TechFlow
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

TechFlow
The first step for AI to disrupt humanity: understanding the human mind.
Text: Lexie
Editor: Lu
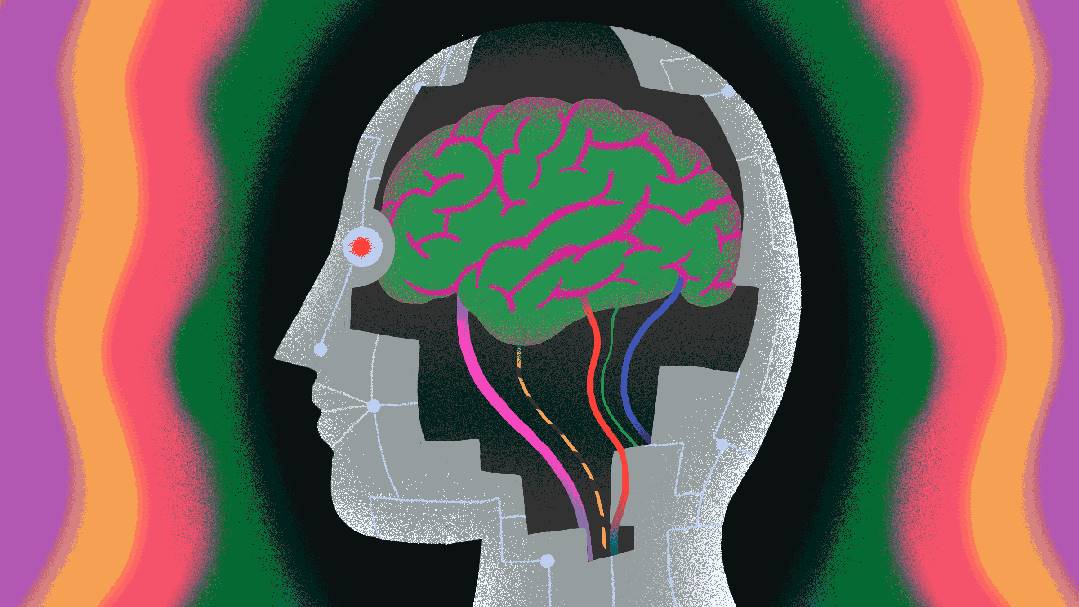
In the broader discourse around AI, it is cast either as our most efficient assistant or as a "mechanical army" that could disrupt us. Friend or foe, AI is expected not only to complete tasks assigned by humans but also to "read" human minds—an ability that has become one of the focal points in the AI field this year.
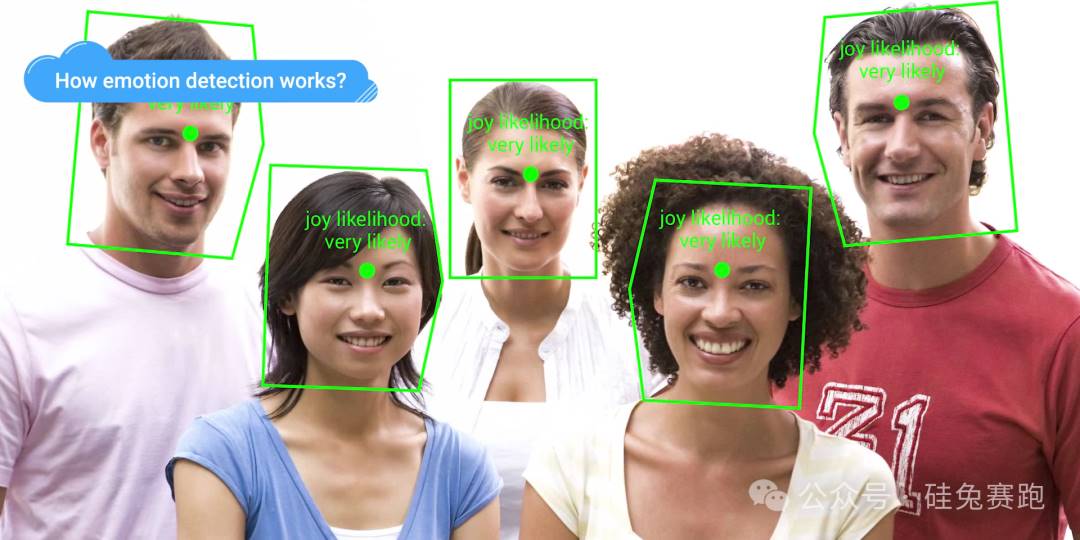
In PitchBook’s 2024 Emerging Technology Report for enterprise SaaS, "Emotion AI" emerged as a key technological highlight. It refers to using affective computing and artificial intelligence to sense, understand, and interact with human emotions—analyzing text, facial expressions, voice, and other physiological signals to interpret emotional states. Simply put, Emotion AI aims to enable machines to understand emotions like humans do—or even better.
