via fiat or cryptocurrency.
-
Programmable Policy Enforcement: Each transaction follows user-defined rules, such as exact amounts for specific tasks.
-
Payment Tracking: Every transaction has a reference ID and real-time status for seamless monitoring.
-
SOC2 Compliance: A framework assessing data security practices. Payman uses data masking and encryption to protect sensitive information.
Workflow
Put yourself in the shoes of someone setting up an agent that will eventually source resources for task completion.
For users setting up agents:
-
Wallet Setup: User sets up a wallet for the agent and adds funds.
-
Task Creation: Agent creates and posts tasks to the marketplace based on user prompts, for human workers to discover.
-
Policy Setting: Define spending limits, approval rules, etc.
-
Task Approval: User receives notifications on dashboard to approve or reject agent requests.
For human workers:
-
Add wallet (crypto or bank account) to the platform.
-
See Payman platform demo
Use Cases
-
Product Managers: Collect user feedback to improve product development.
-
HR: Pay candidates for task completion.
-
Software Engineering: Pay experts for code reviews.
Funding
-
$3 million pre-seed round backed by Visa, Coinbase Ventures, and others.
My Thoughts
-
How sophisticated are the verification agents? For tasks with clear outcomes, verifying completion quality is relatively straightforward. But for ambiguous outcomes, what kind of agents will perform verification?
-
Currently, Payman requires users to manually create tasks. Could agents in the future have autonomy based on general prompts to determine which services to procure? This might be achievable via small language models (SLMs) specialized in domains like automotive or food industries.
-
Overall, the idea is fascinating. It injects a human touch into algorithmically programmed agents. In the AI era, this helps preserve human aesthetics and diverse perception. For instance, a designer’s evaluation of an agent-performed task can add greater value and depth to the outcome.
Catena Labs | @catena_labs
Catena Labs is building the first AI-native financial institution—a regulated entity designed to facilitate collaboration between agents and humans. Catena envisions agents as powerful economic actors, constructing infrastructure including agent identification and AI-specific risk management frameworks.
Architecture – Agent Commerce Kit (ACK)
ACK enables interoperable financial interactions involving agents and consists of two complementary protocols:
-
ACK-ID: Verifiable Agent Identity
-
Verifiable Agent Ownership: Agents cryptographically linked to their human organizational owners.
-
Secure Authentication: Agents prove identity to counterparties and systems they interact with.
-
Privacy-Preserving Verification: Discloses only necessary identity information.
-
Built on Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Verifiable Credentials (VCs).
-
Learn more about ACK-ID
-
-
ACK-PAY: Agent-Native Payments
Learn more about ACK-PAY here.
-
Provides infrastructure for agents to initiate payments and conduct financial transactions.
-
Standardized Payment Flow: Communicates payment requirements from service providers to agents.
-
Flexible Settlement: Agents can settle via multiple channels—traditional finance or crypto.
-
Verifiable Receipts: Secure credentials provide cryptographic proof of payment.
-
Human Oversight: Certain workflow steps may require human approval.
-
Workflow: Example of an agent purchasing proprietary financial data:
-
Request: Agent requests purchase of financial data from Organization M (“M” for Money).
-
Authentication: Organization M uses ACK-ID to verify the agent’s identity (ensure it’s not malicious) and access rights (authorized to access the data).
-
Payment:
-
Organization M sends a standardized ACK-Pay payment request payload to the agent.
-
Agent selects preferred payment method (fiat/crypto).
-
This step may require human approval.
-
-
Receipt:
-
Upon payment confirmation, a verifiable ACK receipt (as a VC) is generated.
-
Receipt delivered to agent, who then accesses the data.
-
See a more detailed workflow
Funding Update
-
Catena Labs raised $18 million backed by a16z Crypto, Circle Ventures, Coinbase Ventures, and others.
My Take Catena Labs appears to be building a comprehensive infrastructure suite for “agentic capital.” Their roadmap includes enhancing agent identity mechanisms, protocol interoperability, compliance and risk monitoring tools, and building a reputation system for agents.
Nevermined | @Nevermined_io
Nevermined is building a payment platform designed for AI agents, enabling agents to initiate and receive payments.
Workflow
Agent Setup Phase
-
Agent Registration: AI developers register their agents and payment plans via the Nevermined app.
-
Payment Plan: A record of how developers wish to charge for their agent—when sold, Nevermined takes a 1% fee.
-
Plan Creation: Nevermined links a Decentralized Identifier (DID) to the developer’s wallet.
-
Discovery Setup: Nevermined creates a widget with plan details for display on its marketplace.
User Access Flow
-
Purchase: User subscribes to a payment plan via the Nevermined marketplace.
-
If user chooses stablecoin payment, funds are locked in a smart contract until they claim credits.
-
-
Distribution: User receives credits corresponding to their purchased plan.
-
Consumption: User sends requests to the AI agent via the Nevermined app.
-
Access Control: Two types of credits determine agent usage:
-
Time-based: User gets access for a fixed duration (e.g., 1 day or 1 month).
-
Request-based: Credits redeemed per request:
-
Fixed: Fixed credit cost per request.
-
Dynamic: Credit cost varies based on request complexity.
-
-
Learn more about payment types in this detailed article on Nevermined payments.
Advantages
-
Discovery Engine: Nevermined becomes an agent discovery platform by storing metadata provided during registration.
-
If you’re a developer looking to monetize your agent, click here. If you’re a user wanting to hire an agent, click here.
-
Fewsats | @fewsats
Fewsats enables agents to pay for services without relying on external payment services.
Architecture & Features
-
L402: When a server responds with HTTP 402 “Payment Required,” it includes machine-readable payment terms for agents to fulfill.
-
Authentication: Cryptographic proof protocols authenticate agents.
-
Access Control: Defines transaction limits and approval workflows.
See demo
Currently, there is limited public information on Fewsats, but rumors suggest integration with the Bitcoin Lightning Network to enable low-cost, near-instant payments for agents.
Conclusion
In this article, I covered companies active in AI payment infrastructure: Visa, Stripe, PayPal, Coinbase, Mastercard, Skyfire, Payman, Catena Labs, Nevermined, and Fewsats (future updates will include Nekuda, Protegee, and Brahma Finance). Undoubtedly, this is a fast-evolving emerging field—innovations by traditional payment firms and investments in payment networks confirm this trend.
In the coming years, key infrastructure questions remain to be answered:
-
Agent Identity Verification: How will large-scale KYA (Know Your Agent) be implemented?
-
Access Control: How granular will controls be? How much autonomy can be delegated to agents? Will this increase as “good behavior” accumulates?
Still, some concerns remain:
-
Funding Sources: Currently, most infrastructure focuses on verifying agent identity and confirming funds. Once agents start handling larger transactions, will money laundering concerns arise?
By studying company architectures and products, I believe dominant players in this space will be those who build applications enabling retail and enterprise customers to seamlessly access needed services through agents. Will this become a battle of partnerships—seeing which platform can attract the most providers? Perhaps.
To me, the data generated from these agent transactions will be extremely valuable, creating a data flywheel. For example, a purchasing agent could optimize its behavior by learning from its own transactions and interactions with other agents. Meanwhile, service-providing agents could observe others’ purchasing behaviors and potentially create new services to capture larger markets.
This is part two of the agentic capital series. In part three, we’ll explore real-world applications.
Disclaimer This article is based on company documents and public articles. If there are inaccuracies or points you disagree with, please comment—I’m happy to discuss further.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News















