Interpreting Binance Research Report: The 2024 Rate Cut Cycle Begins, A Comprehensive Analysis of Fed Policy Impacts
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Interpreting Binance Research Report: The 2024 Rate Cut Cycle Begins, A Comprehensive Analysis of Fed Policy Impacts
The global easing cycle has begun, presenting both market opportunities and challenges.
Written by: TechFlow
Overview
In today's ever-changing global economic landscape, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy direction has profound implications for financial markets worldwide. In September 2024, the Fed cut interest rates for the first time since 2020, marking the beginning of a new easing cycle.
Binance Research recently released a comprehensive report detailing the evolution of the Fed’s interest rate policies and their impact on the economy and various asset classes.
The report systematically analyzes the relationships between core economic indicators—such as interest rates, inflation, and employment—by combining foundational economic theory with the latest data and historical experience. It also provides a thorough assessment of how different asset classes, including equities, bonds, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, perform during rate-cutting cycles, offering investors clear guidance for decision-making.
TechFlow summarizes the key insights from this report below.

Key Takeaways
• Latest Rate Cut Developments: The Federal Reserve announced a 0.5% rate cut in September 2024, followed by an additional 0.25% reduction in November—marking its first rate cuts since March 2020, when it responded to the pandemic. Markets anticipate further cuts of 1–2 percentage points in 2025, with a 62% probability of another 0.25% cut in December.
Policy Background: Guided by its "dual mandate" of maximizing employment and maintaining price stability (with a 2% inflation target), the Fed aggressively raised rates after inflation surged above 9% in mid-2022, pushing interest rates to their highest level in two decades. As inflation cools, the Fed has now shifted toward monetary easing.
Mechanisms of Rate Impact: Interest rates, known as the "price of money," influence markets through two primary channels:
-
Lower borrowing costs make it easier for businesses and consumers to access credit and reduce existing debt burdens
-
Reduced risk-free yields push investors to seek higher returns in alternative assets