Its core technologies include:
-
Facial Expression Analysis: Using cameras, computer vision, and deep learning to detect micro-expressions and facial muscle movements.
-
Voice Analysis: Identifying emotional states through voiceprints, intonation, and speech rhythm.
-
Text Analysis: Leveraging natural language processing (NLP) to interpret sentences and context.
-
Physiological Signal Monitoring: Using wearable devices to analyze heart rate and skin response, enhancing personalization and emotional richness in interactions.

Emotion AI
Emotion AI evolved from earlier sentiment analysis technology, which primarily analyzed textual interactions—such as extracting user emotions from social media posts. With the integration of AI, combining visual and audio inputs, Emotion AI promises more accurate and comprehensive emotional insights.
01 VC Funding Surge, Startups Secure Major Investments
TechFlow observes that the potential of Emotion AI has drawn significant investor interest, with startups such as Uniphore and MorphCast securing substantial funding in this space.
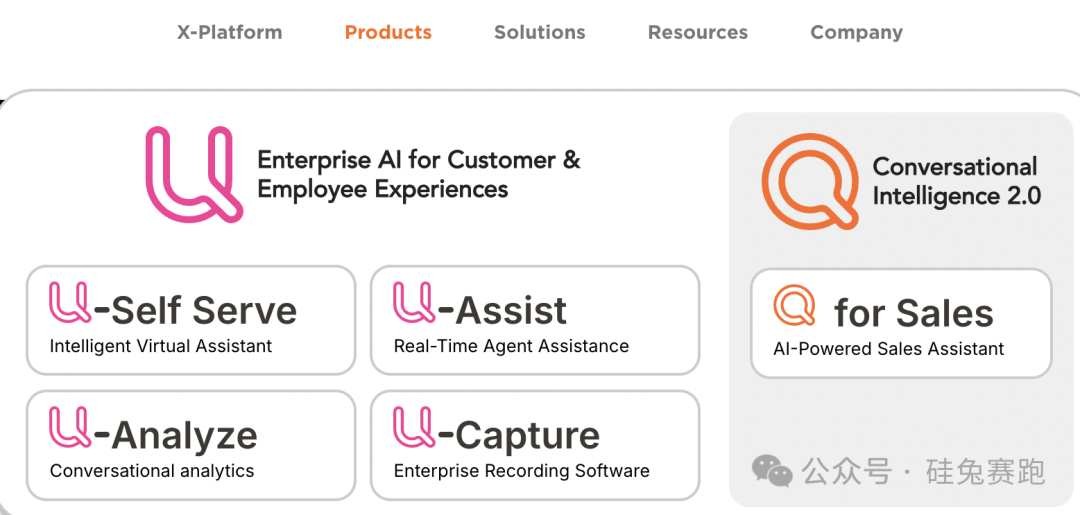
Born in California, Uniphore has been developing automated conversation solutions for enterprises since 2008. It has launched multiple product lines including U-Self Serve, U-Assist, U-Capture, and U-Analyze, helping clients deliver more personalized and emotionally intelligent interactions via voice, text, video, and emotion AI. U-Self Serve specializes in precisely identifying emotions and tone in conversations, enabling businesses to offer more tailored services and improve user engagement and satisfaction.

U-Self Serve
U-Assist boosts customer service agent efficiency through real-time guidance and workflow automation. U-Capture enables deep insights into customer needs and satisfaction through automated emotional data collection and analysis. U-Analyze helps identify key trends and emotional shifts in interactions, providing data-driven decision support to strengthen brand loyalty.
Uniphore’s technology goes beyond mere language comprehension—it seeks to capture and interpret the underlying emotions hidden in tone and facial expressions during human-machine interactions. This capability allows companies to move beyond robotic responses and better meet customers’ emotional needs. Enterprises using Uniphore report achieving 87% user satisfaction and a 30% improvement in agent performance.
To date, Uniphore has raised over $620 million in funding, including a $400 million round led by NEA in 2022, with participation from existing investors such as March Capital. The company reached a post-funding valuation of $2.5 billion.
Uniphore
Hume AI has introduced the world’s first empathetic voice AI, founded by former Google scientist Alan Cowen, known for pioneering the theory of semantic spaces. His research reveals subtle differences in voice, facial expression, and gesture to understand emotional experiences and expressions. Cowen's work has been published in journals such as *Nature* and *Trends in Cognitive Sciences*, covering the broadest and most diverse samples of emotions studied to date.
Building on this research, Hume developed EVI, a conversational voice API that combines large language models with empathy algorithms. It deeply understands and interprets human emotional states—not just detecting emotion in speech, but responding with nuanced, personalized reactions. Developers can integrate these capabilities into any application with just a few lines of code.