Historical Trends: Over the past 50 years, U.S. interest rates have exhibited a structural downward trend—from 8–10% in the 1980s, to near-zero levels in the 2010s, rising above 5% more recently, and now entering a new phase of decline.
Asset Class Performance:
-
Equities (S&P 500) generally rise following rate cuts, though exceptions occur during recessions
-
Commodities have a complex relationship with rates, influenced by carry costs, lack of yield, and exchange rates
-
Bond prices move inversely to interest rates
-
Cryptocurrencies, despite limited historical data, have performed strongly during easing cycles, such as surging 537% within 12 months after the March 2020 rate cut
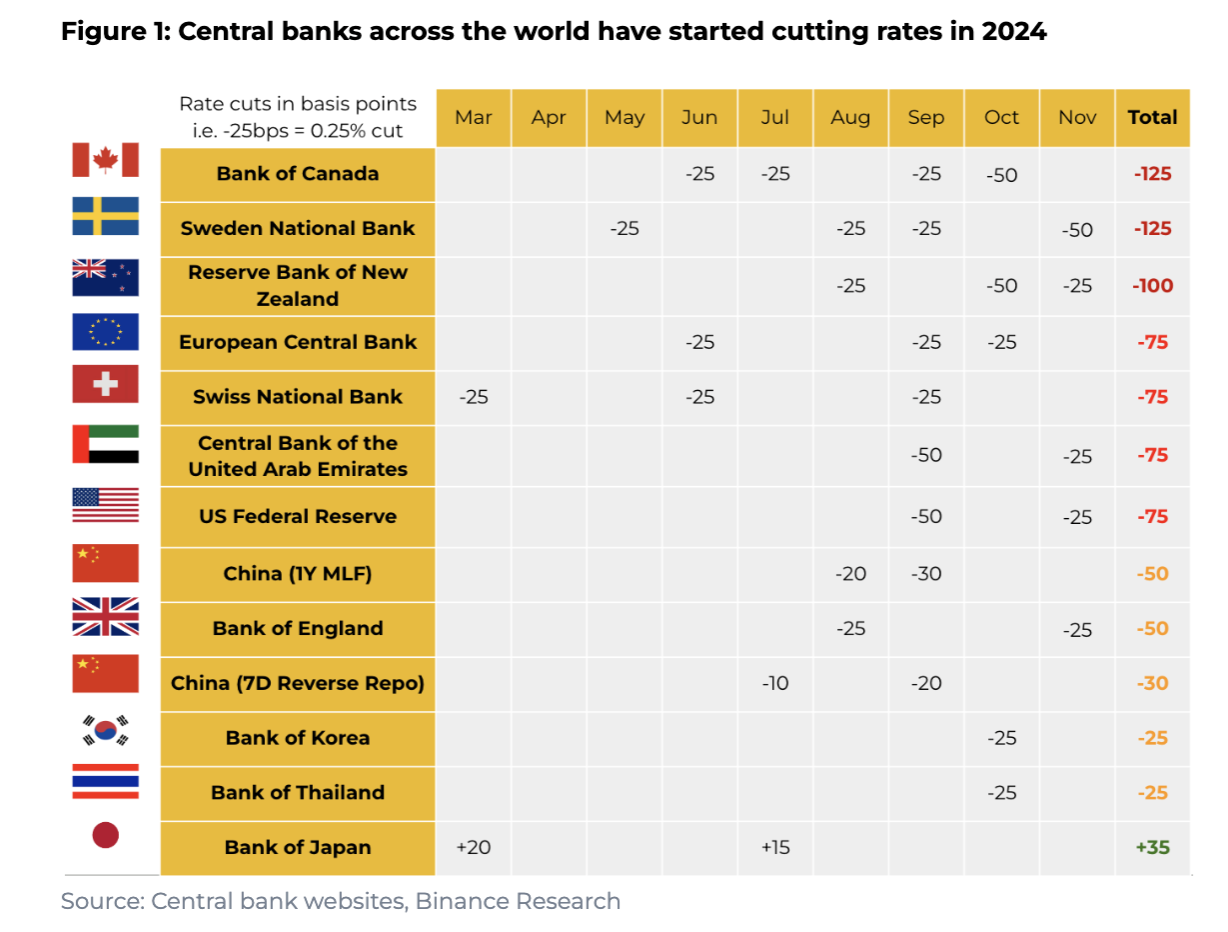
Policy Shift: Global Central Banks Begin Easing
On September 18, 2024, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate target range by 0.5 percentage points to 4.75–5.00%, marking its first rate cut since March 2020 in response to the pandemic. Prior to this, the Fed had implemented aggressive rate hikes from March 2022 to July 2023 to combat rising inflation, then held rates steady across eight consecutive meetings before initiating the current easing cycle. The subsequent 0.25% cut in November further confirmed the start of a new monetary easing phase.
The Fed’s actions are consistently guided by its dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and ensuring price stability. In the post-pandemic period, rapid price increases drove inflation above 9% in mid-2022, prompting the most aggressive hiking cycle in 20 years—raising the target rate from 0–0.25% during the pandemic to 5.25–5.50%. With inflation now cooling, the Fed has begun shifting toward accommodative policy. Market expectations point to 1–1.5 percentage points of additional easing in 2025, with a 62% chance of a 0.25% cut in December (versus 38% probability of no change).
The interplay among inflation, rate cuts, and broader economic dynamics—including asset performance—is complex and warrants close attention from market participants.
Notably, multiple central banks around the world began cutting rates in 2024, a trend that will significantly impact global financial markets.
Foundational Concepts: Interest Rates and Economic Mechanisms
As Warren Buffett once said: "Interest rates move everything in the economic universe." Let's begin with fundamental concepts to understand how interest rates shape economic activity.
Basic Principles of Interest Rates
• Core Definition: Interest rates represent the "price of money"
-
Raising rates = money becomes more expensive
-
Lowering rates = money becomes cheaper
Two Major Effects of the Current Rate-Cutting Environment
-
Debt and Borrowing Effect
-
Businesses and institutions can finance at lower costs, encouraging investment and expansion
-
Existing debt servicing costs decline, improving cash flow
-
Consumer borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating consumption and housing demand
-
Overall economic activity is boosted, supporting growth
-
-
Yield Effect
-
Yields on risk-free assets like government bonds fall
-
Investors are pushed to seek higher returns elsewhere
-
Risk assets such as equities and real estate receive valuation support
-
Capital shifts from low-risk to higher-risk assets
-
Main Economic Variables
-
Inflation
-
The Fed targets a long-term inflation rate of 2%
-
Inflation peaked above 9% in mid-2022
-
-
Labor Market
-
Unemployment remains at a relatively healthy 4.1%
-
Non-farm payrolls data, released on the first Friday of each month, is a key market indicator
-
-
Market Conditions and External Factors

-
Corporate earnings: Quarterly results and outlooks serve as a barometer of market sentiment
-
Regulatory policies: Regulatory stance on financial innovation, including crypto (as shown in the chart below, the number of crypto-friendly lawmakers in both the House and Senate has significantly increased in U.S. elections represented in green)
-
Geopolitics: International trade relations, regional conflicts, and other external shocks
-
Macro indicators: Trade balance, consumer confidence, PMI, etc.
-
Historical Perspective: Past Fed Rate Cuts and Asset Performance
Interest Rate Trends
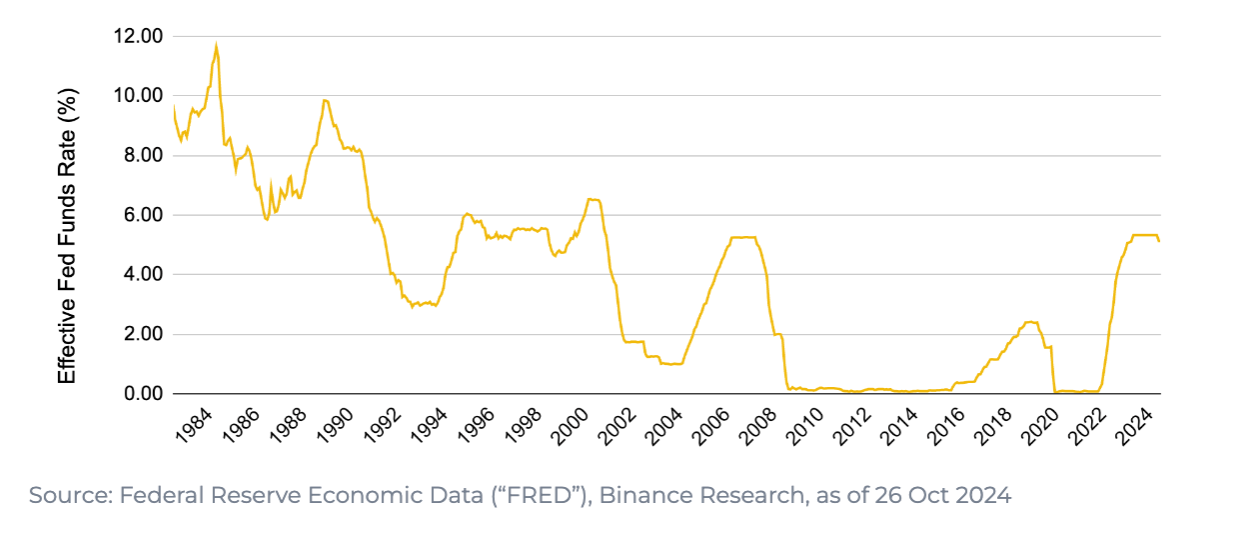
U.S. interest rates have followed a structural downward trajectory over the past 50 years:
-
1980s: Sustained at high levels of 8–10%
-
2010s: Near-zero interest rate environment
-
Recent years: Rose above 5%
-
September and November 2024: A new easing cycle begins
Historical Performance Across Asset Classes
-
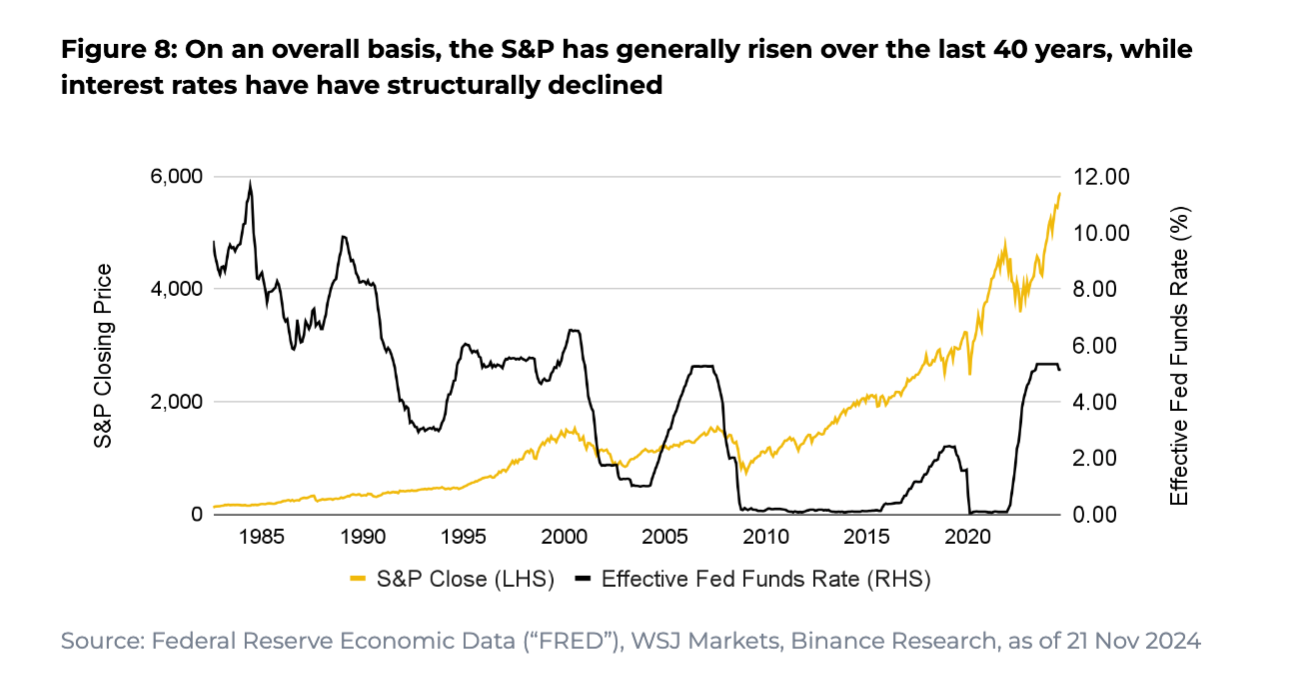
Stock Market (S&P 500)
-
Overall Trend: Typically rises after rate cuts
-
Detailed Performance:
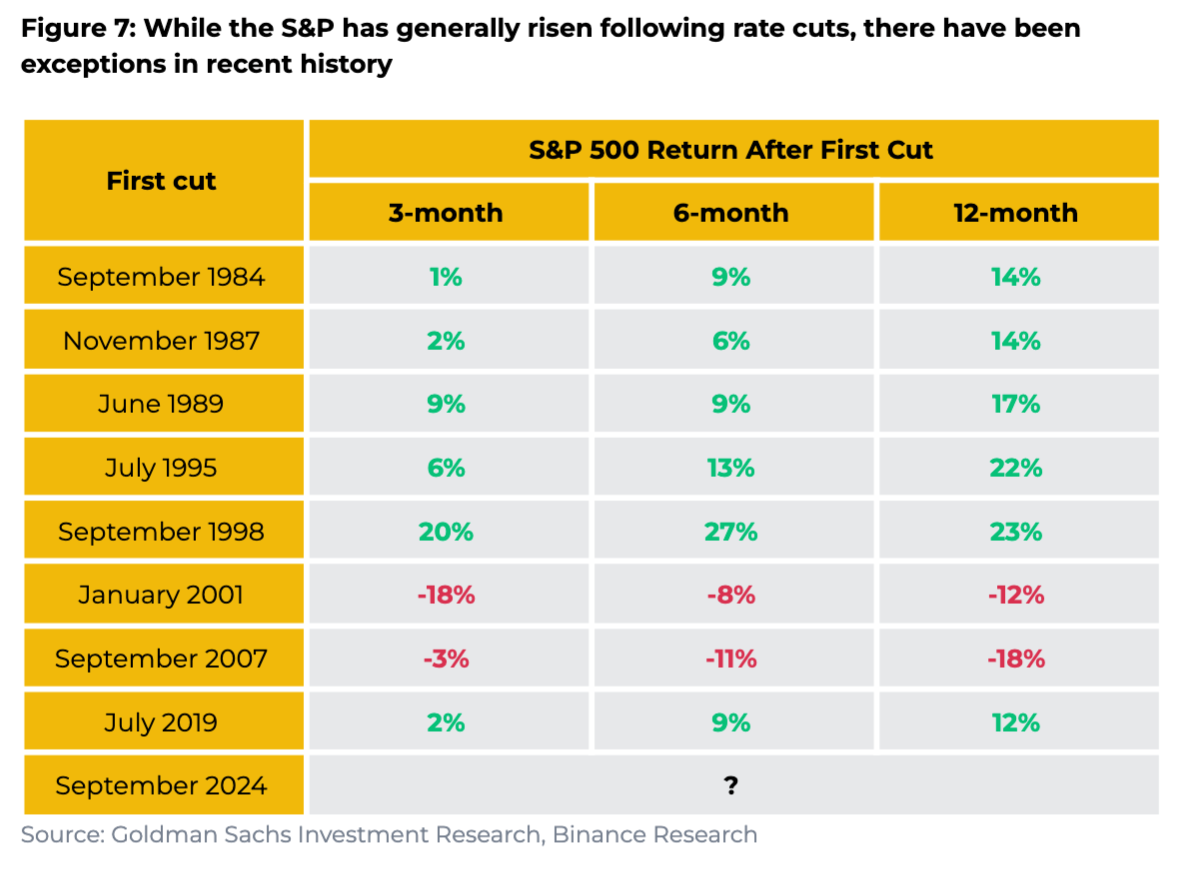
-
First cut in September 1984: +1% in 3 months, +9% in 6 months, +14% in 12 months
-
July 1995 cut: +6% in 3 months, +13% in 6 months, +22% in 12 months
-
Exceptions during recessions: Negative returns in 2001 and 2007
-
January 2001: -12% over 12 months
-
September 2007: -18% over 12 months
-
-
-
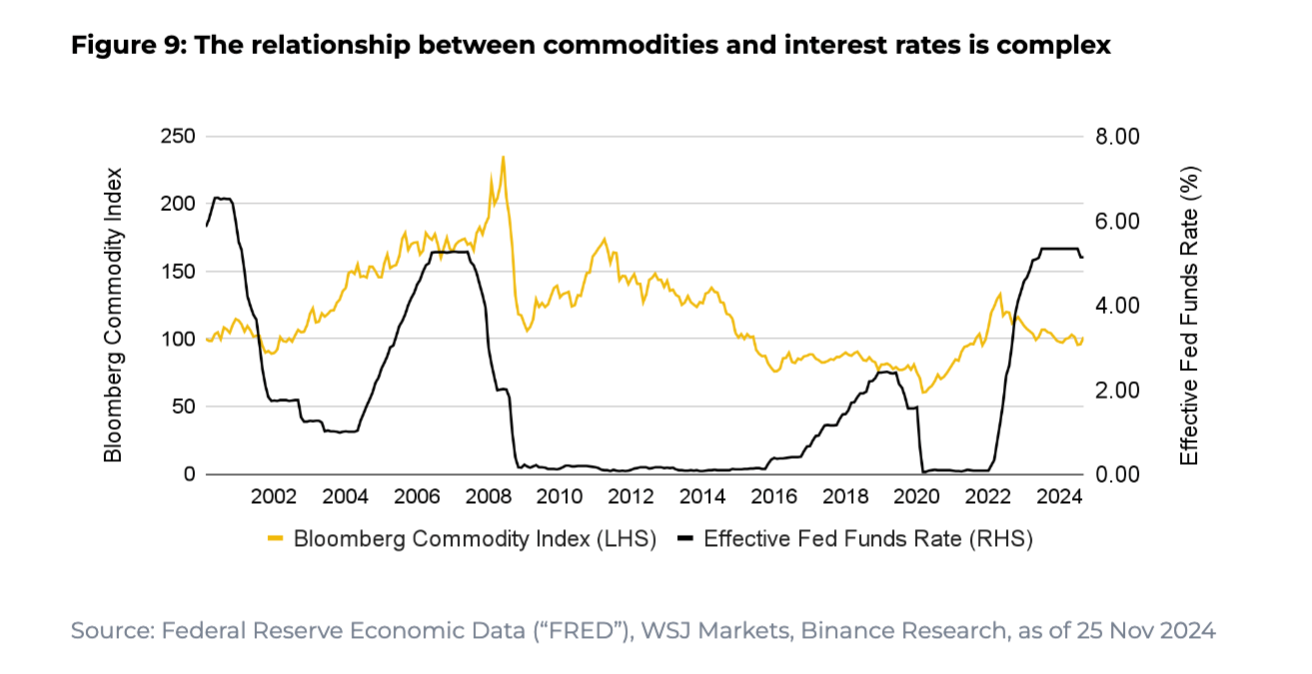
Commodities
-
Key Influences:
-
Carry costs: Interest rates affect holding costs
-
Yield characteristics: No fixed income
-
U.S. dollar exchange rate: Most commodities are priced in USD