Hume AI
One major limitation of current AI systems is their reliance on human-provided instructions, which are often error-prone and fail to unlock AI’s full potential. In contrast, Hume’s empathetic large language model (eLLM) dynamically adjusts its word choice and tone based on context and user emotion. By prioritizing human well-being as a core principle in machine learning, interaction, and adaptation, Hume delivers more natural and authentic experiences across mental health, education, emergency response, brand analytics, and more.
In March this year, Hume AI secured a $50 million Series B round led by EQT Ventures, with additional investments from Union Square Ventures, Nat Friedman & Daniel Gross, Metaplanet, and Northwell Holdings.
Another player in this space is Entropik, which specializes in measuring consumer cognitive and emotional responses. Its platform Decode integrates Emotion AI, Behavioral AI, Generative AI, and Predictive AI to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior and preferences, offering more personalized marketing recommendations. Entropik closed a $25 million Series B round in February 2023, backed by SIG Venture Capital and Bessemer Venture Partners.
Entropik
02 Tech Giants Enter the Fray
Leveraging their scale and resources, major tech companies have also entered the Emotion AI arena.
Microsoft Azure's Cognitive Services Emotion API analyzes facial expressions to detect various emotions—including joy, anger, sadness, and surprise—in images and videos.
IBM Watson's Natural Language Understanding API processes vast amounts of textual data to identify emotional tones (positive, negative, neutral), enabling more precise interpretation of user intent.
Google Cloud AI's Vision API offers powerful image analysis, quickly identifying emotional expressions in photos, while supporting text recognition and emotion correlation.
AWS Rekognition detects emotions, identifies facial features, tracks expression changes, and can be integrated with other AWS services to build full-scale social media analytics or emotion-driven marketing applications.
Cloud Vision API
Some startups are advancing so rapidly in Emotion AI that even tech giants are resorting to talent acquisition. For instance, Microsoft took interest in Inflection AI’s AI team and models. After co-investing $1.3 billion alongside Bill Gates, Eric Schmidt, and NVIDIA, Microsoft recruited Mustafa Suleyman—one of Inflection AI’s co-founders and AI leaders—along with over 70 employees. Microsoft reportedly paid nearly $650 million for this transition.
Nonetheless, Inflection AI quickly regrouped, assembling a new team with backgrounds from Google Translate, AI consulting, and AR, continuing to advance its core product, Pi. Pi is an emotionally intelligent personal assistant designed not just to respond, but to understand and empathize with users. Unlike traditional AI assistants, Pi emphasizes emotional connection, perceiving emotions through voice and text inputs and demonstrating empathy in conversations. Inflection AI positions Pi as a coach, confidant, listener, and creative partner—not merely a functional AI tool. Additionally, Pi features robust memory capabilities, retaining users’ conversation history to enhance continuity and personalization in interactions.
Inflection AI Pi
03 Progress Amid Scrutiny and Concerns
While Emotion AI embodies our aspirations for more human-like interactions, its development is accompanied by both enthusiasm and skepticism. First, can Emotion AI truly and accurately interpret human emotions? In theory, this technology could enrich experiences with services, devices, and systems. But in reality, human emotions are inherently ambiguous and subjective. As early as 2019, researchers questioned the reliability of facial expressions as indicators of true emotional states. Relying solely on machines to simulate understanding through facial cues, posture, and tone may therefore face inherent limitations.
Second, strict regulatory oversight remains a hurdle for AI development. For example, the EU AI Act prohibits the use of computer vision-based emotion detection systems in areas such as education, potentially limiting the deployment of certain Emotion AI solutions. Similarly, states like Illinois in the U.S. have laws banning biometric data collection without consent, directly restricting the foundational conditions for some Emotion AI technologies. Moreover, data privacy and protection remain critical issues. Given Emotion AI’s frequent application in high-stakes domains like education, healthcare, and insurance—where data sensitivity is paramount—ensuring the secure and lawful use of emotional data is a challenge every Emotion AI company must confront.
Finally, cross-cultural differences pose significant challenges. Interpreting emotions across regions is difficult even for humans, let alone AI. Diverse cultural norms shape how emotions are expressed and understood, potentially undermining the effectiveness and universality of Emotion AI systems. Furthermore, Emotion AI may struggle with biases related to race, gender, and gender identity.
Emotion AI promises both efficiency and emotional sensitivity—but will it become a universal solution for human interaction, or end up as another Siri-like assistant that underperforms when genuine emotional understanding is required? Perhaps in the future, AI’s “mind-reading” abilities will revolutionize human-machine—and even human-human—interactions. But for now, truly understanding and responding to human emotion may still require thoughtful human involvement.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News