-
-
Inflation Linkage:
-
Often seen as a leading indicator of inflation
-
Commonly used as an inflation hedge
-
-
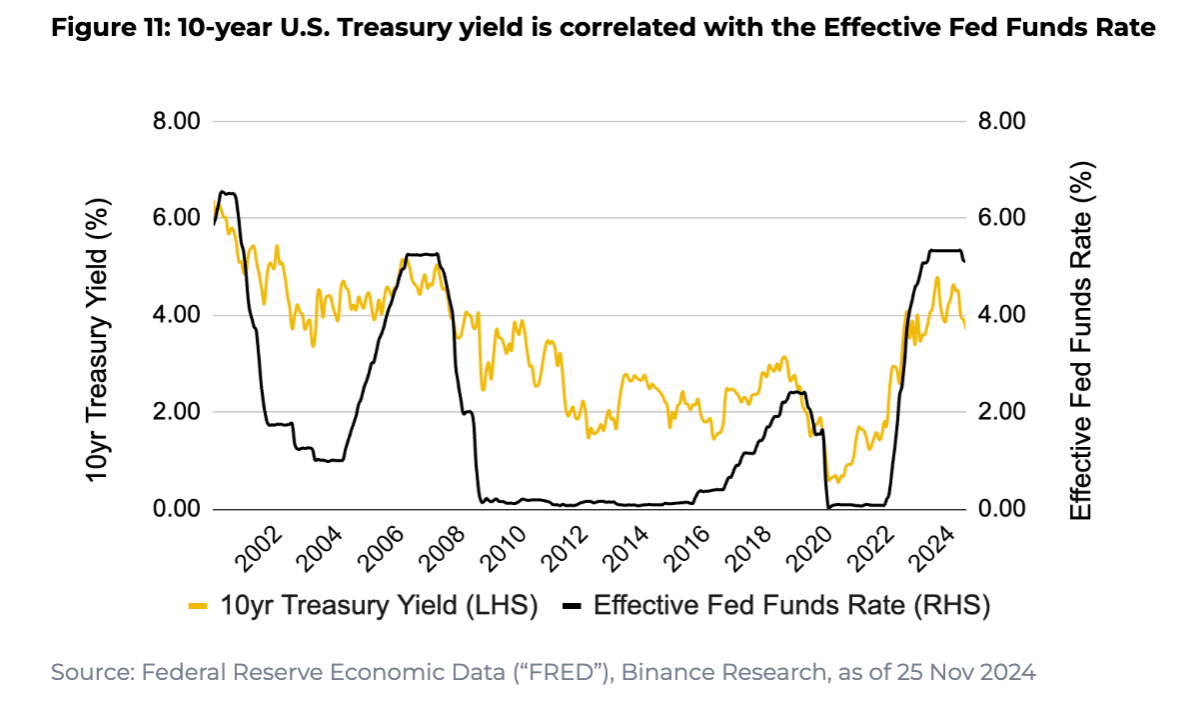
Bonds
-
Core Feature: Strong inverse correlation with interest rates
-
Mechanism:
-
Rising rates → falling bond prices
-
Falling rates → rising bond prices
-
-
10-Year Treasury Yield: Highly correlated with the federal funds rate
-
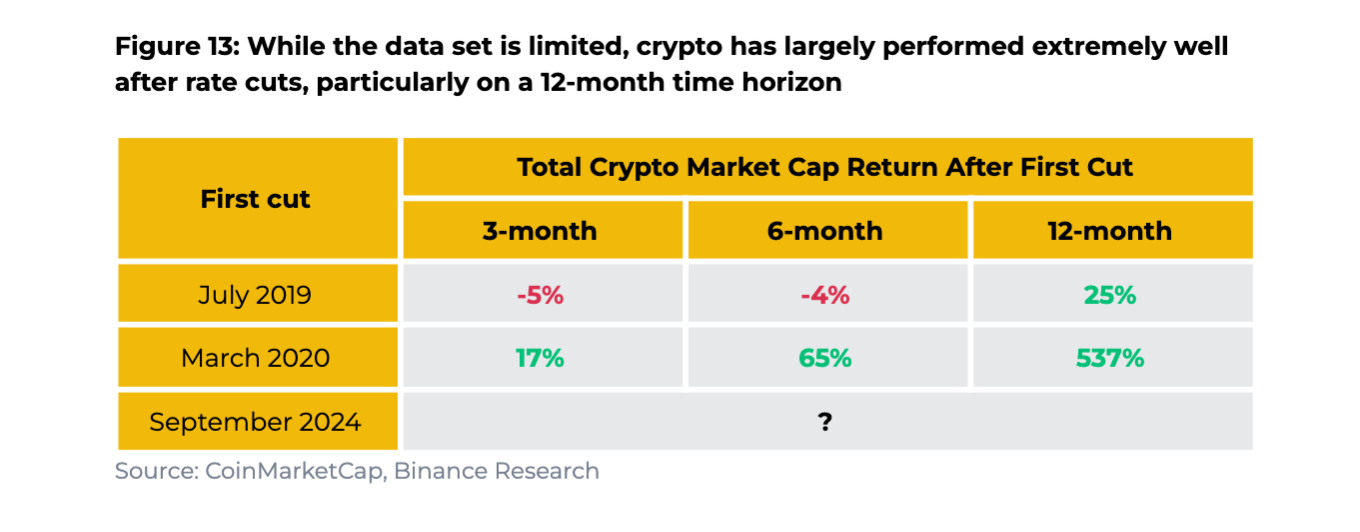
Cryptocurrencies
-
Historical Data: Has only experienced two rate-cutting cycles (late 2019 and March 2020)
-
Performance Highlights:
-
July 2019 cut: +25% over 12 months
-
March 2020 cut: +537% over 12 months
-
-
Special Considerations:
-
Limited sample size
-
Relatively small market size and high volatility
-
Driven by multiple factors beyond just interest rates
-
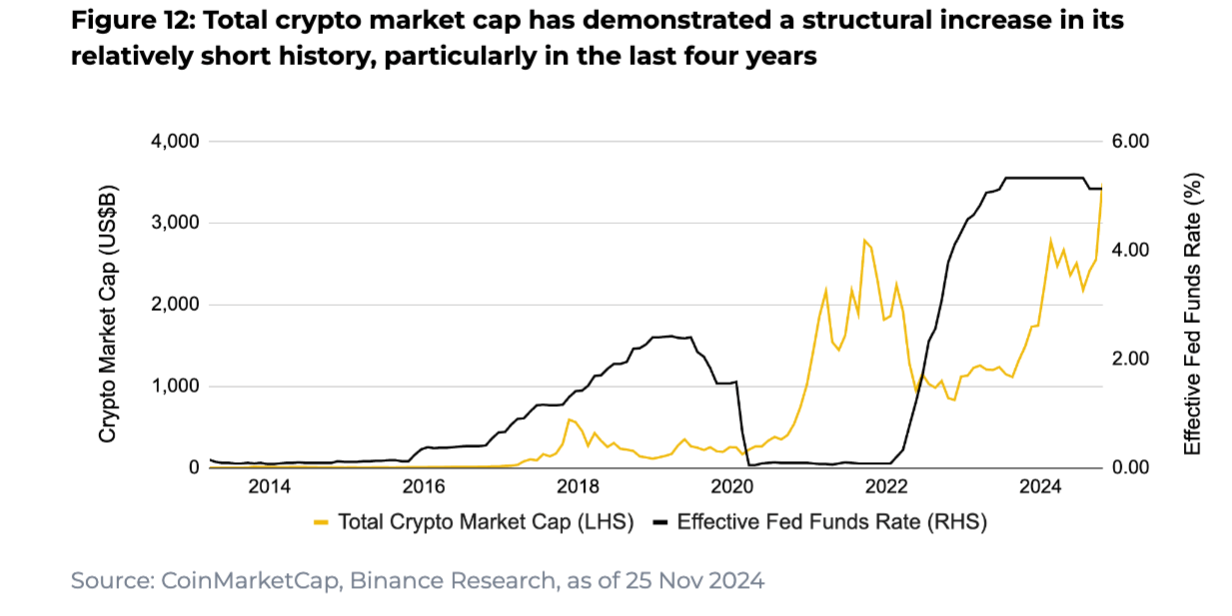
This historical review shows that while rate cuts generally support asset prices, actual performance varies significantly by asset class and macroeconomic context. Especially during recessions, even rate cuts may fail to prevent declines in asset values—highlighting the need for investors to consider multiple factors rather than making decisions based solely on rate movements.
Conclusion: The Global Rate-Cutting Cycle Begins—Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
As highlighted in the report, September 2024 became the fourth-largest rate-cutting month of the century, with 26 central banks implementing easing measures. This trend continued into October and November, signaling a new phase in global monetary policy. The Federal Reserve, as the world’s most influential central bank, delivered two rate cuts in September and November—events with far-reaching consequences and indications that 2025 may bring even broader policy loosening.
Historically, rate-cutting cycles tend to lower funding costs and improve liquidity, providing support for asset prices. However, this cycle is unique: While global inflation has clearly retreated from 2022 highs, the risk of resurgence remains. Labor markets remain stable, with unemployment at a healthy 4.1%, but geopolitical tensions add an extra layer of uncertainty.
Looking ahead to 2025, markets widely expect the Fed to cut rates by 1–1.5 percentage points. Under this backdrop, major global central banks are likely to follow suit, further improving liquidity conditions. Yet, while opportunities emerge, investors must remain vigilant: Different asset classes may perform divergently during this easing cycle, and simply chasing rate cuts may not yield optimal returns. Investors are advised to focus on structural opportunities based on solid fundamental understanding, deploy capital cautiously, and prepare strategically for this evolving market environment.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News